W11, Ch 76 Glucocorticoids and 31 Opioids
1/231
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
232 Terms
What is main endogenous glucocorticoid called?
Cortisol
Where is cortisol produced?
By adrenal glands located on top of kidneys
What is function of cortisol?
To decrease inflammation in body and they also help with stress response
What should nurse remember when giving patient glucocorticoids?
If patient is given glucocorticoids, body will decrease or stop producing natural steroid, cortisol
True/False: If patient is given glucocorticoids, body will decrease or stop producing natural steroid, cortisol
True
What are glucocorticoid drugs also known as?
Corticosteroids
Are glucocorticoid drugs identical or opposite to steroids produced by adrenal cortex?
Nearly identical
What are physiologic effects of glucocorticoid drugs at low doses?
Modulation of glucose metabolism in adrenocortical insufficiency, aka long-term use for those with chronic endocrine disorders
What are pharmacologic effects of glucocorticoid drugs at high doses?
Suppression of inflammation in respiratory, mobility, and masses or tumors
What are side effects of glucocorticoid drugs dependent on?
Dosage, duration of treatment
True/False: High doses of glucocorticoid drugs are used long-term for those with chronic endocrine disorders (modulation of glucose metabolism in adrenocortical insufficiency)
False; LOW doses of glucocorticoid drugs are used long-term for those with chronic endocrine disorders (modulation of glucose metabolism in adrenocortical insufficiency), whereas high doses are used for suppression of inflammation in respiratory, mobility, and masses or tumors
What is prototype of glucocorticoid drug?
Cortisone
What is classification of cortisone?
Glucocorticoid drug
What does -one ending indicate?
Cortisone or derivative of cortisone (glucocorticoid)
What are derivatives of cortisone?
Prednisone, methylprednisolone, hydrocortisone, dexamethasone
What is mechanism of cortisone (and derivatives; prednisone, methylprednisolone, hydrocortisone, dexamethasone)?
Glucocorticoid with anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive actions
What does major clinical application of glucocorticoids stem from?
From their ability to suppress immune response and inflammation
Since glucocorticoids have ability to suppress immune response and inflammation, what do they help with?
Autoimmune disorders
Why do glucocorticoids help with autoimmune disorders?
Due to their ability to suppress immune response and inflammation
What are therapeutic uses of cortisone (and derivatives; prednisone, methylprednisolone, hydrocortisone, dexamethasone)?
Rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, inflammatory bowel disease, allergy, asthma, dermatologic disorder, suppression of allograft rejection, prevention of respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants
What are important therapeutic uses of cortisone (and derivatives; prednisone, methylprednisolone, hydrocortisone, dexamethasone)?
Asthma, prevention of respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants

How is this used?
Remove stopper (orange in middle) by pushing on top
Roll bottle between hands to mix powder (originally on bottom) and fluid (originally on top)
Needle goes at top when all mixed
What are 2 main effects of glucocorticoid physiology when used to treat nonendocrine disorders?
Metabolic effects, cardiovascular effects
What are metabolic effects of glucocorticoids in nonendocrine disorders (when used to treat diseases)?
Elevates blood glucose, promotes storage of glucose in form of glycogen, reduces muscle mass, decreases protein matrix of bone, causes thinning of skin, causes negative nitrogen balance which decreases total body protein, lipolysis, redistribution of fat
What is function of glucocorticoids in nonendocrine disorders?
To treat diseases (with metabolic and cardiovascular effects)
True/False: Most of time patients on glucocorticoids gain weight or develop diabetes
True, so nurse should monitor blood sugar levels (if too high, give patients insulin)
Why do patients on glucocorticoids gain weight or develop diabetes?
Glucocorticoids elevate blood glucose which promotes storage of glucose in form of glycogen
How do glucocorticoids reduce muscle mass?
Protein synthesis is decreased
When glucocorticoids are used and they create a negative nitrogen balance, what happens?
Negative nitrogen balance affects building of amino acids by decreasing it, causing decrease in total body protein
What happens when glucocorticoids cause lipolysis in body?
Fat is broken down and deposited in different areas
What are some names of redistribution of fat that use of glucocorticoids can cause?
Potbelly, moon face, buffalo hump
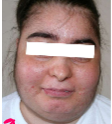
What is this?
Moon face that is caused by glucocorticoids redistributing fat (metabolic effect)
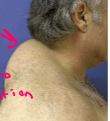
What is this?
Buffalo hump that is caused by glucocorticoids redistributing fat (metabolic effect)
What are cardiovascular effects of glucocorticoids in nonendocrine disorders (when used to treat diseases) with LOW LEVELS OF ENDOGENOUS GLUCOCORTICOIDS?
Capillaries become more permeable, vasoconstriction is suppressed, blood pressure falls due to vasodilation
True/False: With high levels of endogenous glucocorticoids, cardiovascular effects cause capillaries become more permeable, vasoconstriction is suppressed, blood pressure falls due to vasodilation
False; with LOW LEVELS of endogenous glucocorticoids, cardiovascular effects cause capillaries become more permeable, vasoconstriction is suppressed, blood pressure falls due to vasodilation
What are cardiovascular effects of glucocorticoids in nonendocrine disorders (when used to treat diseases)?
Glucocorticoids increase circulating red blood cells and polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and decrease lymphocytes, eosinophils, basophils, and monocytes (WBCs mostly)
True/False: Glucocorticoids decrease circulating red blood cells and polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and increase lymphocytes, eosinophils, basophils, and monocytes (WBCs mostly) as their cardiovascular effect in nonendocrine disorders (when used to treat diseases)
False; glucocorticoids INCREASE circulating red blood cells and polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and DECREASE lymphocytes, eosinophils, basophils, and monocytes (WBCs mostly) as their cardiovascular effect in nonendocrine disorders (when used to treat diseases)
What are effects of endogenous glucocorticoids in nonendocrine disorders during stress?
Help with physiologic stress (like surgery, infection, trauma, hypovolemia) because adrenal glands secrete large quantities of glucocorticoids and epinephrine
Why are glucocorticoids (and epinephrine) secreted in large quantities by adrenal glands during physiologic stress?
Hormones help maintain blood pressure and blood glucose levels
What would happen if there aren’t enough glucocorticoids (and epinephrine) secreted by adrenal glands during physiologic stress?
Insufficient release of glucocorticoids causes hypotension and hypoglycemia to occur
What would happen if there are too many glucocorticoids (and epinephrine) secreted by adrenal glands during physiologic stress?
Too much would cause hypertension and hyperglycemia to occur
What would happen if there aren’t enough glucocorticoids (and epinephrine) secreted by adrenal glands during very severe physiologic stress?
Glucocorticoid insufficiency can result in circulatory failure and death
True/False: If there aren’t enough glucocorticoids (and epinephrine) secreted by adrenal glands during very severe physiologic stress, this can result in circulatory failure and death
True
If patient is on glucocorticoids for long-term and body is suddenly under stress, should dosage be increased or decreased temporarily?
Will likely need to temporarily increase dose
What are adverse effects of cortisone?
Adrenal insufficiency, osteoporosis, infections, glucose intolerance (hyperglycemia), myopathy, Iatrogenic (physician-produced disease) Cushing’s syndrome, cataracts or glaucoma, peptic ulcers, hypokalemia, fluid imbalances, hypertension, growth retardation or suppression, psychologic disturbances, if crosses placenta can affect fetus, and if enters breast milk in large dose would cause growth retardation
What are 4 main adverse effects if too much cortisone is taken?
Adrenal insufficiency, osteoporosis, infections, glucose intolerance (hyperglycemia)
What are common adverse effects of cortisone?
Adrenal insufficiency, osteoporosis, infections, glucose intolerance (hyperglycemia), Cushing’s syndrome, cataracts or glaucoma, peptic ulcers, fluid imbalances, hypertension
What does iatrogenic (seen in iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome) mean?
Physician-produced disease
What could adverse effect of cortisone, fluid imbalances, lead to?
Edema
What causes Cushing’s Syndrome to happen?
Due to long-term use of glucocorticoids even if dose isn’t that high
What are main signs and symptoms of Cushing’s Syndrome?
Red face, fat deposition on abdomen and back of neck to create “buffalo hump”, fat found “moon face”
What are all signs and symptoms of Cushing’s Syndrome?
Personality changes, red face, increased susceptibility to infection, fat deposition on abdomen and back of neck to cause “buffalo hump”, osteoporosis, hyperglycemia, CNS irritability, fat round “moon" face, fluid retention causing edema, thin extremities, GI distress leading to increased acid, purple striae along stomach, thin skin leading to bruises and petechiae
What are signs and symptoms of Cushing’s Syndrome unique to males?
Gynecomastia (breast enlargement)
What are signs and symptoms of Cushing’s Syndrome unique to females?
Amenorrhea, hirsutism
What are drug interactions that patient taking glucocorticoids should avoid?
Digoxin, thiazide, or loop diuretics (as they are interactions related to potassium) loss, NSAIDs, insulin and oral hypoglycemics, vaccines (live vaccines)
Why should glucocorticoids and digoxin, thiazide, or loop diuretics (interactions related to potassium loss) not be taken together?
If potassium is low due to hypokalemia that glucocorticoids cause, this can cause digoxin toxicity which can cause low blood pressure, patient to see halos around lights (changes in vision), and confusion
Why should glucocorticoids and NSAIDs not be taken together?
Increases risk of ulcer and causes erosion
Why should glucocorticoids and insulin or oral hypoglycemics not be taken together?
Dose of glucocorticoids might have to be adjusted
Why should glucocorticoids and vaccines, especially live ones, not be taken together?
Glucocorticoids suppress immune system so if patient receives vaccine (especially live), patient can develop that disease
What are contraindications for taking glucocorticoids?
Patients with systemic fungal infections, those receiving live virus vaccines
When should nurse use caution when giving glucocorticoids?
In pediatric patients, in pregnancy or breast feeding, in older females because risk of osteoporosis is increased
Since risk of osteoporosis in older females is increased when they are taking glucocorticoids, what is a way to offset this risk?
Give calcium and vitamin D for bone health (with K2 because K2 helps vitamin D deposit and keeps calcium in bones)
Why are glucocorticoids contraindicated for patients with systemic fungal infections?
Can cause pain to drink or eat really bad
What is typical glucocorticoid dosage?
Glucocorticoid dosage is highly individualized
True/False: Glucocorticoid dosage is same for everyone taking them
False; glucocorticoid dosage is highly individualized
How is glucocorticoid dosage determined?
Determined empirically (trial and error)
Why should glucocorticoids be started low and slow?
There is no immediate threat
Why shouldn’t glucocorticoids be started high and decreased as possible?
There is immediate threat
If patient is just starting glucocorticoids, how should nurse give them to patient?
Start low and slow as there is no immediate threat that way
If patient is taking glucocorticoids for long-term use, what should dosing look like?
Smallest effective amount
In what instance would patient have prolonged treatment with high doses of glucocorticoids?
Only if disorder is life-threatening or has potential to cause permanent disability
True/False: Patient have prolonged treatment with high doses of glucocorticoids only if disorder is life-threatening or has potential to cause permanent disability
True
When should dose of glucocorticoids be taken (morning or night)?
Dose in morning to mimic “normal” body production
Why are glucocorticoids taken in morning?
To mimic “normal” body production
When would regular dose of glucocorticoids be increased?
In times of stress (physical, emotional, anxiety)
True/False: If patient’s dose of glucocorticoids is too high, patient should immediately stop taking glucocorticoids altogether to be safe
False; taper doses to wean gradually off glucocorticoids
If patient wants to decrease dosage of glucocorticoids or stop them altogether, how should doses be taken?
Taper doses to wean gradually off glucocorticoids
What are routes of administration of glucocorticoids?
Oral, parenteral (IV, IM, subQ), topical
True/False: Glucocorticoids can only be taken orally
False; glucocorticoids can be given orally, via parenteral (IV, IM, subQ), topical
What are 3 ways individual glucocorticoids differ?
Biologic half-life, mineralocorticoid potency, glucocorticoid potency
Since glucocorticoids differ by their biologic half-life, mineralocorticoid potency, and glucocorticoid potency, what does nurse have to do?
Read about each glucocorticoid before administration to determine these 3 factors
What is benefit of using glucocorticoids topically vs. another route?
There are not many systemic side effects when taken topically
True/False: If patient has inflammation in their joint, glucocorticoids can be given/injected right at joint
True
True/False: Individual glucocorticoids differ in their biologic half-life, mineralocorticoid potency, and glucocorticoid potency
True
What should nurse do as pre-administration assessment for glucocorticoids?
Look at baseline bloop pressure, fluid and electrolyte status and weight, monitor glucose level
How should nurse administer glucocorticoids?
Administer drug in the day to mimic circadian rhythm, and give with food to prevent GI irritation
Why should glucocorticoids not be given at night?
Patient wouldn’t be able to sleep
How should nurse perform ongoing evaluation and interventions for patient taking glucocorticoids?
Reassess patient’s condition and response to therapy, reassess BP, weight, and fluid and electrolytes, patient with diabetes mellitus may need adjustment of insulin whereas patients without diabetes may require insulin or antidiabetic drugs
True/False: When taking glucocorticoids, patient with diabetes mellitus may need adjustment of insulin whereas patients without diabetes may require insulin or antidiabetic drugs
True
How should nurse educate patient?
Do not stop drug abruptly, avoid NSAIDS, avoid prolonged use of corticosteroids unless directed by provider, notify provider with adverse reaction or signs of infection
Why should patient taking glucocorticoids not stop the drug abruptly?
Can lead to adrenal insufficiency
What can happen if patient stops taking glucocorticoids abruptly?
Can lead to adrenal insufficiency
Why should patient taking glucocorticoids avoid NSAIDs?
Can increase risk of GI ulceration
When should patient notify provider if taking glucocorticoids?
If patient experiences adverse reaction or signs of infection
A patient with systemic lupus erythematosus is prescribed prednisone. The nurse will monitor patient for what?
Neck and back pain
A patient taking pharmacologic doses of glucocorticoids should be instructed to what?
Never abruptly withdraw therapy
What are opioids derived from?
Opium poppy or synthesized
What is goal of opioids?
Bind to opioid receptors in CNS, so in brain and spinal cord, to alter perception of pain
What happens when opioids alter perception of pain?
Opioids manage the sensation; they do not cure source of pain
True/False: Opioids and receptors for opioids mimic lock-and-key style
True