UWORLD Missed Questions (Bio and Biochem)
1/533
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
534 Terms
What does renin do?
vasoconstriction
Thyroid horomones play roles in…
metabolic rate and development
What is a measure of thermodynamic stability of a compound
heat of combustion
An increase in hydrostatic pressure causes osmotic pressure to _________, and causes fluid to move into/out of tissues
increase, out of
what do malnourished people tend to have less….
oncoic pressure in the glomerular capillary
the glomerulus is surroundinded by the…
bowman’s capsule
the notochord develops from the….
mesoderm
The low energy conformation of myosin in a sarcomere is when…
it is bound to ATP only
In the sarcomere, calcium binds to
troponin
a decrease in protein in the blood causes osmotic pressure to ________ and causes fluid to move into/out of tissues
decrease, into
where does the first trna bind to in translation in the rRNA
P site
process by which one X chromosome is inactivated to tegulate X chromosome expression dosage (occurs in females)
barr bodies
process by which one allele of a gene is expressed in a parent specific way
gene imprinting
What type opf process is gene imprinting?
epigenetic
DNA that reads the same on its forward and complement sequence is called
palindorme DNA
A sequence that needs to be cut has nucleotides CCCCGGGC. What types of restriction enzumes can cut this?
4 and 6 base pair recongition sequence
restriciton enzymes recognize….and cut them
palindromic sequences
Ionotropic recpetors are a fancy way of saying
ligand gated ion channel
metabotropic recpetors are just another way of saying
GPCR
how many and where are the ions pumped for all sodium potassium channels in the body
3 Na out of cell, 2 K into cell
what type of protein is caspase? (remember it destorys proteins)
hydrolase
Assume that a certain species with sex chromosomes R and S exists such that RR individuals develop as males and RS individuals develop as females. Which of the following mechanisms would most likely compensate for the potential imbalance of sex-chromosome gene productsbetween males and females of this species?
inactivation
if two married inidivudals are both affected by a genetic mutation, and 50% of their children also have the mutatuon, this means that the miutaution is….
autosomal dominant
during anarobic conditions, does the ETC function?
NO
during anaerobic conditions, the cytoplasm will become
acidic
what are three necessary conditions for michelis menton
steady state conditions, constnat pH, enzyme concentration is lower than the substrate
in a graph, the period of a wave is the…
peak of one wave to the peak of the other wave on the same side
UV absorbption spectra is used to determine what for organic compounds
functional group
does affinity chromatography utilize charges to separate molecules?
NO
glyceraldehyde, glucose, galatocse, and mannose are all forms of
aldoses
how many protons does NADH pump across the mitcohdrial mermbrane?
10
how many protons does NADH pump across the mitochondria membrane?
10
how many protons does FADH2 pump across the mitochdonria membrane?
6
What is complex 1 of the ETC called
NADh dehydrogenase
What is complex 2 of the ETC called?
succinate dehydrogenase
an inactive enyzme is reffered to as a
zymogen
multipotent cells can differentiate into fewer types of tissue than ________ and __________
pluripotent and totipotent
a morphogen is a juxtacrine, paracrine, endocrine factor
paracrine
a signmoidal enzyme binding curve means that there are…
multiple activer sites
which muscle cells have gap junctions?
smooth and cardiac
a molecule that alters cell differentiation in a concentration-dependent manner is known as a…
morphogen
pluripotent cells can differnetiate into everything but
placental cells
in the muscle contraction unit, calcium will bind to
troponin
to determine if L or D in a sugar, look at the…
highest numbered carbon
what generates toruqe in bacteria with flagella
basal body
What is the carnitine shuttle used for?
fatty acid into mitochondria for beta oxidation
What is the rate limiting step of the pentose phosphate pathway
g6p dehydrogenase (converts g6p to 6 phosphogluconate)
what activates the pyrvate dehydrogenase complex?
calcium
where does the kreb’s cycle take place
mitochondria
wich fermentation produces acetylaldehyde prior to the final product?
lactic acid fermentation
how many ATP do the processes of lactic acid and alcohol fermentation?
2
what does active PDH make?
NADH and acetyl Co A
Where is O2 converted to H2O in the ETC
complex 4
How many protons pumped acorss the membrane yield 1 ATP
4
in the citric acid cycle, NADH production takes place at the
carbon drops and final step
plasmids are always what shape?
circular
what happens to the anomeric carbon during the linearization of cyclical sugars
it becomes an aldehyde
On a lineweaver burk plot, V max gets larger closer or furtherfrom the origin?
closer
later peaks of column chomatography stick stronger to the _________ phase
stationary
in anion exchange chromatography, which molecules will be the last to elute?
those with a negative charge
if double stranded DNA is kept in a low pH environment, this will cause it to…
come apart
double stranded DNA is most stable in high/low salt envivornments
high
a native gel will tell about a protein/DNA’s…
original shape
if a denaturing gel of different samples of DNA/mRNA has lines occuring at the same latitude, this means they have the same…
number of base pairs
What charge does the mobile phase have in an anion exchange column? what about a cation exvhange column?
positive. negative
in cation exchange chromatography, which molecules will be the last to elute?
those with a positive charge
insulin and glucagon are hydrophobic/hydrophilic
hydrophilic
how are disulfide bonds broken?
cysteine residues are reduced
if NaOh is dissolved in water, what happens to entropy
it increases?
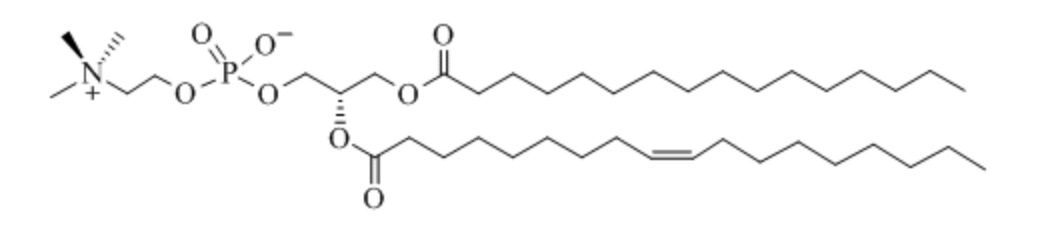
What is the general name for this compound?
phosphatide
What is the general structure of a phosphatide?
fatty acid esters with a nitrogen linked to a phosphate group
lower temperatures favor _________ control of a reaction
kinetic
thermodynamic is irreversible/reversible and kinetic is irreversible/reversible
reversible, irreversible
Which product is more stable? thermodynamic or kinetic
thermodynamic
how are disulfide bonds broken?
which protein moves the furthest for an SDS page gel under non-reducing conditions?
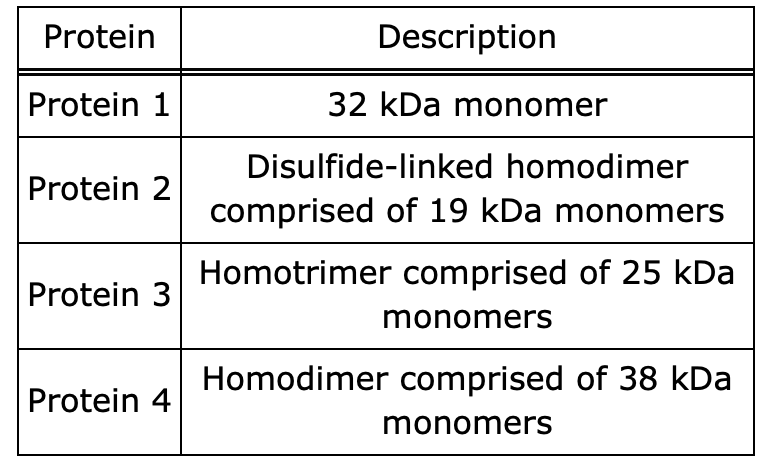
protien 3
“steric contraints” is also known as
steric hinderance
write the michaelis menton equation
V0 = Vmax(S)/(Km+(S))
kinetic products form slower/quicker because they have a lower/higher activation energy tan thermodynamic products
quicker, lower
conjugation is when
you have alternating double bonds
higher temperatures favor _______ control of a reaction
thermodynamic
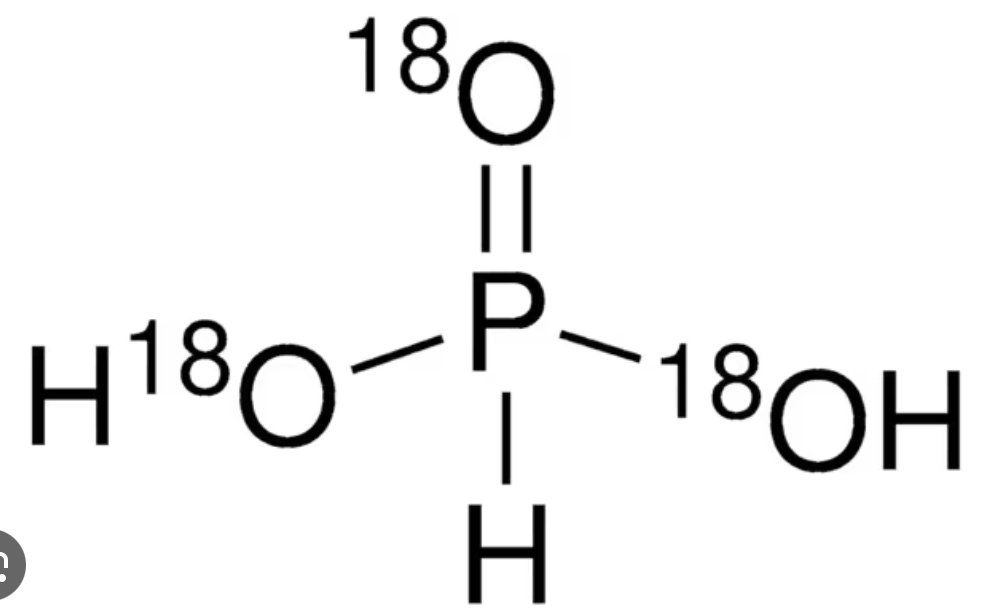
What is this called?
phosphonic acid
accepting/donating electron pairs is characteristic of _______ acids/bases
lewis
if delta h has gone up, that means that enthalpy has increased/decreased?
increased
the the temperature of a solution increases after dissolution of a salt, that measn that the reaciton is exothermic/endothermic
exothermic
A sparingly soluble metal hydroxide, M(OH)2 has a molar solubility of S mol/L at 25°C. Its Kspvalue is:
4S³
ncuelar factors are also known as
transcription factors
when a G protein is activated, what happens to the GDP bound to the alpha subunit
it will turn to GTP and detach from subunit
what does ion exchange chromatagoraphy sperate proteins based on?
charge
what enzyme converts acetyl co A to malonyl co A for fatty acid synthesis?
acetyl co A carboxylase
What is the regulatory step in Fatty Acid synthesis
conversion of acetyl co A to malonyl co A
triglycerides are typically used for
storage in adipocytes
list all gluconeogenic precursors
glycerol, alanine, lactate, oxaloacetate
where does glcuoenogensis occur?
liver and kidneys
What are gluconeogenic only amino acid?
those that are not ketogenic or both glucoenogenic and ketogenic
What are ketogenic and gluconeogenic amino acids
PITT
what are ketogenic only amino acids?
lecuine lysine
how does acetyl co A get to the cytoplasm for fatty acid oxidation?
citrate shuttle