Macroeconomics Exam 2: Chapters 9, 10, 12
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Labor Force
the sum of employed and unemployed workers in the economy
Employed
someone who worked 1+ hours in reference week (or were temporarily away from their jobs).
Unemployed
someone who is not currently at work but who is available for work and who has actively looked for work during the previous month
Not in Labor Force
a person who is not looking for work because he or she does not want a job or has given up looking
Discouraged Worker
people who are available for work, but have no looked for a job in the previous four weeks because they believe no jobs are available
Natural Rate of Employment
frictional unemployment + structural unemployment
Structural Unemployment
unemployment that arises from a persistent mismatch between the skills and attributes of workers and the requirement of jobs
Frictional Unemployment
short-term unemployment that arises from the process of matching workers with jobs
Cyclical Unemployment
unemployment caused by a business cycle recession
Consumer Price Index
a measure of the average change over time in the prices a typical urban family of four pays for the goods and services they purchase
Unemployment Rate
(Unemployed / (Unemployed + Employed) x 100 = ?
Unemployment Rate
(Unemployed / Labor Force) x 100 =
Labor Force Participation Rate
(Labor Force / Adult Population) x 100
CPI (Calculation)
(Cost of the Basket in Current Price / Cost of Basket in Base Year Price) x 100
Inflation Rate
(CPI New Year - CPI Old Year) / CPI Old Year) x 100
CPI Amount in Today's ($)
Amount in Year X(Old)'s $ x (CPI Today / CPI in Year X)
Real Interest Rate
Nominal Interest Rate - Inflation Rate
Structural Unemployment
this type of unemployment occurs when you have lack of skill or when there is organizational problem in the labor market
Frictional Unemployment
this type of unemployment affects skilled workers and happens because of labor market inefficiencies
Cyclical Unemployment
occurs because of business cycle fluctuations
Frictional
most people who are unemployed are unemployed due to _______ unemployment
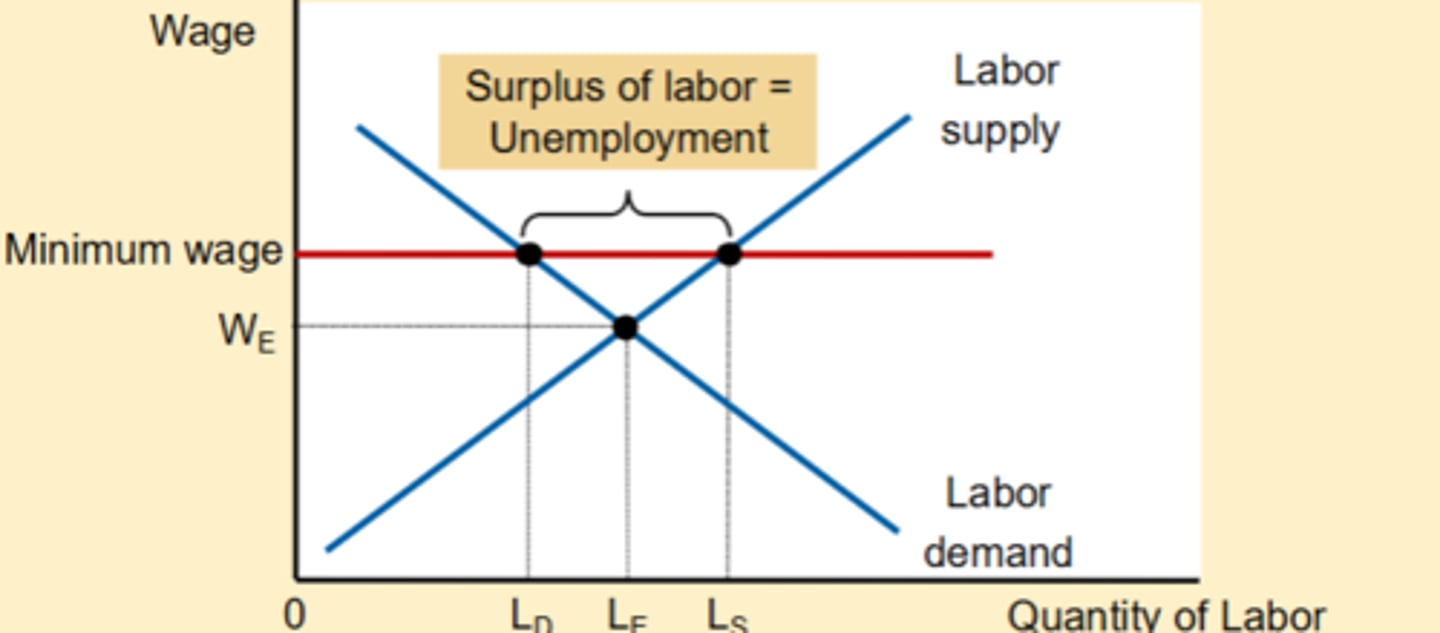
Binding
when there is a surplus of labor in the market the minimum wage rate is ______
Binding
this minimum wage is _______
Substitution Bias
Limitation of CPI - consumers may change their purchasing habits away from goods that have increased in price
Quality Bias
Limitation of CPI - products like cars and computers have become more durable and better quality over time (it is hard to isolate the pure inflation part of price increases)
New Product Bias
Limitation of CPI - the basket of goods changes only every 10 years; there is a delay to including new goods (ex. cell phones in 2010s)
GDP Deflator
measures the average change in prices of all goods and services produced domestically in an economy
Constant
the natural rate of employment is stable but not _______
Higher
the CPI and GDP deflator show similar long-run inflation trends, but the CPI usually reports slightly _______ inflation since it captures changes in consumer import prices, while the GDP deflator reflects price changes in all domestically produced goods and services.
Business Cycle
alternating periods of economic expansion and economic recession
Rule of 70
a shortcut to estimate how many years it takes for an economy (or any variable) to double in size, by dividing 70 by its annual percentage growth rate
Labor Productivity
the quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker or by one hour of work
Labor Productivity
Y/L = (Y = real output, L = Quantity of Labor)
Capital
manufactured good that are used to produce other goods and services
Technological Change
improvements in capital or methods to combine inputs into outputs
Potential GDP
refers to the level of real GDP attained when all firms are operating at capacity
Financial Markets
markets where financial securities, such as stocks and bonds, are bought and sold
Stocks
a financial security representing partial ownership of a firm
Bonds
a financial security promising to repay a fixed amount of funds; essentially a loan from a household to a firm
Financial System
Financial System
the system of financial markets and financial intermediaries through which firms acquire funds from households
Liquidity
the fianncial system allows savers to quickly convert their investment into cash through _______
Risk Sharing
by allowing investors to spread their money over many different assets, investors can reduce their risk while maintaining a high expected return on their investment through _______
National Saving
Private Saving + Public Saving
National Saving
National Income (GDP) - Consumption - Government Purchases = ?
Transfer Payments
TR = ?
Factors of Production
Y = ?
Government Purchases
G = ?
Consumption
C = ?
Taxes
T = ?
Private Saving
Y + TR - C - T = ?
Public Saving
T - G - TR = ?
Total Saving
Y - C - G = ?
Budget Surplus
T > G + TR = ?
Budget Deficit
T < G + TR = ?
Balanced Budget
T = G + TR = ?
Investment
Savings = _______ ?
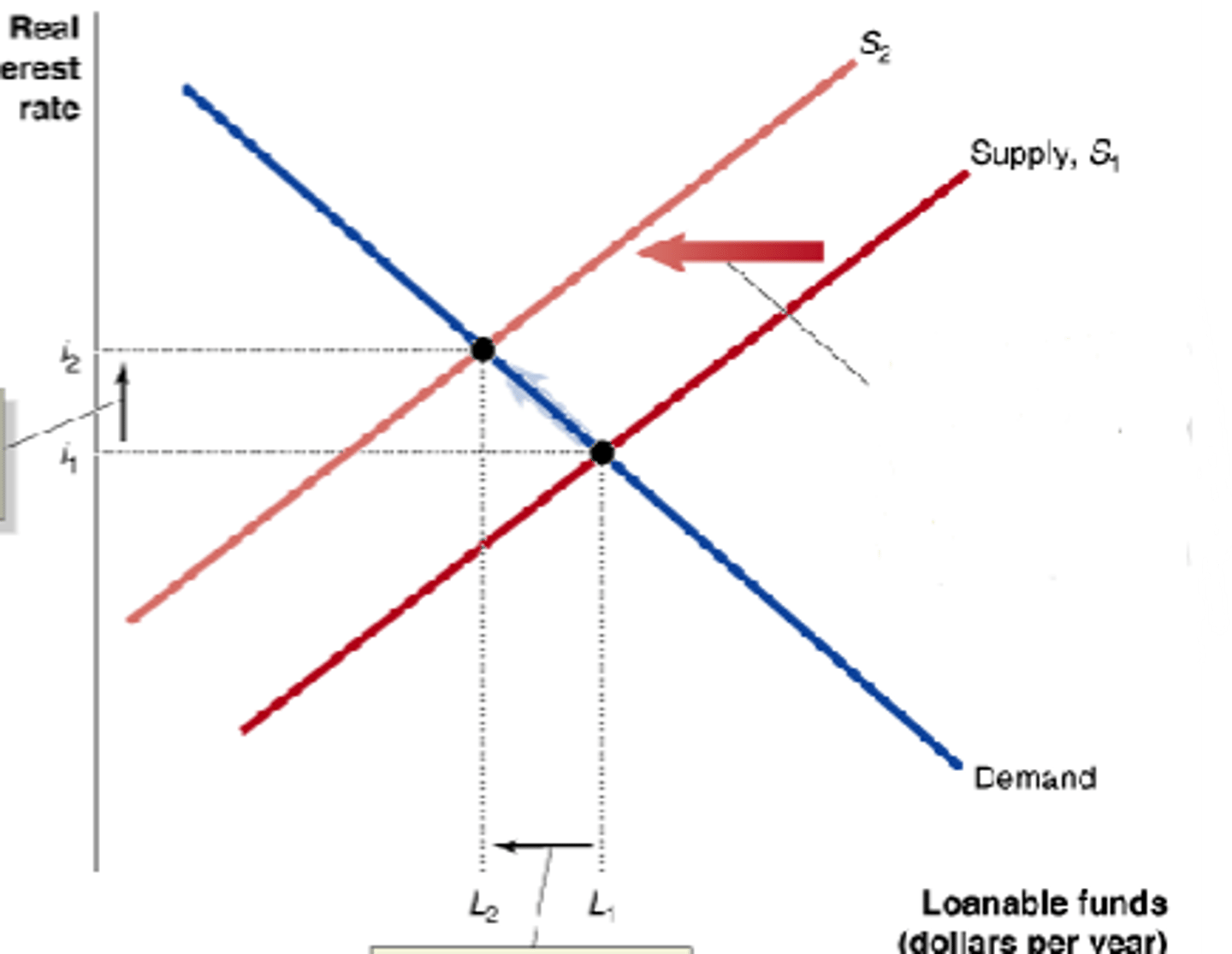
Crowding Out
the decline in private expenditures as a result of increases in government purchases
Crowding Out
this figure shows _______ _______
Expansion (Boom)
a period when economic activity is rising
Peak
the highest point of the business cycle — the economy is at full capacity
Recession
a period when economic activity declines
Trough
the lowest point of the business cycle — the end of the recession
The Great Moderation
relative stability of average annual growth rate of GDP since the 1950's
Rule of 70
Number of Years to Double = 70 / Annual Growth Rate
Three Key Roles of The Financial System
1. Risk Sharing
2. Liquidity
3. Information Sharing
Supply
in the market for loanable funds, households are on the _______ side
Demand
in the market for loanable funds, firms are on the _______ side
Services
manufacturing (especially durable goods) is more strongly affected by recessions; the economy is based more on _______ now, decreasing the effect of the business cycle on GDP
Unemployment Insurance
before the 1930s, _______ _______and other government transfer programs like Social Security did not exist; these programs increase the ability of consumers to purchase goods and services during recessions
Government Policies
economist believe that active _______ _______ to lengthen expansions and minimize the affects of recessions have had the desired effect; the debate over the role of government in this way became particularly intense during the recession of 2007-2009
Instability
the severity of the Great Depression of the 1930s was in part caused by _______ in the financial system; similar _______ exacerbated the recession of 2007-2009
Low
inflation rate is (usually) _______ during a recession
High
unemployment rate is (usually) _______ during a recession
1
average length of recession since the 1950's is less than _______ year(s)
Low
real interests are _______ during a recession
Hurt
durable goods tend to _______ during a recession
Aggregate Expenditure
total spending in the economy: the sum of consumption, planned investment, government purchases, and net exports
Planned investment
I = ?
Planned Investment
planned spending by firms on capital goods, and by households on new homes
Planned Investment
Actual Investment - Unplanned Changes in Inventories
Net Exports
NX = ?
Net Exports
the value of exports minus the value of imports
Aggregate Expenditure
C + I + G + NX =
Actual Investment
the total amount that businesses actually spend on capital goods plus changes in inventories during a given period
=
if AE /= GDP, inventories are unchanged and the economy is in equilibrium
<
if AE /= GDP, inventories rise and GDP + unemployment decrease
>
if AE /= GDP, inventories fall and GDP + unemployment increase
Consumption-Smoothing
most people prefer to keep their consumption fairly stable from year to year, a process known as _______-_______
Consumption Function (C)
a + m x YD =
Autonomous Consumption
a = ?
Autonomous Consumption
consumption that does not depend on income
Induced Consumption
m x YD = ?
Induced Consumption
consumption that depends on income
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
m = ?
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
Changes in Consumption / Changes in Disposable Income
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
Changes in Saving / Changes in Disposable Income
1
MPS + MPC = ?
Potential GDP
GDP at natural rate of unemployment
Multiplier Effect
Changes in Real GDP / Changes in Autonomous Spending