covalent & ionic bonds and polarity
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
covalent bond
a bond where two nuclei of nonmetals are bonded together by their mutual attraction to the same pair of electrons
how does a covalent bond occur?
two nonmetal atoms collide so that the nuclei are closer than two times the radius
the electron pair is drawn to the internuclear distance where they can create a concentration of charge
side ways repulsion increased
mutual attraction to same pair of electron bonds atoms together
creates a covalent bond

differences between ionic and covalent bonds
ionic:
attraction from ions in all directions
non localized and non directional
all ions pack together
forms ionic crystal lattice
covalent
attraction is localized to the internuclear distance
attraction is directional along internuclear distance
ex. in a H2 bond, another extra hydrogen will not bond as no attraction is available
forms molecule
How and why do ionic compounds form?
a non metal and metal must physically collide with enough energy that an electron from the metal is dislodged
the metal has low IE, easier to remove electron
the non metal has high EA, the dislodged electron is attracted to the non metal
it is always true that…
丨IE丨 (energy required) > 丨EA丨 (energy released) therefore the electron transfer from metal to nonmetal always requires energy and the ions are less stable than the neutral atoms
how does an ionic crystal lattice form?
the positive and negative ions attract
every cation surrounded by a number of anions and so on to maximize attraction
a great amount of energy is required to create the crystal lattice, but much more is needed to break it apart, so it is stable
ionic compound is more stable than neutral elements due to high attraction necessary to break apart
endothermic vs exothermic
Endothermic: Process that absorbs/requires energy
Exothermic: releases energy
Why does covalent bonding result in molecules and not ionic crystal lattices?
ionic bond: sodium can attract chloride as long as they are relatively close, it is non directional and non localized, which is why they pack together to create a crystal lattice
covalent bond: the attraction is localized and directional to the internuclear distance and not just anywhere, so ions cannot pack together
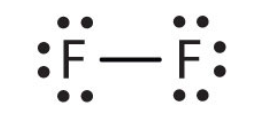
what type of bond is this?
single bond
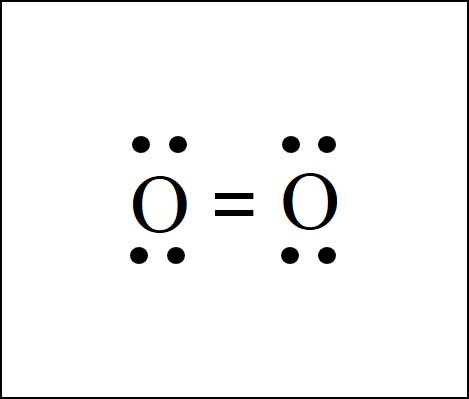
what type of bond is this?
double bond
polarity
uneven distribution of netgative charge in a bond
Partial charges: δ + or δ-
used to indicate the polarity of a covalent bond
detla positive on less EN element
detla negative on more EN element
how do you predict what kind of bond will form between elements in a compound?
use differences in electronegativity

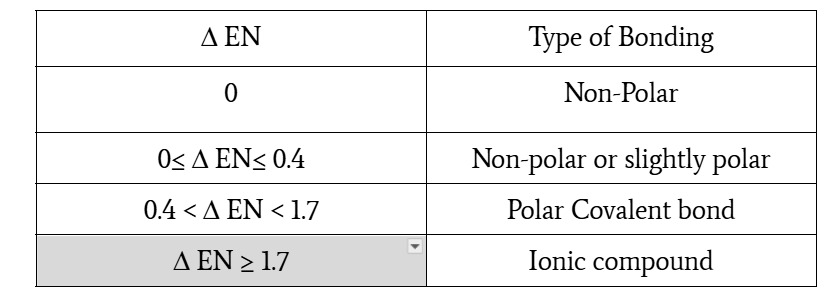
electronegativity differences and type of bond
0≤ Δ EN≤ 0.4, non-polar or slightly polar
0.4 < Δ EN < 1.7, polar covalent bond
Δ EN ≥ 1.7, ionic compound