Topic 2.4- Structure of Metals and Alloys
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Metallic Bonds
Positive metals ions surrounded by a 'sea of mobile valence electrons' (delocalized electrons)
Properties of Metallic bonds
- Good conductors of electricity
- Malleable- bendable
- Ductile- pulled in a wire
Metals
Mobile valence electron
Ionic Compunds
Mobile charged particles
Alloys
Combining two or more metallic elements
Substitutional Alloy
- Atoms of comparable radii
- one atom substitutes for another atom in the lattice
- Brass- copper and Zinc
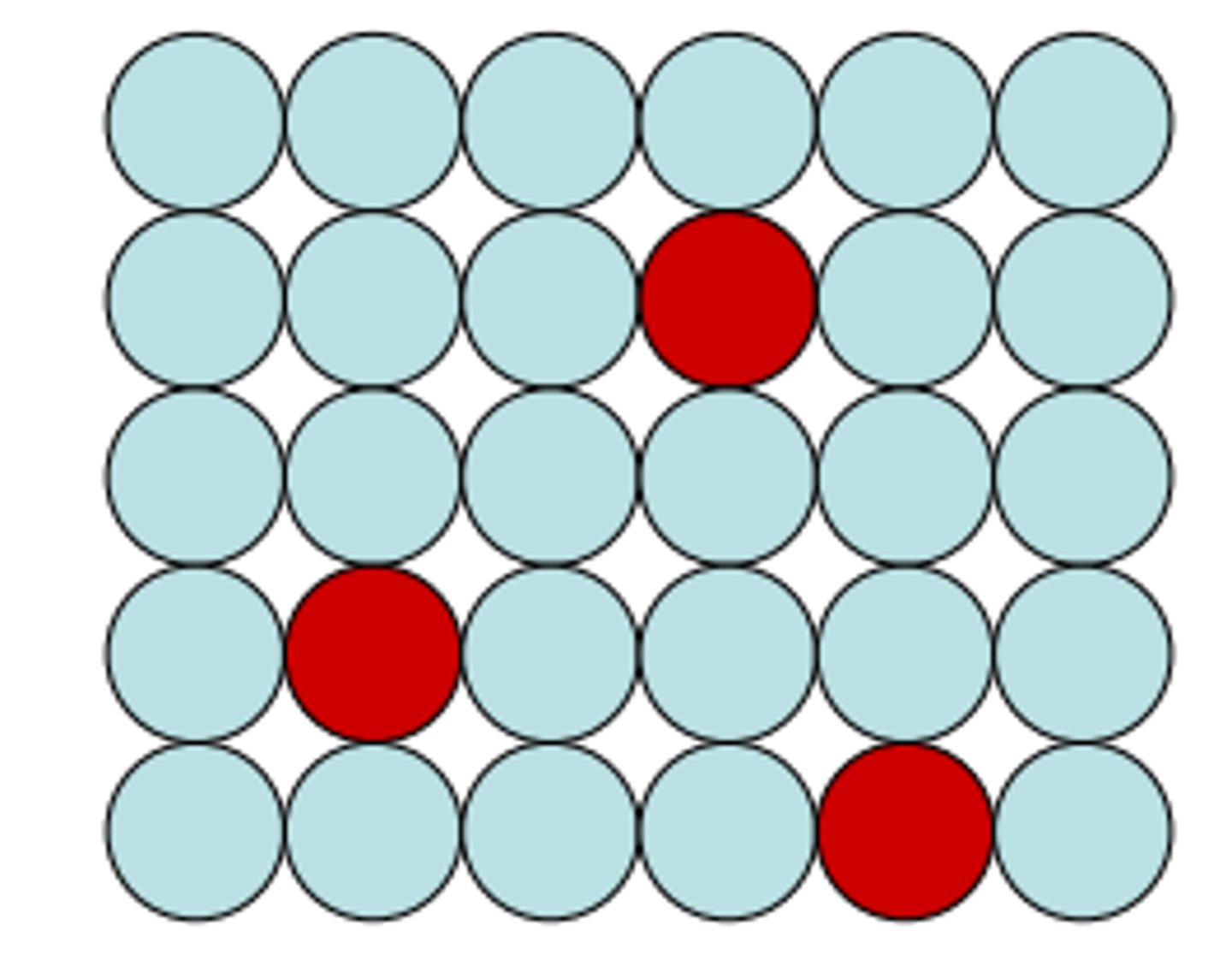
Interstitial Alloy
- Atoms of different radii
- Smaller atoms fills the spaces b/t larger atoms
- usually the alloy is stronger than the base metal
- Steel- carbon atoms fill space between iron atoms
Metals are composed of cations that are embedded in delocalized sea of valence electrons.
This means that the electrons do not stay with one atom, rather they are able to move throughout the entire substance. The cations and the electrons are attracted to one another through a Coulombic Attraction which holds the metal atoms together.
The number of valence electron determines
the amount of electrons in the delocalized sea of electrons.
When the charge on the cations and the number of electrons increases
the attractions are greater. Additionally, when the ionic radius decreases the attraction increases.
Mixtures of metals are called
alloys; they can be examples of a solution. Two types of alloys are interstitial and substitutional. The difference between them is the size of the atoms that are being added to the metal.
Compare the metals calcium and magnesium, which metal would be stronger (more tightly held together), justify your selection.
Magnesium is stronger, smaller radii therefore stronger attractions.
A pure metal and an interstitial alloy containing the same metal were examined. Predict which substance will have a greater density and justify your selection.
Interstitial alloy would be more dense since more atoms are packed in the same space.
Interstitial alloys are usually less malleable than the pure metals. Based on their structure, propose a reason for this decrease in malleability.
They disrupt the regular arrangement of ions and make it more difficult for the layers to slide over each other. This makes the alloy harder and less malleable and ductile than the pure metal (in which the layers slip over each other more easily)