Chapter 5 - Businesses In The Market Economy
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What is a business firm
An organisation using entrepreneurial skills to combine factors of production to produce a good or service for sale
What is an industry
An industry consists of firms involved in making a similar range of items that usually compete with each other
Business firms are the ………….. in our economy
major production units
Business firms size, behaviour and performance influence
overall productive capacity
Several factors may influence the decisions of investors and entrepreneurs
The skills and experience of the business operator
Industries where there is a strong consumer demand
Specific business opportunities
The amount of capital required to start the business
How do businesses decide how much to produce
Based on its assessment of the level of consumer demand and its ability to convert that demand into sales
How do businesses decide how to produce
The production process involves combining a range of resources (inputs) to create goods and services (outputs)
What is the sharing economy
A socio-economic ecosystem built around the sharing of human, physical and intellectual resources
What does the sharing economy include
Creation, production, distribution, trade and consumption of goods and services by different people and organisations
Businesses can also contribute to regional development
What are the benefits of regional development?
Better regional infrastructure
Improved liveability
Population attraction and retention
Growth in individual businesses also increases an economy’s
productive capacity
Increasing a nation’s productive capacity results in
greater economic output
greater competitive pressures, which leads to lower inflation and translated into improved living standards
Goals of a business firm
Maximising profits
Meeting the expectation of shareholders
Increasing market share
Maximising growth
Satisfying behaviour
What is productivity
Refers to how much we produce with a given quantity of resources, per unit of time
An increase in productivity can be defined as
an increase in output per factor of production
What is the formula for productivity
Total output/ Total input
What is production
Refers to the total amount of goods and services produced
How can we increase production
Increasing the amount of resources we use, or working those resources for a longer period of time
How can we increase productivity
Increase production proportionately more than the increase in input of resources
What are the benefits to an economy when firms use resources more efficiently
Increase in living standards
Productivity contributes to an improvement in our standard of living in several ways:
Less wastage of scarce resources
Lower production costs and higher profits for the business firms
Lower inflation rate
Higher incomes
Improved international competitiveness of Australia’s industries
One of the major ways business firms can increase their productivity is
specialisation
What is specialisation
Where factors of production are used more intensely for a smaller number of production processes
What is the specialisation of labour
Division of labour
What is division of labour and give an example
Occurs when businesses break down their production process into a number of sub-processes, allowing labour to specialise in a particular part of the process, and thus avoiding the time and effort of moving from one process to another
eg. assembly line for car production
What is the specialisation of land (natural resources)
Location of industry
What is location of industry and give an example
Occurs when a large number of businesses that produce similar goods and services congregate in the same area to reduce production costs by sharing common infrastructure requirements
Eg. concentration of advanced technology industries in Macquarie Park Industrial Area
What is the specialisation of capital
Large scale production
What is large scale production and give an example
Occurs when businesses grow so large they can use highly specialised capital equipment in their production process
Eg. large wine producer that uses specialised machines to bottle, cap and label wines
Firms are able to reduce their per-unit costs of production as
their output increases
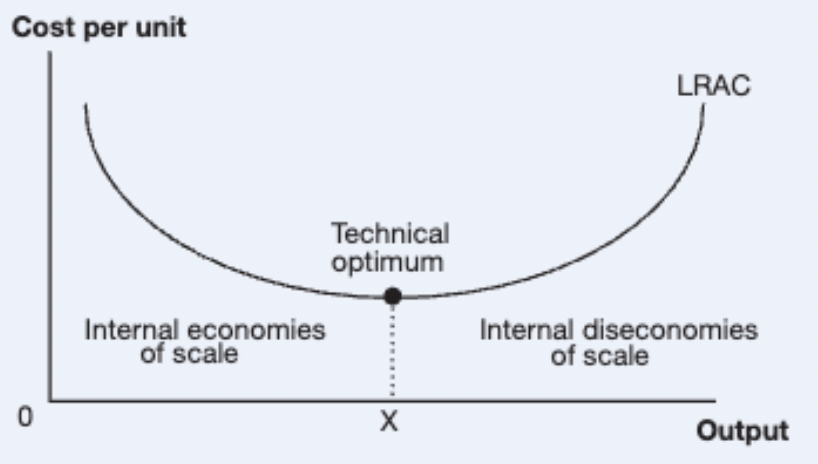
What is internal economies of scale
Concept that a firm needs to achieve a large scale production in order to minimise costs
Economies of scale occur when (in relation to graph)
a firm’s output level is below the technical optimum
Economies of scale are experienced when average costs per unit of production fall as
the size of output grows
Average cost is
the per-unit cost of production:
total cost of producing a certain level of output / the total quantity produced
The manufacturer will continue to expand the business, while the firm can lower per-unit costs because
this will increase the firm’s overall profitability
As a firm continues to lower per-unit costs of production, there will eventually reach a point where
the costs of production will start to rise because of certain disadvantages of being too big
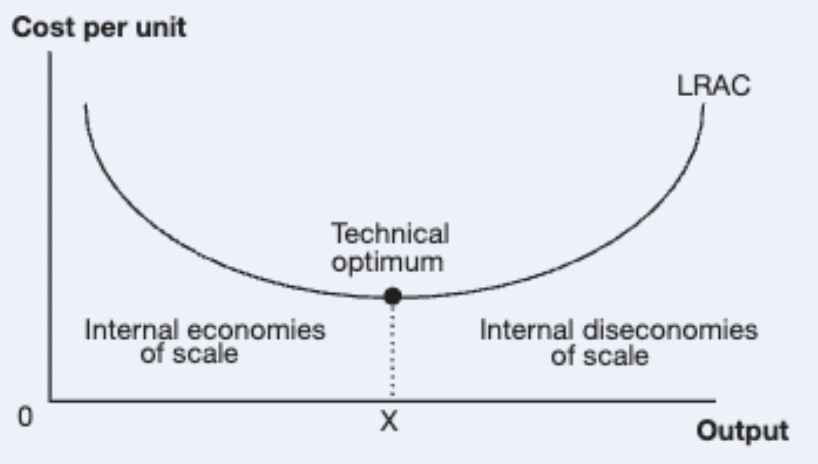
When the costs of production will start to rise because of certain disadvantages of being too big, this is known as
internal diseconomies of scale
Most of the factors that cause diseconomies of scale are related to
management problems
How can management cause internal diseconomies of scale
Management may not be able to:
Efficiently organise all areas of the business
Creating organisational congestion/lack of communication
Slowing down the production process and increasing costs
What are the cost-saving advantages of internal economies of scale (6)
By becoming bigger, the firm can specialise their labour
A large firm can invest in more efficient capital equipment
A large firm can buy its raw materials in bulk (generally reduces the per-unit cost of these inputs)
A large firm can generally find a market for its by-products instead of discarding them as waste
A large firm can put resources into research which can lead to improved production techniques and investing in human capital, improving the labour force by training
Larger firms find it easier and cheaper to raise finance for business expansion
What are the disadvantages of internal diseconomies of scale (4)
Management can lose touch with the running of the firm and inefficiency can increase due to a lack of communication in a big firm
Larger size of the firm can lead to duplication and paperwork
Problems arise in workplace relations because management no longer knows the staff and leads to misunderstandings and disputes
Decrease in managerial and administrative efficiency, overshadows the advantages of being large and leads to increasing per-unit production costs
What does the long-run average cost curve show
Shows the relationship between production costs and internal economies and diseconomies of scale
Point X is the technical optimum.
What does this represent
Most efficient level of production for the firm
What is a benefit of continuously repeating production processes
A firm can become more efficient at completing the same tasks in production processes over time
How is ‘learning by doing’ represented as a curve?
Results in a downward shift of the firm’s long-run average cost-curve meaning lower per-unit production costs at each level of output
What are external economies and diseconomies of scale
Other cost advantages and disadvantages that can affect a business that exists completely outside its control and occur regardless of a firm’s level of production
What are external economies of scale
Cost saving advantages that occur to a firm because of outside influences, are not the result of the firm changing its own scale of operations
What are three examples of external economies of scale that could benefit a business?
Increasing localisation of industry means that all firms in a certain region would enjoy certain cost-advantages like locating in area of skilled labour, plentiful inputs and major consumer market
As an industry grows, all firms in that industry derive some extra benefits like government funding to promote special research
A growing and competitive market would be of benefit to all firms as it could provide cheaper investment funds from a variety of sources
What are external diseconomies of scale
Result from the growth of the industry in which the firm is operating, but they can also result from rapid growth across the entire economy
What are three examples of external diseconomies of scale that would disadvantage a business?
The growth of industry causes increased pollution, which contributes to illness, premature deaths and occasional closures of factories
Increasing the concentration of industry and people in existing urban areas increases transport costs of all firms and causes transport bottlenecks
As an industry grows, the cost of a firm’s new materials can rise, as the increasing demand for materials increases relative to the demand and supply
The modern business environment is highly competitive and dynamic.
Thus businesses leader need to be alert to
trends and new technologies
Improved technological innovations enable a business to
improve their efficiency and increase their output using existing resources
Businesses that invest in technology have generally experienced
lower production costs
increased efficiency
reduction in the size of the workforce
Larger production runs
Why has online shopping reduced the profit margins of firms
Consumers have more options to compare prices, especially with overseas firms
What is a negative of technological change for individuals
Can lead to the redundancy of many jobs
In order to compete globally, manufacturing and other labour work has been
outsourced overseas
Businesses that invest in technology are able to
offer better quality products at a lower price
better able to respond to changes in the market demand
provide goods tailored for their customers
What is a negative of investing in technology
Not all technology performs to expectations
What does environmental sustainability refer to
Minimising pollution and waste, preserving the natural environment and using renewable energy
Businesses may change their activities because of (3)
Government regulations
Consumer demands
Ethical commitment