Biology I- Chapter 11 questions
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is DNA and what does DNA stand for?
The genetic material that provides the blueprint to produce an individual’s traits
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
What are the structural levels of complexity of DNA?
nucleotides→DNA strand→double helix→chromosomes→genome
What is the structure of the DNA nucleotide? know the three parts and be able to identify them; you do not need to know the details at the atomic level
sugar, phosphate, and base
What are Chargaff’s (AT/GC) rules?
the amount of adenine was similar to the amount of thymine; the amount of guanine was similar to the amount of cytosine
What was the role of Watson and Crick in determining the overall structure of the DNA molecule?
in 1953 they realized the DNA molecule is made up of two chains of nucleotide that are intertwined; i.e a double helix
Explain how the structure of the DNA molecule is analogous to a “rope” ladder
the sugar-phosphate group act as the sides of the ladder, the backbone. the bases act as the steps of the ladder
What does “base pairing is complementary” mean? *What are the base pairings?
The bases are paired in specific combinations. Adenine forms hydrogen bonds with Thymine, Guanine forms hydrogen bonds goes with Cytosine
What does antiparallel mean in the context of DNA? *How do you determine the 5’ end? The 3’ end?
The two strands run in opposite directions to one another. DNA replicates from 5’ to 3’ and reads from the 3 to 5’
How does the leading strand of DNA get replicated? *What is the semiconservative model of replication? What stage during the cll cycle does this occur?
Parent strands separate (open up like a notebook) and each strand serves as a template for ordering nucleotides into a new complementary strand (daughter strands)
The daughter molecules will have one old strand and one newly made strand. Occurs during DNA replication
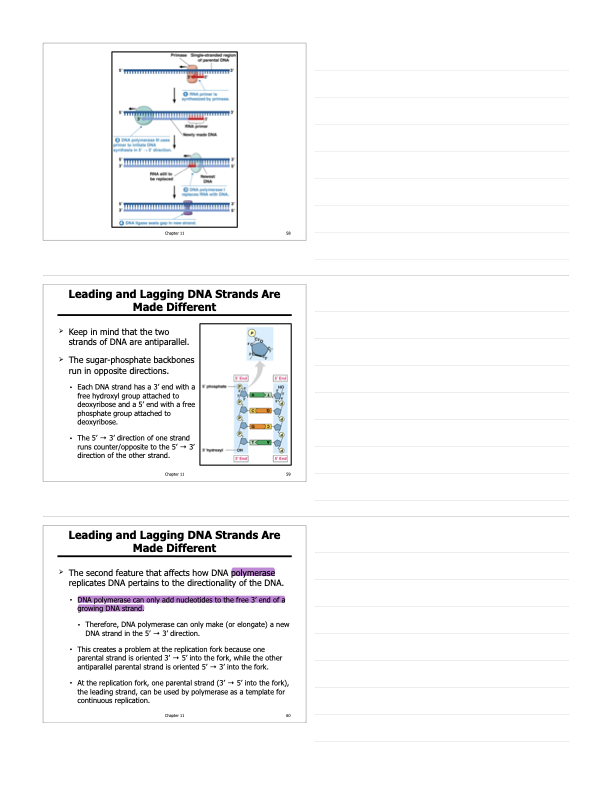
What are the major “players” involved in how the leading strand of DNA gets replicated and what are their roles? *Helicase, DNA single-stranded binding proteins, primase, primer, and DNA polymerase?
-First event in DNA replication is the separation and unwinding of the two strands of DNA occurs by enzymes DNA helicase and DNA topoisomerase
-DNA single-stranded binding proteins then bind to the separated strands to keep them from re-forming the double helix
-As nucleotides align with complementary bases, they are added to the growing end of the new strand by the polymerase.
-DNA polymerase cannot initiate synthesis of new DNA on a bare template strand; can only add nucleotides to the end of an existing chain that is base-paired with the template strand.
-DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the free 3’ end of a growing DNA strand.
-DNA primase, a type of RNA polymerase, makes the primer
-To start a new strand requires a primer, a short, complementary segment of RNA; primer is about 10 to 12 nucleotides long in eukaryotes.
What are telomeres? *What is their function and the role of telomerase?
ends of eukaryotic chromosomal DNA molecules that are specialized regions/structures and protect genes from being eroded through multiple rounds of DNA replication.
What does it mean by DNA having proofreading ability?
DNA polymerase has a proofreading capability that checks (and corrects) each new nucleotide against the template nucleotide as soon as it is added.
What are chromosomes and their structure?
double stranded, helical DNA, associated with different proteins to form a more compact structure.