Biology: Module 6 - Genetic Change
1/127
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
what are two types of ways mutations are formed?
spontaneous or induced
what is mutagenesis?
process of inducing mutagens
what are the three types of mutagens?
chemical, naturally occuring, physical
what are chemical mutagens?
chemicals that cause mutations if cells are exposed for large periods of time
what is the effect of chemical mutagens?
inserts incorrect nucleotides (mispairing) —> changes DNA —> changes function of proteins.
what are examples of chemical mutagens?
ingested: alcohol, tar
environmental: benzene, asbestos
what are naturally occuring mutagens?
present at normal levels within natural environments and may cause mutations
what does naturally occuring mutagens effect?
change the function of genes —> can reduce efficiency of DNA repair systems
examples of naturally occuring mutagens?
hepatitis B, HIV, mercury, cadmium
what is physical mutagens?
includes heat and ionising radiation
what is radiation
transfer of energy through space from a source
what is ionising radiation
harmful radiation that has enough energy to break chemical bonds in molecules (DNA)
when ionising radiation breaks DNA what are some effects of that:
causes deletions, chromosome loss, rearranging DNA sequences, crosslinking of DNA, disturbs cell division, cell metabolism
what is electromagnetic radiation
short wavelengths with high ionising energy —> split electrons that causes damage in cells
what is the effect UV radiation
produces pyrimidine dimers (cross-linked nucleotides) that prevents nucleotides from pairing with complementary bases —> ends the strand prematurely —> affects cell cycle and gene products
what are pyrimidine dimers?
adjacent pair of bases on the same strand become attached to each other
what is the relationship between wavelength and ionising energy?
increasing ionising energy means shorter wavelengths
list the waves in increasing frequency:
radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, UV, X-rays, gamma rays
give some examples of physical mutagens
Electromagnetic Radiation: radio waves, gamma rays
Ultraviolet Radiation: UVA, UVB
Artificial: radioactive material, atomic bombs, nuclear power, X-rays
what is UVA’s effect
more related to ageing rather than mutagenic and carcinogenic
what is UVB’s and UVC’s effect?
have shorter wavelengths so are higher in ionising energy
is mutagenic and carcinogenic
what are the two types of DNA repair mechanisms?
nucleotide excision repair
mismatch repair
what is nucleotide excision repair
a damaged or incorrect base pair is removed by a nuclease enzyme and replaced
what is mismatch repair
once DNA has replicated, DNA polymerase carries out a spell check for accuracy of replication
what is good mutations
creates new alleles that benefit an organism
what are bad mutations
affect the survival of organisms
can neutral alleles change frequency?
have a fixed frequency unless gene flow or genetic drift occurs
why are mutations important?
mutation creates new alleles → creates variation → necessary for evolution
what two genes lead to cancer if mutated?
Proto Oncogenes
Tumour Suppressor Genes
what are proto oncogenes
code for proteins that stimulate cell cycle, promote cell growth
what are tumour suppressor genes?
code for proteins that repress cell cycle progression —> promote apoptosis (cell death)
what is cancer
uncontrolled cell division
what are spontaneous mutations
arise randomly from an error within natural process of DNA replication
what are induced mutations?
arose from environmental agents (chemical/radiation) that increases the change of nucleotide sequences being changed
what are point mutations
changes a single base pair of DNA - only affects a single gene (gene mutation)
what are chromosomal mutations
moves whole blocks or genes to different parts of a chromosome —> changes a series of bases = several genes
what is the effect of chromosomal mutations?
overall chromosome structure changes or the number of chromosomes in a cell changes
what is the affect of mutation on DNA
nucleotide base may be substituted, deleted, inserted
change change one amino acid or none
what is frameshift mutation
a type of point mutation that causes all subsequent codons to be read wrong
includes insertion and deletion
what are types of point mutations
substitution, frameshift (includes insertion, deletion)
what are three types of point mutation effects?
nonsense mutations
silent mutations
missense mutations
what are nonsense mutations
changes an amino acid to a stop codon
what are silent mutations
changes in DNA sequence that doesn’t change an amino acid
what are missense mutations
non-conservative missense: results in a different amino acid with a different type (basic or polar)
conservative missense: results in a different amino acid with the same type as the original amino acid
what are the 4 types of chromosomal mutations
deletion
duplication
inversion
translocation
what is deletion in chromosomal mutations?
Removal of sections of DNA
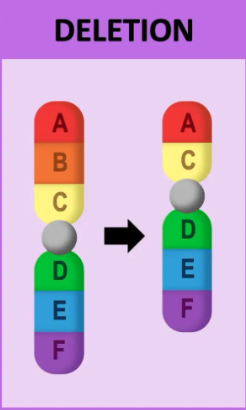
Reduces the gene number
Cause: high heat, viruses, radiation
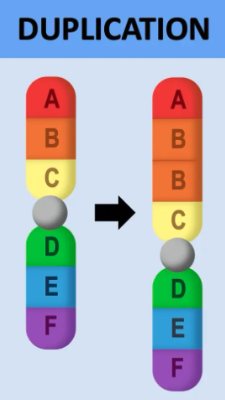
what is duplication in chromosomal mutations?
Portion of DNA is duplicated/inserted → increases total number of genes
Location of duplication (intron/exon) and number of repeats → determines phenotypic effect
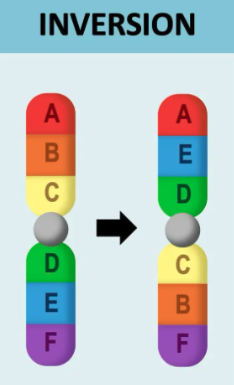
what is inversion in chromosomal mutation?
When a section of DNA is removed, turned around 180o , and reinserted into the chromosome
The bases are in reverse order
E.g. haemophilia
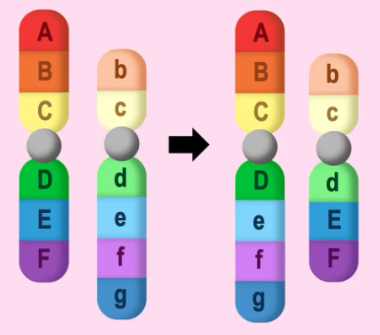
what is translocation in chromosomal mutation?
When a section of DNA is moved from one chromosome to a non-homologous chromosome
Leads to gene fusion → region joins two normally separate genes
Some scientists think transposons (transposable elements) inserted into DNA millions of years ago = making up a large portion of non-coding DNA
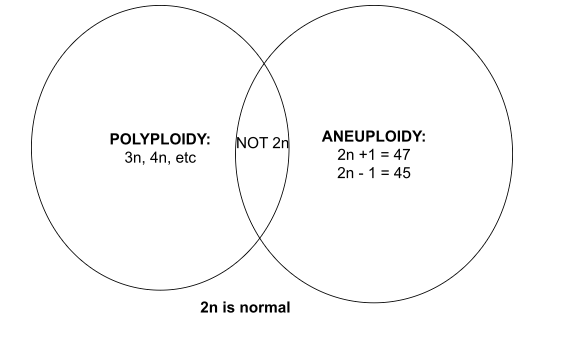
what is aneuploidy
a chromosomal abnormality when 1 or more copies of an entire chromosome are made or an entire chromosome is missing
when is aneuploidy caused?
usually by non-disjunction (in anaphase) during meiosis I or II
what is an example of aneuploidy?
Trisomy 21 → 3 copies of 21st chromosome = Down’s Syndrome
what is polyploidy?
Def. contains more than two full sets of chromosomes
what is the difference between polyploidy and aneuploidy?
how does mutations affect organisms?
the type of cells where mutations occur determine the extent of the effect
what are germline mutations?
Germline mutations (in gametes)
A mutation occurs in the cells that produce gametes → appears in gametes
Passed onto every cell in the offspring formed from that gamete
The offsprings gametes will have it too
what are somatic mutations? its cause? its result?
Somatic Mutations (rest of body)
Cause: DNA replication errors prior to mitosis
Spontaneous mutations may occur in the S phase of the cell cycle → go unrepaired by the cell → will go to the daughter cells through mitosis
May result in an observable phenotypic difference e.g skin cancer
May lead to a localised effect (e.g tumour) → NOT heritable
what is coding DNA
DNA transcribed into mRNA → translated into amino acid sequences → forms proteins
is prokaryotes DNA mainly non-coding or coding?
Prokaryotes’ DNA is mainly coding DNA
Many genes are responsible for DNA repair enzymes to maintain the DNA
If these genes are deactivated → prokaryotes have an ⬆ in the rate of mutation
(same for eukaryotes)
what is the importance of coding DNA
an organism’s phenotype is dependent on the direct result of the coding DNA
what is the effect of mutations on coding DNA
Proteins aren’t produced or Proteins aren’t produced properly → effect of that protein on the organism is changed
Mutations that occur on the tumour suppressor genes → cancer (gene for suppressing mitosis is deactivated)
examples of mutated coding DNA?
E.g. mutated BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes can lead to breast or prostate cancer
E.g. Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP): recessive genetic disease
Without XP → DNA repair enzymes work → fix damaged DNA
With XP → DNA repair enzymes don’t work → damaged DNA doesn’t get fix → can lead to cancer
XP → more susceptible to UV damage → skin cancer
what is non-coding DNA
DNA which does not result in a direct protein product (polypeptide)
Can be important as acting as a buffer to separate genes → if mutation occurs it won’t affect coding DNA
what are the roles of non-coding DNA? (sting)
satellite DNA: repeating sequences
telomeres: repetitive DNA at the end of chromosomes
introns: non-coding sequences within genes
non-coding RNA genes (e.g. tRNA)
gene regulatory sequences (sequences involved in transcription: promoters, enhancers, silencers)
what are enhancers
increase the frequency of gene expression by attaching proteins that help turn on particular genes
what is the effect of mutations on non-coding DNA?
Changes gene expression (light switch 💡)
Mutation can turn on a gene → causes a protein to produced at the wrong point
Can close a gene → eliminates the production of necessary proteins
Have NO effect
what are some examples of non-coding DNA mutation?
E.g. isolated pierre robin sequence
Caused by changes in non-coding DNA → changes the enhancer elements (SOX9 gene)
SOX9 is important in embryonic development
E.g. Lactose Tolerance:
Mutation is in lactase enhancer region → causes a binding site for transcription factors
Lactase gene is constantly expressed → allows adults to consume lactase
what are the causes of genetic variation (3)
fertilisation
meiosis
mutation
what is fertilisation and its sources of variation?
(Def.) 2 gametes fuse together to form a zygote
sources of variation:
Requires 2 gametes, infinite number of combinations |
Random, equal probability |
Dominant and recessive interaction |
what id the definition of meiosis and its sources of variation
Gamete production as parent cells divide into 4 haploid daughter cells
sources of variation:
Random mutations during DNA replication or during separation/disjunction of chromosomes
Crossing over, combinations of alleles - prophase I
Random segregation (corresponding alleles), anaphase I & II (in meiosis)
Independent assortment (non-corresponding alleles), anaphase I & II
what is the definition of mutation and its sources of variation
(Def.) A permanent change to an organism’s DNA sequence
sources of variation:
Introduction of new alleles
Missense, nonsense, silence
what are the 5 factors of mutation on population
selective pressure
sexual selection
mutation
genetic drift (more obvious in smaller populations)
gene flow (more obvious in larger populations)
what is selective pressure, the reasons alleles change and its effect on the next generation?
Selective Pressure | natural selection | Variations that are passed on = individuals are more likely to survive | Alleles that make individuals more likely to survive become most frequent |
what is sexual selection, the reasons alleles change and its effect on the next generation?
Certain individuals more attractive to mate - more likely to breed | Non-random mating | Alleles of attractive individuals are more common |
what is mutation, the reasons alleles change and its effect on the next generation?
New genes arise due to errors in DNA replication | New alleles arise during gametogenesis | New alleles that are beneficial are frequent |
what is genetic drift, the reasons alleles change and its effect on the next generation?
Random events (e.g. tornado) lead to a change in gene frequency because some indiv are dead | Random chance (non-selective) | Individuals within a population to be different because they were lucky |
what is gene flow, the reasons alleles change and its effect on the next generation?
Indiv with different genes come into a population and spread their alleles | Mix with genetically different individuals (immigration/emigration) | Allele frequency in population changes |
what is the definition of biotechnology?
use of biological organisms, their products or their processes to make new products that are useful to humans in areas (industry, agriculture, medicine)
what is ancient biotechnology and its features? (before 1800s)
Relied on observation, trial-and-error No actual understanding of genetics |
|
what is classical biotechnology (1800s - 1950s) and its features
More systematic approach, used microbiology and chemistry to refine techniques |
|
what is modern biotechnology and its features?
Modern (1952 - today) 1952 - discovery of DNA | Direct genetic manipulation, very advanced understanding of genetics/reproduction |
|
what ethical frameworks are biotechnologies deemed ethical from?
Utilitarianism: greatest amount of good for most people
Rights: people have the right to choose
Fairness/Justice: ethical choices are free from discrimination/favouritism
Common Good: assumes individual’s own good is linked to the good of society
Virtue: everyone holds internal morals that we maintain and hold onto
what are disadvantages of biotechnologies?
Unequal access based on factors like race,sex, socioeconomic status
Patenting of technology by private companies
human/animal rights violation
Violation of privacy
Impacts on health
give the social and ethical benefits and disadvantages of Bt Cotton (pest resistant cotton)
Social | ✅
❌
|
Ethical | ❌
|
give the social and ethical benefits and disadvantages of Transgenic Salmon (GMO that grows faster)
Social ✅
❌
|
Ethical ❌
|
what are some future directions for biotechnology?
Personalised Medicine: gene therapy could allow doctors to give treatments based off an individual’s genetic profile → more effective
Lab-Grown Meat: cultured meat from animal cells which reduces the need for livestock slaughter, sustainable, lower environmental impact, food security
De-extinction: using cloning and genetic technology to revive extinct species
Biodegradable plastic: engineering bacteria to make sustainable materials
what are potential benefits for using genetic technology?
Disease prevention and treatment
Agricultural productivity
Environmental protection: reduce pesticide/fertiliser use, lower greenhouse emissions
Sustainable food production: higher yield, faster rates
Industrial and environmental applications: biofuels, biodegradable materials, bioremediation
what are positive changes to earth’s biodiversity due to genetic techniques?
Increased genetic diversity in crops
Conservation efforts → cloning endangered species, preserve genetic material
Bioremediation: restore ecosystems through GMOs
what are negative changes to earth’s biodiversity due to genetic techniques?
Loss of natural biodiversity: GM crops outcompete wild relatives
Monocultures: Heavy reliance on specific crops makes them vulnerable to disease
Transgenes could spread to wild species
what are 4 methods of reproductive technologies?
artificial insemination
in vitro fertilisation
artificial pollination
selective breeding
what is the use of artificial insemination and its advantages?
use: livestock, infertility treatment in humans
advantages:
Synchronise pregnancies
Combat infertility issues
Easier to transport frozen sperm
Combats endangered species
what is the use of IVF and its advantages
use: occurs outside the body for infertility treatments in humans
advantages: freeze embryos, genetic screening
what is the use and advantages of artificial pollination?
use: Pollinating crops for desired offspring, Genetic experiments
advantages: controlled inheritance of traits
what is the use of selective breeding and it’s advantages?
use: Breeding offspring with desirable traits → agriculture, Friesian Bull: produces creamy milk
advantages: Desirable traits in offspring, is fertile, hybrid vigour
what are 3 types of cloning techniques
organism cloning
therapeutic cloning
gene cloning
what is the use and advantage of organism cloning?
Livestock industry | Definite inheritance of traits |
what is the use and advantage of therapeutic cloning (SCNT)?
def. a technique used to create stem cells that are genetically matched to a patient
Medicine, stem cell technologies | Stem cells can differentiate |
what is the use and advantage of gene cloning?
Medicine and industry | Large scale production of relevant proteins |
what is the use and advantage of transgenesis?
Agriculture eg. golden rice and frost berries | Organisms with multiple functions |
what is the use and advantage of gene sequencing?
Medicine treatments and genetic research eg. BRCA1 gene | Identification of genetic disorders, risks, inheritance, forensic biology |