TEJ201 Exam Review Flashcards
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What is ESD, and how do you stay safe against it?
ESD (electrostatic discharge) occurs when objects, specifically the human body and clothes, get charged with electrons from friction and discharge them into the computer hardware. To protect yourself, you can wear a special bracelet that discharges the electrons into the ground, making it safe.
Name 3 ways to stay safe in a computer lab.
Make sure to tightly close all liquid containers to prevent spills. Be mindful of cables and make sure not to place them in ways where people may trip over them. If an unsafe environment is created or someone is injured, notify the instructor immediately. Instructors are the people who are most capable and knowledgeable on safety concerns inside a computer lab; they know best.
What is tool safety?
Tool safety refers to making sure that everyone stays safe while tools are being used in a lab. In order to stay safe while using tools, you should: Notify the teacher prior to the use of tools. Handle and store tools carefully and stay vigilant so no one gets hurt. Notify the instructor if any issues or hazards occur.
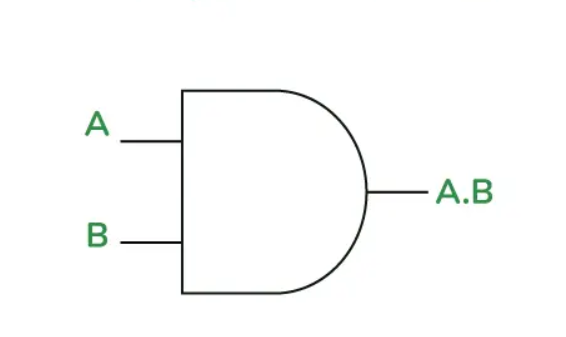
What is this gate? When does it output a HIGH/on/1?
This diagram shows an AND gate, it outputs a true signal when both inputs A and B are true.
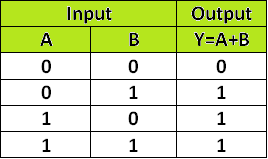
To what gate does this truth table correspond to?
This is an OR gate.