Equine Anatomy Exam
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
clinical anatomy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
what is diagnostic perineural anesthesia
nerve block
what are the 4 types of nerve blocks
palmar/plantar digital
abaxial sesamoid
low 4-point
high 4-point
why do we do nerve blocks
to dx lameness & to desensitize an area for sx
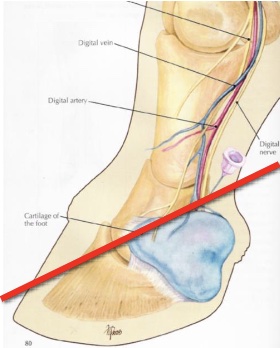
what is desensitized in a palmar/plantar nerve block
palmar/plantar 2/3 of foot
entire sole, navicular structures, distal interphalangeal joint, distal DDFT, distal sesamoidean ligaments
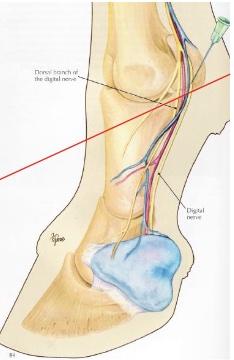
what is desensitized in an abaxial sesamoid nerve block “basisesamoid block”
foot, second phalanx, proximal interphalangeal joint, distopalmar/plantar aspect of proximal phalanx, distal portions of DDFT & SDFT, distal sesamoidean ligaments, digital annular ligament
v shaped area at front of P1 may not be blocked
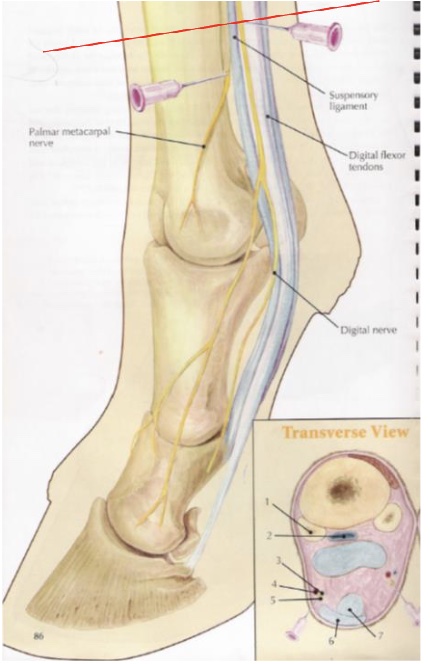
what is desensitized in a low 4 point nerve block (proximal to fetlock)
metocarpo(tarso)phalangeal joint & structures distal
distal aspects of suspensory branches
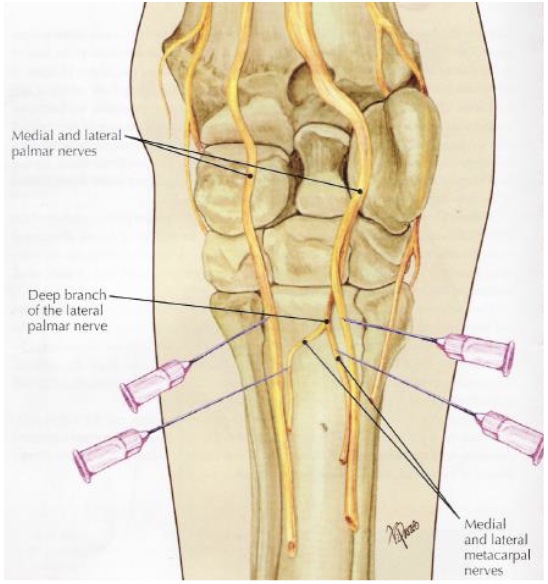
what is desensitized in a high 4 point nerve block (below carpus)
medial & lateral plantar nerves (DDFT & SDFT)
medial & lateral palmar metacarpal nerves (MC2, MC4, prox suspensory ligament & origin)
inferior check ligament
why do we perform arthrocentesis
joint injections to tx arthritis
joint fluid sample to dx sepsis
joint lavage to dx communication w/ wound/laceration
joint lavage to tx sepsis
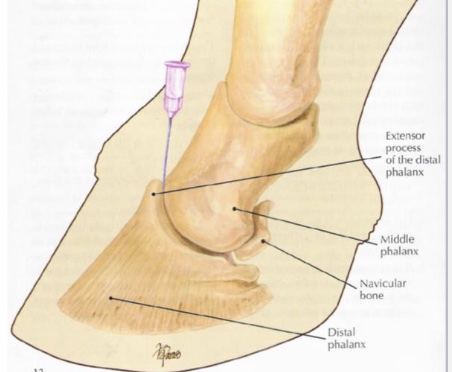
what is desensitized in distal interphalangeal joint
joint
navicular bursa
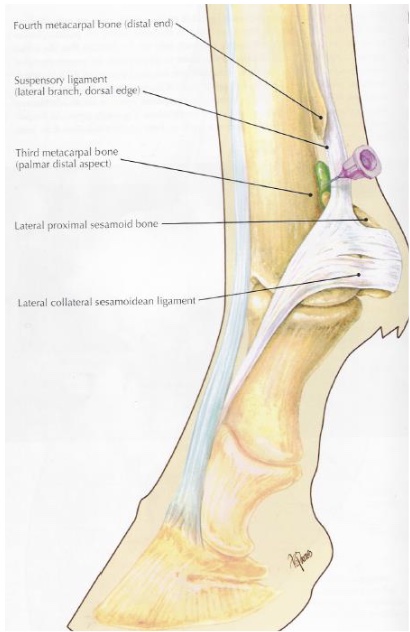
what is desensitized in metacarpo(tarso)phalangeal joint
joint
what are the names of the proximal row of carpal bones (medial to lateral)
radial, intermediate, ulnar
what are the names of the distal row of carpal bones (medial to lateral)
2nd, 3rd, 4th
what are the 3 joints of the carpus
radiocarpal (antebrachial) joint
middle/intercarpal joint
carpometacarpal joint
what two joints are the carpus are in communication with e/o
middle/intercarpal joint & carpometacarpal joint
“down in front”
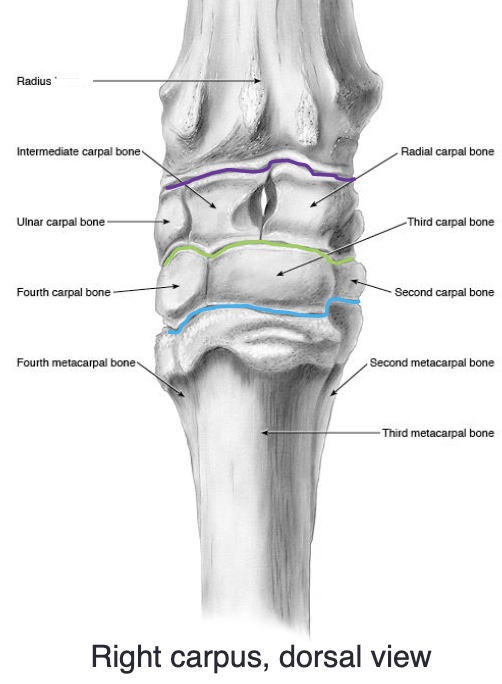
identify the image
purple- radiocarpal joint
green- middle/intercarpal joint
blue- carpometacarpal joint
proximal row of carpal bones: radial, intermediate, ulnar
distal row of carpal bones: 2, 3, 4
(medial to lateral)
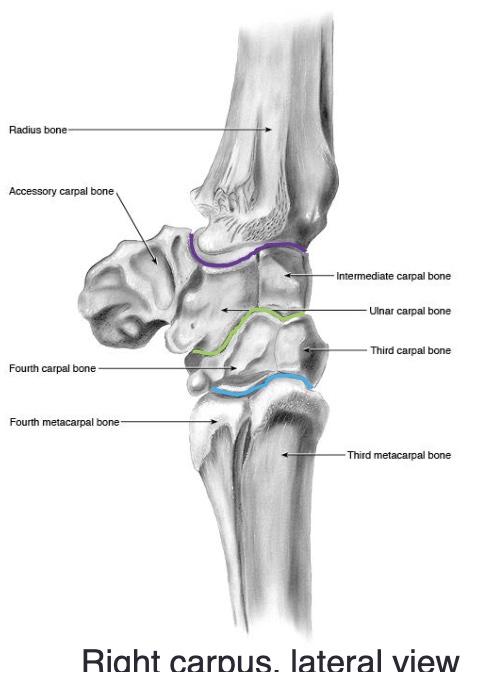
the accessory carpal bone is medial or lateral
lateral
what is desensitized in radiocarpal joint
joint
what is desensitized in middle/intercarpal joint
middle/intercarpal joint + carpometacarpal joint
the equine foot
P3 is suspended within the hoof by laminae
-epidermal laminae attached to hoof wall
-dermal laminae attached to P3
laminitis (founder)
inflammation of the laminae
degeneration of the laminae
can lead to rotation of P3 (more common) or sinking of P3 within hoof capsule (worse, can feel a depression)w
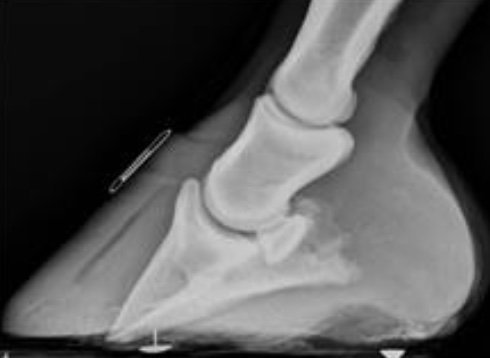
what is this condition
laminitis, rotation of P3
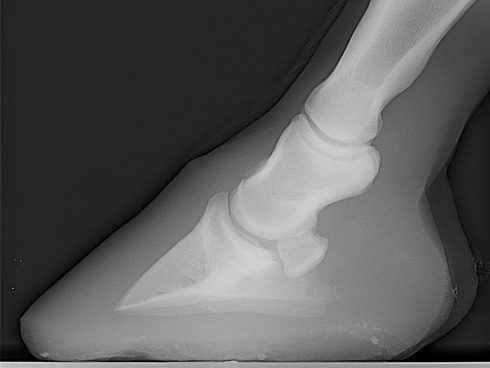
what is this
a normal hoof, note parallel angle
navicular disease
most common cause of chronic forelimb lameness
chronic degenerative condition of the navicular bone
-loss of medullary structure (+ lollipop synovial invaginations)
-bone sclerosis (hardening)
-enthesiophyte formation (excessive mineralization of soft tissue) on proximal and distal borders of the bone
-traumatic fibrilation of DDFT from contact w/ damaged flexor surface of the bone with adhesion formation btwn tendon and bone
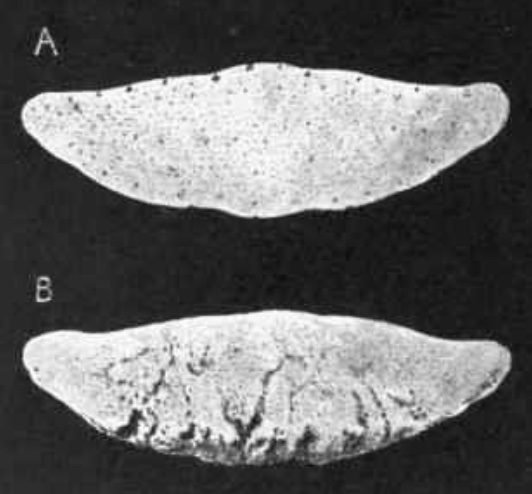
what is this
a- normal
b- navicular dz w/ synovial invaginations (lollipops)
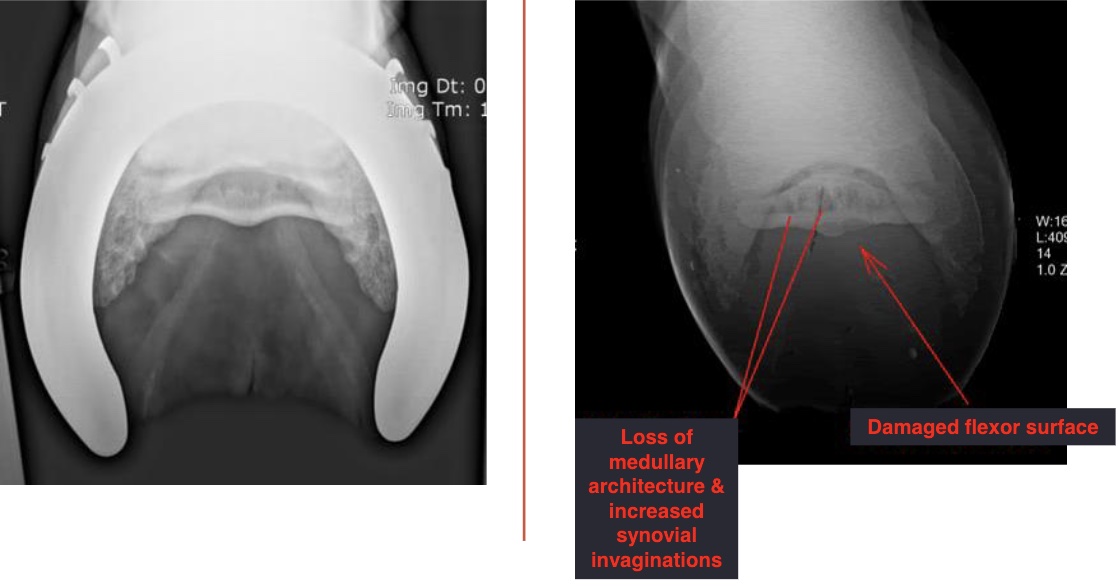
left vs right images
left: normal
right: navicular disease with loss of medullar architecture and increased synovial invaginations (lollipops) and damaged flexor surface (loss of mineralization)
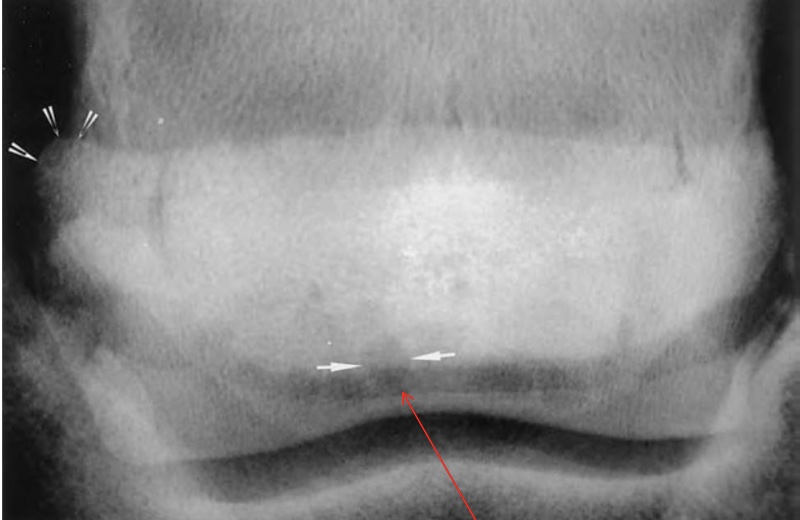
what is this
arrow on left- enthesiophyte (rounded edge)
arrow on bottom- synovial invaginations
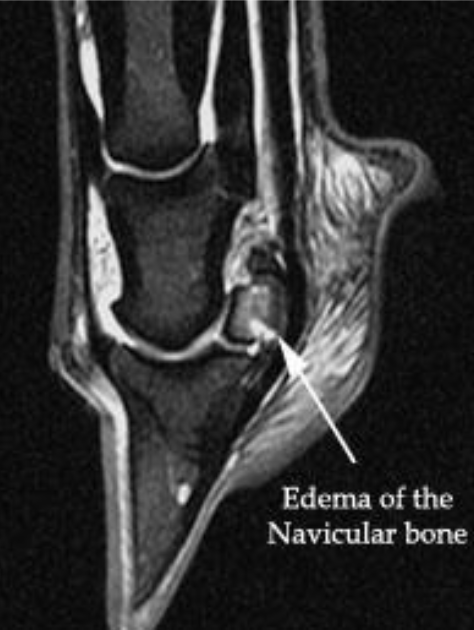
what is arrow pointing at on MRI
edema of the navicular bone
white spots on mri are indicative of pathology (bc of fluid, inflammation)
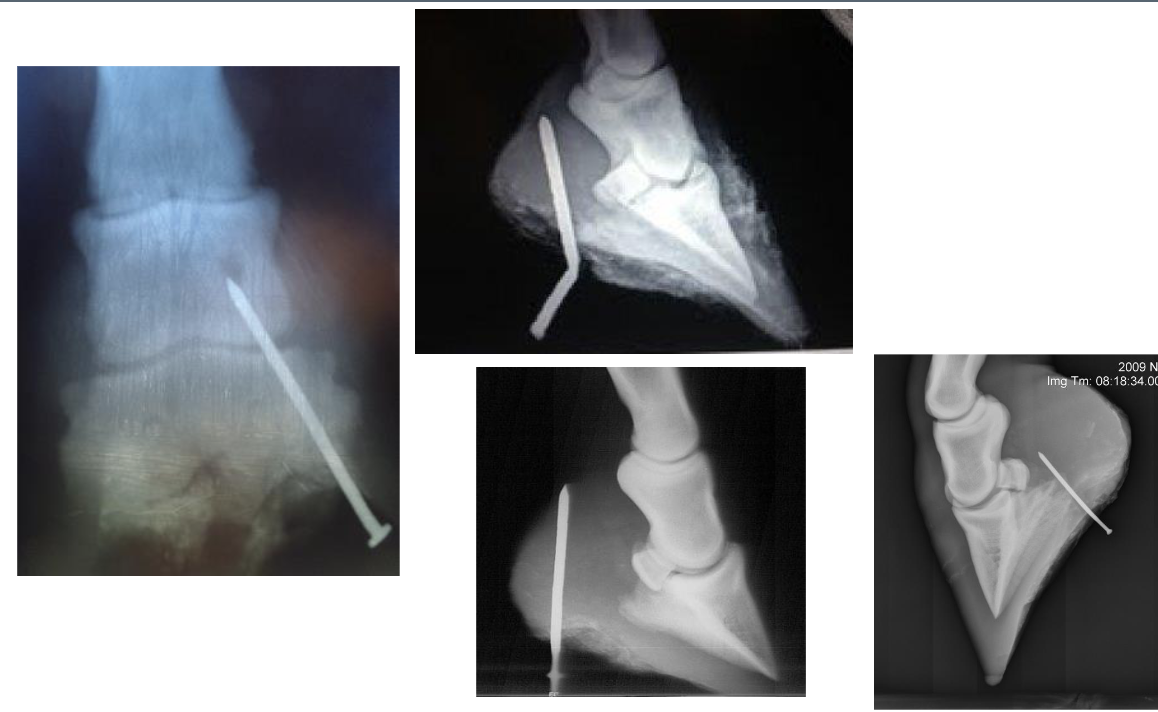
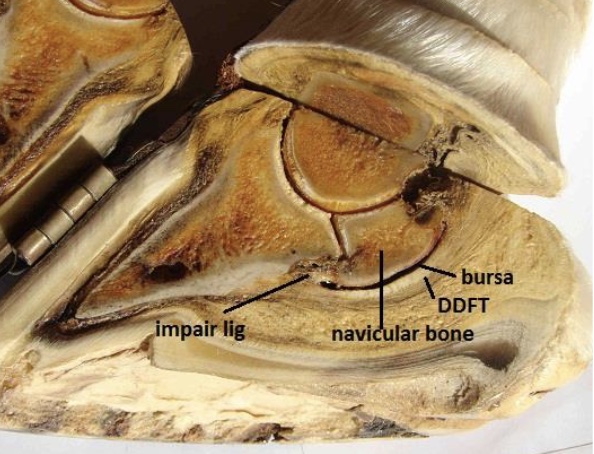
penetrating wounds of the foot
anything towards the frog: BAD
ungual/collateral cartilage, DDFT sheath (synovial structure), DDFT, navicular bursa (synovial structure), navicular bone, distal interphalangeal joint (synovial structure) P3
if damage to synovial structure, risk of infxn arises & considered an emergency
tendonitis
inflammation of the tendon
desmitis
inflammation of a ligament
tendonitis & desmitis
common injuries in horses, tendons and ligaments lack a good blood supply (but rather have scar tissue so more prone to recurrence) so these injuries take a while to heal
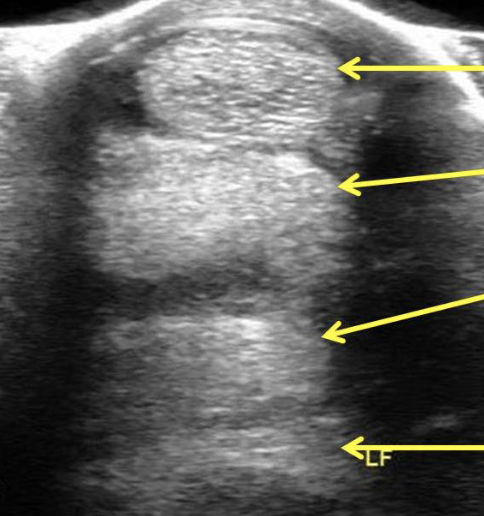
label equine distal limb ultrasound (top to bottom)
superficial digital flexor
deep digital flexor
check ligament
suspensory ligament
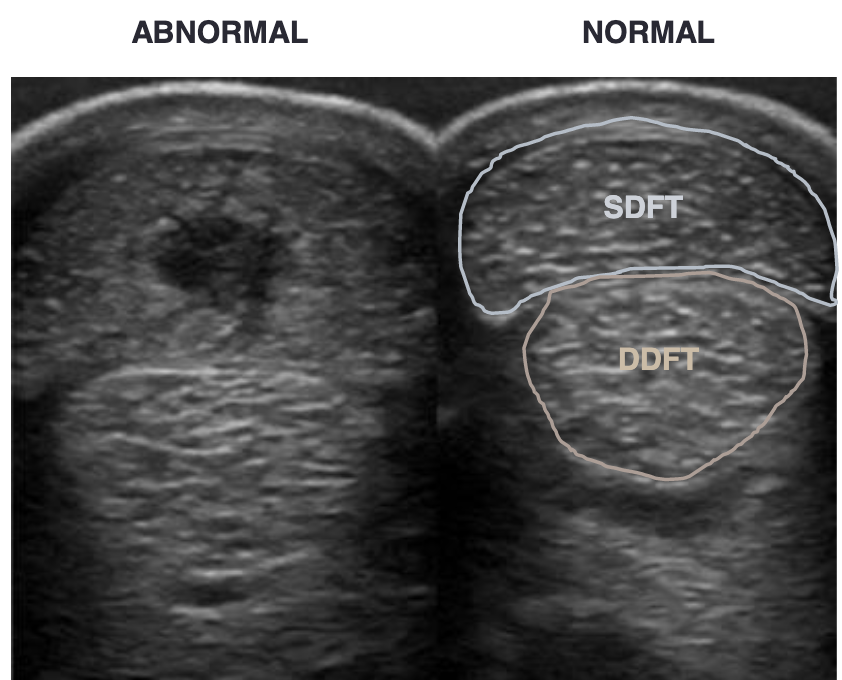
what is this
superficial digital flexor tendonitis
black round object on imaging= hematoma
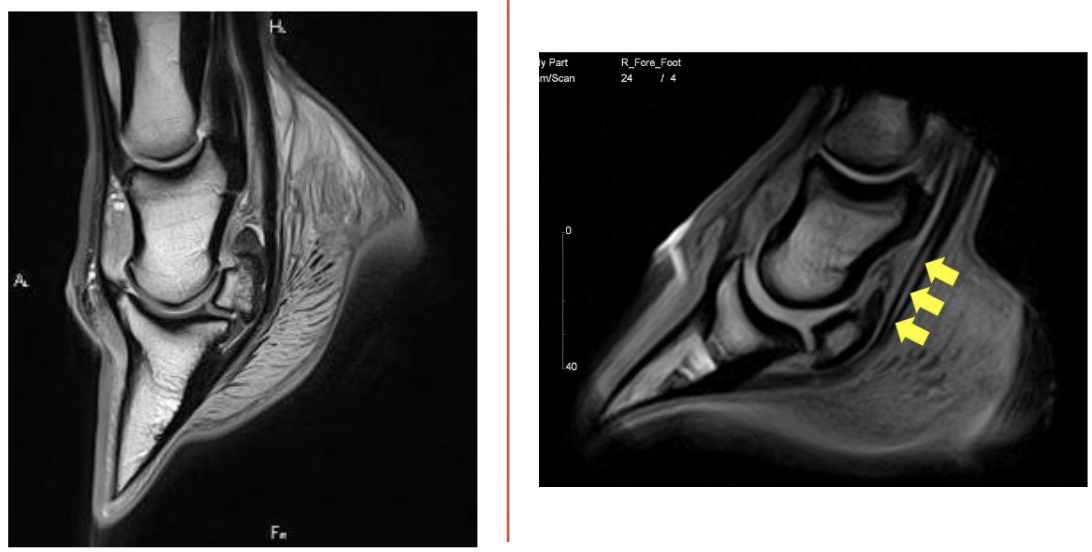
what is this
left= normal
right= deep digital flexor tendonitis
yellow arrows= tear in deep digitial flexor tendon
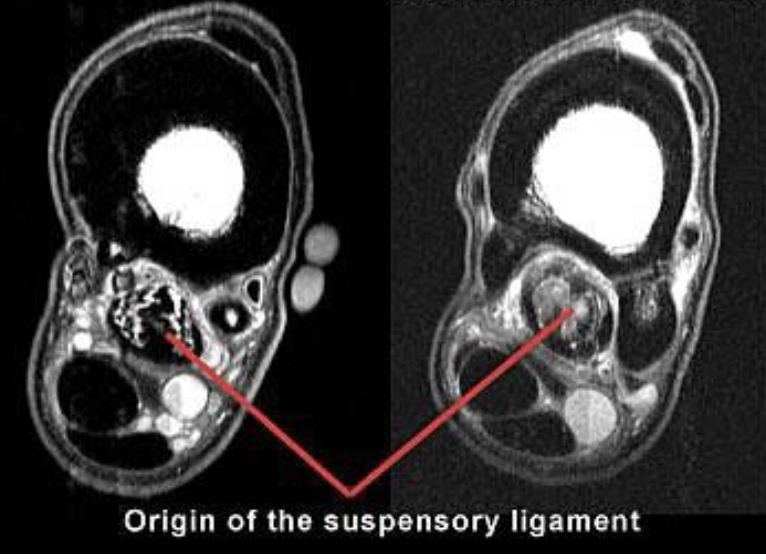
what is this
left= normal
right= suspensory ligament desmitis
cloudyness (red arrow) is showing fluid injury
white lines on left image is normal for comparison
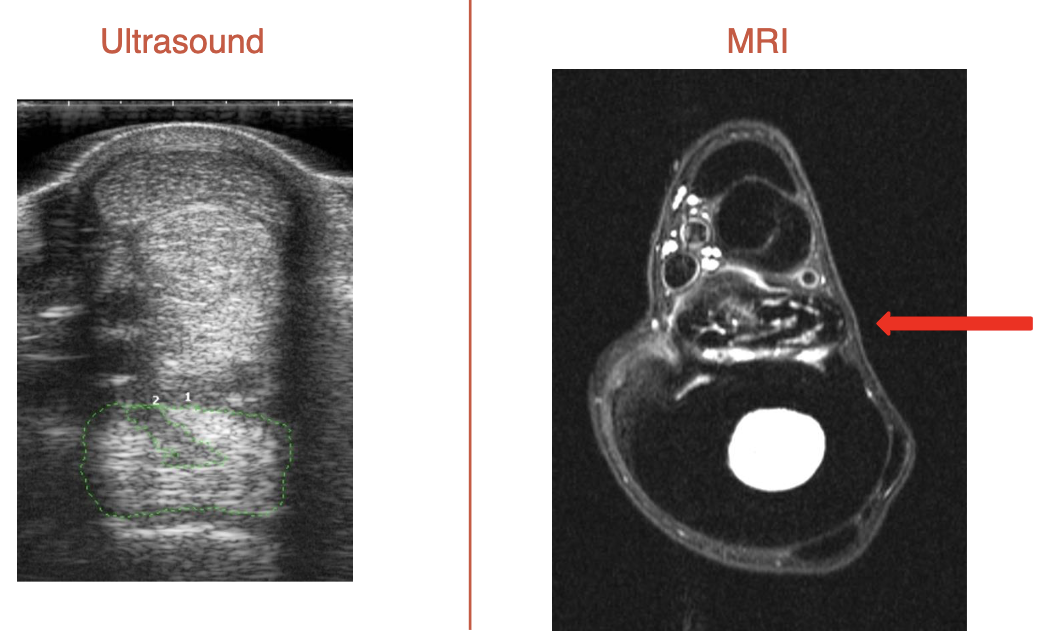
what is this
suspensory ligament desmitis
green is surrounding tear
on left side of MRI, bulging out is visible, hitting neurovascular bundle and causing pain
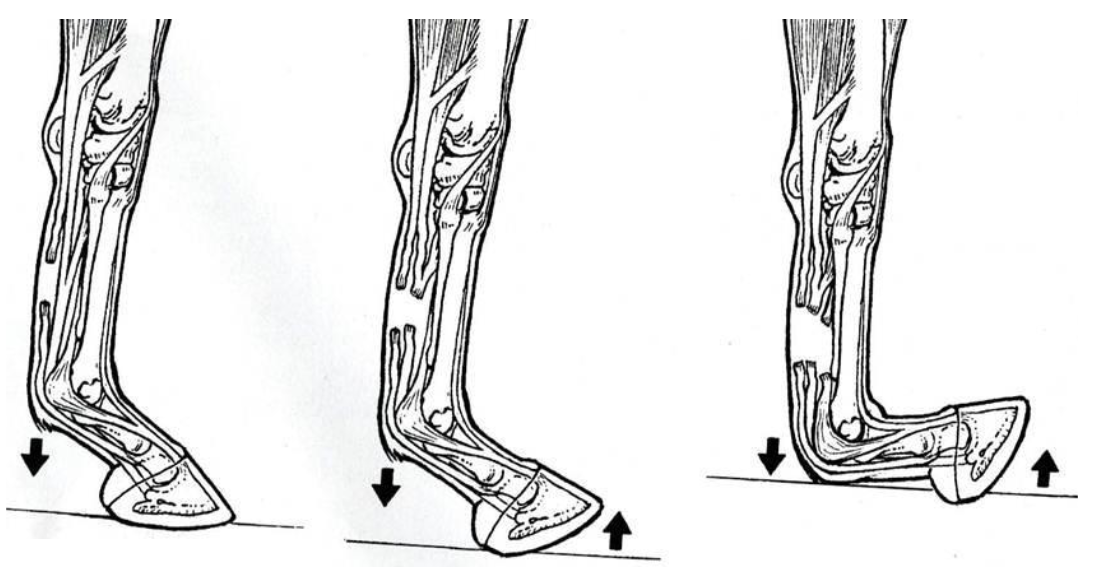
what tendons are torn for these lacerations (L to R)
SDFT only
SDFT & DDFT
SDFT, DDFT, & SL (completely plantigrade)
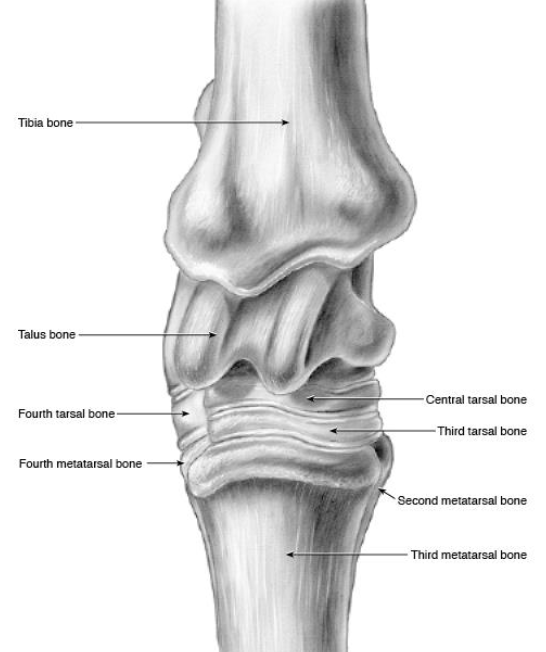
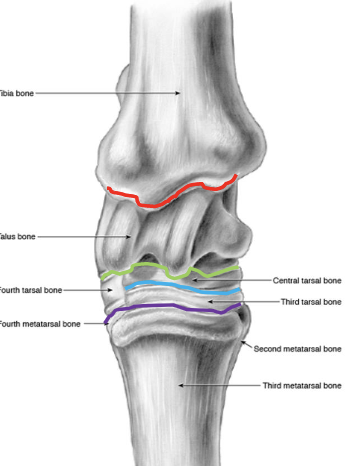
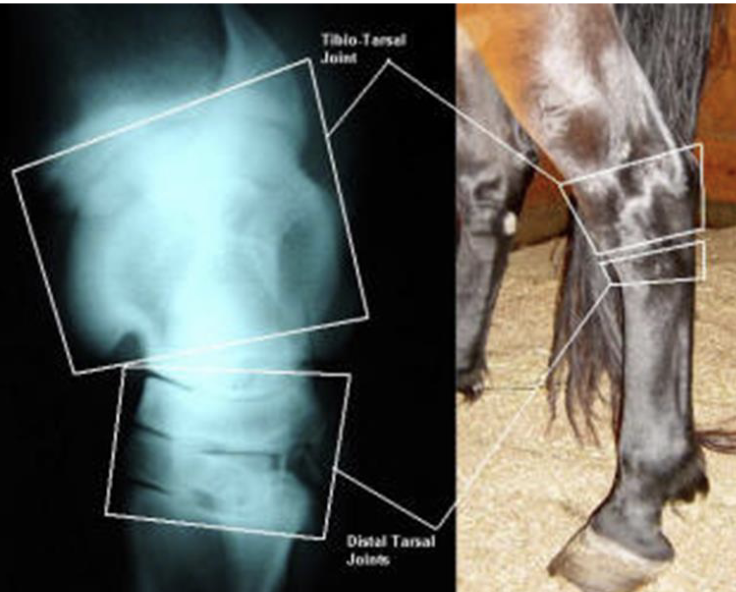
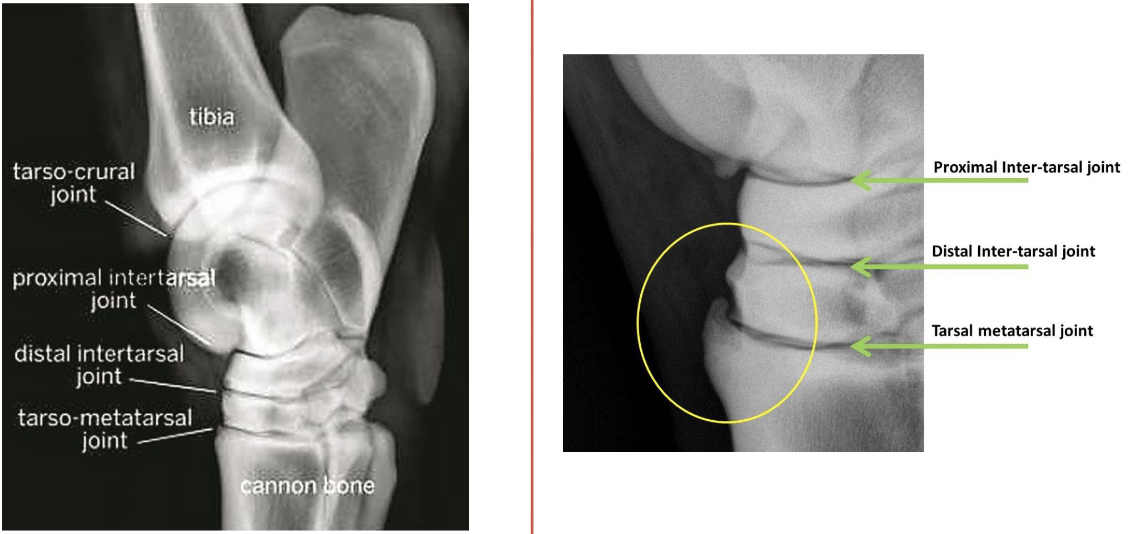
what are the bones of the tarsus
distal tibia, calcaneus + sustentaculum tali (fused), talus (+ medial and lateral trochlea), central tarsal bone, 3rd tarsal bone, 4th tarsal bone, fused 1 & 2 tarsal bone, proximal 2 3 and 4 metatarsal bones
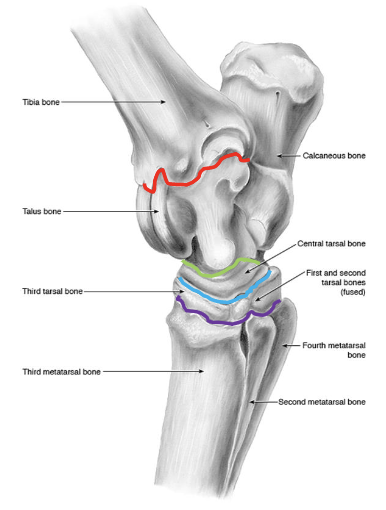
joints of the tarsus
red- tibiotarsal (or tarsocrural)
green- proximal intertarsal
blue- distal intertarsal
purple- tarsometatarsal
which joints of the tarsus communicate w/ e/o
tibiotarsal and proximal intertarsal joints
which tarsal joints are the most common sites of arthritis in horses
distal intertarsal and tarsometatarsal
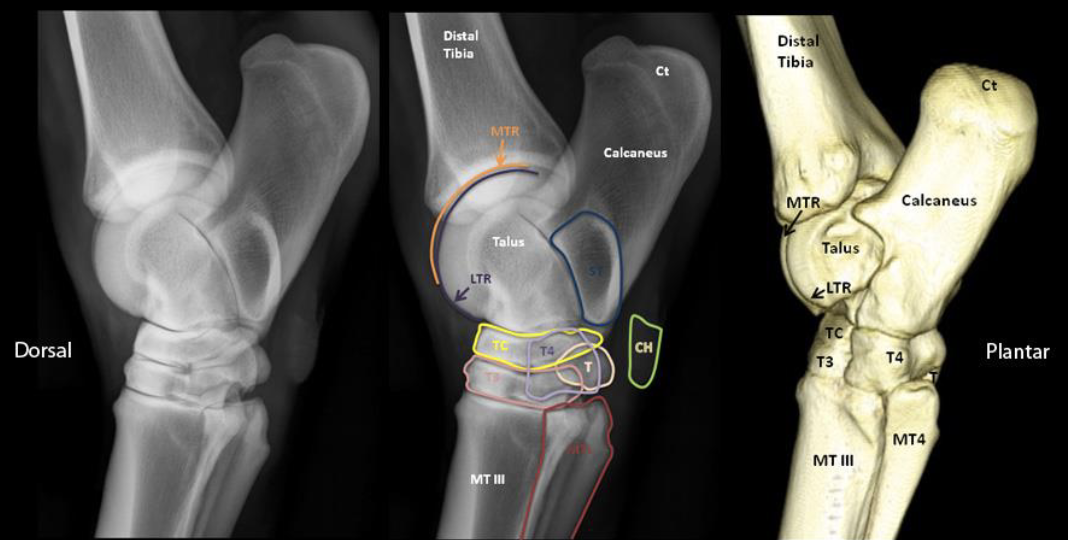
identify middle image
orange- medial trochlear ridge (of talus bone)
purple- lateral trochlear ridge (of talus bone)
blue= sustentaculum tali
green= chestnut
yellow= central tarsal bone
pink= 3rd tarsal bone
light purple= 4th tarsal bone
cream= fused 1 & 2 tarsal bone
red= metatarsal 2 and 4
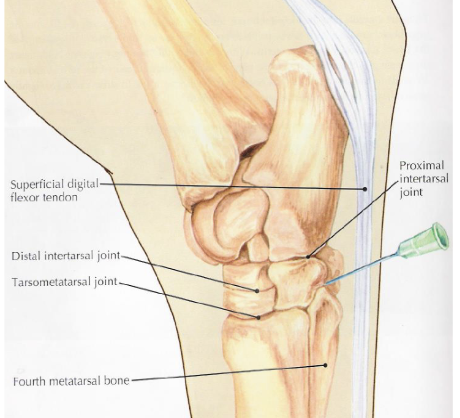
what is desensitized in a tarsometatarsal joint block
joint
what is desensitized in a distal intertarsal joint block
joint
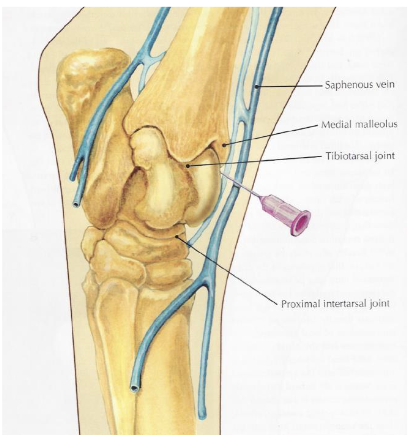
what is desensitized in a tibiotarsal joint block (dont hit saphenous vein)
tibiotarsal joint & proximal intertarsal joint (communicate w/ e/o)
stifle
bones- patella, distal femur (+ medial and lateral trochlear ridges), tibia
lateral trochlear ridge of femur is shorter and smaller than medial
soft tissue structures- 3 patellar lig (medial middle lateral), medial & lateral collateral lig
joints- femoropatellar, medial femorotibial, lateral femorotibial
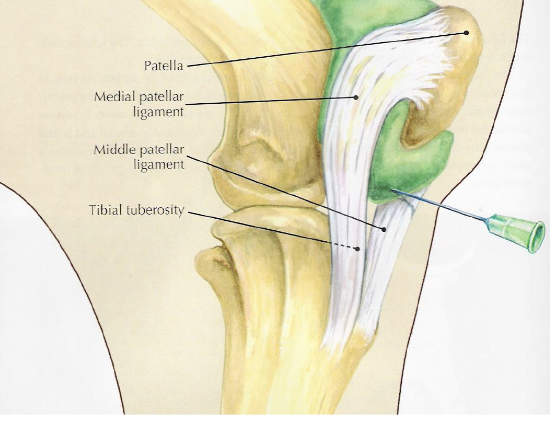
what is desensitized with a femoropatellar joint block
joint, in 65% of horses it can communicate w/ medial femorotibial joint but youre never sure which horses so you treat them all separately
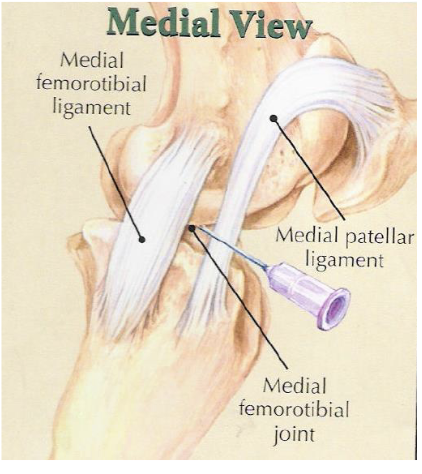
what is desensitized with a medial femorotibial joint block
joint, +/- communication w/ femoropatellar joint in some horses
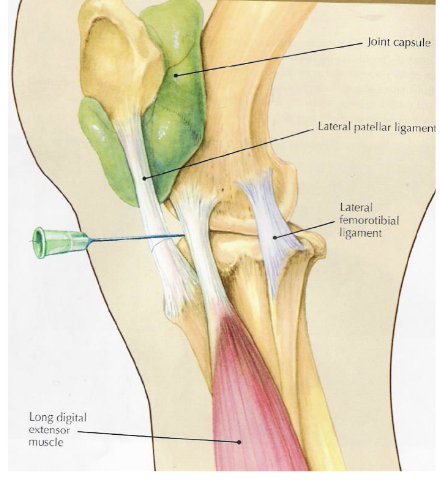
what is desensitized with a lateral femorotibial joint block
joint
degenerative joint disease “arthritis”
a radiographic diagnosis
most common location in horse are distal tarsal joints: distal intertarsal, tarsometatarsal
what are the radiographic abnormalities that dx arthritis (in order of apperance)
osteophytes & enthesiophytes (bone spurs)
joint space thinning
subchondral bone sclerosis (more opaque)
periosteal proliferation (sunburst, more mineralized on surface of bone)
subchondral bone lysis (darker on rad)
ankylosis (joint fusion)
what is this
distal tarsal joint osteoarthritis (OA)
what is circled on image on the right
osteophyte (bone spur, body is trying to fuse joint)
patient has distal tarsal joint osteoarthritis
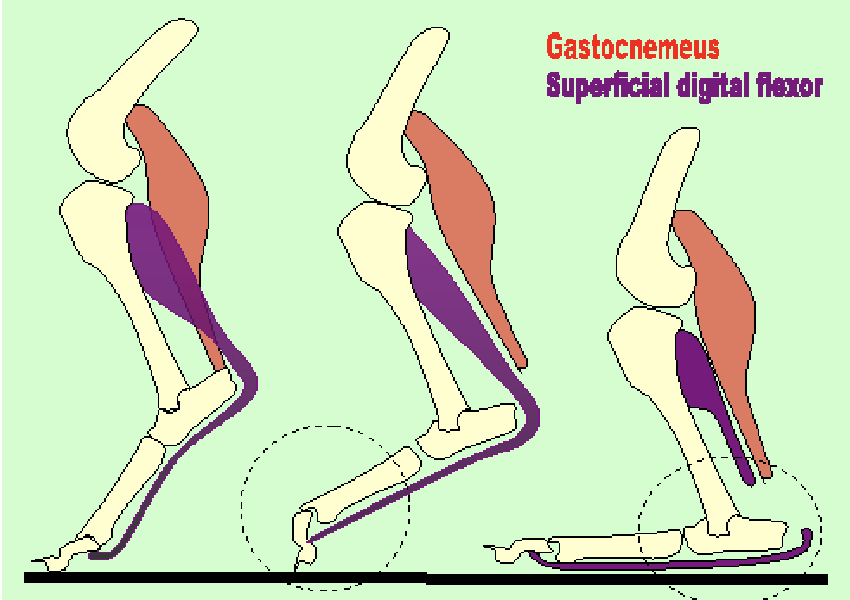
gastrocnemius lacerations, left to right
normal
gastrocnemeus only (plantigrade stance)
gastroc & SDFT → cannot stand
pathway for normal abdomen anatomy
esophagus→stomach→duodenum→jejunum→ileum→cecum(R side, blind ending sac)→right ventral colon→sternal flexure→left ventral colon→pelvic flexure→left dorsal colon→diaphragmatic flexure→right dorsal colon→transverse colon→small colon→rectum
what makes the horse a hind gut fermenter
large/ascending colon
difference btwn dorsal and ventral colons
dorsal= smooth
ventral= has sacculations (bumpy)
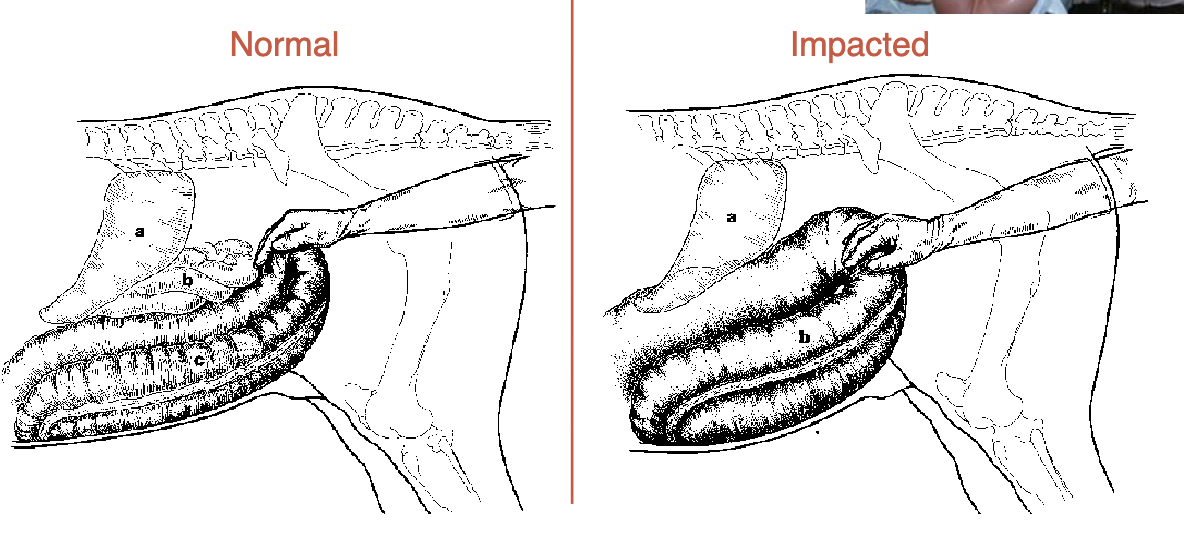
what is a common cause of colic
pelvic flexure impaction
sx→pelvic flexure enterotomy
normally, can feel at lower L of colon but when impacted it is very easily reached (at anus)
what is this
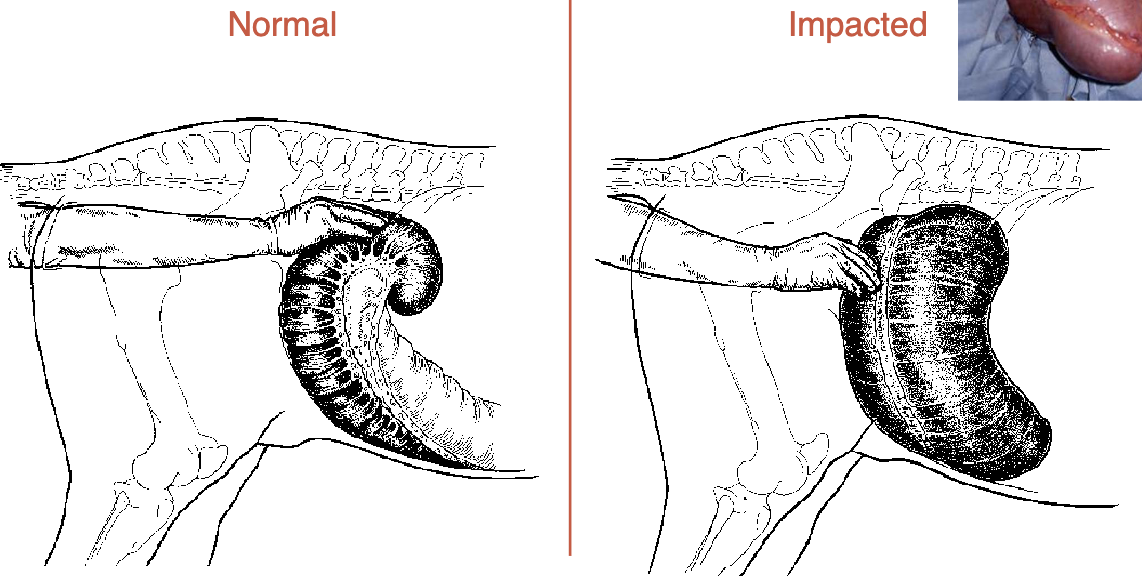
cecal impaction
sx→ typhlotomy
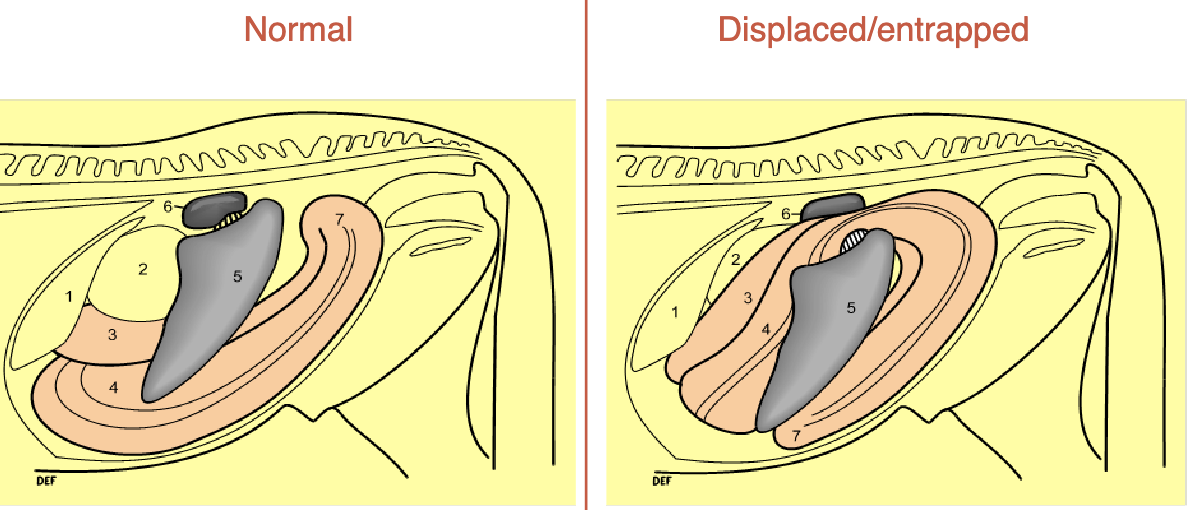
left dorsal displacement is aka
nephrosplenic entrapment
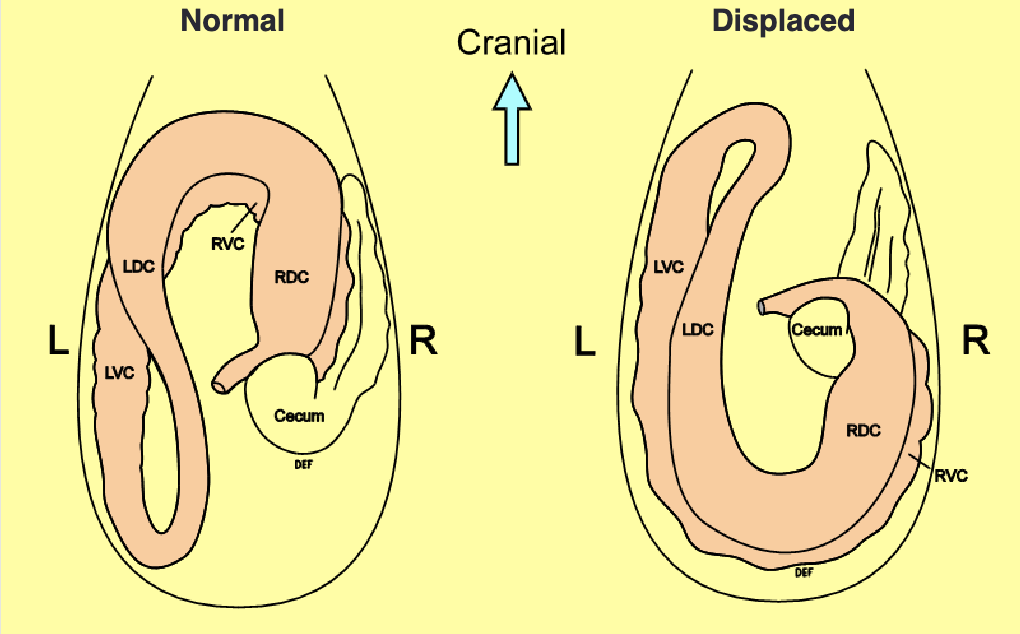
right dorsal displacement
pelvic flexure is high and on R side (normally low and L)
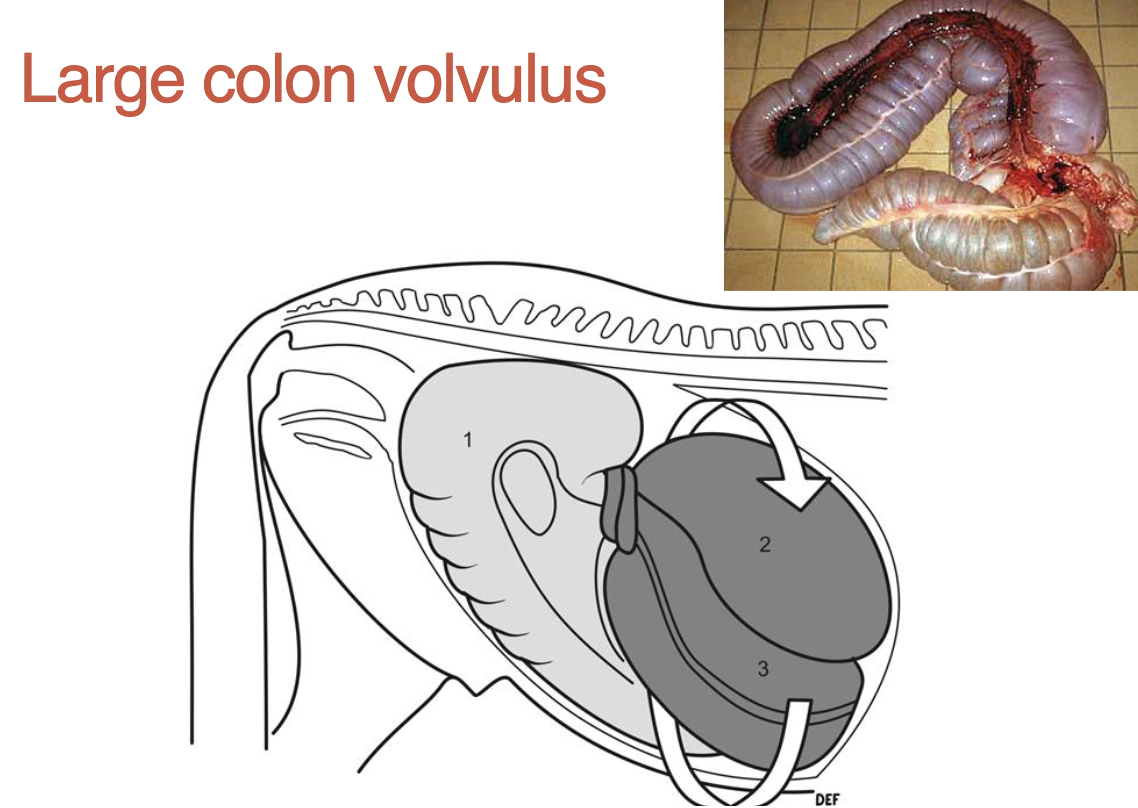
what is a large colon volvulus
twist on mesentery (location of blood vessels, cuts off supply & colon dies)
small intestine distension
blown up w/ fluid & gas, always feels abnormal (normally its smooth, texture is abnormal)
enterolith
stones of calcium and magnesium in intestine, common in southwest, usually in right dorsal colon theyre single
from transverse colon → small/descending colon theyre multiple
where does a nasogastric inubation occur
ventral nasal meatus (no ethmoid turbinates here)
what happens if you hit the carotid while getting a jugular stick
p will seizure
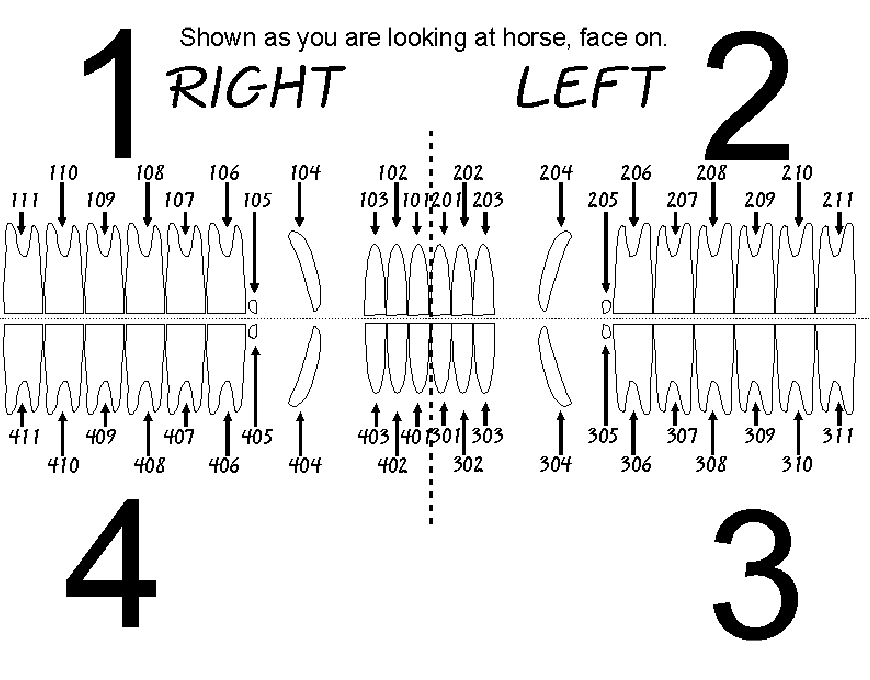
dental anatomy- triadan system
1-upper right
2-upper left
3- lower left
4-lower right
x01= first incisor
x04= canine
x05= wolf tooth
x08= last premolar
x09= first molar
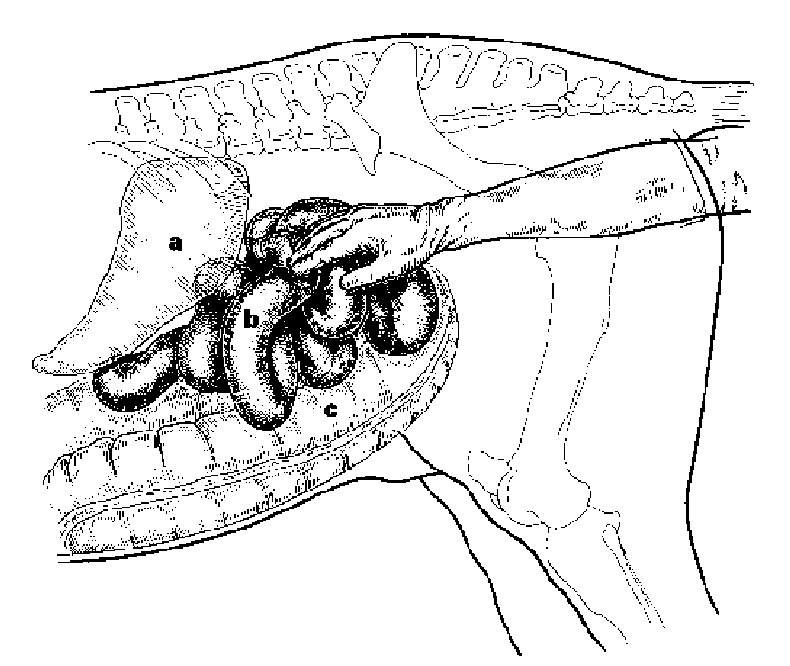
paranasal sinuses
frontal
maxillary (rostral and caudal compartments)
sphenopalatine
dorsal conchal
middle conchal
ventral conchal
bold= clinically relevant
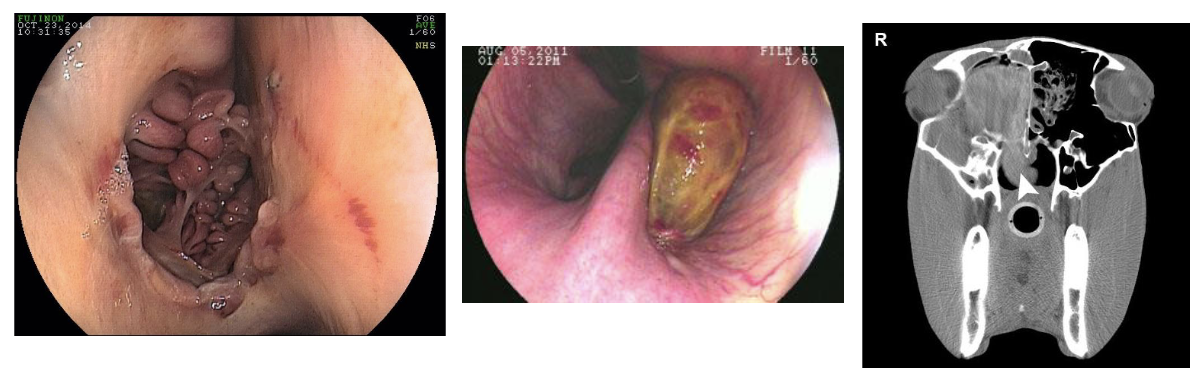
frontal sinus: ethmoid hematoma
mild, intermittent, unilateral, spontanous epistaxis (bloody nose)
smooth, glistening mottled green surface
unknown cause
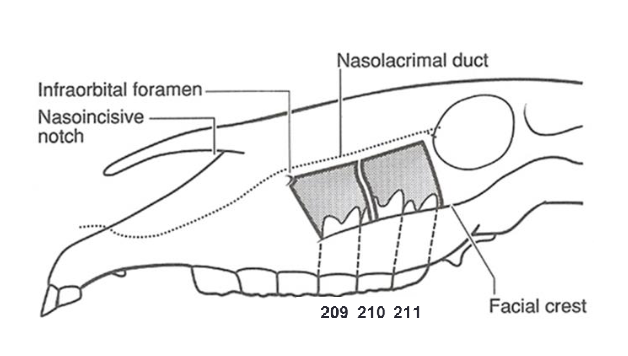
maxillary sinuses
109/209 teeth communicate w/ rostral compartment
110/210 and 111/211 communicate w/ caudal compartment
tooth root infections =
secondary sinusitis
guttural pouch
paired extensions of the eustachian tubes
connects pharynx to middle ear
has various theorized functions
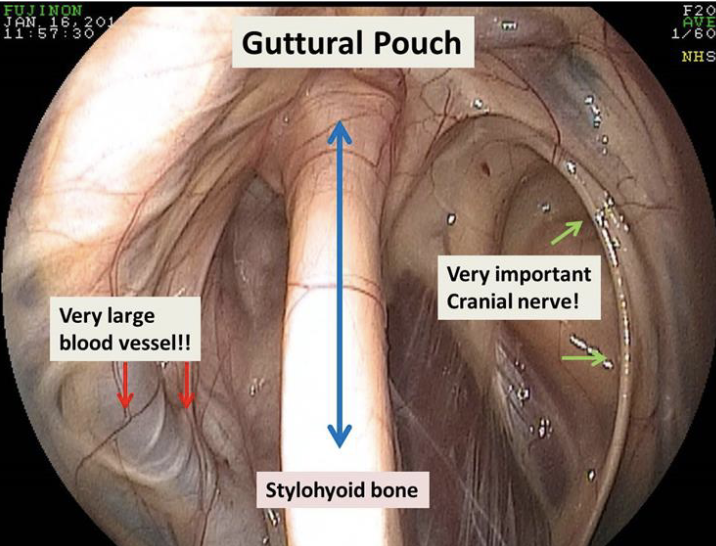
what divides the guttural pouch into medial and lateral compartments
stylohyoid bone
how does the guttural pouch communicate with the pharynx
through the nasopharyngeal orifice of the eustachian tube
this orifice also allows access to guttoral pouch w/ endoscope
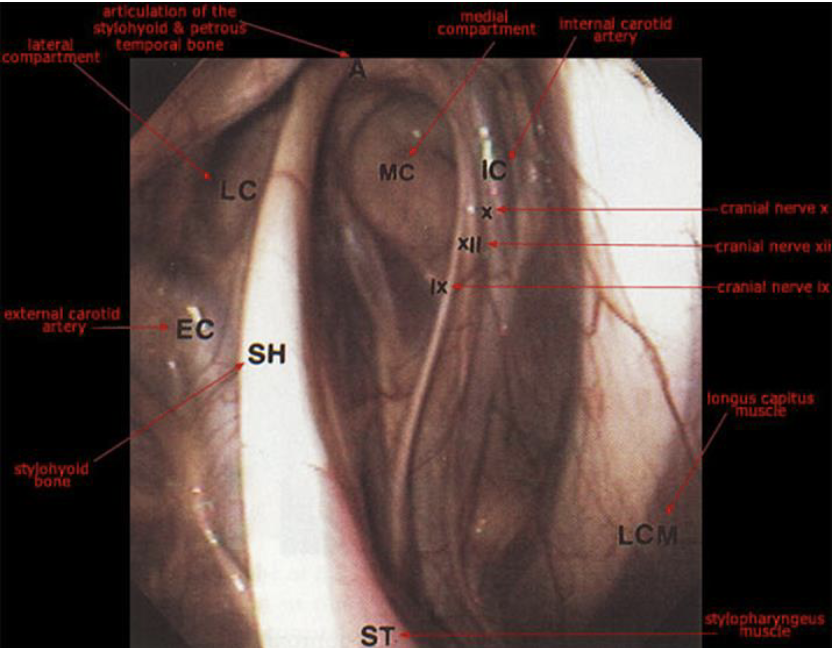
what runs in the guttural pouch
external carotid artery (lateral compartment)
cranial nerves 9-12 and internal carotid a. (medial compartment, contained within a fold of mucous membrane on caudal wall)g
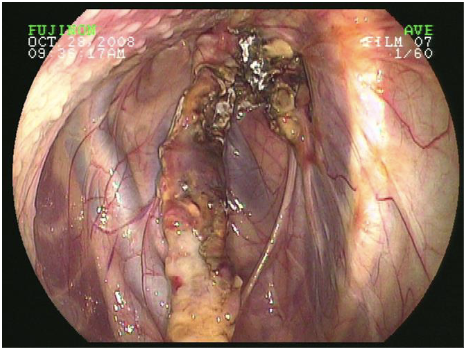
guttural pouch mycosis
fungal infxn caused by Aspergillus species
unilateral dz
no predisposition
diphtheritic membrane composed of necrotic tissue, cellular debris, bacteria, and fungal mycelia
can lead to severe & often fatal bilateral epistaxis
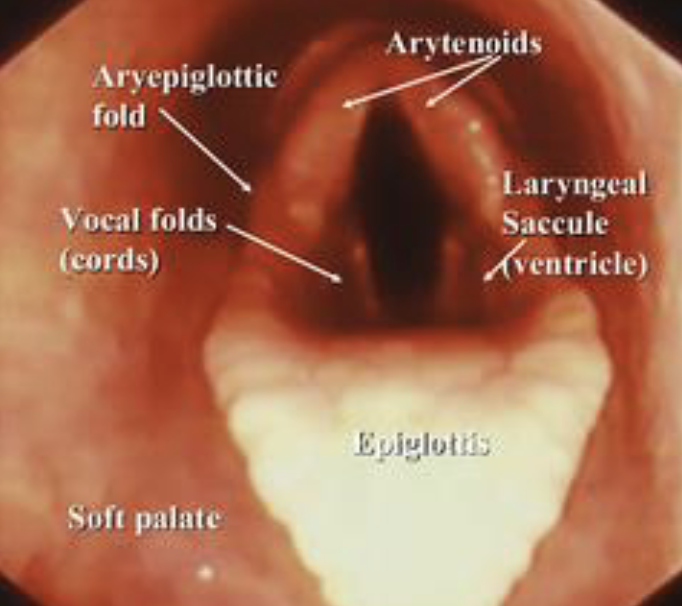
larynx endoscopic view
arytenoids, aryepiglottic fold, vocal folds, laryngeal saccule, epiglottis
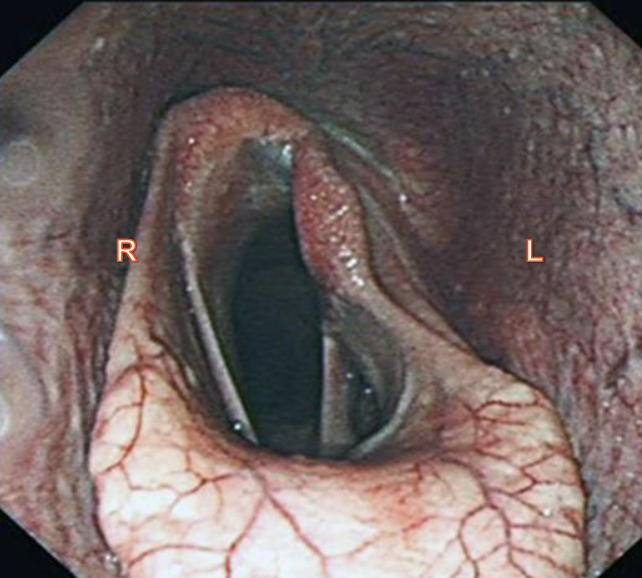
laryngeal hemiplagia
half paralysis
aBduct- to move away from midline done by dorsal cricoarytenoid muscle (innervated by left recurrent laryneal nerve)
aDduct- move towards middline
jugular venipuncture
omohyoideus muscle, between carotid a and jugular v
muscle is thicker top 2/3 which will separate carotid and jugular for easier venipuncturegu
guttural pouch cranial nerves cause
9- dysphagia
10- facial paralysis
11- n/a
12- dysphagia