Chapter 8 - Energy, Enzymes and Metabolism
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Chemical Reaction
The change in the composition or distribution of atoms of a substance with consequent alterations in properties
A chemical reaction has the following two components:
Reactants
Products
Sucrose + H2O reacts to form ____ and ____
Glucose and fructose
* This is a hydrolysis reaction. Water is added to sucrose in order to break it down into glucose and fructose.
Metabolism
Sum total of all chemical reactions occurring in a biological system at a given time
Metabolism involves changes in _______
Energy
Energy is the capacity to do ______, or the capacity for change
Work
What are the two forms of energy?
Kinetic
Potential
Potential energy is energy stored as _______, _______, or ________
Chemical bonds
Concentration gradients
Charge imbalance
Kinetic energy is the energy of _______
Movement
First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy is neither _____ nor ______
Neither created nor destroyed
* You can only change the form of the energy. The total energy before and after the conversion is the same.
Second Law of Thermodynamics states that when energy is converted from one form to another, some of that energy becomes __________
Unavailable to do work
The second law of thermodynamics states that some energy becomes unavailable to do work when energy is converted from one form to another. Some energy is lost to ______
Disorder
Entropy (S) is a measure of the ______ in a system
Disorder
The amount of disorder tends to increase because of _____________
Energy transformations
In a biological system, the total amount of energy is called ________
Enthalpy (H)
In a biological system, ________ is the usable energy that can do work.
Free energy (G)
In a biological system, usable energy is called free energy (G). Unusable energy is represented by the product of ____ and ____
Entropy (S) and Absolute temperature (T)
* Enthalpy = Free energy + Absolute Temp x Entropy
* H = G + TS
What’s the equation for enthalpy in terms of free energy, entropy, and absolute temperature?
H = G + T(S)
* You can rearrange this formula in order to solve for each individual variable.

What part of this formula is missing?
G (reactants)
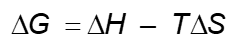
Change in energy can be measured in ______ or ______
* A picture of the formula for free energy was attached
Calories
Joules
If ΔG is a positive value, then this indicates that energy is _______
Required
If ΔG is a negative value, then this indicates that energy is _______
Released
If ΔG is zero, then this indicates ___________
No reaction is occurring
Endergonic reactions are reactions that ______ free energy. This reaction is represented by a positive ΔG value.
Consume
Endergonic reactions are represented by a _______ ΔG value
Positive
Exergonic reactions are reactions that ______ free energy. This reaction is represented by a negative ΔG value.
Release
Exergonic are represented by a ______ ΔG value.
Negative
Helpful Info - How to remember that Endergonic reactions consume free energy:
Match the word endergonic with the word enter. Something is being consumed or entering into
Helpful Info - How to remember that Exergonic reactions release free energy:
Match the word exergonic with the word exit. When something exits, it is also being released.
Anabolism results in more _____ but less ______
More complexity, but less disorder
Catabolism results in less_____ but more______
Less complexity, but more disorder
Chemical Equilibrium is when the rate of a reaction forward is equal to the rate of the _______ reaction.
Reverse
At chemical equilibrium there is no net change. ΔG is equal to ______ at chemical equilibrium.
Zero
Food is broken down by ______ reactions
Catabolic
The components of food are used in ______ reactions
Anabolic
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
ADP
Adenosine Diphosphate
AMP
Adenosine Monophosphate
ATP captures and ______ free energy
transfers
ATP can be hydrolyzed to _____ and _____, releasing a lot of energy for endergonic reactions.
ADP and Pi
ATP can also ____ other molecules, which gain some energy
Phosphorylate
Phosphorylation
Donation of a phosphate group to a molecule
Is the formation of ATP endergonic or exergonic?
Endergonic
The formation and hydrolysis of ATP couple _____ and _____ reactions
Endergonic and exergonic
Is cell respiration endergonic or exergonic?
Exergonic (releases energy)
Is active transport endergonic or exergonic?
Endergonic (requires energy)
Is cell movement endergonic or exergonic?
Endergonic (requires energy)
The synthesis of ATP from ADP and Pi requires _______
Energy
ATP ______ energy to endergonic reactions
Releases
Catalysts _____ rates of chemical reactions
Increase
Are catalysts altered by the reactions?
No
Most biological catalysts are ______, that act as a framework in which reactions can take place
Enzymes
Which type of RNA can be catalytic?
Ribozymes
Catalysts speed up reactions by ____________
Providing space for the reactants to bond
Activation Energy (Ea) is the amount of energy required to ______ the reaction
start
Activation energy puts the reactants in a reactive mode called the _________
Transitive state
Activation energy changes the reactants into _________ with higher free energy—transition state intermediates.
unstable forms
Enzymes lower the energy barrier by bringing the _______ together
reactants
Enzymes are highly specific in the reactions with substrates. The part of the enzyme that interacts with the substrate is called the ________
Active site
* Substrate molecules bind to this part
Reactants are called ______. These molecules bind to the active site of the enzyme
Substrates
The ______ of the enzyme determines specificity
3D shape
What are the 6 categories of enzymes
Oxidoreductases (oxidization)
Hydrolases (hydrolysis)
Transferases (transfer functional groups)
Isomerases (make isomers)
Lyases (break bonds)
Ligases (forms bonds)
The _________ is held together by hydrogen bonds, electrical attraction, or covalent bonds
Enzyme-substrate complex (ES)
An uncatalyzed reaction has greater ______________ than a catalyzed reaction
activation energy
There is no difference in __________ between catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions
free energy
Enzymes can increase reaction rates by __________
1 million to 10^17
Enzymes do not change ________ and _______
Final equilibrium
Energy released as a result of the reaction
Enzymes reduce ________ and increase ________
Reduce energy barrier
Increase rate of reactions
3 Ways for Enzymes to Catalyze a Reaction
Orient substrates to fit each other
Induce substrates (stretching the substrate)
Temporarily add chemical groups
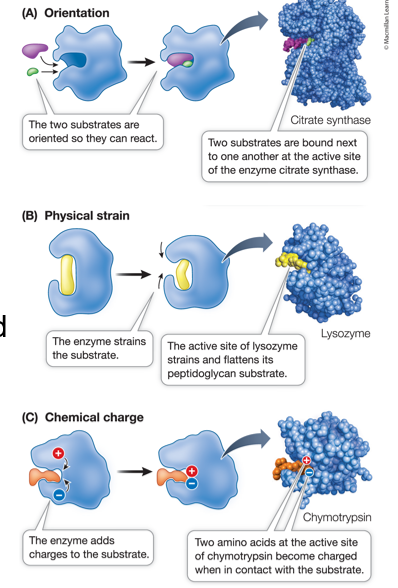
Enzymes can catalyze a reaction by temporarily adding a chemical group. Acid Base Catalysis is an example of this. Define this:
Add/Remove H+ in order to destabilize covalent bonds
Enzymes can catalyze a reaction by temporarily adding a chemical group. Metal Ion Catalysis is an example of this. Define this:
Add/Remove electrons
Enzymes can catalyze a reaction by temporarily adding a chemical group. Covalent Catalysis is an example of this. Define this:
Form covalent bonds
What 3 features determine an enzymes function?
Specificity
Shape
Induced fit (change in enzyme shape when binding to substrate, which also changes active site shape)
Induced Fit
A change in the shape of the enzyme when binding to a substrate. The shape of the active sit is changed.
Ribozymes
RNA molecules that act as biological catalysts
Some enzymes require “partners” or additional groups. What is a Prosthetic group?
Non-amino acid groups permanently bound to enzymes
Some enzymes require “partners” or additional groups. What is a inorganic cofactor?
Ions permanently bound to the enzyme
Some enzymes require “partners” or additional groups. What is a Coenzyme?
Temporarily-bound small carbon containing molecules (Ex: vitamins)
Rate of a catalyzed reaction depends on ________
Substrate concentration
The concentration of an enzyme is usually _____ than the substrate
Much lower
At low substrate concentration, the presence of an enzyme _______ the reaction rate
Greatly increases
At __________, all enzyme is bound to substrate; it is working at maximum rate.
Saturation
Turnover Number
# of substrate molecules converted to product per unit time (ranges from 1 to 40 million molecules per second)
One of two ways of controlling enzyme activity is Regulation of Gene Expression. What does this do?
Regulates how many enzyme molecules are made
One of two ways of controlling enzyme activity is Regulation of Enzyme Activity. What does this do?
Can block or change the shape of enzymes
Chemical reactions in cells are organized in metabolic pathways that are interconnected. Enzymes help organize and regulate ___________
Metabolic pathways
What are enzyme inhibitors?
Molecules that bind to the enzyme and slow reaction rates
Enzyme inhibitors bind to the enzyme and slow reaction rates. They can be naturally occurring or artificial. What is the purpose of naturally occurring inhibitors?
Regulate metabolism
Enzyme inhibitors bind to the enzyme and slow reaction rates. They can be naturally occurring or artificial. What is the purpose of artificial inhibitors?
Treat disease
Kill pest
Study how enzymes work
What type of bond occurs in reversible inhibitors and what is the effect on the enzyme?
Noncovalent bonds
Reversible (prevents substrates from binding)
What type of bond occurs in irreversible inhibition and what is the effect on the enzyme?
Covalent bonds
Permanently inactivate enzyme
Competitive inhibitors compute with the _______ for binding sites
Natural substrate
* The degree of inhibition depends on concentrations of substrate and inhibitor
Methotrexate
Anti-cancer drug
Binds to the enzyme that catalyzes formation of a coenzyme for purine formation
Purine
Needed for DNA replication and cell division
Allosteric Regulation is when a non-substrate molecule binds the enzyme at __________, which ____________
A site different from the active site, which changes enzyme shape
Active Form of Enzyme
Enzyme has the proper shape to bind substrate
Inactive Form of Enzyme
Enzyme cannot bind substrate
Non-substrate molecules may be an ________ or _______
Inhibitor or an activator
Most allosteric enzymes are proteins with _______ structure
Quaternary
The active site of allosteric enzymes is located on the __________
Catalytic subunit