A&P C1.2
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Integumentary System
Protects the body, helps regulate temperature, eliminates some waste, helps make vitamin D and detects sensations.
Skeletal System
Supports and protects the body, surface for muscle attachments, aids movement, cells that produce blood cells, stores minerals and lipids
Muscular System
Body movement, stabilization, heat production
Nervous System
Generates Action Potentials to regulate activities. Detects, interprets and responds to changes in internal and external environment
Endocrine System
Regulate body activities via blood borne chemical messengers
Lymphatic System
Returns protein and fluid to blood, carries lipids from GI tract to blood, houses structures for lymphocyte maturation and proliferation
Cardiovascular System
Heart pumps blood through vessels. Transport of gasses, nutrients and waste. Helps regulate Acid/Base balance, temperature, water content of body fluids. Blood components help defend against disease and mend vessels
Respiratory System
Transfer of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide to / from blood. Helps regulate Acid/Base balance, produce sound
Digestive System
Physical / Chemical breakdown of food. Absorbs nutrients and eliminates solid waste.
Urinary System
Produces, stores and eliminates urine. Helps regulate volume and composition of blood, maintain Acid/Base balance, maintain mineral balance and regulate red blood cell production
Reproductive Systems
Gonads produce and store gametes, release hormones
Body positions- assume anatomical position
Standing, arms at sides, palms forward, feet flat on floo
Prone position
body lying face down
Supine position
body lying face up
Regional names
terms given to specific regions (Head, neck, trunk, upper limbs, and lower limbs).
Directional terms
Special words used to describe where one body part is located compared to another such as anterior/distal
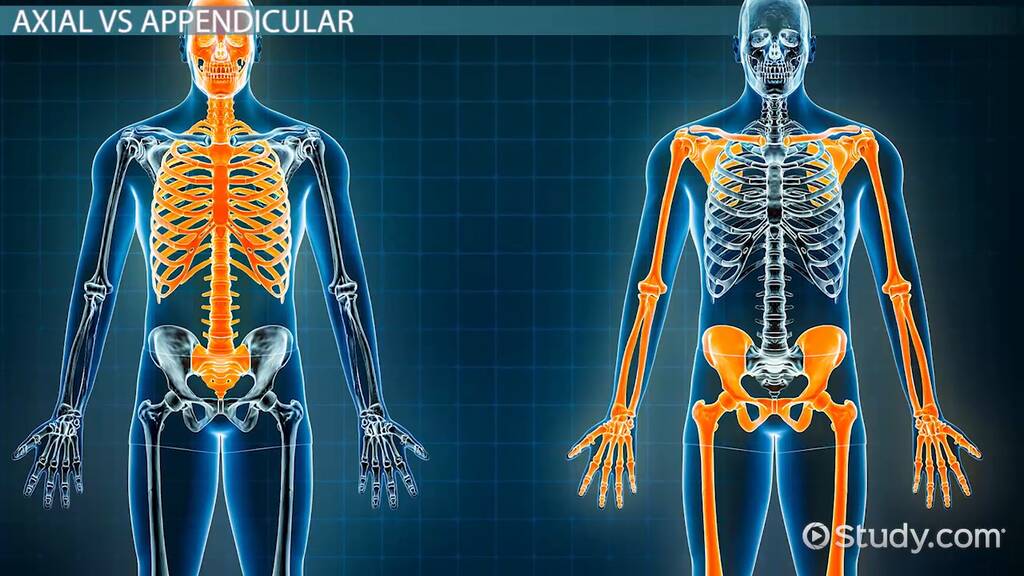
Regional Anatomy
Axial region (The body’s core (center)
Appendicular region (Upper and lower limbs)
Lateral
farther from the midline
Intermediate
Between two structures
Ipsilateral
On the same side of the body as another structure
Contralateral
On the opposite side of the body from another structure
Proximal
Nearer to the attachment of a limb to the trunk; nearer to the origination of a structure
Distal
Farther from the attachment of a limb to the trunk; father from the origination of a structure
Superficial
Toward or on the surface of the body
Deep
Away from the surface of the body
Sagittal Plane
Vertical plane that divides the body into left and right. Midsagittal (or median) plane Parasagittal plane
Frontal (or coronal) Plane
Vertical plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior portions
Transverse (or cross-sectional) Plan
Horizontal plane that divides the body into superior and inferior portions
Oblique Plane
Plane that passes through the body at an angle between the transverse and sagittal or frontal plane
Posterior aspect
Completely encased by bones and is subdivided into the cranial cavity and the vertebral canal.
Cranial cavity (endocranium)
formed by bones of the cranium and houses the brain
Vertebral canal
formed by the bones of the vertebral column and houses the spinal cord
Ventral (anterior) body cavity
larger than the posterior cavity and is divided into the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities, which are separated by the thoracic diaphragm
subdivisions of ventral cavity are lined with
serous membranes
Two layers of serous membranes
Parietal layer lines internal surface of body wall.
Visceral layer covers the outside of the organs (viscera)
Serous cavity
space between membranes
Serous fluid
liquid secreted by serous membranes that acts as a lubricant, reducing friction as organs move against the body wall.
Mediastinum
median space in the thoracic cavity
Pericardium
two-layered serous membrane that surrounds the heart
Parietal pericardium
Outer layer, which forms the sac around the heart
Visceral pericardium
Forms the heart’s external surface
Pericardial cavity
Space between parietal and visceral layers containing serous fluid
Pleura
two-layered serous membrane associated with lungs
Parietal pleura
Outer layer lines internal surface of thoracic wall
Visceral pleura
the inner layer that wraps around the outside of the lungs.
Pleural cavity
Space between parietal and visceral layers containing serous fluid