B11 - Hormonal coordination
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/4
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
1
New cards
Describe the principles of hormonal coordination and control by the human endocrine system.
Principles of hormonal coordination and control:
1. Feedback loops: Hormone levels regulated by positive/negative feedback.
2. Specificity: Hormones only affect target cells with specific receptors.
3. Signal amplification: Small hormone amounts trigger large cellular responses.
4. Synergy/antagonism: Hormones work together or oppose each other's effects.
5. Rhythmicity: Hormone release follows daily, monthly, or yearly patterns.
6. Integration: Endocrine system coordinates with other body systems for optimal functioning.
1. Feedback loops: Hormone levels regulated by positive/negative feedback.
2. Specificity: Hormones only affect target cells with specific receptors.
3. Signal amplification: Small hormone amounts trigger large cellular responses.
4. Synergy/antagonism: Hormones work together or oppose each other's effects.
5. Rhythmicity: Hormone release follows daily, monthly, or yearly patterns.
6. Integration: Endocrine system coordinates with other body systems for optimal functioning.
2
New cards
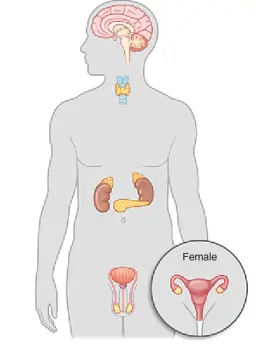
Identify the position of the following on a diagram of the human body and state their purpose: Write answer with body part
• pituitary gland
• pancreas
• thyroid
• adrenal gland
• ovary
• testes.
• pituitary gland
• pancreas
• thyroid
• adrenal gland
• ovary
• testes.
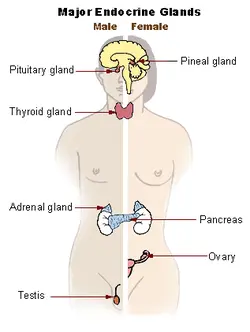
Pituitary gland: Located in the brain, it regulates hormone production and controls growth and development.
Pancreas: Found in the abdomen, it produces insulin and aids in digestion.
Thyroid: Situated in the neck, it regulates metabolism and produces hormones.
Adrenal gland: Positioned on top of the kidneys, it releases stress hormones and regulates salt balance.
Ovary: In the female reproductive system, it produces eggs and releases hormones.
Testes: Part of the male reproductive system, they produce sperm and release testosterone.
Pancreas: Found in the abdomen, it produces insulin and aids in digestion.
Thyroid: Situated in the neck, it regulates metabolism and produces hormones.
Adrenal gland: Positioned on top of the kidneys, it releases stress hormones and regulates salt balance.
Ovary: In the female reproductive system, it produces eggs and releases hormones.
Testes: Part of the male reproductive system, they produce sperm and release testosterone.
3
New cards
Explain how insulin controls blood glucose (sugar) levels in the body.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood glucose levels.
When blood glucose levels rise, such as after a meal, insulin is released into the bloodstream.
Insulin helps glucose enter cells, where it is used for energy or stored as glycogen.
It also inhibits the liver from releasing stored glucose into the bloodstream.
As a result, insulin lowers blood glucose levels.
When blood glucose levels drop, insulin secretion decreases, allowing the liver to release stored glucose and maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Overall, insulin plays a crucial role in maintaining blood glucose homeostasis in the body.
When blood glucose levels rise, such as after a meal, insulin is released into the bloodstream.
Insulin helps glucose enter cells, where it is used for energy or stored as glycogen.
It also inhibits the liver from releasing stored glucose into the bloodstream.
As a result, insulin lowers blood glucose levels.
When blood glucose levels drop, insulin secretion decreases, allowing the liver to release stored glucose and maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Overall, insulin plays a crucial role in maintaining blood glucose homeostasis in the body.
4
New cards
What is the difference between type 1 and 2 diabetes?
cf
5
New cards