BIOL 251 Exam 4 Microbial Diseases of the Skin & Eyes
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
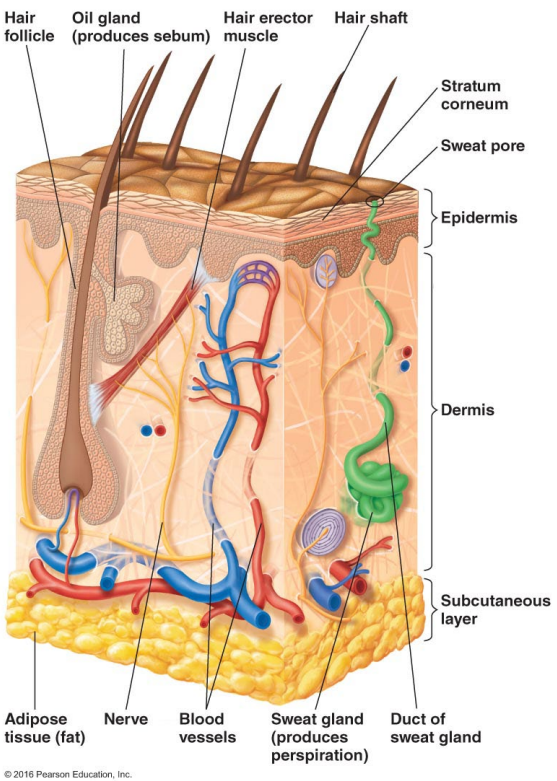
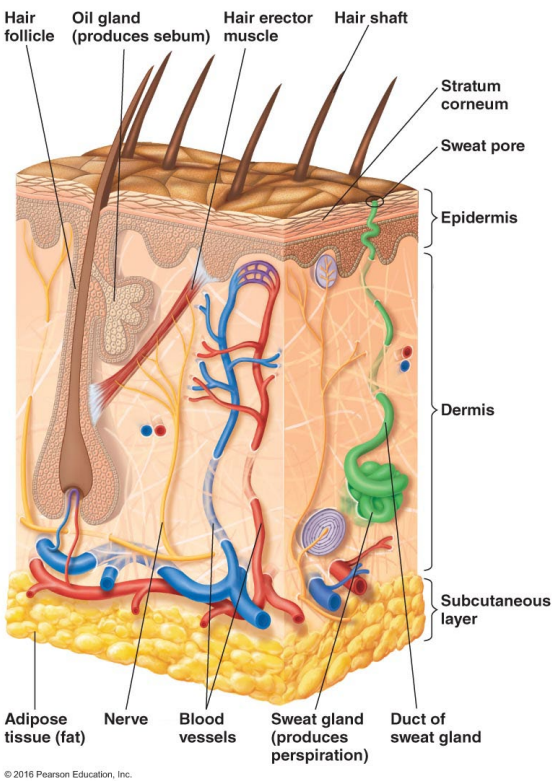
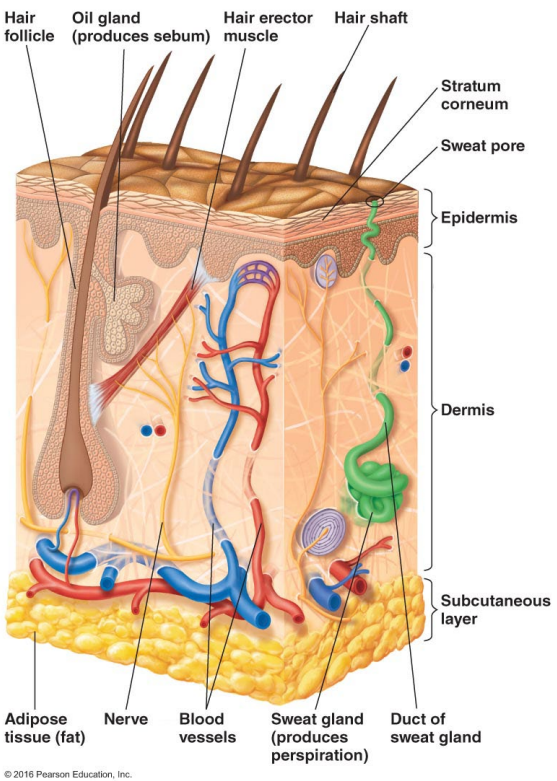
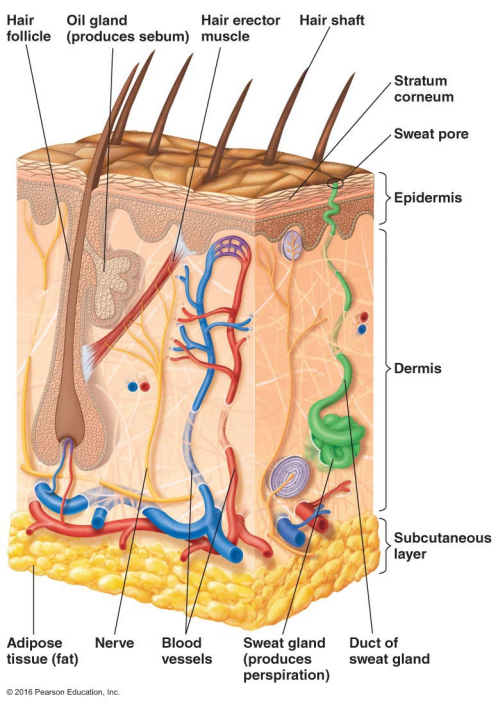
Thin outer layers of epithelial cells, including keratin, are called
The epidermis
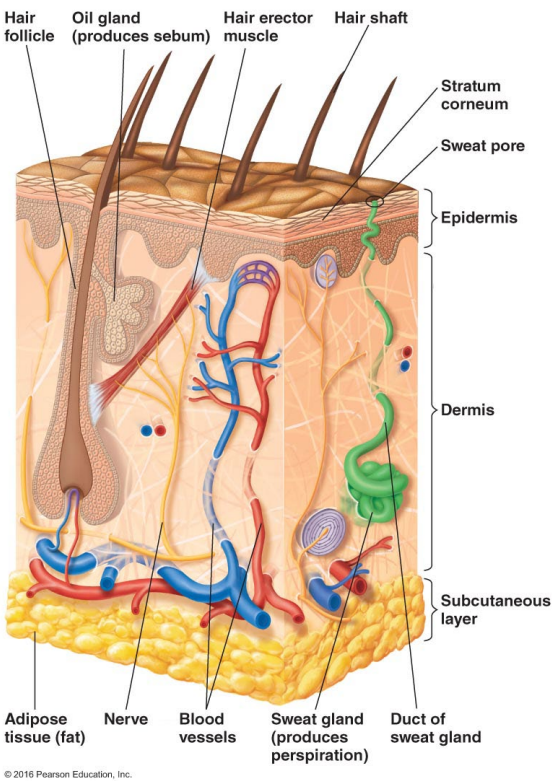
Thick inner layers, Hair follicles, and Sweat and oil ducts are called
The dermis
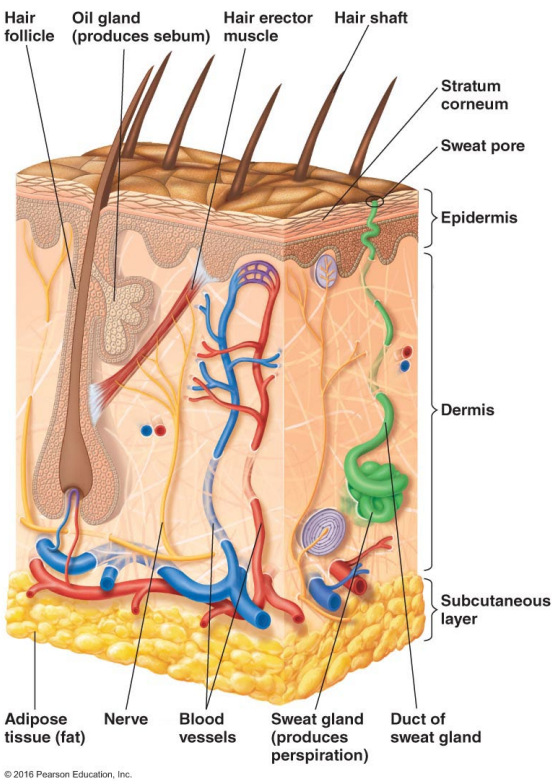
Describe the structure of the skin.
Epidermis: Thin outer layers of epithelial cells, including keratin
Dermis: Thick inner layers, Hair follicles, and Sweat and oil ducts
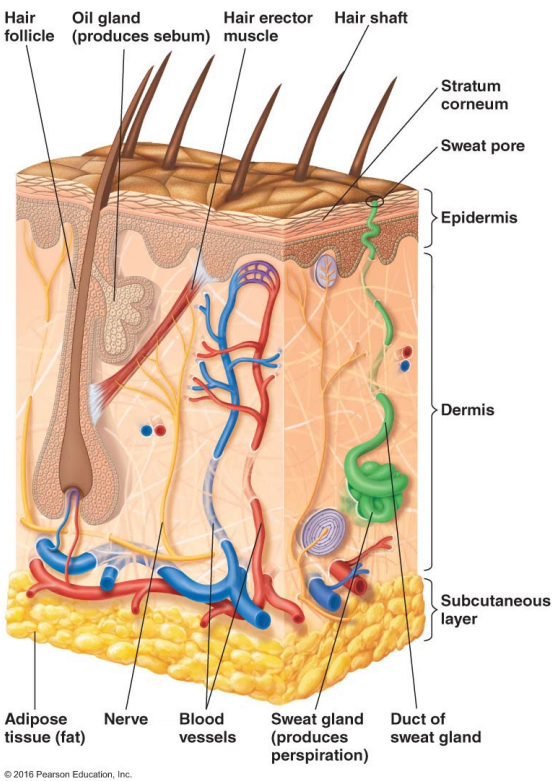
What does the epidermis, a structure of the skin, consist of?
Thin outer layers of epithelial cells, including keratin
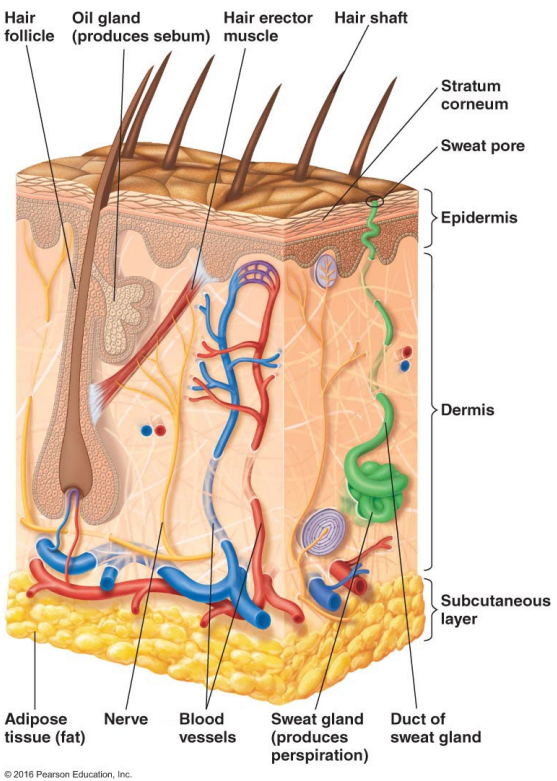
What does the dermis, a structure of the skin, consist of?
Thick inner layers, Hair follicles, and Sweat and oil ducts
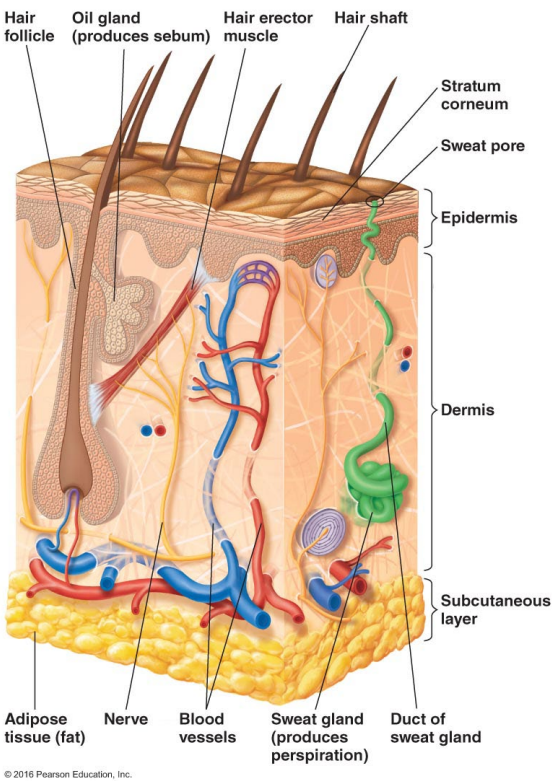
The skin has secretions like perspiration and sebum. Describe persipiration.
Perspiration
Provides moisture
Contains lysozyme and antimicrobial peptides (directly kill or inhibit microbes)
It’s also kinda salty which makes the environment acidic
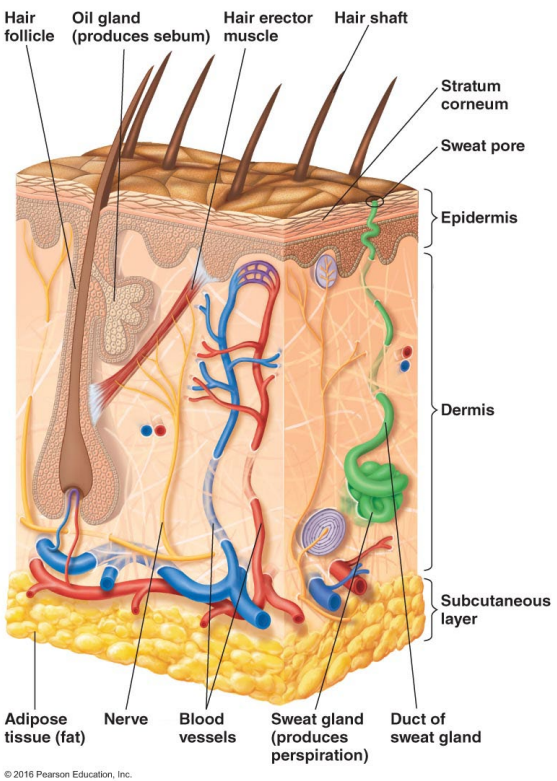
The skin has secretions like perspiration and sebum. Describe sebum.
Sebum
Lipids, proteins, and salt
Provides nutrients
Fatty acids can be inhibitory to microbes
Overall: Sebum feeds normal skin microbes while creating an acidic, fatty environment that discourages pathogens.
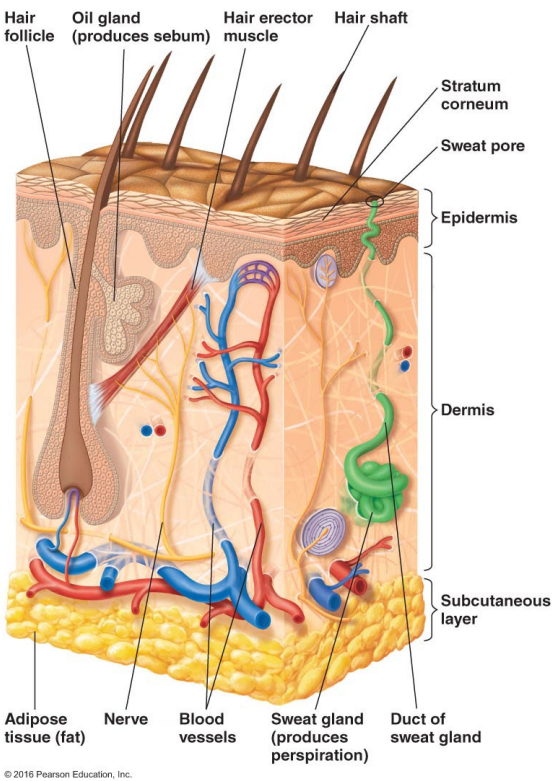
Sebum has fatty acids that can be inhibitory to ______
Fatty acids can be inhibitory to microbes
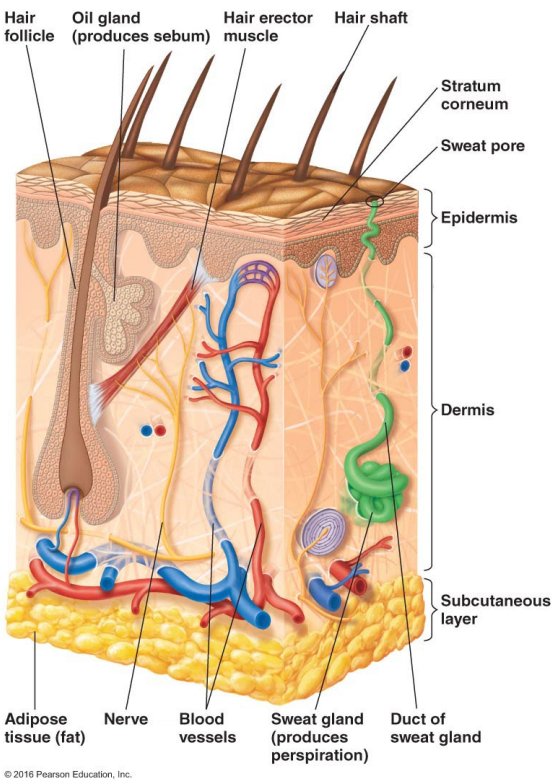
What makes up sebum?
Lipids, proteins, and salt
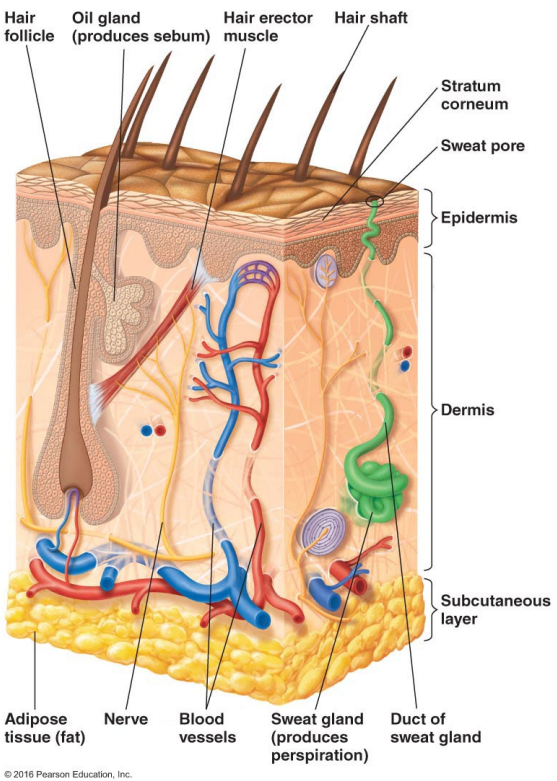
Perspiration provides moisture and contains what two antimicrobial substances?
Contains lysozyme and antimicrobial peptides
T/F: The skin is not particularly hospitable to microorganisms.
T. This is because the skin is resistant to drying and high salt concentrations and consists of antimicrobial substances like lysozyme and antimicrobial peptides.
T/F: The skin is particularly hospitable to microorganisms.
F. The skin is not particularly hospitable to microorganisms because the skin is resistant to drying and high salt concentrations and consists of antimicrobial substances like lysozyme and antimicrobial peptides.
Who make up the normal microbiota of the skin?
Many Gram positive cocci
Staphylococcus
Micrococcus
Gram positive rods (diptheroids)
Propionibacterium acnes
Corynebacterium xerosis
T/F: Some members of the normal microbiome in the skin may cause illness under certain conditions.
T
T/F: Members of the normal microbiome in the skin never cause illness.
F. Some members of the normal microbiome in the skin may cause illness under certain conditions.
T/F: Skin lesions are indicative of an infection of the skin.
F. Skin lesions are not necessarily indicative of an infection of the skin.
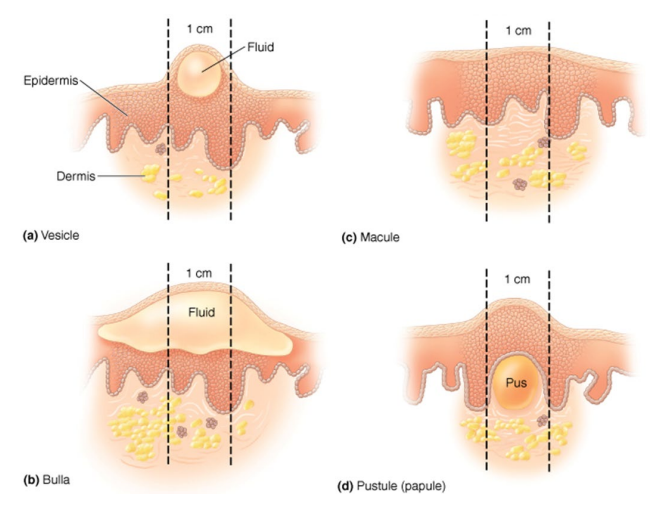
In context of skin lesions, what is a Vesicle?
small fluid-filled lesions
In context of skin lesions, what is a Bullae?
large (> 1 cm) vesicles
In context of skin lesions, what is a Macule?
flat, reddened lesions
In context of skin lesions, what is a Papule?
raised lesion
In context of skin lesions, what is a Pustule?
raised lesion containing pus
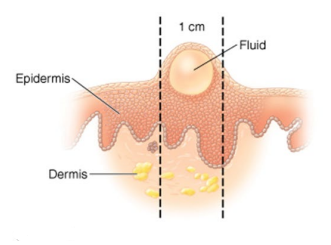
What type of skin lesion is this?
Vesicle – small fluid-filled lesions
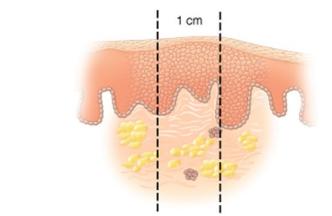
What type of skin lesion is this?
Macule – flat, reddened lesions
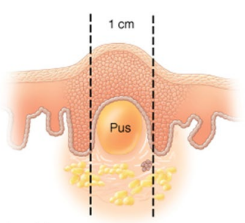
What type of skin lesion is this?
Pustule (papule) – raised lesion containing pus
Papule – raised lesion
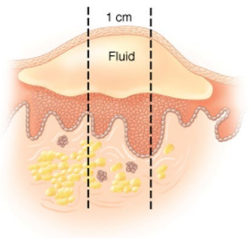
What type of skin lesion is this?
Bullae – large (> 1 cm) vesicles
Staphylococcal skin infections are separated into groups based on
the activity of coagulase
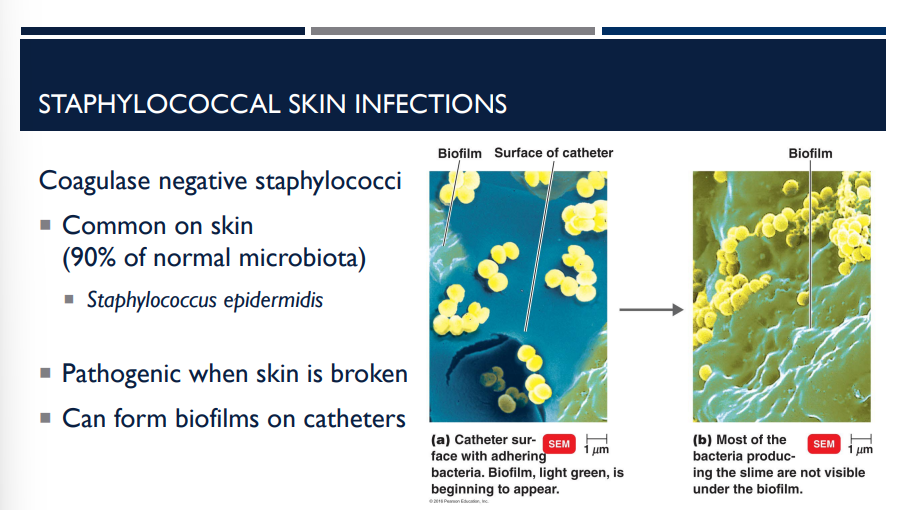
What type of staphylococcal skin infection is common on skin (90% of normal microbiota)?
Coagulase negative staphylococci.
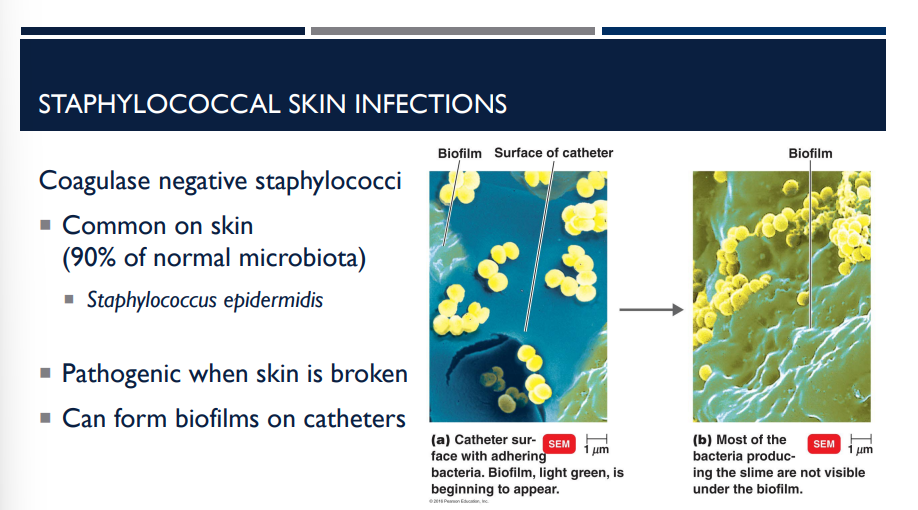
Describe Coagulase negative staphylococci and its characteristics.
Common on skin (90% of normal microbiota)
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Pathogenic when skin is broken
Can form biofilms on catheters
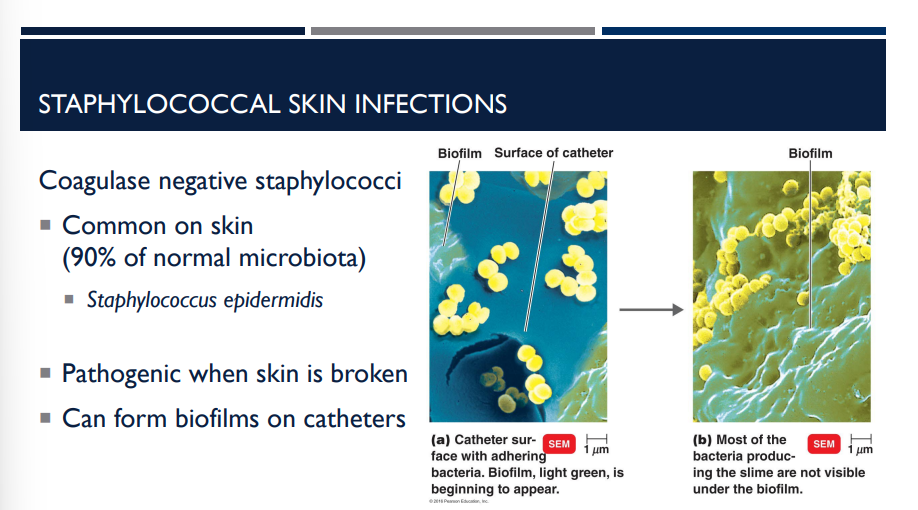
Which type of staphylococcal skin infection can form biofilms on catheters?
Coagulase negative staphylococci
Staphyloccous (aureus/epidermidis) is coagulase-positive staphylococci.
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphyloccous (aureus/epidermidis) is coagulase-negative staphylococci.
Staphylococcus epidermidis
T/F: Coagulase-positive staphylococci is the most pathogenic staphylococci.
T
T/F: Coagulase-negative staphylococci is the most pathogenic staphylococci.
F, coagulase-positive staphylococci is the most pathogenic staphylococci.
Why is coagulase-positive staphylococci the most pathogenic staphylococci?
Produces toxins that kill phagocytes
Evade host defenses – blocking chemotaxis, survival in phagosome, coagulase
Antibiotic resistance
Methicillin (MRSA) – beta-lactamase
Vancomycin (VRSA) – modification of target molecule
Coagulase also converts fibrinogen to fibrin, causing clot formation around the bacteria.
➡ This “protective clot” shields the bacteria from phagocytes and immune attack.
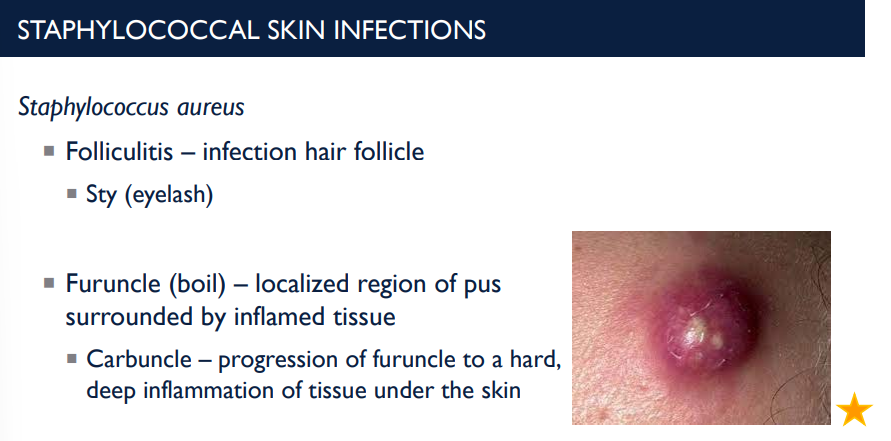
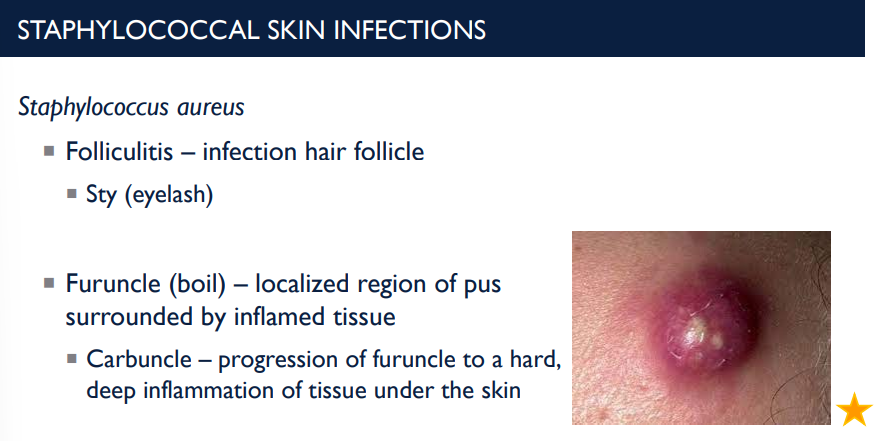
Folliculitis is an infection of the _____ ____ and is a result of what type of skin infection?
hair follicle; Staphylococcus aureus skin infection.
An eyelash stye is a painful, red, and swollen bump on the eyelid caused by a bacterial infection in an oil gland or eyelash follicle. It is a result of what type of skin infection?
Staphylococcus aureus skin infection in the hair follicle.
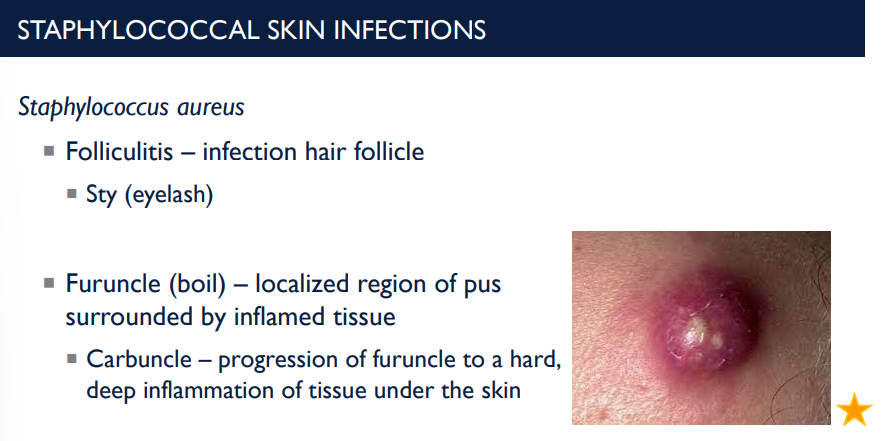
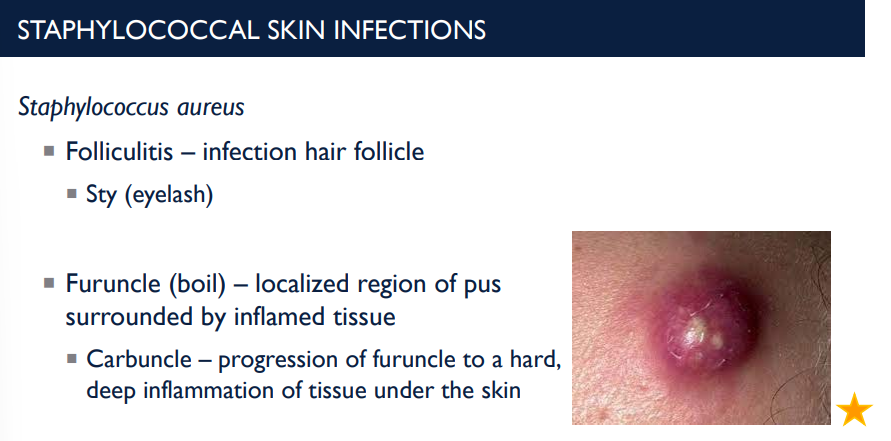
What is a furuncle (boil)? What is a carbuncle?
localized region of pus surrounded by inflamed tissue.
Carbuncle – progression of furuncle to a hard, deep inflammation of tissue under the skin
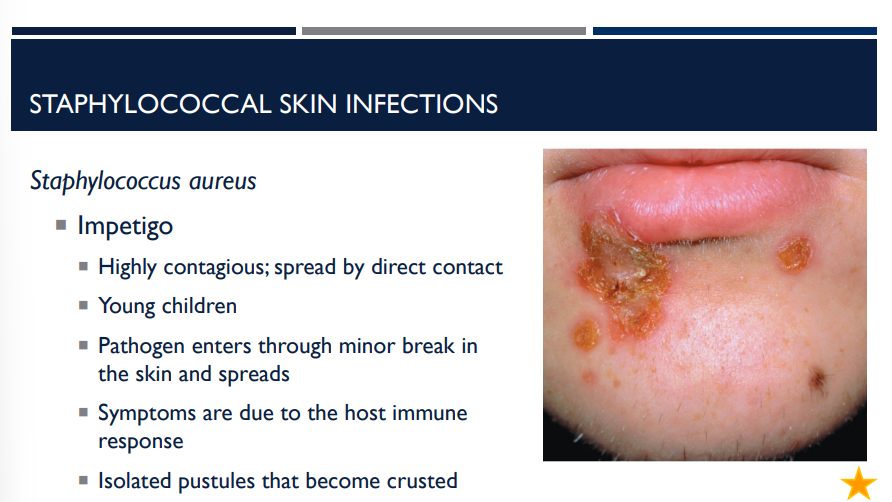
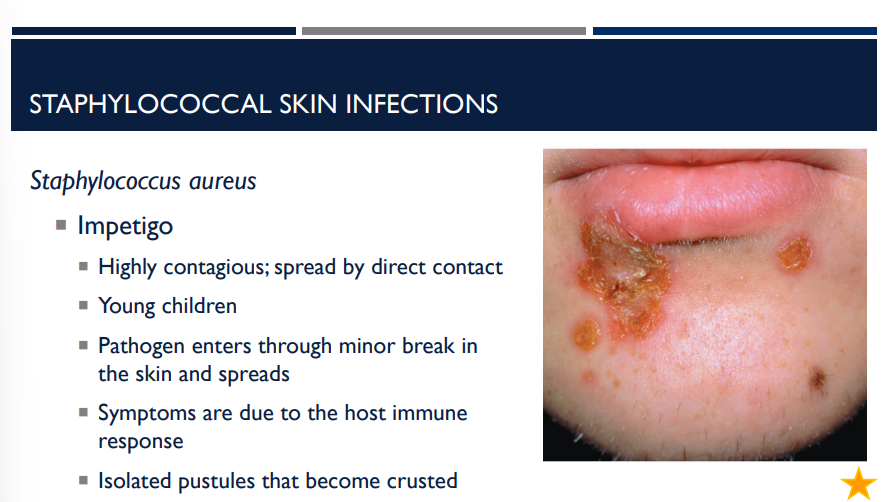
Staphylococcus aureus can cause a skin infection called impetigo. Describe it.
Highly contagious; spread by direct contact
Young children
Pathogen enters through minor break in the skin and spreads
Symptoms are due to the host immune response
Isolated pustules that become crusted
Staphylococcus aureus can cause a skin infection called folliculitis. Describe it.
Folliculitis is an infection of the hair follicle. A stye is a painful, red, and swollen bump on the eyelid caused by a bacterial infection in an oil gland or eyelash follicle.
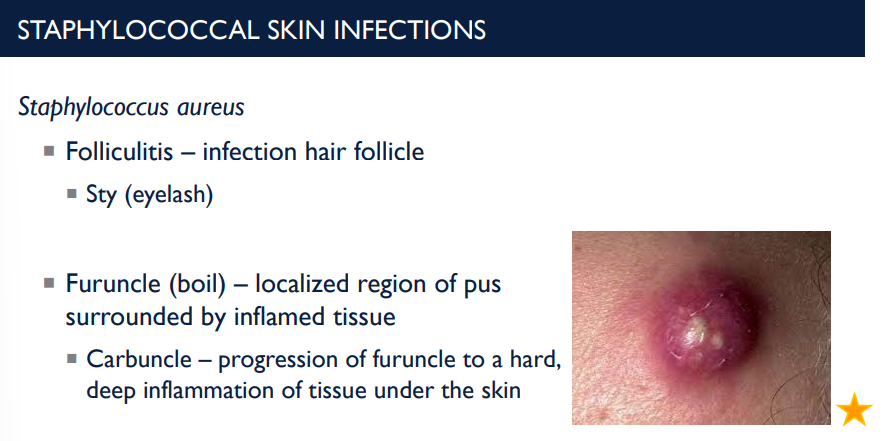
Staphylococcus aureus can cause a skin infection called furuncle (boil). Describe it.
A furuncle is a localized region of pus surrounded by inflamed tissue.
Carbuncle – progression of furuncle to a hard, deep inflammation of tissue under the skin
The symptoms of the staphylococcal skin infection impetigo are due to
the host immune response
Impetigo involves isolated pustules that become ____
crusted
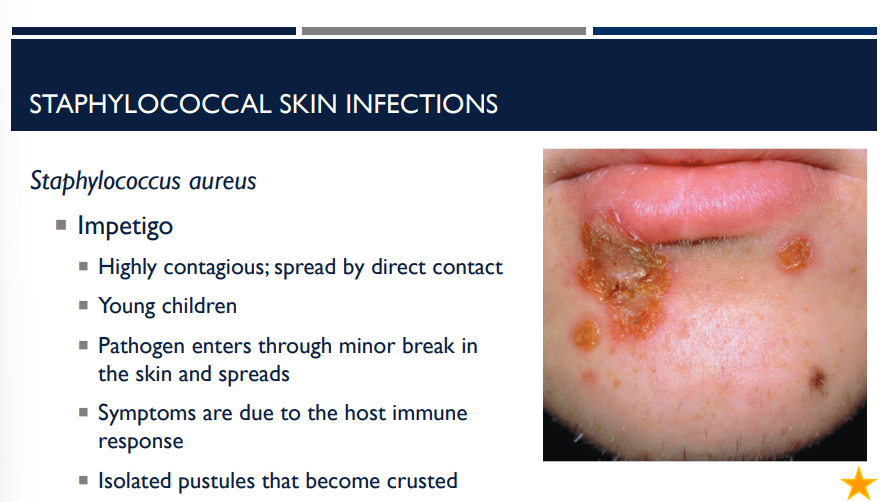
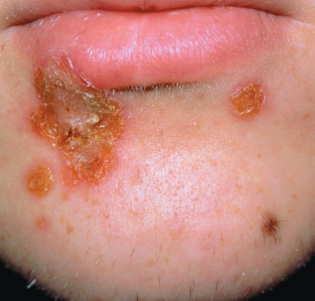
What staphylococcus aureus skin infection is shown?
Impetigo
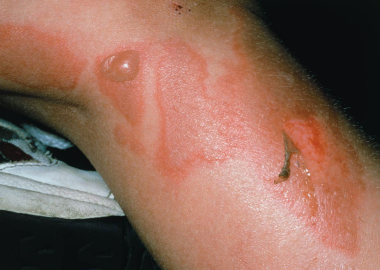
What staphylococcus aureus skin infection is shown?
2 staphylococcal toxins cause separation of skin layers
Exfoliative toxin A – bulbous impetigo at infection side
Exfoliative toxin B – scalded skin syndrome at other sites
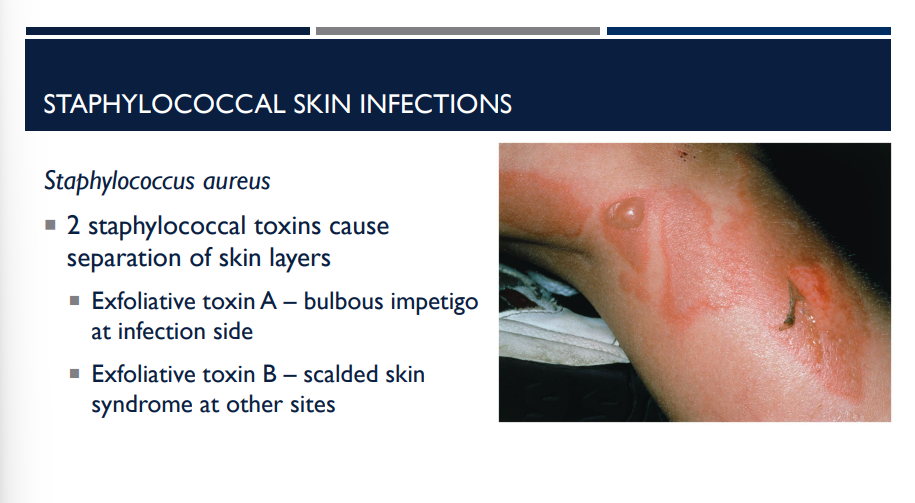
In staphylococcal skin infections, 2 staphylococcal toxins cause separation of skin layers. Describe both.
Exfoliative toxin A – bulbous impetigo at infection side
Exfoliative toxin B – scalded skin syndrome at other sites
This is a gram-positive cocci that forms chains. What enzymes and toxins does it secrete?
Hemolysins
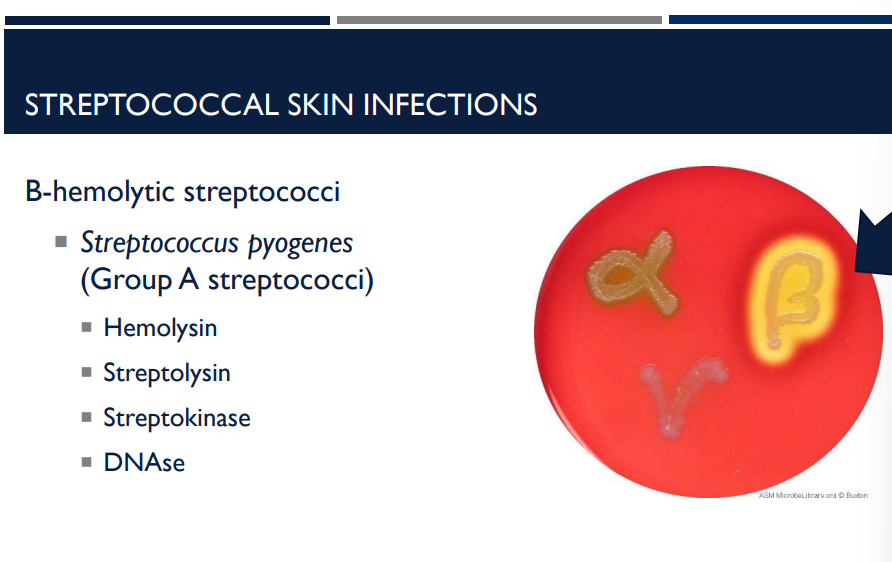
What kind of hemolysis activity does streptococci perform?
streptococci are beta-hemolytic
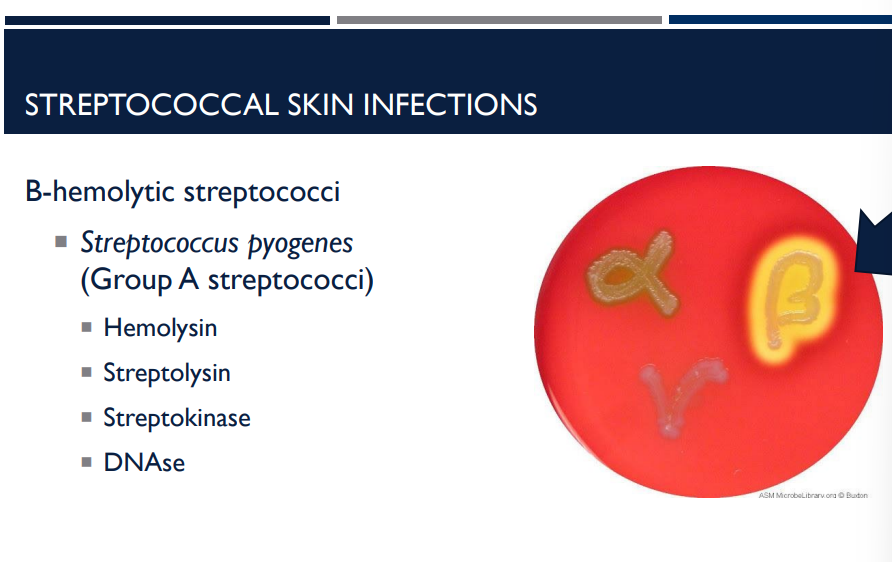
What group of streptococci is streptococcus pyogenes?
Group A streptococci
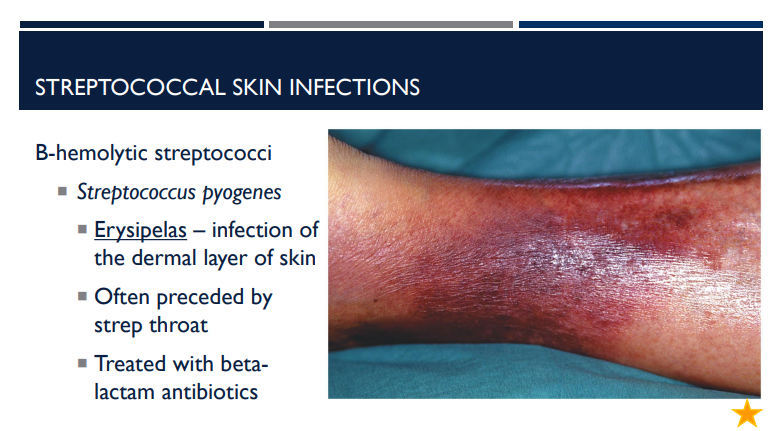
Erysipelas is an infection of the dermal layer of the skin. What bacteria is it caused by?
A beta hemolytic streptococci called Streptococcus pyogenes.
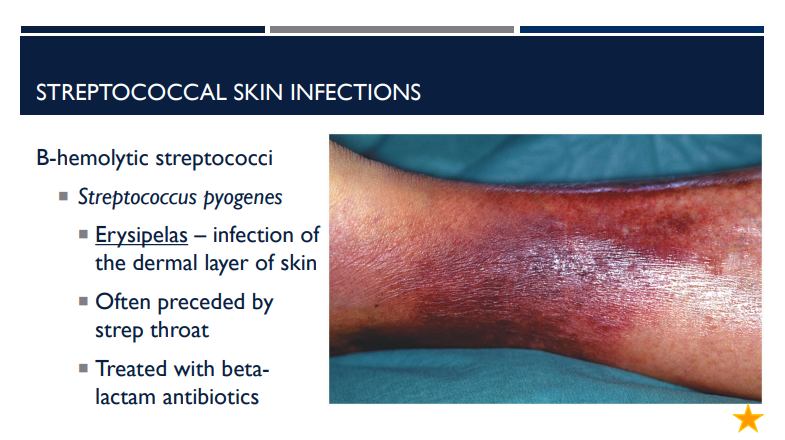
What is Erysipelas?
An infection of the dermal layer of the skin caused by beta hemolytic streptococci called Streptococcus pyogenes.
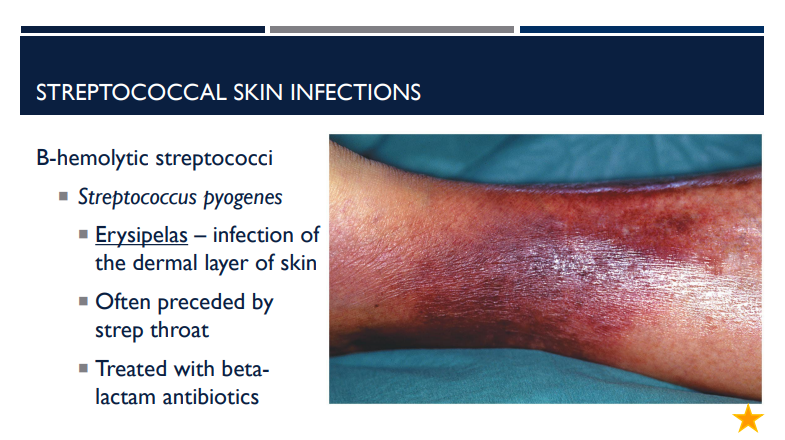
What is erypsipelas, an infection of the dermal layer of the skin, often preceded by and treated with?
Often preceded by strep throat
Treated with beta lactam antibiotics
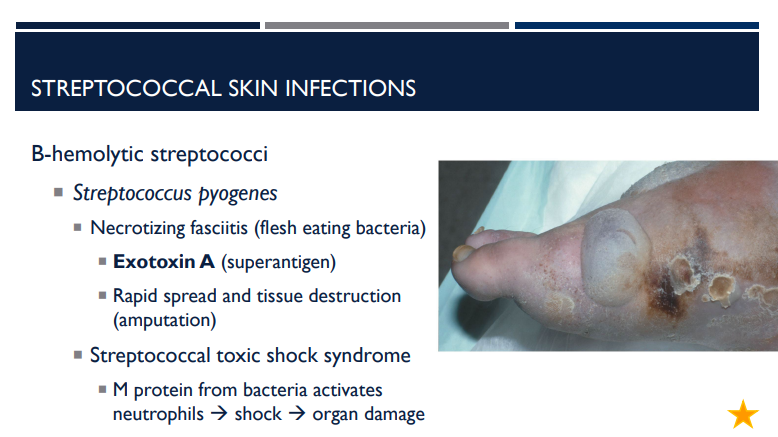
What is necrotizing fasciitis? What exotoxin is it caused by and what does it do?
A type of beta-hemolytic streptococci (specifically from Streptococcus pyogenes) that is flesh eating bacteria caused by exotoxin A (superantigen). Causes rapid spread and tissue destruction, requiring amputation.
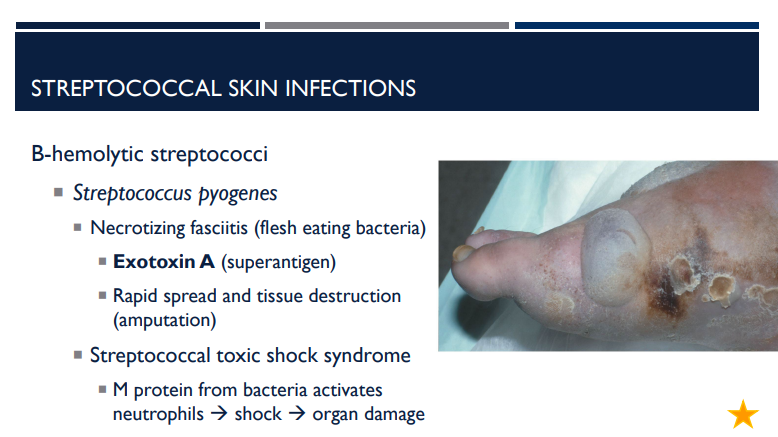
Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome can be caused by
A type of beta hemolytic streptococci called Streptococcus pyogenes.
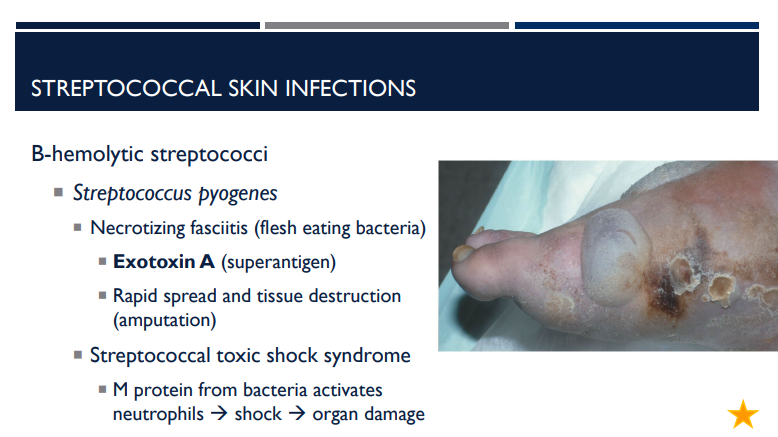
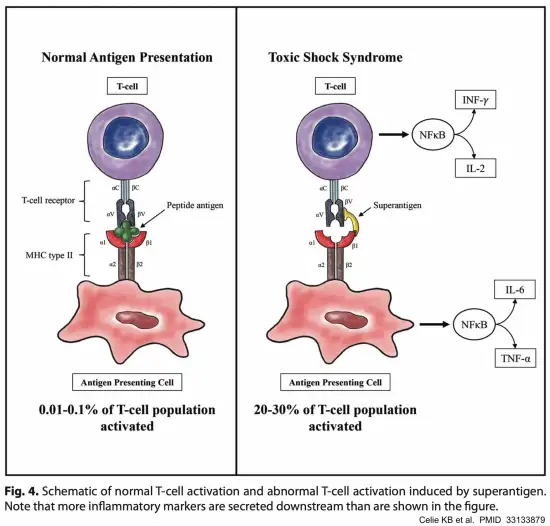
Describe streptococcal toxic shock syndrome.
M protein from bacteria activates neutrophils → shock → organ damage
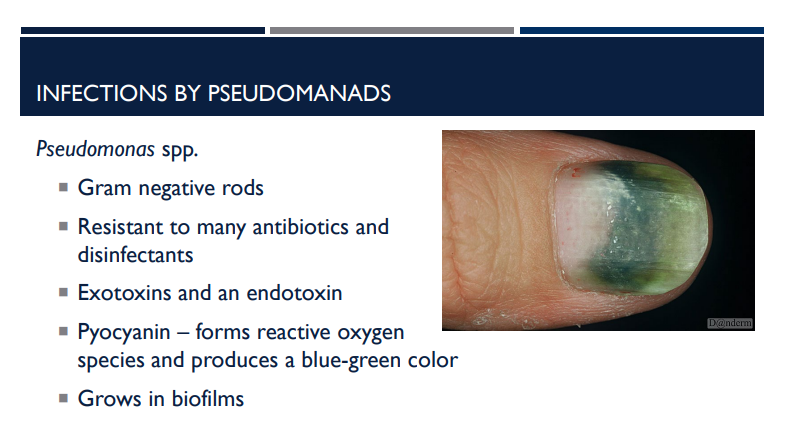
Which bacterial infection has exotoxins and an endotoxin?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
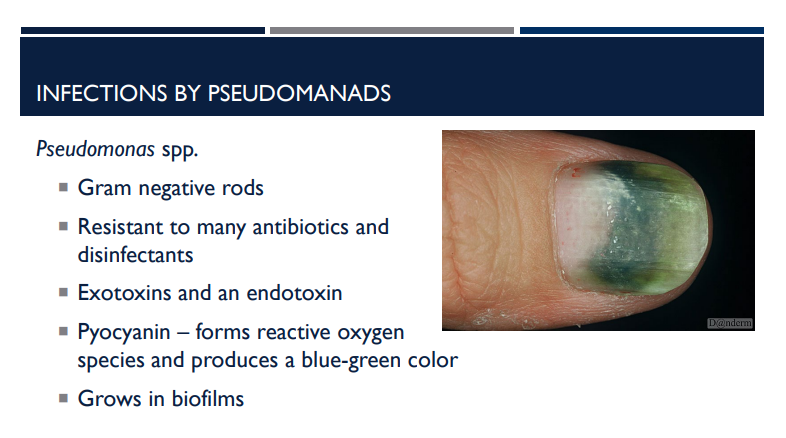
Which bacterial infection has pyocyanin?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
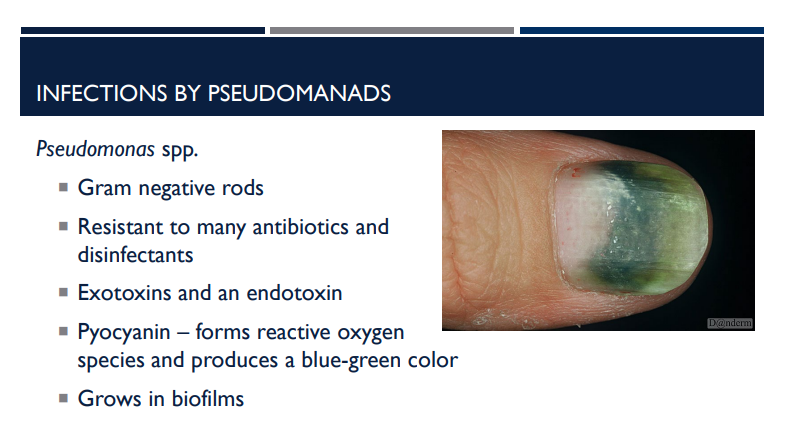
Which bacterial infection is resistant to many antibiotics and disinfectants?
Pseudomonas aerugionosa
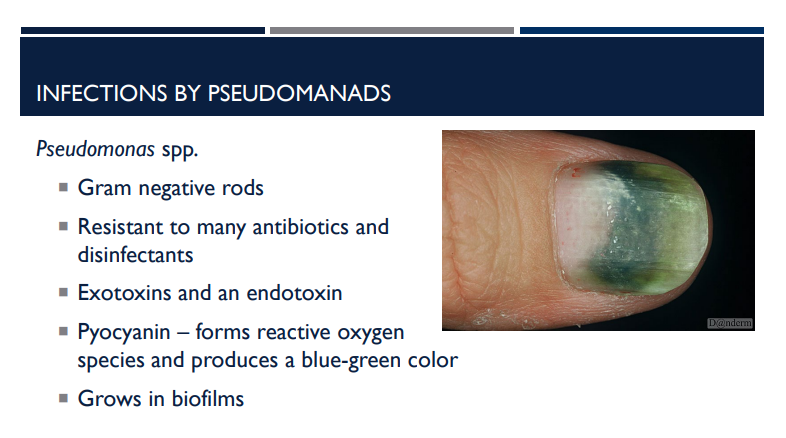
What is pyocyanin?
a blue-green pigment and virulence factor produced by the opportunistic bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa that forms reactive oxygen species and produces a blue green color
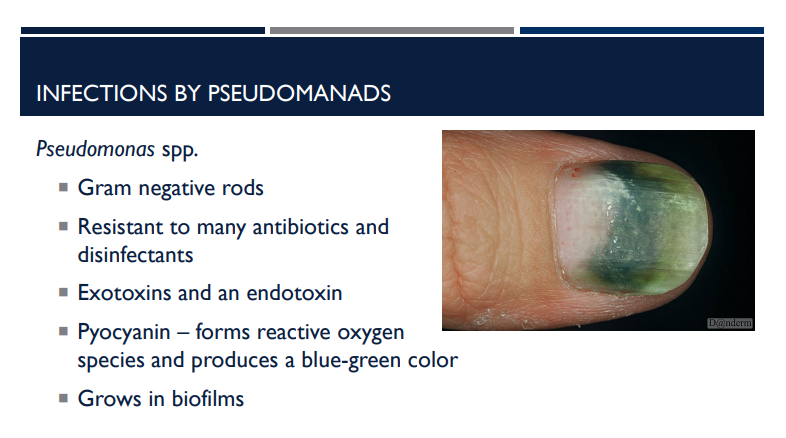
What is pyocyanin?
Pyocyanin — forms reactive oxygen species and produces a blue-green color
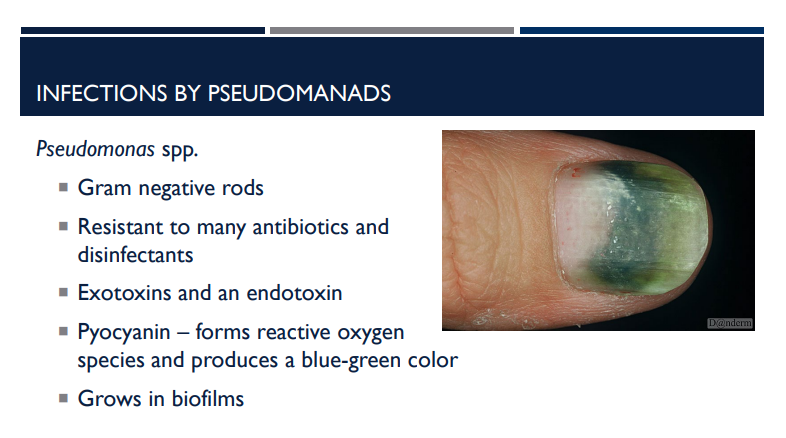
Describe the characteristics of pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Gram negative rods
Resistant to many antibiotics and disinfectants
Exotoxins and an endotoxin
Pyocyanin – forms reactive oxygen species and produces a blue-green color
Grows in biofilms
Which gram-negative rod-shaped bacteria grows in biofilms?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa

Dermatitis, a self-limiting rash (2 weeks) and otitis externa (Swimmer’s ear), is associated with which bacteria?
Infections caused by pseudomonas

Infections caused by Pseudomonas are an opportunistic pathogen. What kind of things or people does it affect?
Burn victims
Biofilm formation in lungs of CF (Cystic Fibrosis) patients
Biofilm formation in catheters
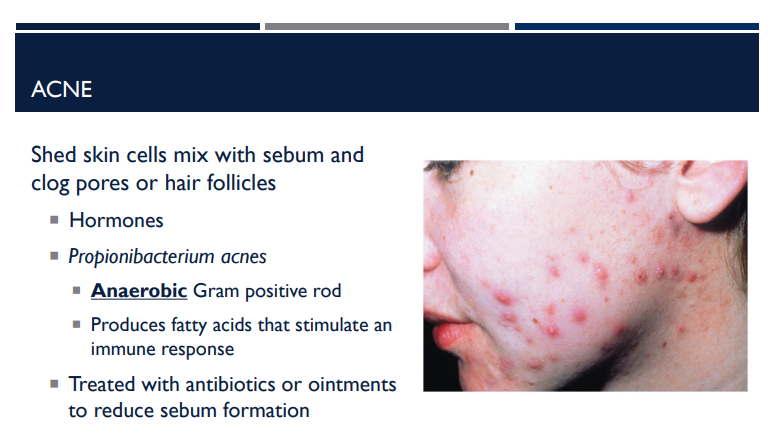
Explain what happens with acne.
Shed skin cells mix with sebum and clog pores or hair follicles, causing hormone changes.
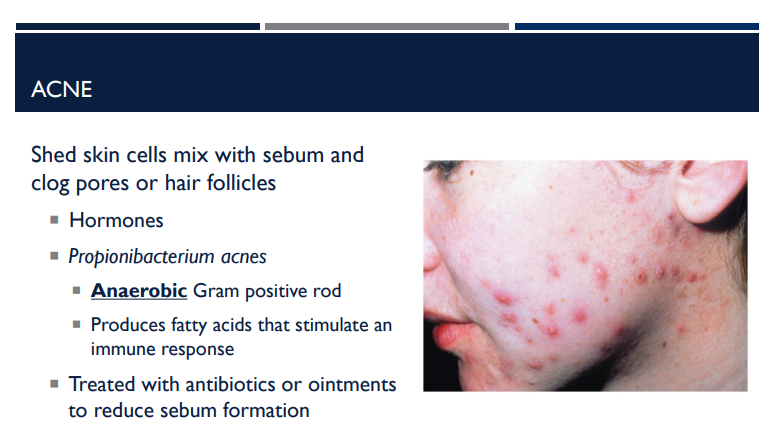
What is the bacteria name for acne?
Propionibacterium acnes
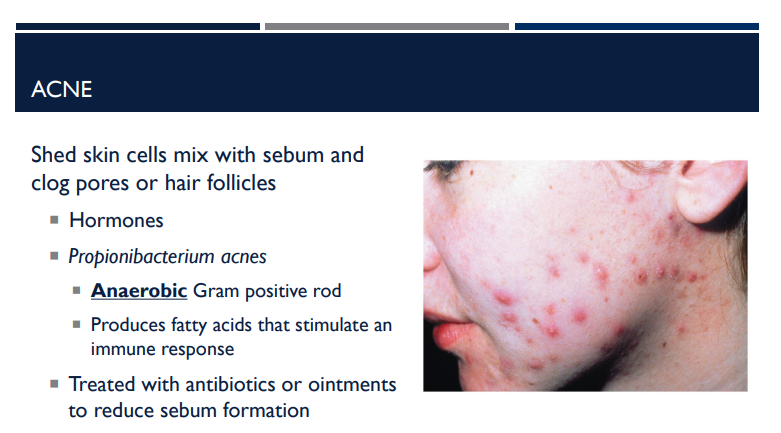
Describe the shape of Propionibacterium acnes and what it does to stimulate an immune response.
It is an anaerobic gram-positive rod, that produces fatty acids that stimulate an immune response.
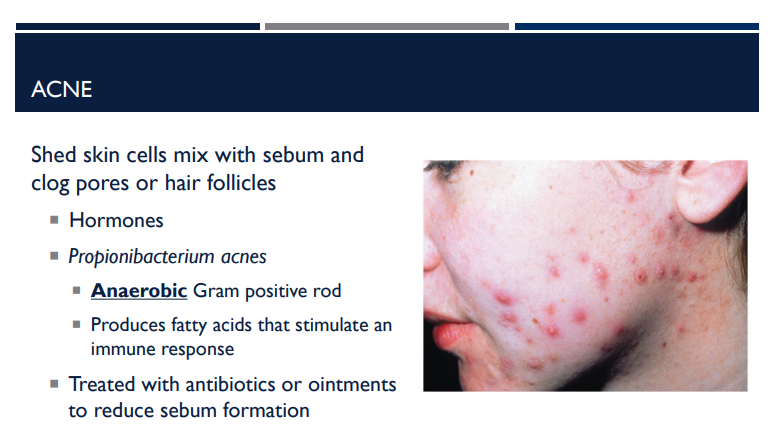
What is Propionibacgerium acnes (acne) treated with?
Since acne is when shed skin cells mix with sebum and clog pores or hair follicles, they are treated with antibiotics or ointments that reduce sebum formation
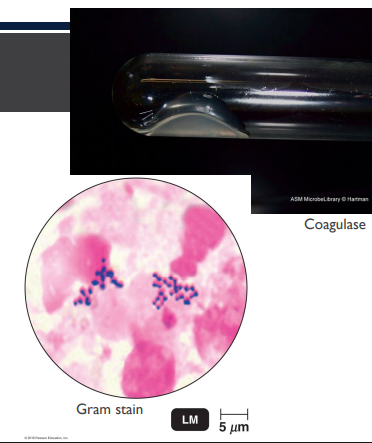
(LC) A patient has a swollen, red area on his thigh. It is warm and tender to the touch. Based on the Gram stain and coagulase test results shown below, what is the likely cause of the infection?
Streptococcus pyogenes
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus aureus
The bacterial cells are Gram positive cocci in clusters. The organism is also coagulase positive. This infection is likely caused by Staphylococcus aureus.

(LC) You perform an antibiotic resistance test and observe these results. Does your patient have a MRSA infection?
Yes
No
It is impossible to tell.
No.
MRSA stands for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. The zone of inhibition indicates that this strain is sensitive to methicillin. Therefore, this is not a MRSA infection.
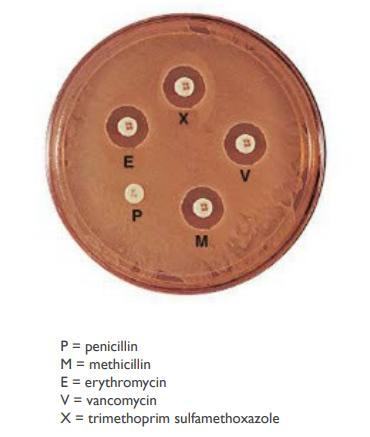
(LC) You perform an antibiotic resistance test and observe these results. Which drug(s) should NOT be used to treat this patient’s infection?
Penicillin
Methicillin
Erythromycin
Vancomycin
Trimethoprim & sulfamethoxazole
All of these drugs could be used treat this infection.
A Penicillin
There is no zone of inhibition around the penicillin disk, indicating that this strain is resistant to penicillin. Thus, penicillin would be in appropriate for treating this infection.
Any of the other drugs would be used, as the organism was inhibited by each of the remaining antibiotics.
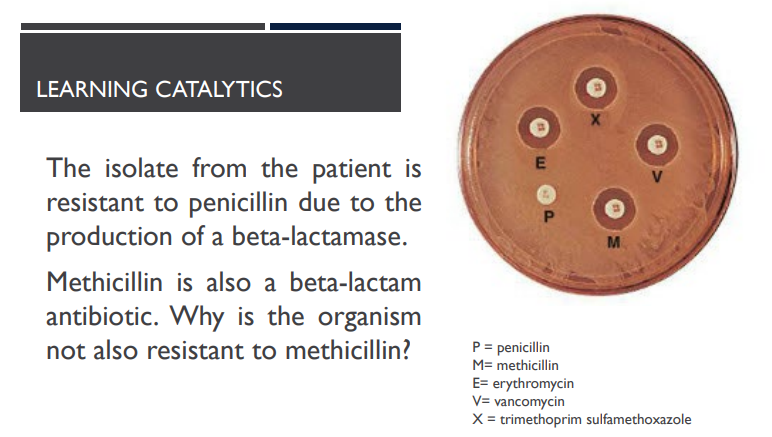
(LC) The isolate from the patient is resistant to penicillin due to the production of a beta-lactamase. Methicillin is also a beta-lactam antibiotic. Why is the organism not also resistant to methicillin?
Penicillin affects cell wall synthesis, while methicillin inhibits protein synthesis.
The different molecular structures allow the beta-lactamase to bind penicllin, but not methicillin.
The bacterium possesses efflux pumps for penicillin, but not for methicillin.
Penicillin easily crosses the bacterial cell membrane, while methicillin does not.
B
Shape = function!
Penicillin and methicillin are both beta-lactam antibiotics, but have different side chains. The beta-lactamase is able to bind to penicillin and deactivate it. However, the structure of methicillin is slightly different and this prevents the beta-lactamase from binding.
Herpesvirus varicella-zoster can lead to multiple infections. What are the most common 2 that it can cause?
Chickenpox & Shingles

What viruses are polyhedral & enveloped?
herpes virus varicella-zoster
herpes simplex virus I (HSV-I)
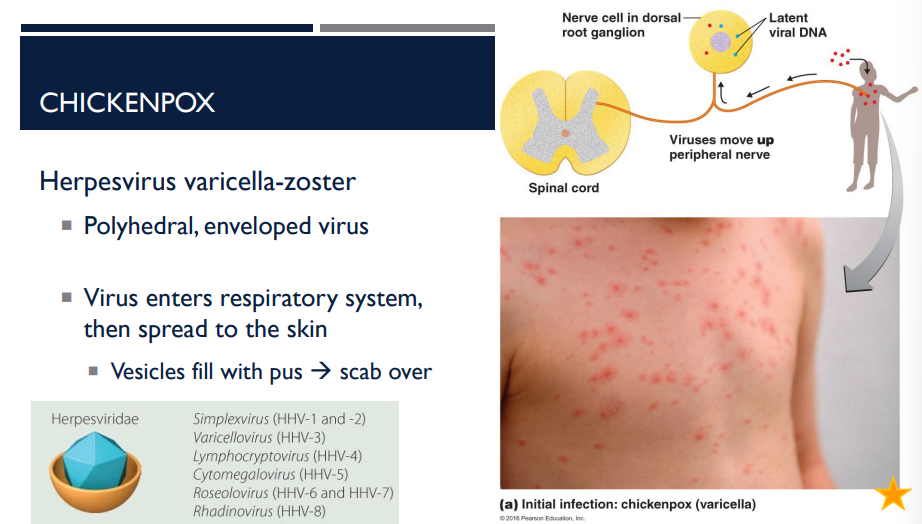
This virus enters the respiratory system then spreads to the skin. The vesicles fill with pus and then over time, they rupture and scab over. What disease am I describing? What virus is it caused by?
Chicken-pox; herpesvirus varicella-zoster
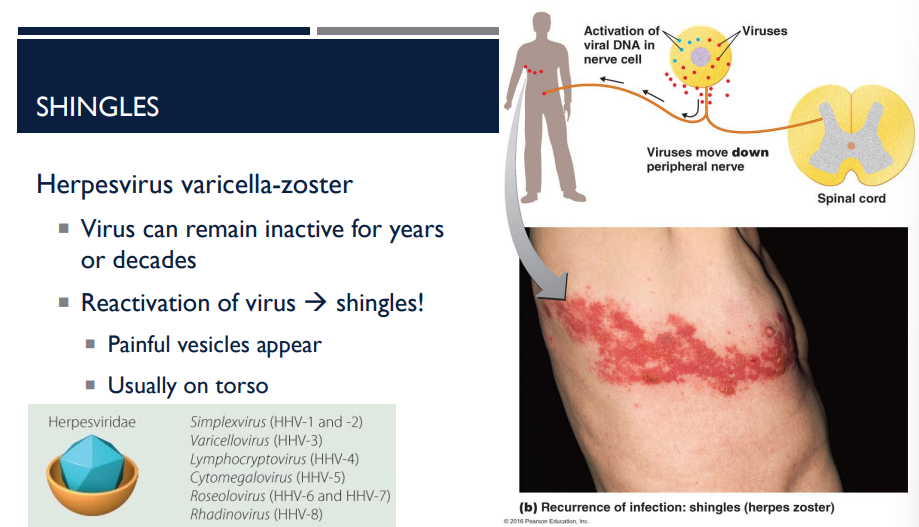
T/F: The herpesvirus varicella-zoster can remain inactive for years or decades.
T
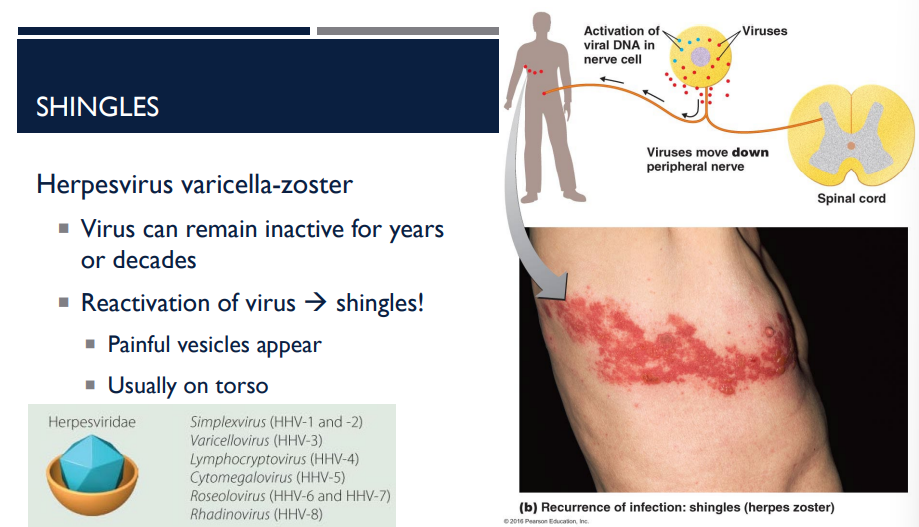
The herpesvirus varicella-zoster can remain inactive for years or decades. The reactivation of the virus causes which disease?
Shingles
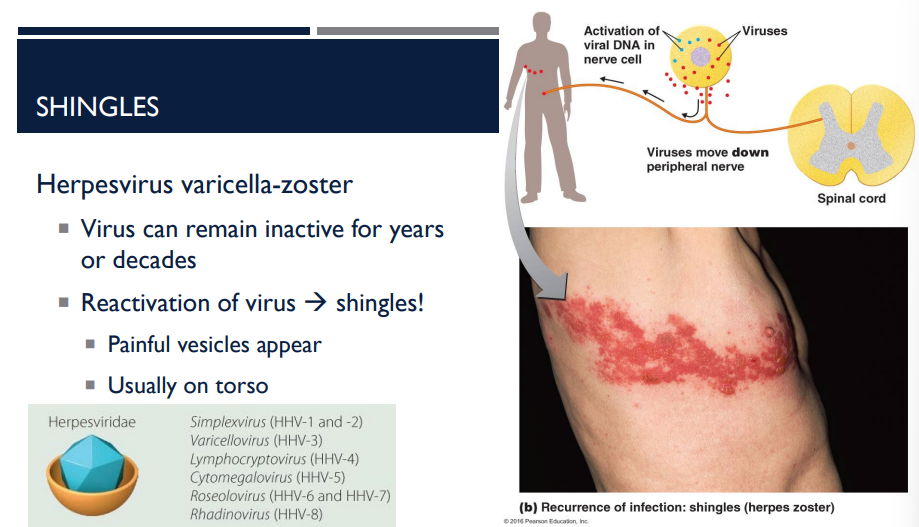
How does a person get shingles?
The reactivation of the herpesvirus varicella-zoster, which can remain inactive for years or decades.
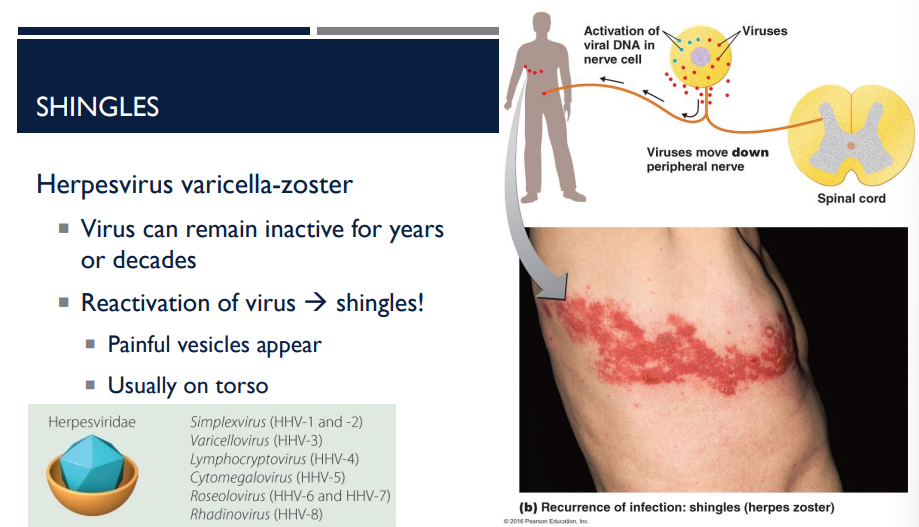
A person has shingles. Where do the painful vesicles usually appear?
usually on the torso (see picture)
(LC) Would you consider shingles to be an acute, latent, or persistent infection?
Acute
Latent
Persistent
None of the above
B
Shingles is an example of a latent infection. The initial case of chickenpox is the acute infection. The virus then remains inactive until conditions trigger the production of new virus particles that cause shingles.

What viruses are helical & enveloped?
morbillivirus
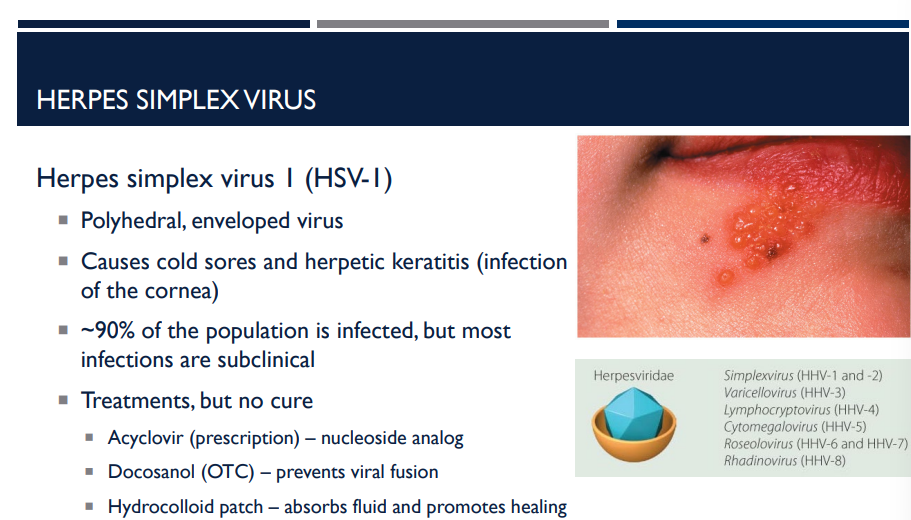
Which virus causes cold sores and herpetic keratitis (infection of the cornea)?
Herpes simplex virus I (HSV-I)
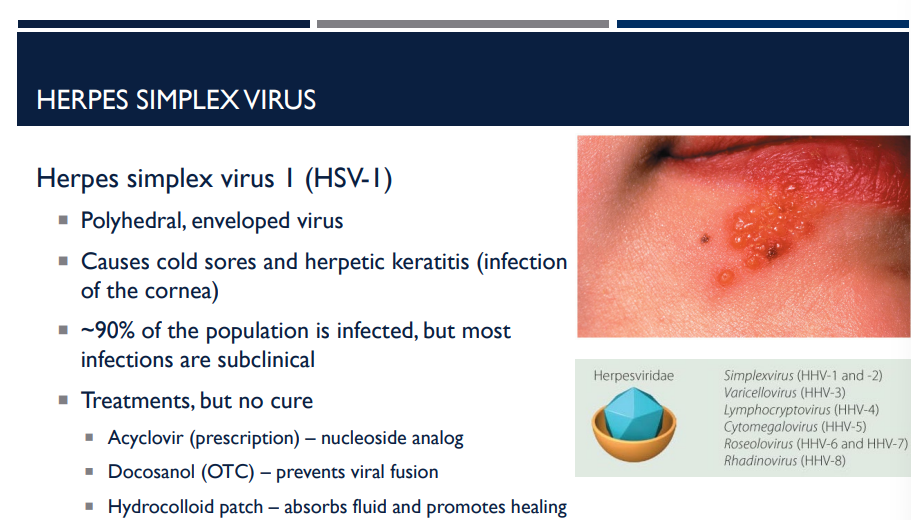
Describe how hydrocolloid patches help treat HSV-1.
absorbs fluid and promotes healing
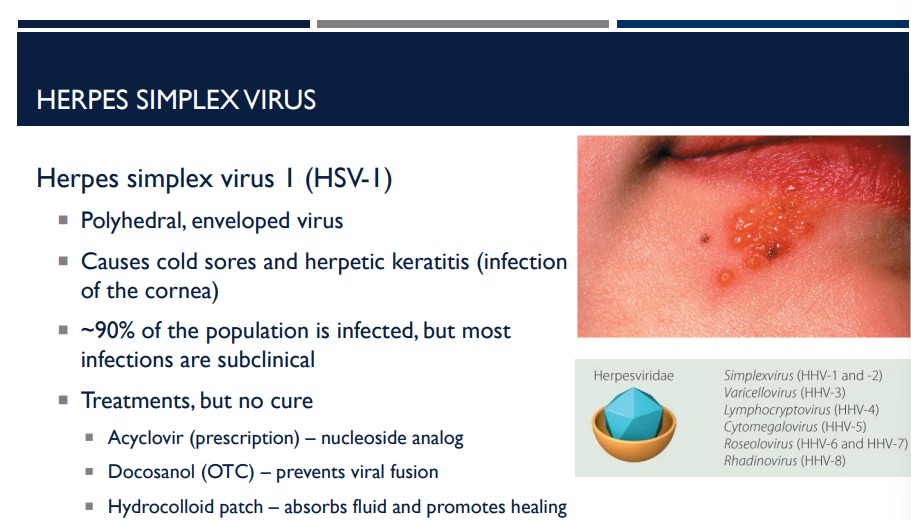
Describe how acyclovir (prescription) and docosanol (OTC) help treat HSV-1.
Acyclovir (prescription) — nucleoside analog
Docosanol (OTC) — prevents viral fusion

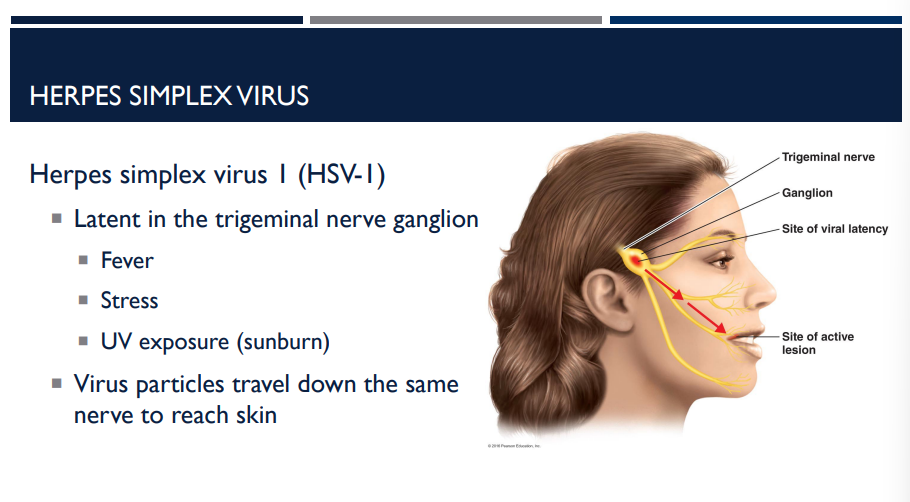
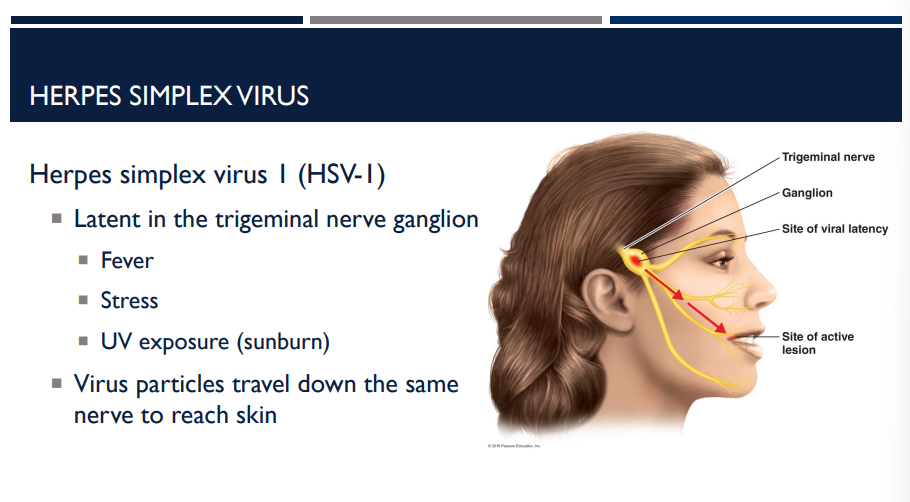
HSV-1 is latent where in the body? How is it reactivated?
trigeminal nerve ganglion
Reactivation can be triggered by factors such as fever, stress, sunlight.
fever
stress
UV exposure (sunburn)
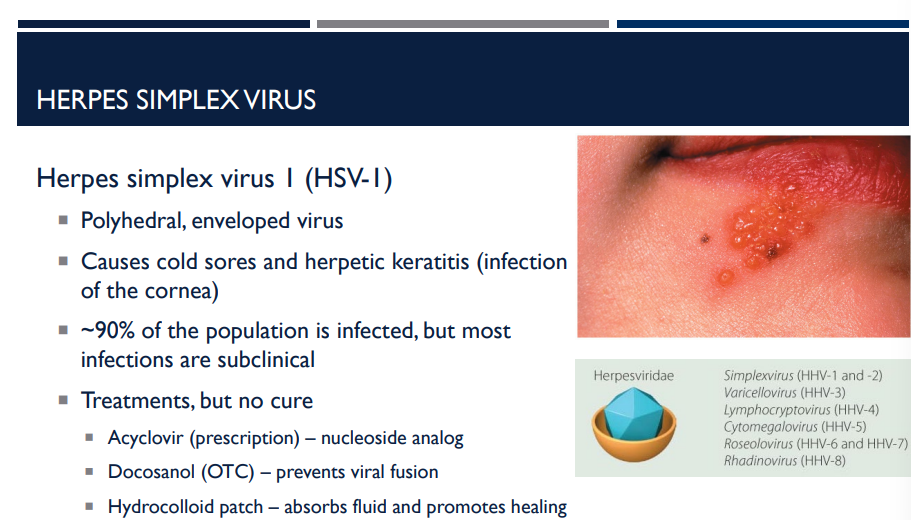
Describe the herpes simplex virus I (HSV-I).
Polyhedral, enveloped virus
Causes cold sores and herpetic keratitis (infection of the cornea)
~90% of the population is infected, but most infections are subclinical
Treatments, but no cure
Acyclovir (prescription) – nucleoside analog
Docosanol (OTC) – prevents viral fusion
Hydrocolloid patch – absorbs fluid and promotes healing
Latent in the trigeminal nerve ganglion
Fever
Stress
UV Exposure (sunburn)
Virus particles travel down the same nerve to reach skin
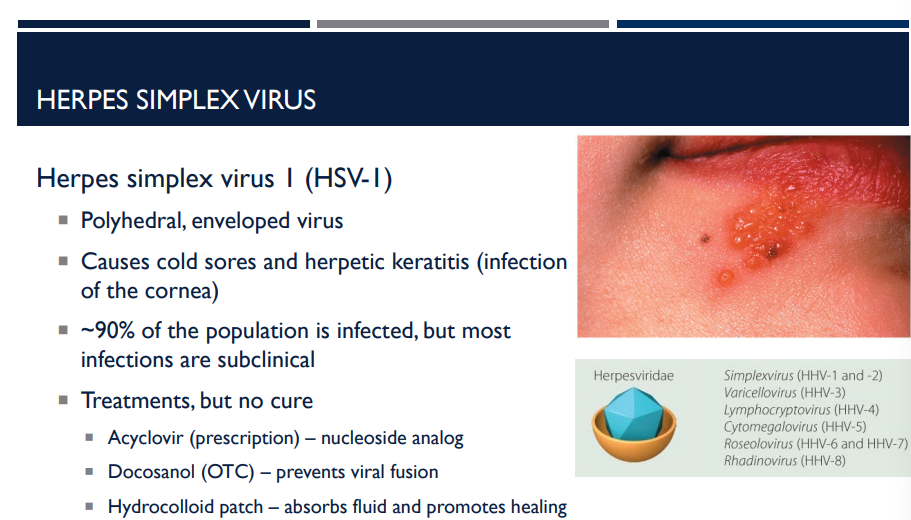
Which virus has infected ~90% of the population, though most infections are subclinical?
Herpes simplex virus (HSV-1)
T/F: Herpes simplex virus I (HSV-I) has infected 90% of the population.
T
T/F: Morbillivirus has infected 90% of the population.
F, it is the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) that has infected 90% of the population, although most infections are subclinical.

This virus is a helical enveloped virus. The virus enters through the respiratory system, then spreads to the skin, resulting in a macular rash (maculopapular rash). What disease am I describing? What virus is it caused by?
Measles; morbillivirus


Which disease has a long-term effect of disabling the immune system, such as by infecting macrophages and causing secondary infections?
Measles

Which disease has a long-term effect of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis? (fatal within 1-3 years)
Measles
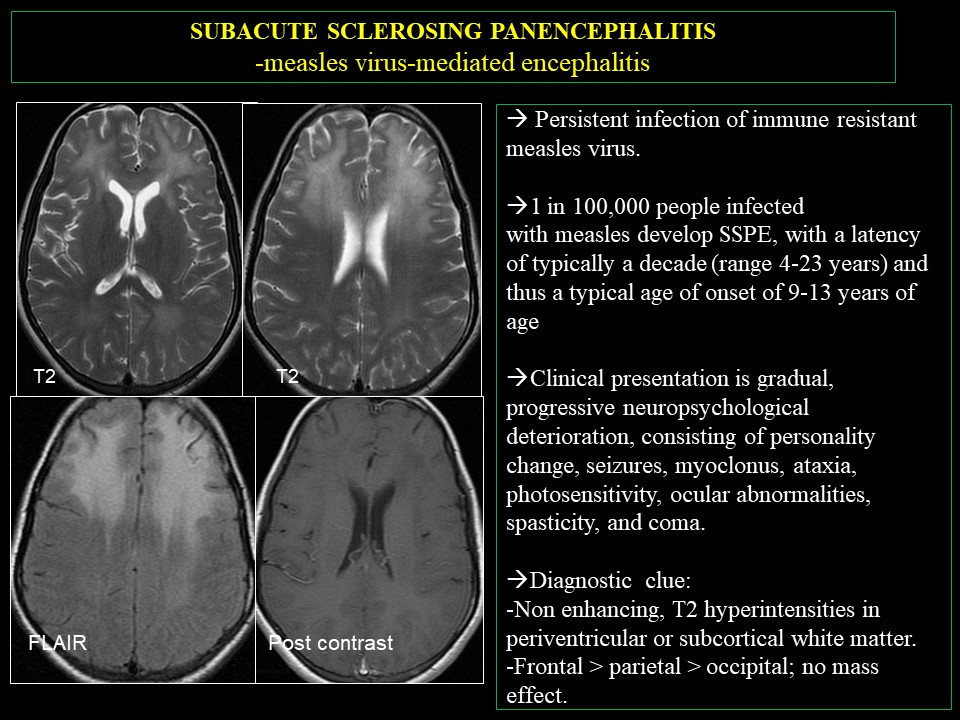

Which disease has a long-term effect of causing blindness and/or deafness?
Measles

Describe the long-term effects of measles.
Disables the immune system
Infects macrophages
Secondary infections
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
Fatal within 1-3 years
Blindness
Deafness
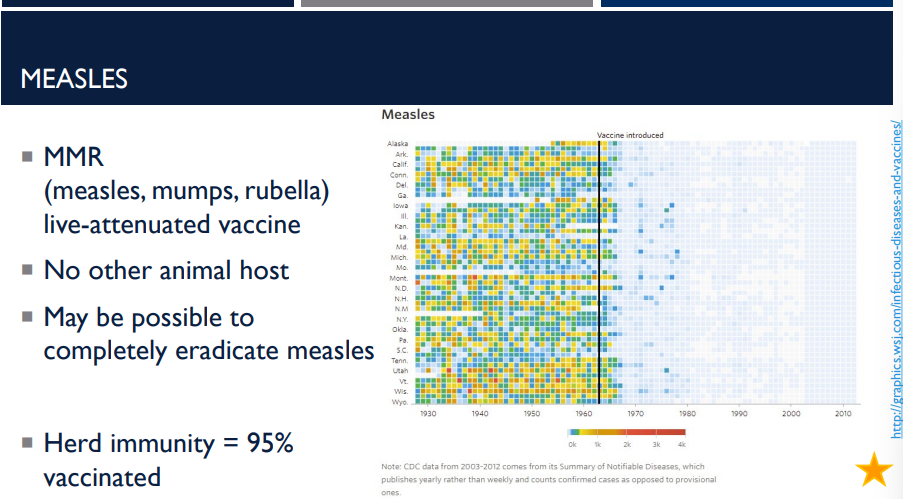
What type of vaccine is the MMR vaccine? (measles, mumps, rubella)
live attenuated vaccine
(A live attenuated vaccine uses a weakened (attenuated) form of a living virus or bacteria to trigger a strong, long-lasting immune response, mimicking a natural infection without causing serious illness, offering lifelong immunity with fewer doses, but generally isn't given to pregnant or severely immunocompromised people due to the risk of illness.)
What does it mean for measles to have no other animal host?
It means that the measles virus infects only humans. So it cannot survive or spread through animals.
This is important because diseases that have only one host (humans) are easier to eliminate. It then becomes possible to completely eradicate measles because only humans carry it (no animal reservoir, an effective vaccine exists, and long-lasting immunity is obtaned after vaccination or infection.
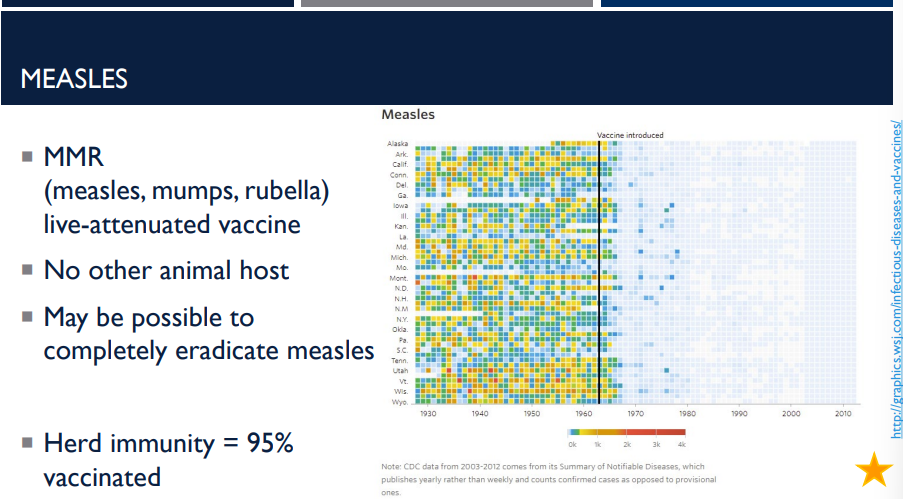
Measles is extremely contagious. It is one of the most infectious viruses. Because it spreads so easily, a very high percentage of the population must be immune to stop outbreaks. This is called herd immunity. What % of the population must be vaccinated?
95%
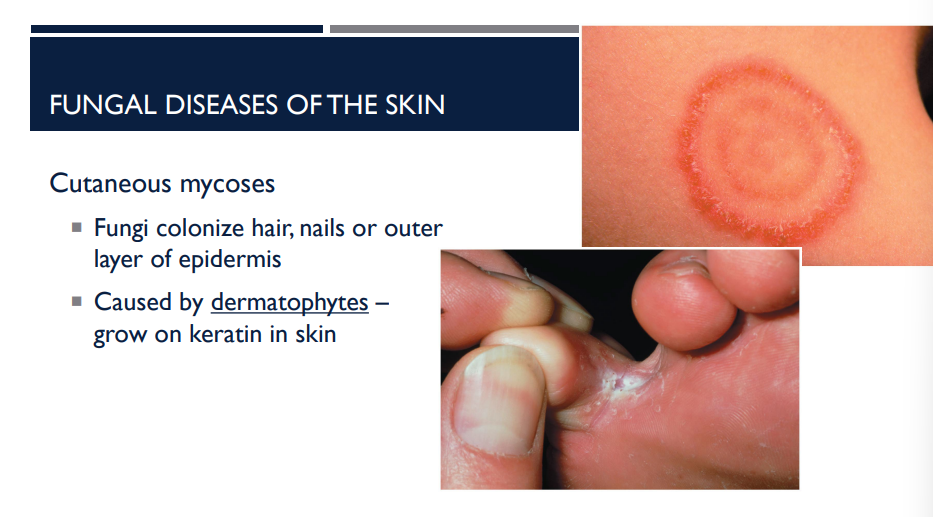
Describe the general type of fungal infection (which cause fungal disease of the skin), cutaneous mycoses.
Fungi colonize hair, nails, or outer layer of the epidermis
Caused by dermatophytes, growing keratin in skin
(Dermatophytes are common fungi that feed on keratin, causing superficial infections like ringworm (tinea) on skin, hair, and nails, leading to itchy, scaly, red rashes, athlete's foot, jock itch, or nail thickening (onychomycosis).
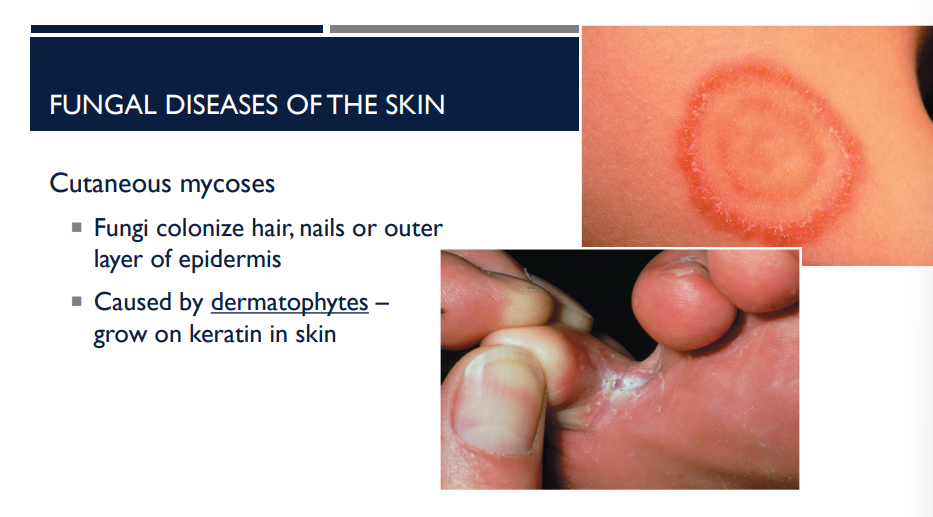
What is cutaneous mycoses caused by?
Caused by dermatophytes, growing keratin in skin.
(Dermatophytes are common fungi that feed on keratin, causing superficial infections like ringworm (tinea) on skin, hair, and nails, leading to itchy, scaly, red rashes, athlete's foot, jock itch, or nail thickening (onychomycosis).
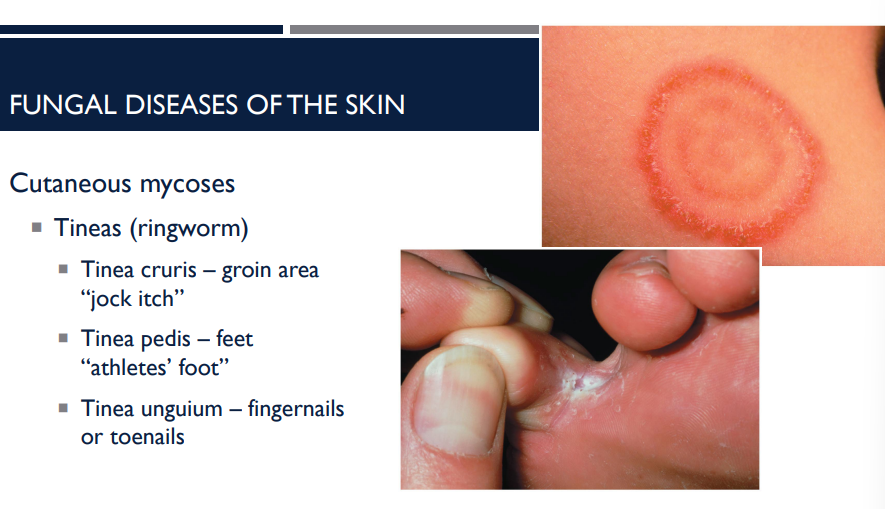
Cutaneous mycoses can cause what fungal disease?
tineas (ringworm)
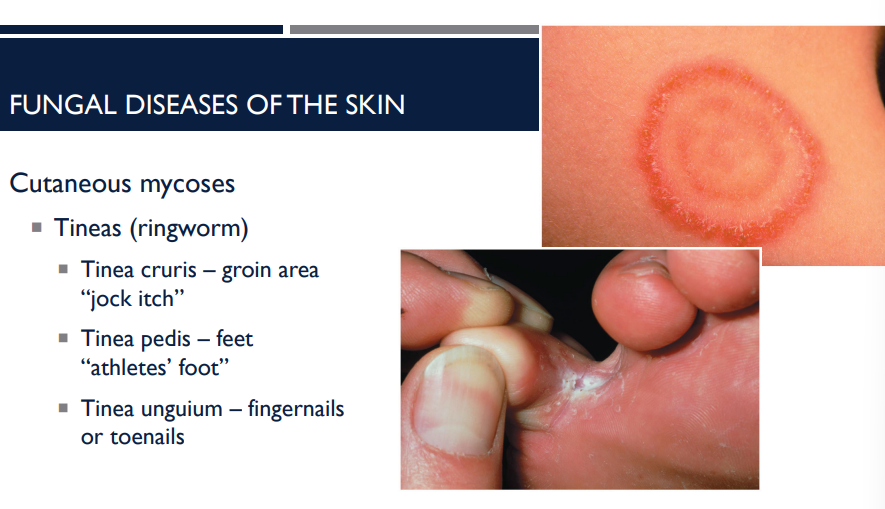
What are the different types of tineas (ringworm)?
Tinea cruris — groin area “jock itch”
Tinea pedis — feet “athletes’ foot”
Tnea unguium — fingernails or toenails