chemistry - states of matter & mixtures: methods of separating & purifying substances (2.5 - 2.12)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
2.5 pure substance vs mixture
pure substance:
only 1 type of element/compound
fixed composition
can’t separate into diff. substances using physical methods
e.g. sucrose
mixture:
elements and/or compounds not chemically joined together
no fixed composition
can separate into diff. substances using physical methods
e.g. air
2.6 pure substances vs mixtures - melting points
pure substances: sharp melting point
mixtures: melt over range of temperatures
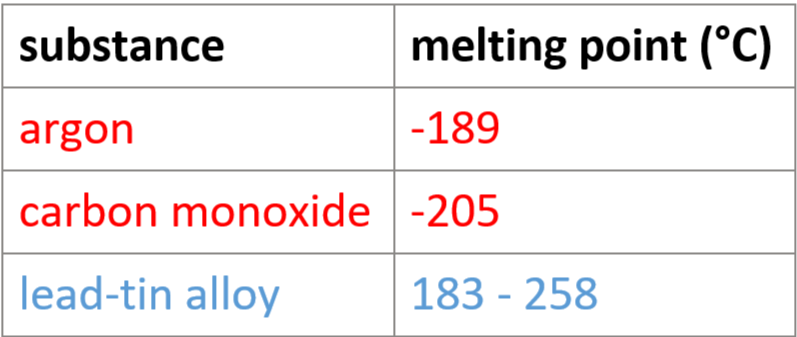
2.7 simple distillation - use
separate solvent from solution/purify liquids
2.7 simple distillation - process
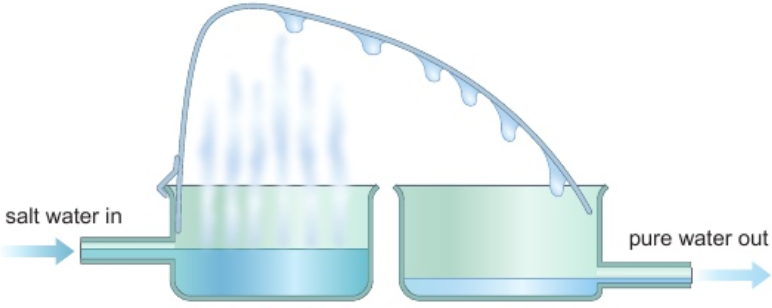
e.g. purifying water
mineral water evaporates - only water turns into gas (pure water vapour)
solid mineral ions have higher boiling points - left behind
vapour condensed - turns back to liquid water (pure)
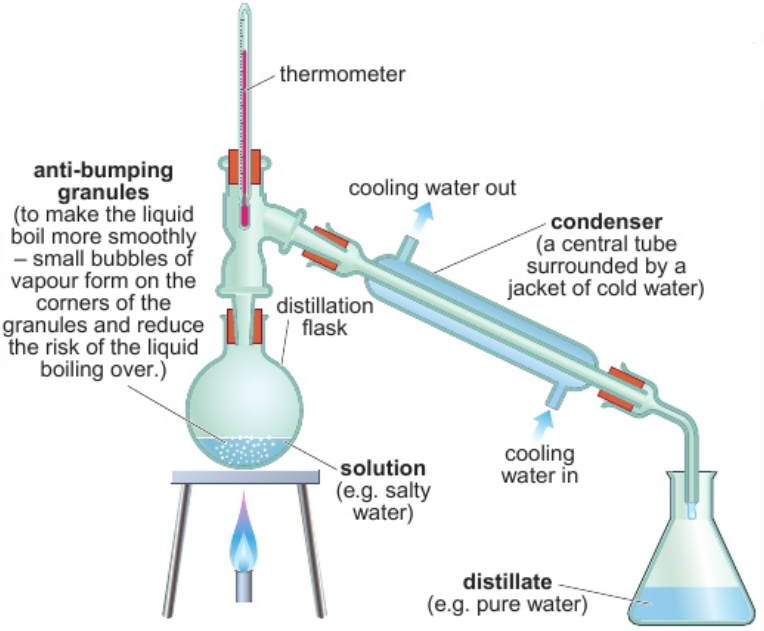
2.7 fractional distillation - use
separate 2/more liquids
2.7 fractional distillation - process
liquids with lower boiling points evaporate first
first fraction collected contains liquid with lowest boiling point
hot vapour rises up column
as column heats up, temp. gradient - bottom = hottest, top = coldest
fraction with lowest bp. reaches top first - vapour → condenser
keep heating - fractions with higher bps. rise up column & collected
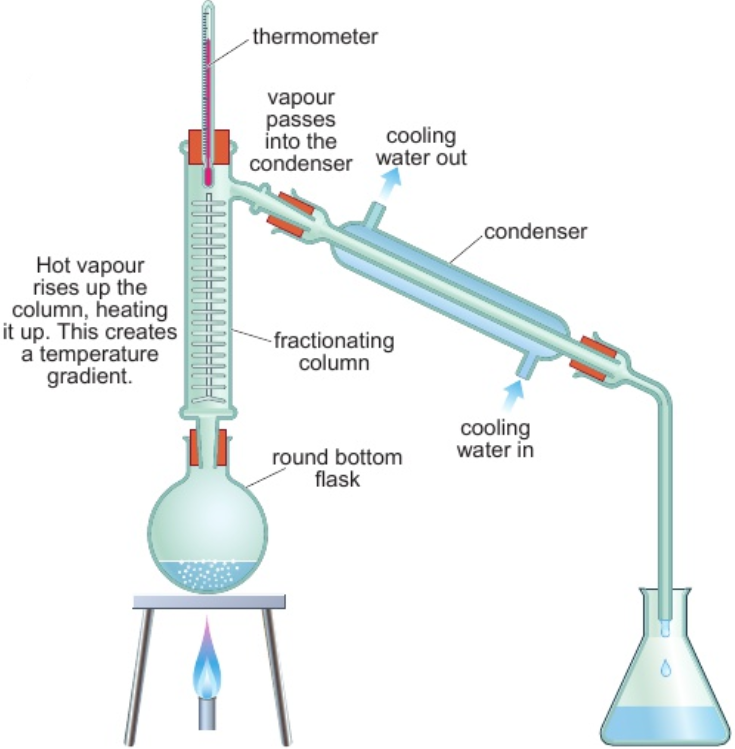
2.7 filtration - use
separate insoluble solid from liquid
2.7 filtration - process
filter funnel lined with filter paper
solvent & solute(s) pass through fine holes - form filtrate
insoluble substances can’t fit through holes - leave residue in paper
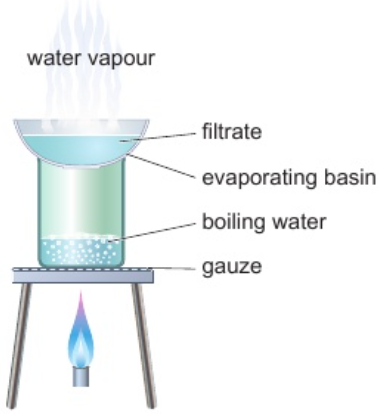
2.7 crystallisation - use
separate solutes from solution by evaporating solvent to leave solutes behind
2.7 crystallisation - process
filtrate placed in evaporating basin over Bunsen burner
solvent evaporates - leaves solutes behind
2.7 paper chromatography - use
find out which coloured compounds a mixture contains
2.7 paper chromatography - process
some compounds dissolve better in solvent than others
solvent moves along strip of paper
carries diff. substances in mixture at diff. speeds - separates them
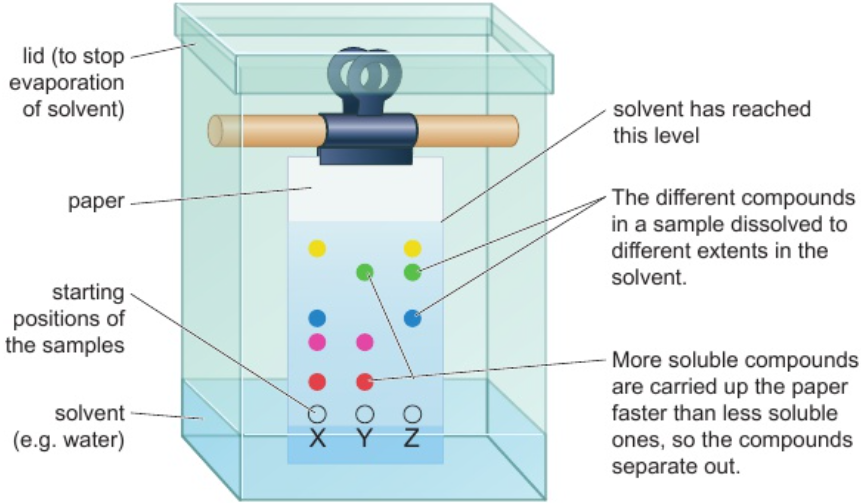
2.9 paper chromatography - definition
separation of mixtures of soluble substances
by running solvent (mobile phase) through mixture on paper (stationary phase)
causes substances to move at diff. rates over paper
2.10 paper chromatogram - pure vs impure substances
pure substances: one spot on chromatogram
impure substances: multiple spots on chromatogram
2.10 paper chromatogram - identify substances by comparing with known substances
do paper chromatography with known & unknown substances on same paper
spots of both = same colour, same number, at same height on paper - unknown substance = known substance
2.10 paper chromatogram - identify substances by calculation
do paper chromatography for unknown substances
calculate Rf values
compare to known values - same Rf value = same substance
2.10 paper chromatography - Rf values
measured from starting positions of samples

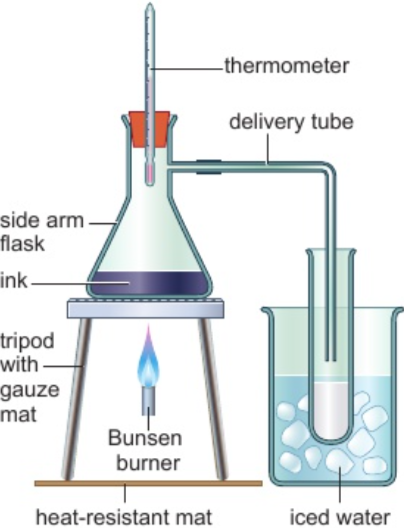
2.11 core practical: composition of inks - simple distillation
set up apparatus like diagram
heat flask of ink using Bunsen burner
ensure ink simmers gentle & doesn’t boil over into delivery tube
continue heating until collected few cm3 of distillate (distilled solvent)
note maximum temperature obtained
2.11 core practical: composition of inks - paper chromatography
draw pencil line on chromatography paper about 2cm from bottom
add small spot of ink to pencil line
add water to container about 1cm deep
place paper into container, let water travel through paper
ensure paper supported so doesn’t fall into water
take paper out before water reaches top, immediately mark position of solvent with pencil, leave paper to dry
measure distance water & each coloured substance travelled from pencil line
calculate Rf values for each coloured substance
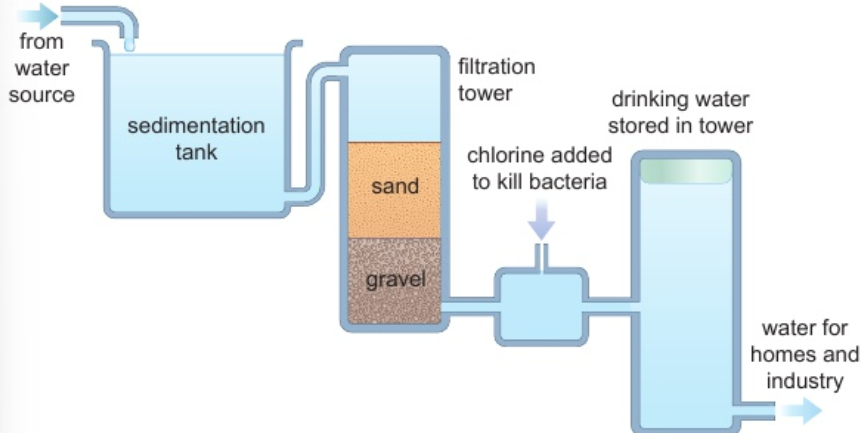
2.12 how are waste & ground water made potable?
sedimentation: large insoluble particles sink to bottom
filtration: beds of sand & gravel - removes small insoluble particles
chlorination: chlorine added - kills microorganisms
2.12 how is sea water made potable?
water separated from dissolved salts by simple distillation
sea water heated - water vapour leaves it
vapour cooled & condensed - forms water without dissolved salts
2.12 water used in analysis
chemical analysis: chemical reactions/sensitive machines identify & measure substances in sample
water used must not contain any dissolved salts - incorrect results obtained
dissolved salts may react to form unexpected cloudy precipitates
machine used for analysis may detect salts