Chapter 17: Special Senses
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What are the 5 special senses?
olfaction
gustatoon
vision
hearing
equilibrium
Constrast the general and special senses
general:
somatic sensations (tactile, thermal, pain, proprioceptive) & visceral sensations
scattered throughout body
relatively simple
special:
smell, taste, vision, hearing, equilibrium
concentrated in specific regions of head
anatomically distinct & have complex neural pathways
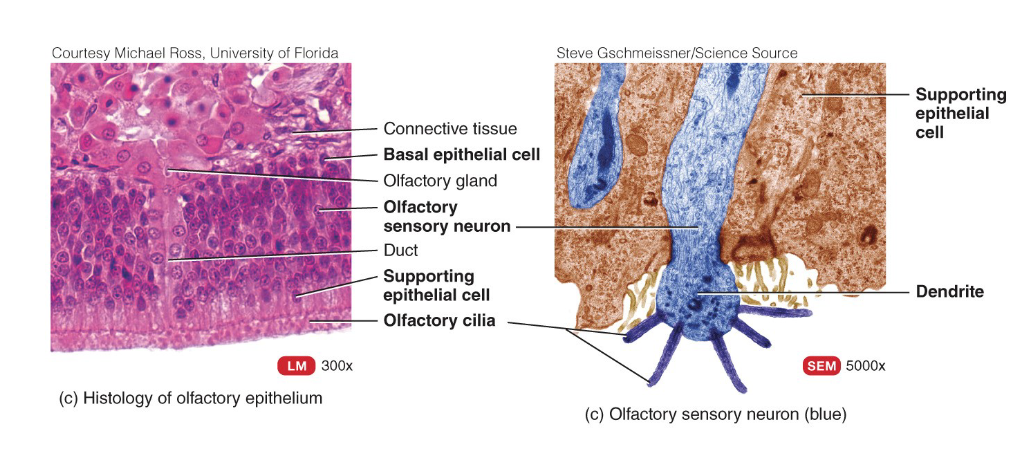
Where is olfactory apithelium located
covers inferior surface of cribiform plate (of ethmoid bone)
extends along superior nasal concha
What are the 3 types of olfaction cells. Briefly describe each
olfactory receptor cells (Bowman’s glands) → produce mucus to dissovle odor molecules for transduction
supporting cells (columnar epithelium) → located in mucus membrane; physical supprt, nourishment, insulation for olfactory receptor cells
basal cells → undergo mitosis to replace olfactory receptor cells
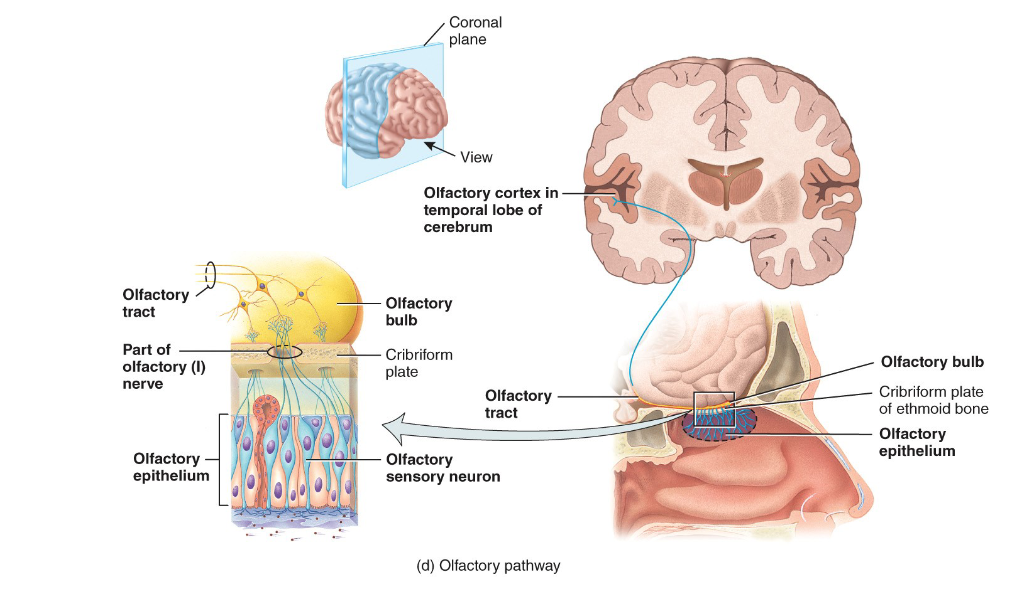
Describe the pathway of impulses along branches of olfactory (I) nerve
through cribiform plate (2 olfactory nerves)
synapse w/ olfactory bulbs
travel along olfactory tract
interpretation in primary olfactory area in cerebral cortex (temporal lobe)
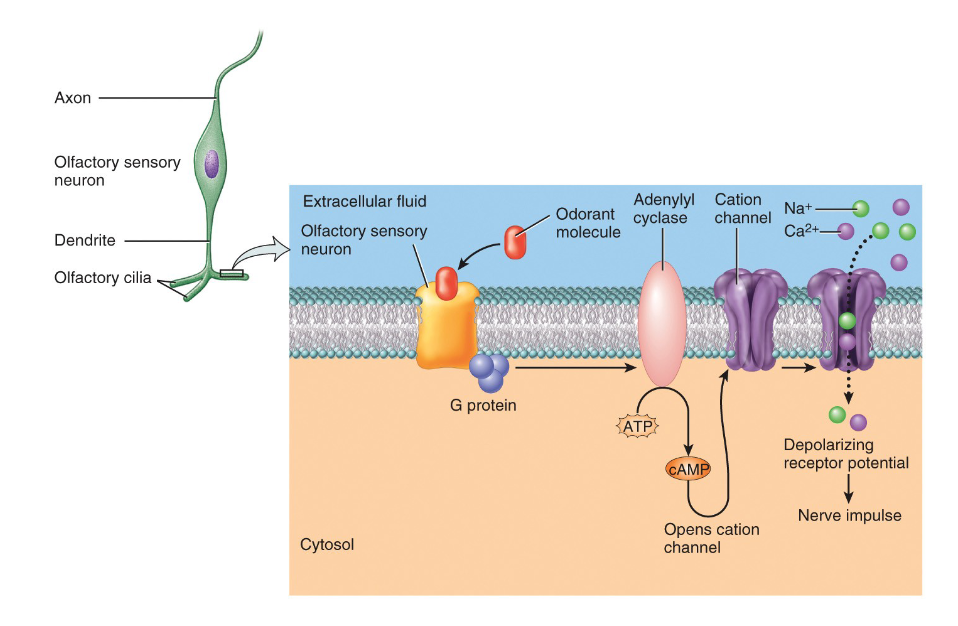
Describe olfactory transduction
binding of an odorant molecle to olfactory receptor protein
chemical reactions involving cyclic AMP (cAMP) cause depolarization
action potential travels to primary olfactory area
impulse travels to frontol lobe for odor identification
Olfaction is the only sensory sytem that has direct _________
cortical projections w/o first going through relay stations in the thalamus
What are the 5 primary tastes (gustation)?
sour
sweet
bitter
salt
umami (meaty, savory)
Taste buds contain 3 kinds of epithelial cells:
supporting cells
gustatory receptor cells
basal stem stells
Describe the function of gustatory hairs
gustatory hairs → long microvillus
projects from each receptor cell to the surface through the taste pore
Each gustatory receptor cell has a lifespan of about __ days
10
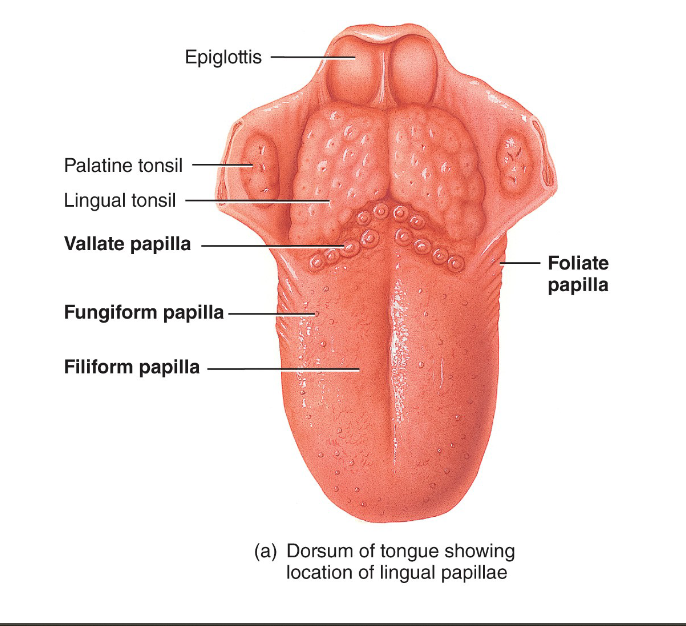
Taste buds are located in elevations on the tongue called ___.
papillae
What are teh 3 types of papillae that contain taste buds?
Vallate pillae → ~12 that contain 100-300 taste buds
Fungiform papillae → scattered on tongue w/ ~5 taste buds each
Foliate papillae → located in lateral tranches of tonuge (most of their taste buds degenerate in early childhood)
Describe filiform papillae
cover entire surface of tonuge
contain tactile receptors but NO taste buds
increase friction to help tongue move food within mouth
Briefly describe the 3 cranial nerves involved in gustation
facial (VII) nerve → carries taste info from anterior 2/3 of tongue
glossopharyngeal (IX) nerve → carries tase info from posterior 1/3 of tongue
Vagus (X) nerve → carries taste info from taste buds on epiglottis & in throat
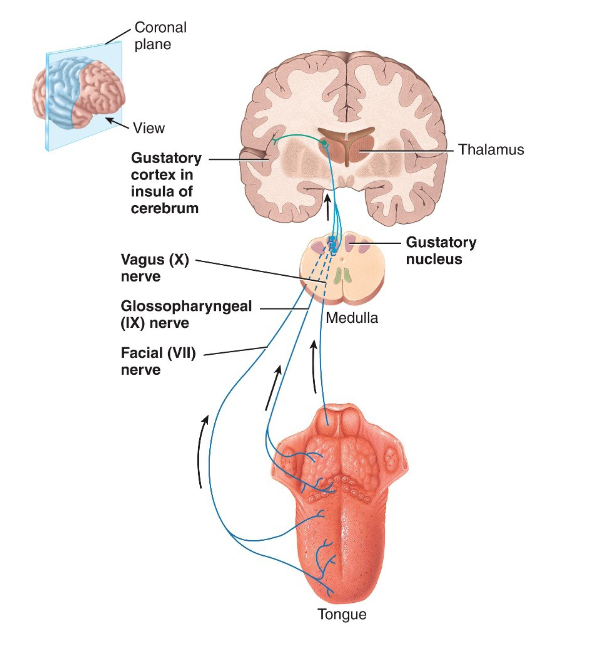
Trace the pathway of nerve impulses along the gustation cranial nerves
propogate along cranial nerves → gustatory nuceleus in medulla oblongata
acons carrying taste signals project into hypothalamus, luimbic system, & thalamus
taste is perceived consciously as signals from the thalamus arrive at the primary gustatory area in parietal lobe
List our sensitivity to different taste/substances from most sensitive to least
bitter
sour
salty/sweet
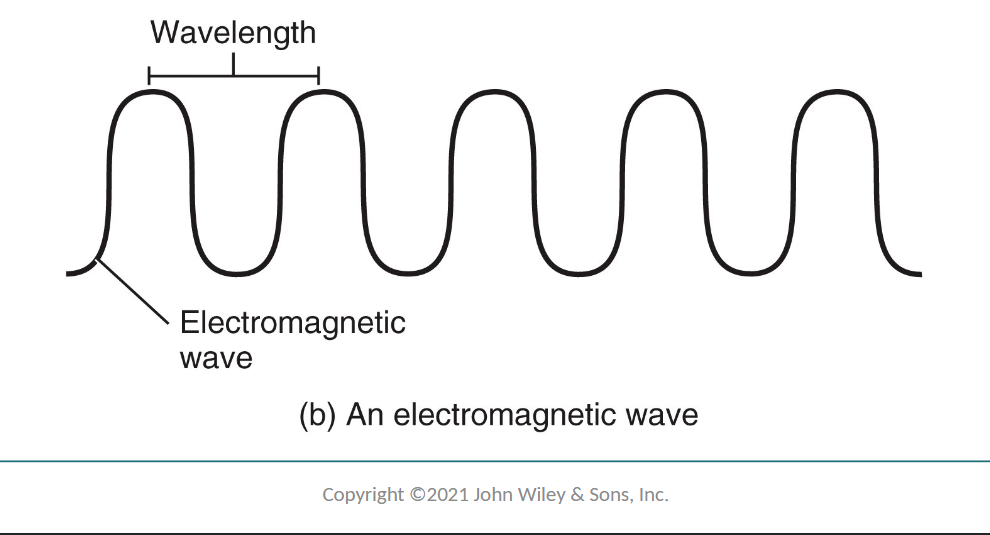
Describe how vision works
uses visible light
part of electromagnetic spectrum w/ wavelengths from 400 → 700 nm
define wavelength
distance between two consecutive peaks of an electromagnetic wave
List the accessory structures of the eyes
eyelids
eyelashes
eyebrows
lacrimal apparatus
extrinsic eye muscles
Which muscles control eyelid movement (1) and which muscles move the eyeball itself in all directions (2)?
palpebral muscles
extrinsic eye muscles
What is the conjunctiva?
thin, protective mucous membrane lining the eyelids & covering the sclera
what is the tarsal plate?
fold of CT that gives form to the eyelids
contains row of sebaceous glands that keep eyelids from sticking
What is another name for the upper and lower eyelids?
upper & lower palpebrae (palpebra singular)
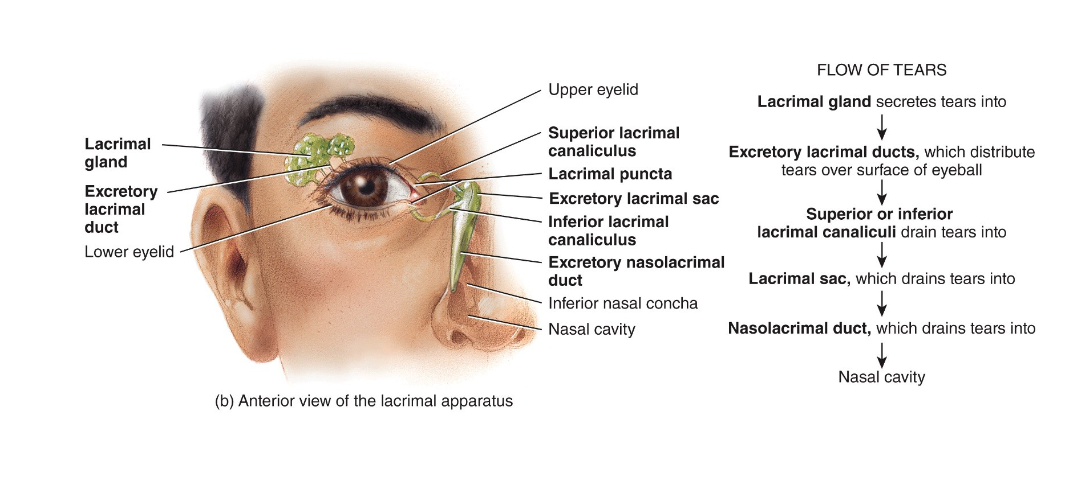
What produces & drains tears?
lacrimal apparatus
Trace the pathway for tears
lacrimal glands
lacrimal ducts
lacrimal puncta
lacrimal canaliculi
lacrimal sac
nasolacrimal ducts carry tears into nasal cavity
list the 6 extrinsic eye muscles
superior rectus
inferior rectus
lateral rectus
medial rectus
superior oblique
inferior oblique
When do watery eyes occur?
lacrimal fluid builds up when smth obstructs the nasolacrimal ducts (e.g. inflammation of nasal mucosa from a viral cold)
overproduction of lacrimal fluid occurs in response to parasympathetic stimulation (emotional crying) → tears spill over edges of eyelids & drain into nasal cavity
List the 3 layers/tunics of the eyeball and what each are composd of
Fibrous tunic (outer) → sclera (white of the eye) & cornea (transparent epithelium)
Vascular tunic (middle) → choroid, ciliary body, iris
Nervous tunic (inner) → retina
Describe the function of