DEVELOPING FUELS
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What volume does 1 mole of gas always occupy at room temperature and pressure?
24.0dm³ (or 24000cm³)
What happens to temperature in exothermic reactions?
Increases
On an enthalpy level diagram, if something is high then whats its stability?
The higher something is the less stable
What is enthalpy? (in the most simple terms)
Stored heat energy
What are the units for enthalpy change?
KJmol-1
What is the ideal gas equation?
pV = nRT
Standard enthalpy change of combustion=
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is completely combusted under standard condition
Standard enthalpy change of formation=
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is formed from its elements under standard condition
Standard enthalpy change of neutralisation=
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of H2O is formed when an acid and alkali react under standard condition
Standard enthalpy change of reaction=
The enthalpy change when the reaction occurs in molar quantities shown in the chemical equation, under standard condition.
Why is the enthalpy change in standard conditions?
It allows for comparison
What are the standard conditions?
298K / 100kPa / 1moldm^-3
Breaking bonds are…
Endothermic
Forming bonds are…
Exothermic
What is enthalpy change?
The heat energy transferred in a reaction at constant pressure (kJmol^-1)
Unit of pressure in the ideal gas equation
Pa
Unit of volume in the ideal gas equation
m³
Unit of temperature in the ideal gas equation
K / kelvin
What is ‘R‘ in the ideal gas equation?
Gas constant
3 ways of finding enthalpy change of reaction
Doing experiments / use Hess cycles / use bond enthalpy values
Does forming bonds make them become more or less stable?
More stable
What are the 2 main procedural problems of enthalpy change of combustion experiments?
Heat loss to surrounding / Incomplete combustion
What is the Hess’s law?
The enthalpy change is independent of the path taken
Why would a reaction be endothermic?
The E needed to break bonds is more than the E released from forming bonds
Describe an experiment they could use to determine the enthalpy change of combustion of liquid hexane in the laboratory (1 mark)
Burn the (known mass of) fuel under a container of (known volume of) water and measure the temperature increase of H2O
6 Ways to make basic experiment more accurate:
Use a lid / Use draught shield / Move calorimeter closer to flame / Use a bomb calorimeter / Stir to improve heat distribution / Use copper calorimeter instead of beaker
What is the empirical formula?
Simplest ratio of atoms in a molecule
What is the molecular formula?
Actual number of each type of atom in a molecule
A property of the molecular formula
No information about structure (ie don‘t show functional group)
What is the general formula?
Describes all member of a homologous series
Aliphatic
Does not contain a benzene ring
Aromatic
Contains a benzene ring
Arene
Contains a benzene ring
What is the functional group?
The part which reacts
All the bond angles (/shape) in saturated hydrocarbons are…
109.5 / tetrahedral
What are the 3 reactions alkanes can do?
Combustion / radical substitution with halogen / Cracking
What is the reason for cracking alkanes?
Long hydrocarbons are not useful, so we have to convert them into shorter, more useful products
What are the 2 types of cracking (in industry)?
Catalytic cracking / Steam cracking
Conditions for catalytic cracking in industry
500 degrees Celsius / zeolite catalyst
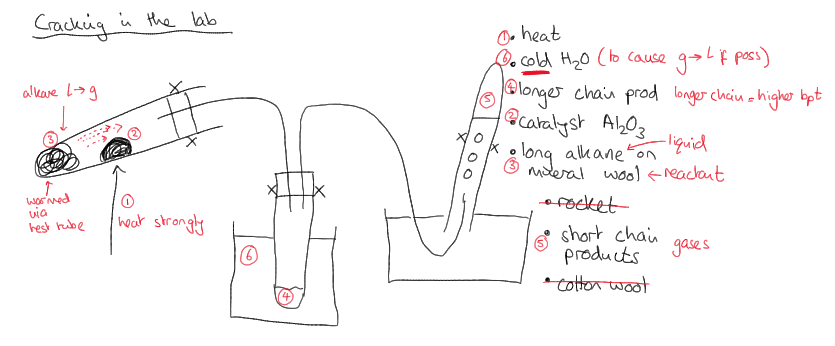
What is this practical?
Cracking in the lab
What is a catalyst?
Provides an alternative pathway with a lower Ea. Chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction.
What are homogeneous catalysts?
Catalysts and reactants are in the same state
What are heterogeneous catalysts?
Catalysts and reactants are in different states
Step 1 of heterogeneous catalysts reaction
The reactant molecules are adsorbed onto the catalyst surface weakening bonds within the reactants
Step 2 of heterogeneous catalysts reaction
Bonds within the reactant molecules break
Step 3 of heterogeneous catalysts reaction
New bonds form, making the product molecules
Step 4 of heterogeneous catalysts reaction
The product molecules leave the catalyst surface (desorption)
Write the chemical equation that happens in the catalytic converters in cars.
CO + NO —> CO2 + 1/2N2
How is CO formed in cars are why is it bad?
Incomplete combustion / its toxic
How is NO formed in cars are why is it bad?
N2 and O2 form the air react due to high temperature / respiratory irritant, causes photochemical smog and causes acid rain
(3) What elements are used as catalyst in cars
Pt / Rh / Pd
How can a catalyst be poisoned?
When other reactants adsorb strongly onto the surface and don’t react, blocking the surface and stopping the normal reactants from adsorbing.
What does ‘Adsorbed’ mean (in catalytic converters)
Form weak bonds with the surface (catalytic surface)
What are structural isomers?
Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but different structural formula
What are stereoisomers?
Stereoisomers have the same structural formula but different arrangement of atoms in space
What are the 2 criteria‘s for stereoisomerism (E/Z)
There must be a C=C as this restricts rotation / There must be 2 different groups on each C of the C=C
What are the 2 electrophilic addition reactions of alkenes with halogens?
Alkenes + X2 —> Dihaloalkane / Alkenes + HX —> Haloalkane
What are the 2 electrophilic addition reactions of alkenes without halogens?
Alkene + H2 —> Alkane / Alkene + H-OH —> Alcohol
What are the conditions for [Alkenes + X2 —> Dihaloalkane]
RTP
What are the conditions for [Alkenes + HX —> Haloalkane]
RTP
What are the conditions for [Alkene + H2 —> Alkane]
Nickle catalyst + high T&P / Platinum catalyst + RTP
What are the conditions for [Alkene + H-OH —> Alcohol]
H2PO4 catalyst + high T&P / conc. H2SO4 + steam
What are curly arrows for?
Curly arrows show the movement of e-
Where can curly arrows start? (2)
From a lone pair / from the middle of a bond
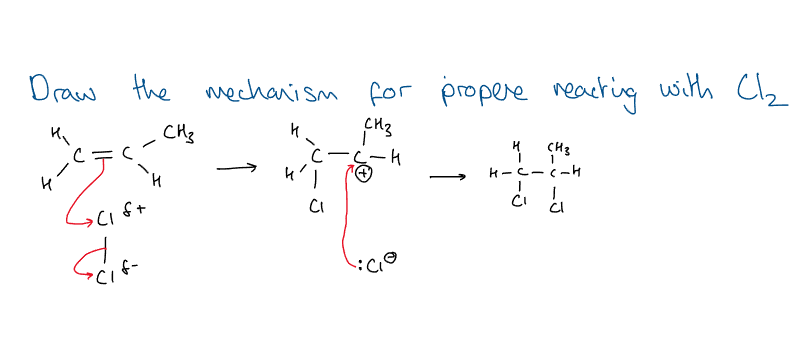
What is this?
Mechanism for propene reacting with Cl2
What is an electrophile?
A positive or partially positive species which forms a dative bond by accepting a pair of electrons
Test for proof for mechanism? (of ethene with bromine)
Add a solution of NaCl, only forms dibromoethane OR 1-bromo2-chloroethane (NEVER dichloroethane).
What does ‘sharing of pairs of electrons‘ suggest about the orbitals?
The orbitals are overlapping
What are the 2 types of overlap (of orbitals)?
End on overlap along the internuclear axis (sigma) / Sideways overlap of 2 parallel p orbitals above and below the internuclear axis (Pi)
A double bond is…
One sigma bond + One Pi bond
A triple bond is…
One sigma bond + Two Pi bonds
Source for CO2
Complete combustion of fossil fuels
Source for CO
Incomplete combustion of fossil fuels
Source for NO / NO2
N2 and O2 from the air react due to high temperatures in engine
Source for SO2
From S impurities in fuels
Source for N2O4
Ploughing fertilized fields
Why is SO2 a problem?
Causes acid rain (H2SO4)
Why is N2O4 a problem?
Respiratory irritant
Example for biofuel (/how its made)
Ethanol, which can be made from plants, by fermentation of their sugars. It is usually mixed with petrol
Advantages for biofuels (4)
Helps car engine perform well / carbon neutral / renewable / produces less CO
Disadvantages of biofuels
Needs a lot of land to grow the crops, which could otherwise be used to grow food / a lot of energy is needed for intensive cultivation of the crop
Shape and bond angles of alkanes
Tetrahedral, 109.5