MME 231 Quiz 3
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Orthogonal Cutting
the cutter edge is perpendicular to the cutting direction
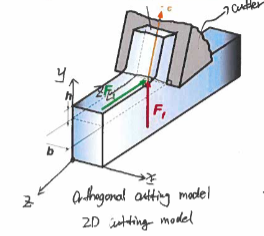
2d cutting
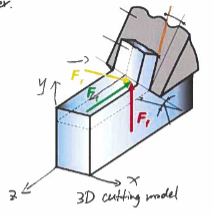
3d cutting
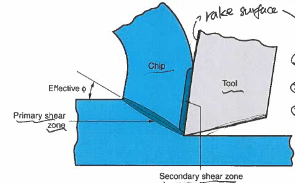
chip formation
Conditions of generating continuous chips
ductile workpiece material, high constant cutting speed
Continuous Chip Advantage
good surface finish
Continuous Chip Disadvantage
tends to entangle around cutting tool
Continuous chip strain hardening
chips are harder and stronger than original workpiece
Chip breaker
integral part of the cutter
Continuous chip with build up edge
material from workpiece deposits on tool forming BUE
Continuous chip with build up edge Conditions
ductile materials, medium cutting speed
CC BUE is affected by
adhesion of workpiece material to rake face of tool
CC BUE can be reduced by
increase cutting speed and decrease depth of cut
Serrated Chips
chips with the appearance of saw teeth
Conditions for generating discontinuous chip
lack of cutting fluid
Cutting tool characteristics
High toughness, wear resistance
Right Hand Cutting Tool
high hardness and wear resistance, only replace insert
Tool life
the duration of time a cutting tool can be used before it becomes ineffective
Tool wear
determines tool life
Three modes of tool failure
fracture failure, temp failure, gradual wear
Gradual wear
preferred as it leads to the longest possible use of the tool
Gradual wear occurs at
both rake surface and flank surface
Flank wear
a prevalent wear that is measured as the average flank bandwidth of wear
Flank wear reasons
sliding of the tool along machined surface which causes abrasive tool wear
Flank wear side effects
loss of dimensional accuracy, deteriorated surface finish
Crater wear reasons
sliding of the chip up the rake face, high localized stress
Notch wear
excessive localized damage on the rake face and flank face
Notch wear reasons
tool rubs against the shoulder of the workpiece causing a small amount of the cutter to adhere to the workpiece
Edge chipping
sudden breakage of a piece from the cutting edge of the tool
Causes of chipping
mechanical shock and thermal fatigue
Catastrophic failure reason
tool made with brittle material
Catastrophic failure solution
cutting fluid
vT^n = C
ln(v) + n ( ln(T) ) = ln(C) -> ln(v) = - n ( ln(T) ) + ln(C)
Cutting fluids
any liquid or gas applied directly to the machining operation to improve cutting performance
Main functions of cutting fluids
Cooling, lubrication, chip removal
Cutting fluids advantages
reduces cutting force and temp of workpiece
Cutting fluid coolant
reduces the effects of heat
Cutting fluid lubricants
reduces tool chip and tool workpiece friction
Methods of applying cutting fluids
flood cooling, mist cooling
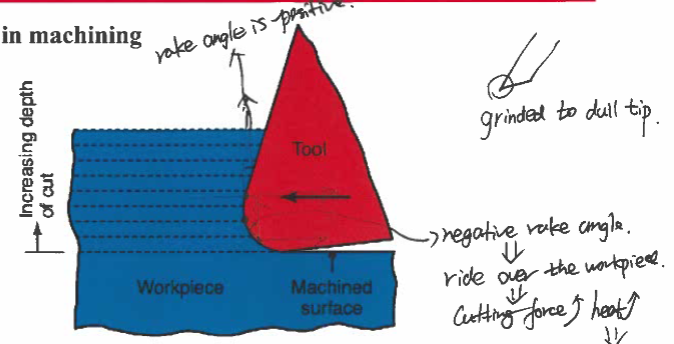
surfaces in machining
Negative rake
rides over the workpiece leading to an increase in the cutting force and workpiece temp
Negative rake angle leads to
cracks and residual stress
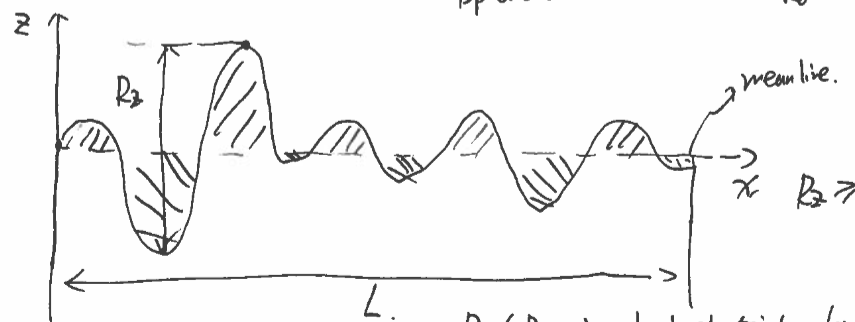
surface roughness, top areas = bottom areas
Rz (Rmean)
highest point - lowest point
Ra
arithmetical mean roughness
Ra =
( integral 0 L abs [ z(x) ] dx) / L
Rmax =
f^2 / 8R
Ra (arithmetic average) ≈
f^2 / 32R
Process parameters surface roughness factors
low cutting speed leads to discontinuous chip formation which cracks surface
Unstable continuous chip w/ BUE surface roughness factors
heavily strain hardened fragments are welded to the surface
Edge chipping, tool wear and dull cutter tip leads to an
increase in surface roughness in transverse direction
Vibration/chatter
introduces variation in surface geometry
Surface integrity
pertains to properties that effect the generated surface
Surface integrity improvments
small depth of cut
Machinability
the ease at which the material can be machined
High Machinability Effects
long tool life, good surface finish
Poor machinability factors
high hardness, strength and ductility
Forced vibrations
the sustaining alternating forces exist independent of motion
Chatter
the alternating force that sustains the motion is created by the motion itself
Forced vibrations solutions
isolate and remove forcing elements
Chatter solutions
damping
Damping
The rate at which vibrations decay