Overview of the Adaptive Immune System
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Antigens
substances that provokes an immune response
Epitope
Specific part of an antigen that an antibody binds.
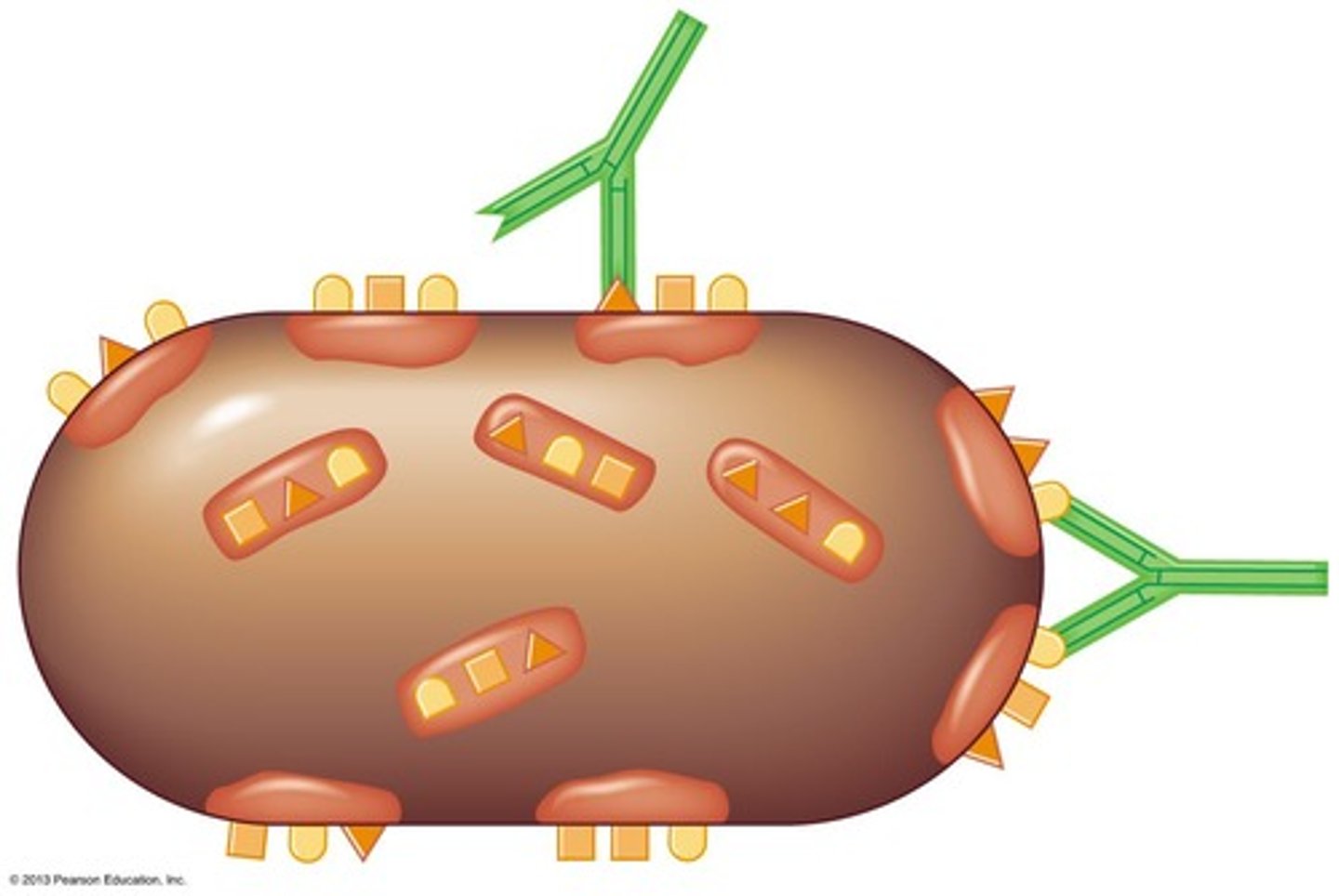
Hapten
Small molecules that induce an immune response but only when they are bound to larger carrier molecule
Adaptive immunity
Defenses that target a specific pathogen
Primary response
First time the immune system combats a particular foreign substance
Secondary response
Later interactions with the same foreign substance; faster and more effective due to 'memory'
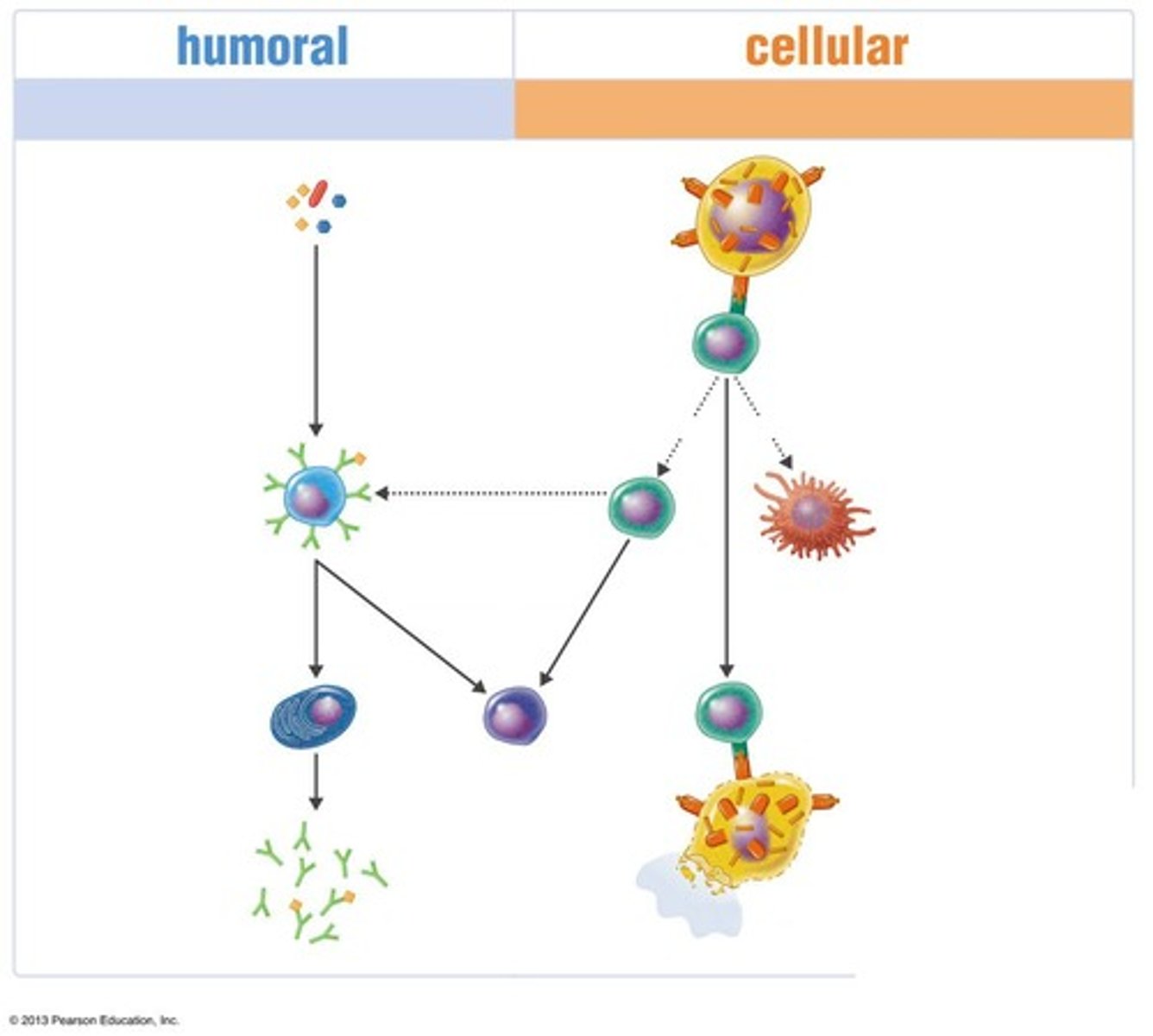
Humoral immunity
Produces antibodies that combat foreign molecules known as antigens
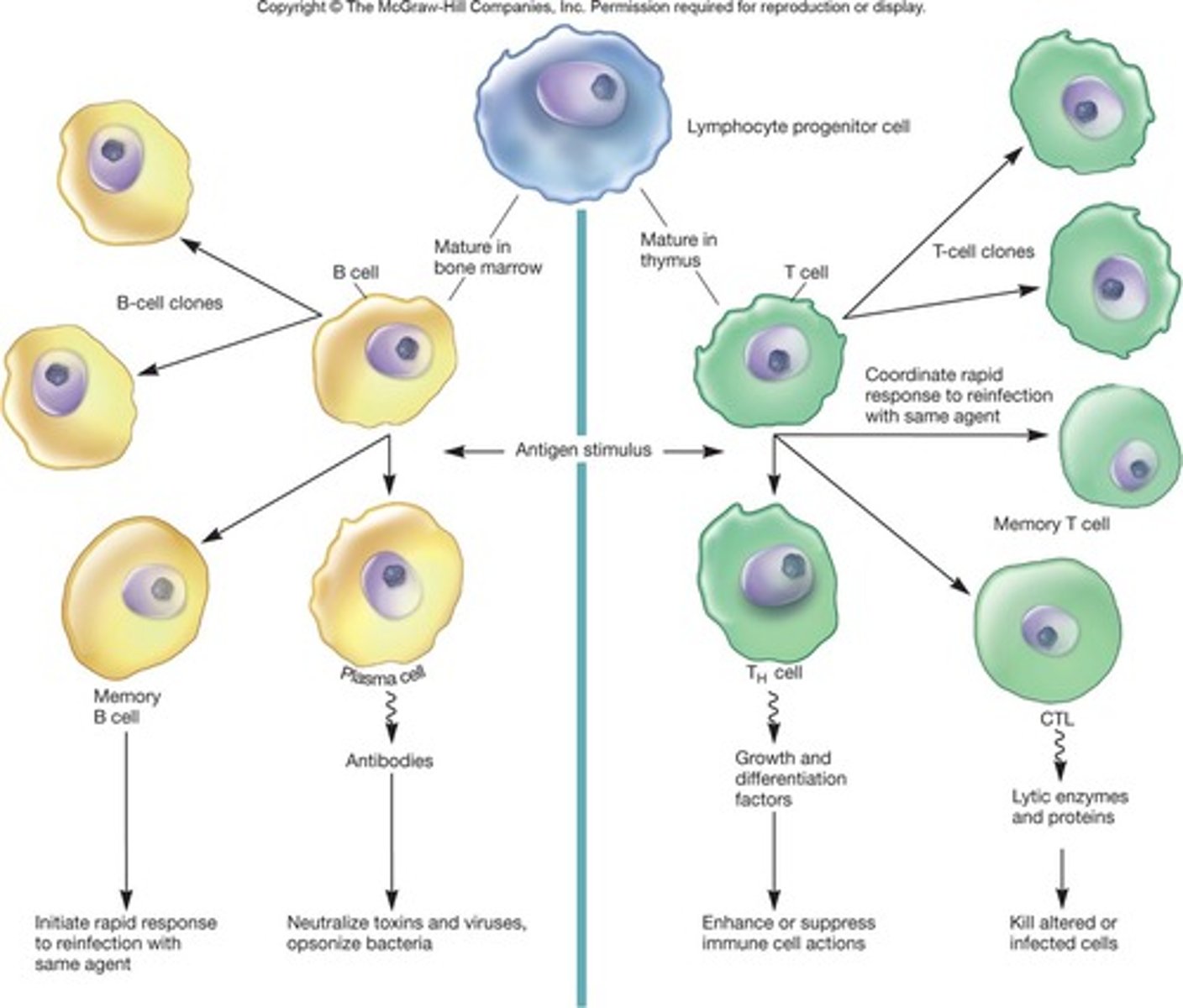
B cells
Lymphocytes that are created and matured in red bone marrow; recognize antigens and upon activation, produce antibodies.
Cellular immunity
the production and activation of T lymphocytes that recognize antigenic peptides presented by phagocytic cells through MHC molecules.
T cell receptors (TCRs)
On the T cell surface contact antigens, causing the T cells to secrete cytokines instead of antibodies
major characteristics of adaptive
1.Discrimination between self and non-self
2. diversity
3. Specificity
4. memory
Discrimination between self and non-self
Responds selectively to non-self, producing specific responses against the stimulus
Diversity
Generates enormous diversity of molecules
Specificity
Can be directed against one specific pathogen or foreign substance among trillions
Memory
Response to a second exposure to a pathogen is so fast that there is no noticeable pathogenesis
Cytokines
Chemical messengers produced in response to a stimulus
Interleukins (ILs)
Cytokines between leukocytes
Chemokines
Induce migration of leukocytes
Interferons (IFNs)
Interfere with viral infections of host cells
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α)
Involved in the inflammation of autoimmune diseases
Hematopoietic cytokines
Control stem cells that develop into red and white blood cells
Cytokine storm
Overproduction of cytokines leads to a cytokine storm
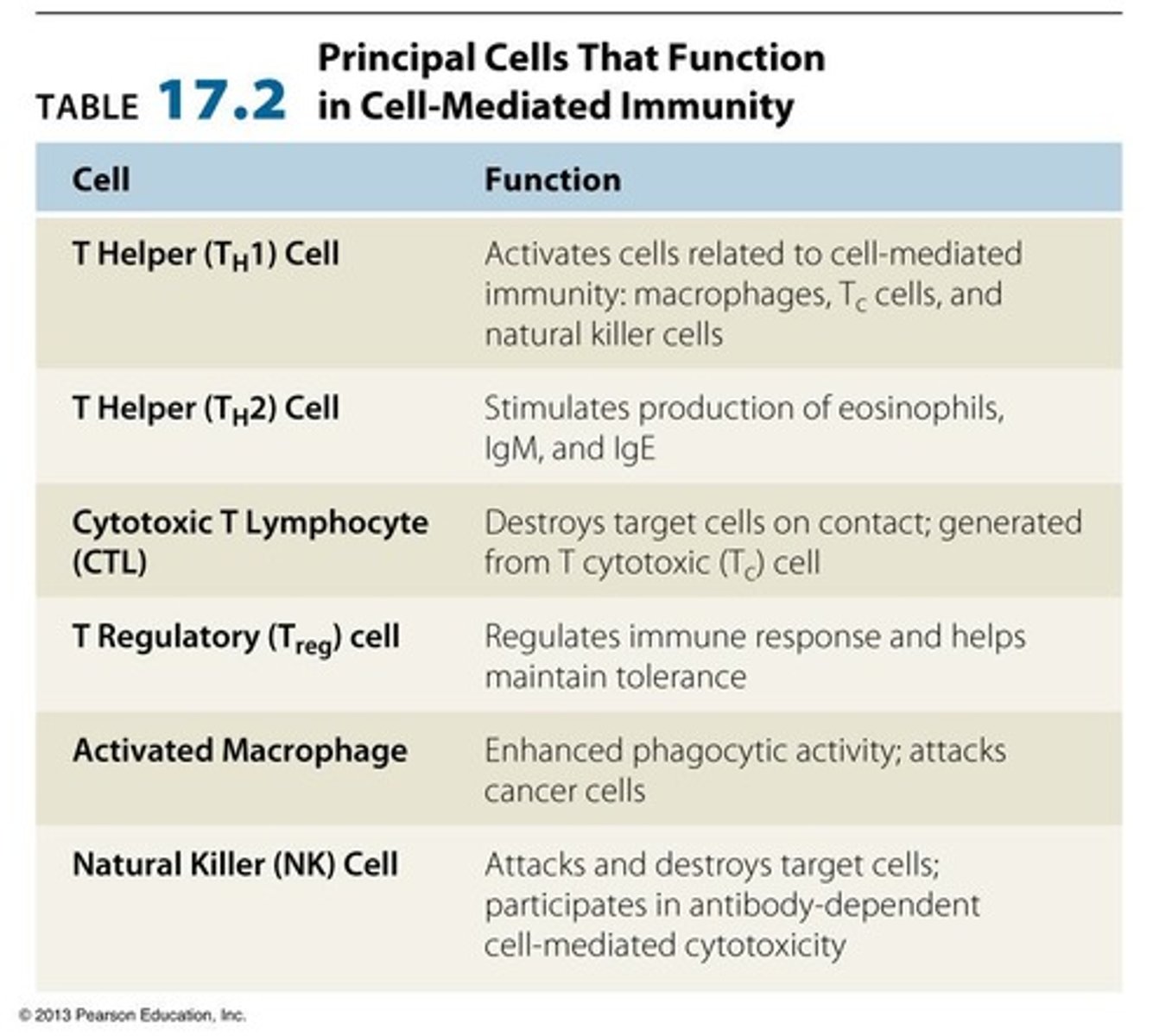
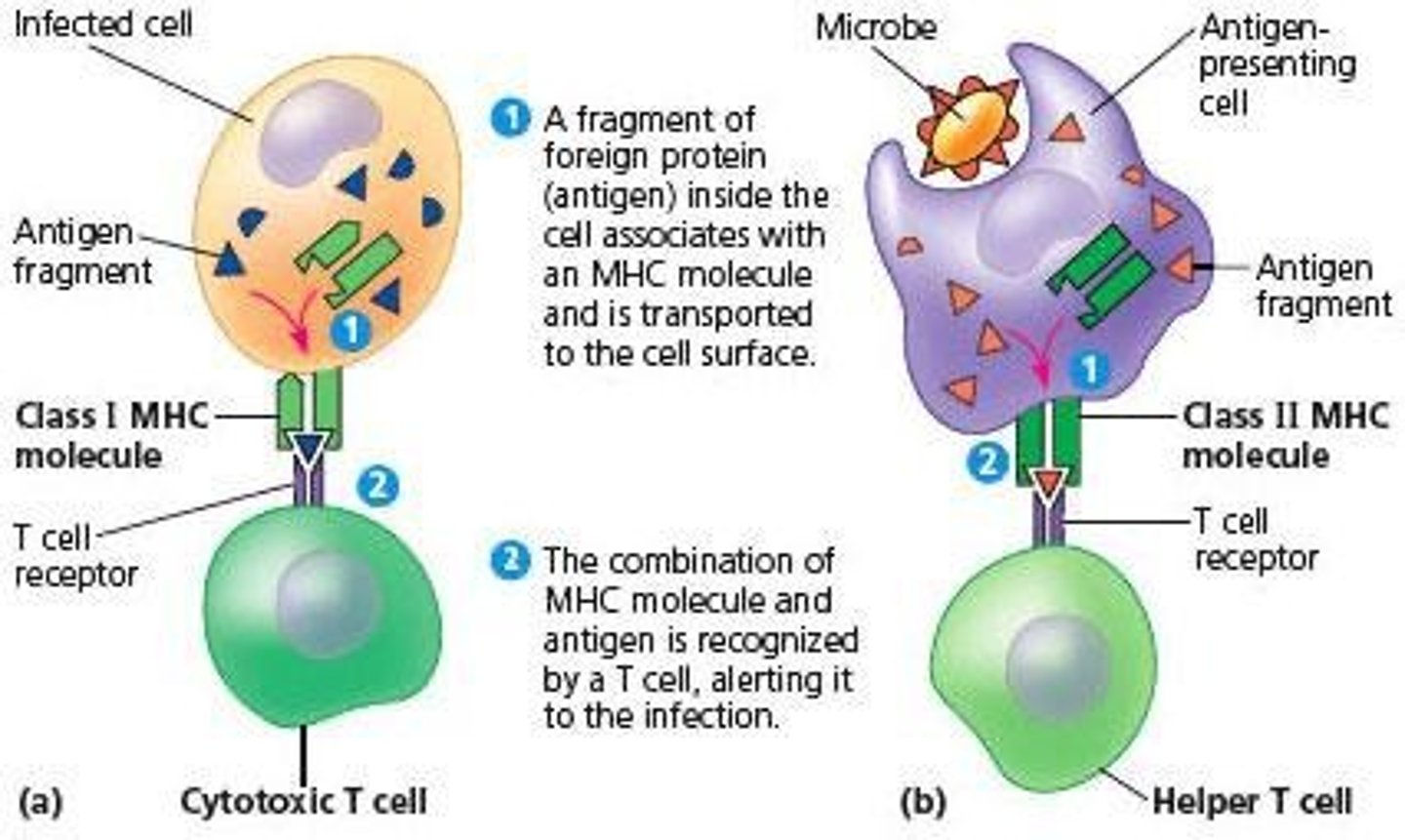
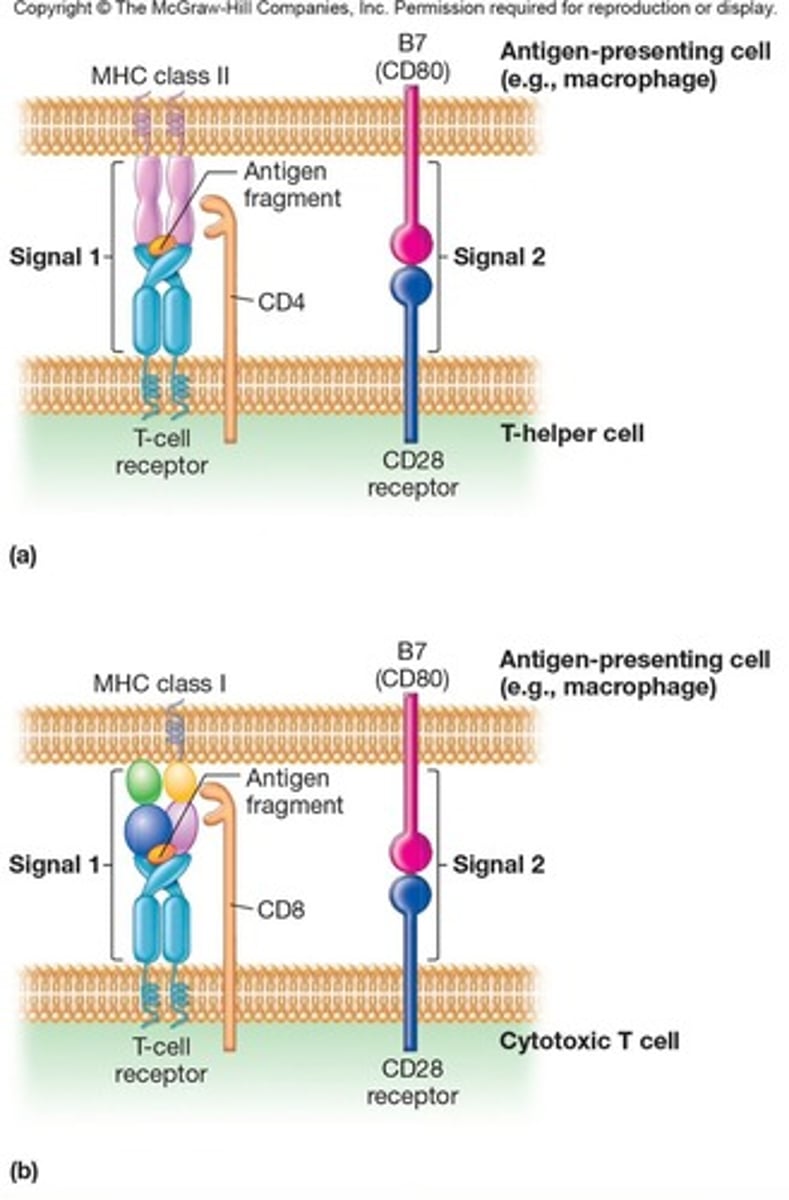
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
plays a critical role in distinguishing between self and non-self, allowing the immune system to selectively destroy invading pathogens without attacking the body's own tissues.
MHC Class I
Proteins found on all nucleated cells that present pieces of proteins from inside the cell (like viral or cancer proteins) to CD8⁺ cytotoxic T cells, which can kill infected or abnormal cells; indicate that a cell is 'self' and involved in endogenous antigen processing
MHC Class II
Proteins found only on antigen-presenting cells (like dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells) that present pieces of external pathogens (like bacteria) to CD4⁺ helper T cells, which help activate other parts of the immune system; essential for T-cell communication and for processing exogenous antigens.
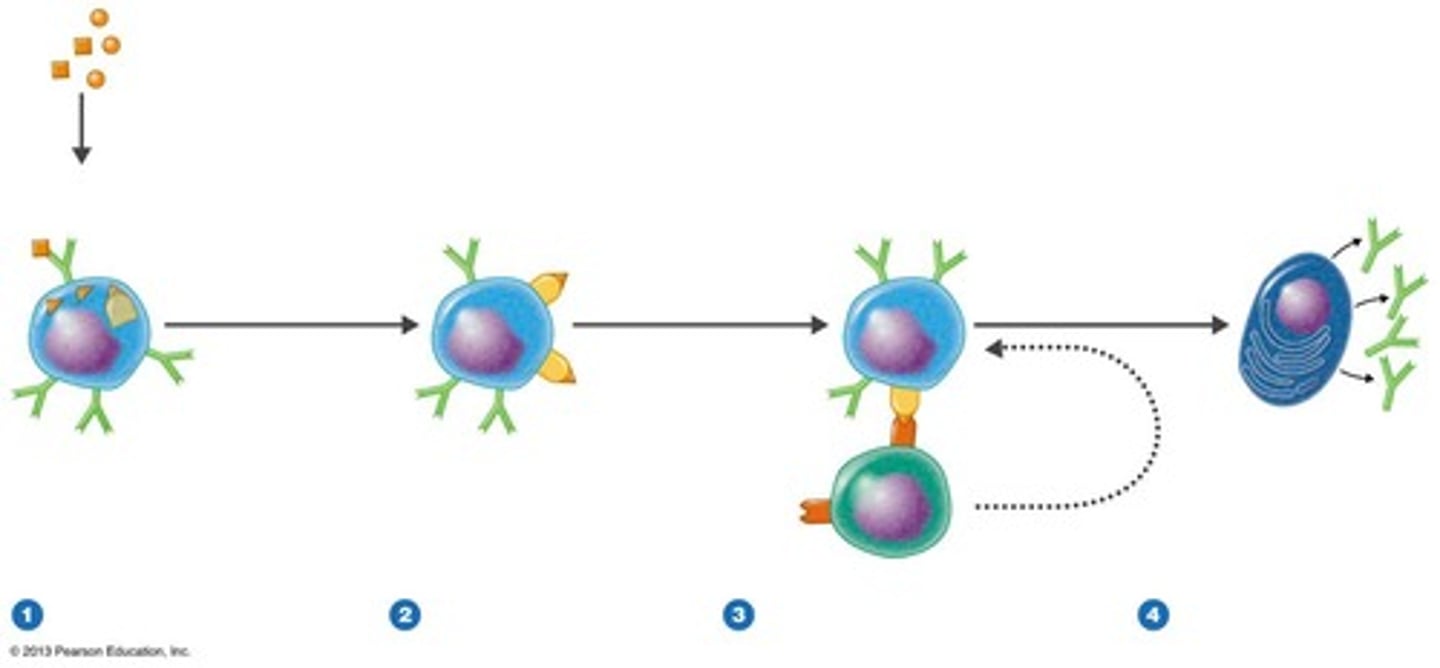
Adaptive Humoral Immunity Pathway
1. Antigen enters the body→ Usually an extracellular pathogen (e.g., bacteria, toxin, or virus in body fluids)
2. B cell recognizes and binds the antigen→ Using its specific B cell receptor (BCR)
3. B cell internalizes and processes the antigen→ Breaks it into fragments inside the cell
4. B cell presents antigen on MHC Class II→ Prepares to communicate with a helper T cell
5. CD4⁺ helper T cell recognizes the antigen-MHC II complex→ Binds to it and releases cytokines
6. Cytokines fully activate the B cell
7. B cell undergoes clonal expansion→ Makes many copies of itself
8. B cells differentiate into: Plasma cells → produce and secrete antibodies
Memory B cells → stay in the body for long-term immunity
9. Antibodies circulate and perform immune functions: Neutralize pathogens, Opsonize (tag pathogens for destruction), Activate complement proteins
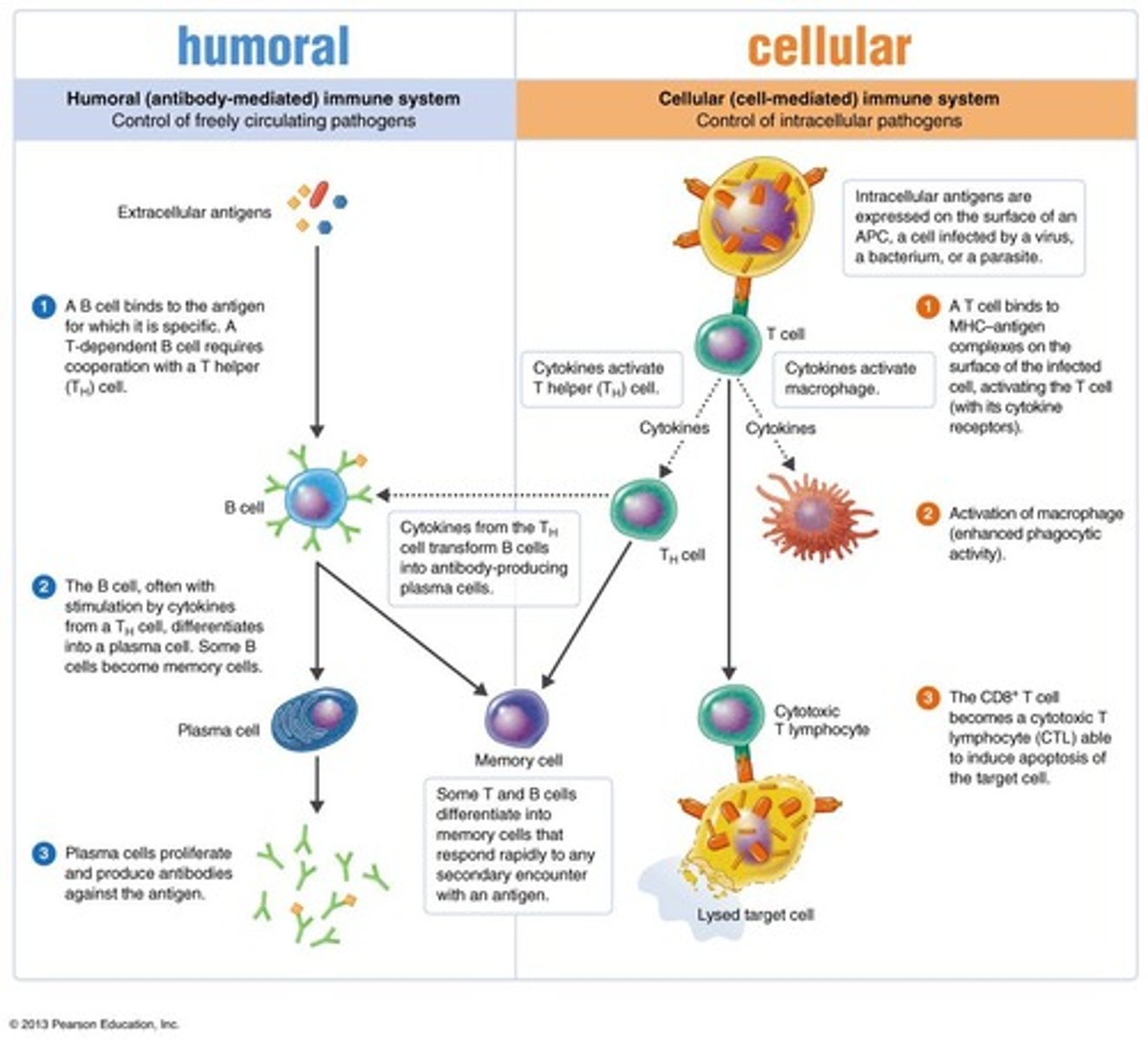
Extracellular antigens
Control of freely circulating pathogens
Intracellular antigens
Expressed on the surface of an APC, a cell infected by a virus, a bacterium, or a parasite
T cell
A T cell binds to MHC-antigen complexes on the surface of the infected cell, activating the T cell (with its cytokine receptors).
B cell
A B cell binds to the antigen for which it is specific. A T-dependent B cell requires cooperation with a T helper (TH) cell.
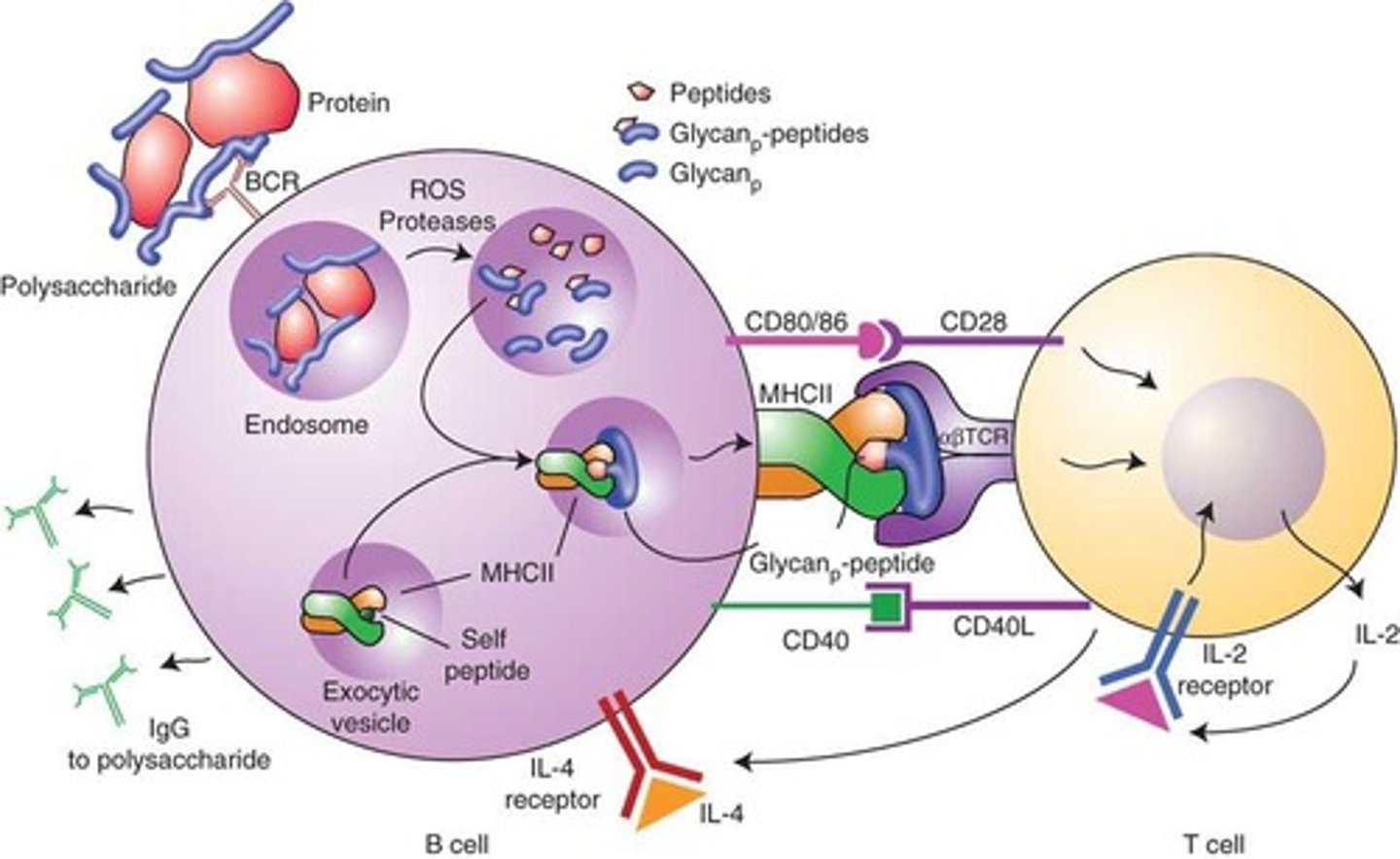
TH cell
Cytokines from the TH cell transform B cells into antibody-producing plasma cells.
Plasma cell
The B cell, often with stimulation by cytokines from a TH cell, differentiates into a plasma cell. Some B cells become memory cells.
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte
The CD8+T cell becomes a cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) able to induce apoptosis of the target cell.
Memory cell
Some T and B cells differentiate into memory cells that respond rapidly to any secondary encounter with an antigen.
Activation of macrophage
Enhanced phagocytic activity.
Antibody-producing plasma cells
Plasma cells proliferate and produce antibodies against the antigen.
Lysed target cell
A cell that has been broken down or destroyed.
Origin of Adaptive Immune Cells
Stem cells develop in bone marrow or in fetal liver.
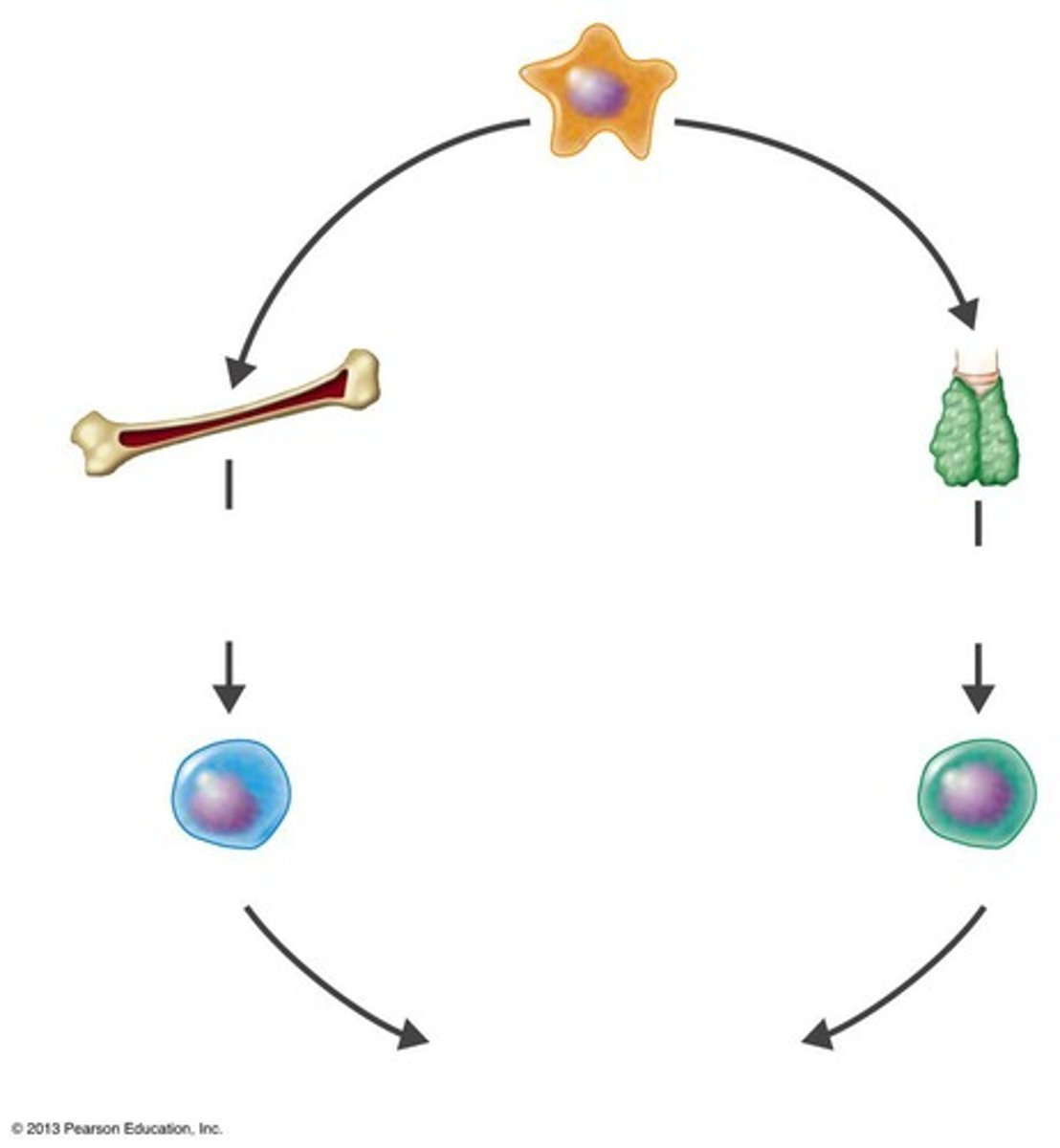
Stem cell
Diverges into two cell lines.
Thymus
Organ where T cells differentiate.
Antibody-Antigen Interaction
The binding of antibodies to epitopes on antigens.
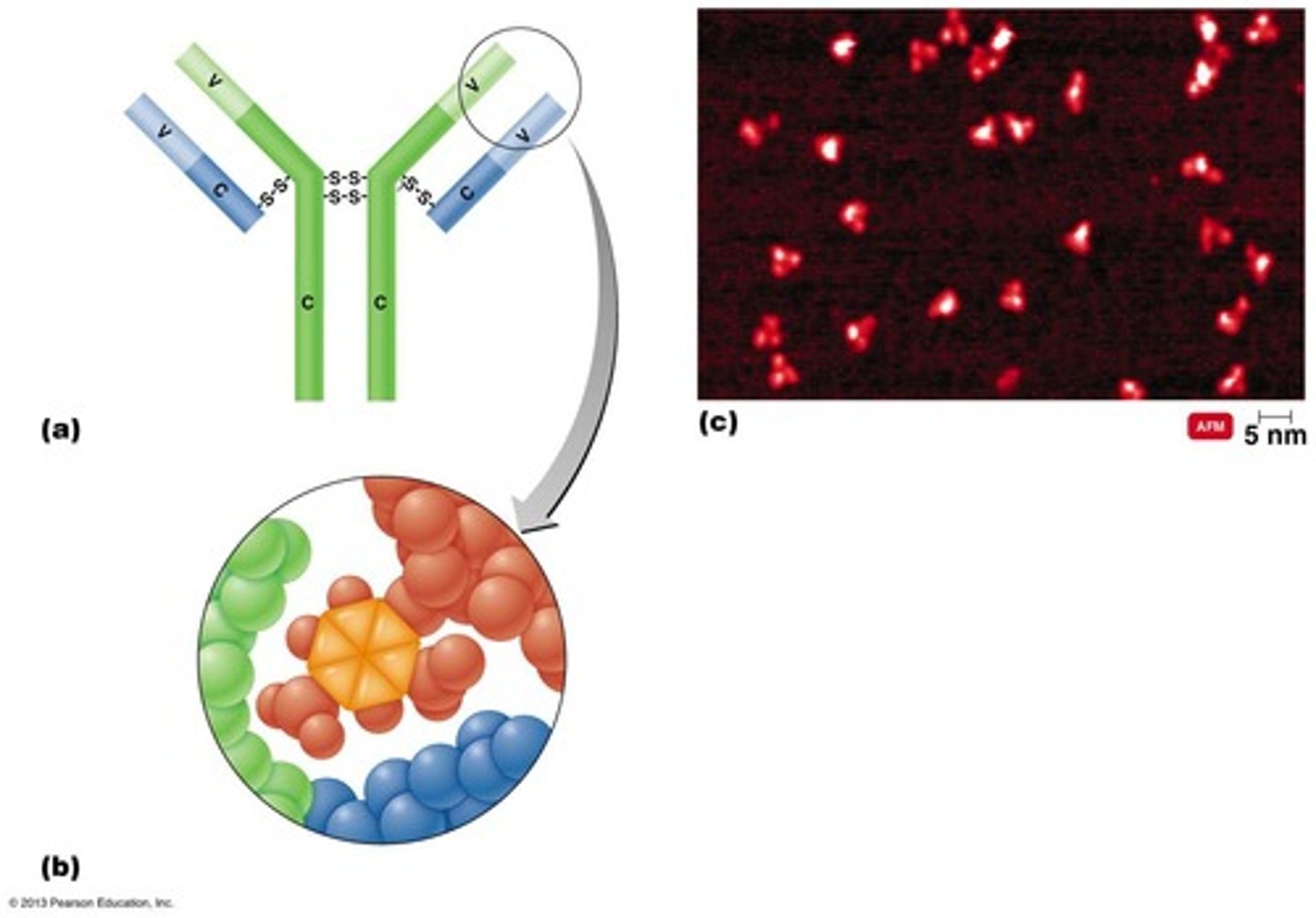
Antibody (immunoglobulin [Ig])
Glycoprotein made by activated B-cells (plasma cells).
Antibodies
Serve as antigen receptor (BCR) on B-cell surface.
effects of antibodies
include opsonization, compliment activation,
agglutination, neutralization and direction of cell mediated components of the immune system
Antibody Structure
Composed of 4 polypeptide chains: 2 identical heavy chains and 2 identical light chains.
Antigen-binding site
The part of the antibody that binds specifically to an epitope.
IgG
Monomer; 80% of serum antibodies, Enhance phagocytosis; neutralize toxins and
viruses; protect fetus and newborn; half-life = 23 days.
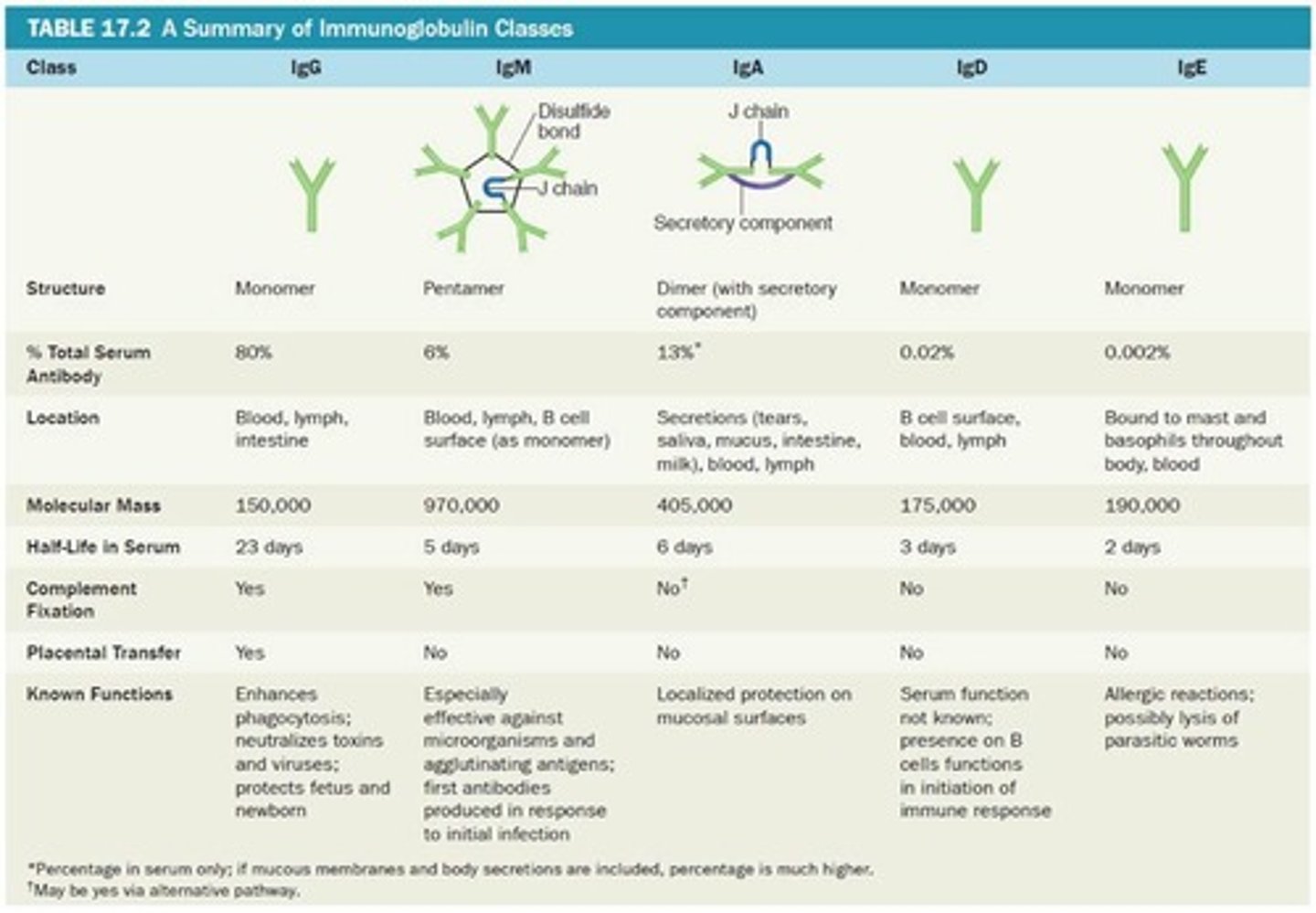
IgM
Pentamer; 5-10% of serum antibodies, Agglutinate microbes; first antibody produced in
response to infection ; half-life = 5 days.
IgA
Dimer; 10-15% of serum antibodies; half-life = 6 days.
IgD
Monomer; 0.2% of serum antibodies; half-life = 3 days.
IgE
Monomer; 0.002% of serum antibodies; half-life = 2 days.
Effects of Antibody Binding Antigen
Includes activation of complement and agglutination.
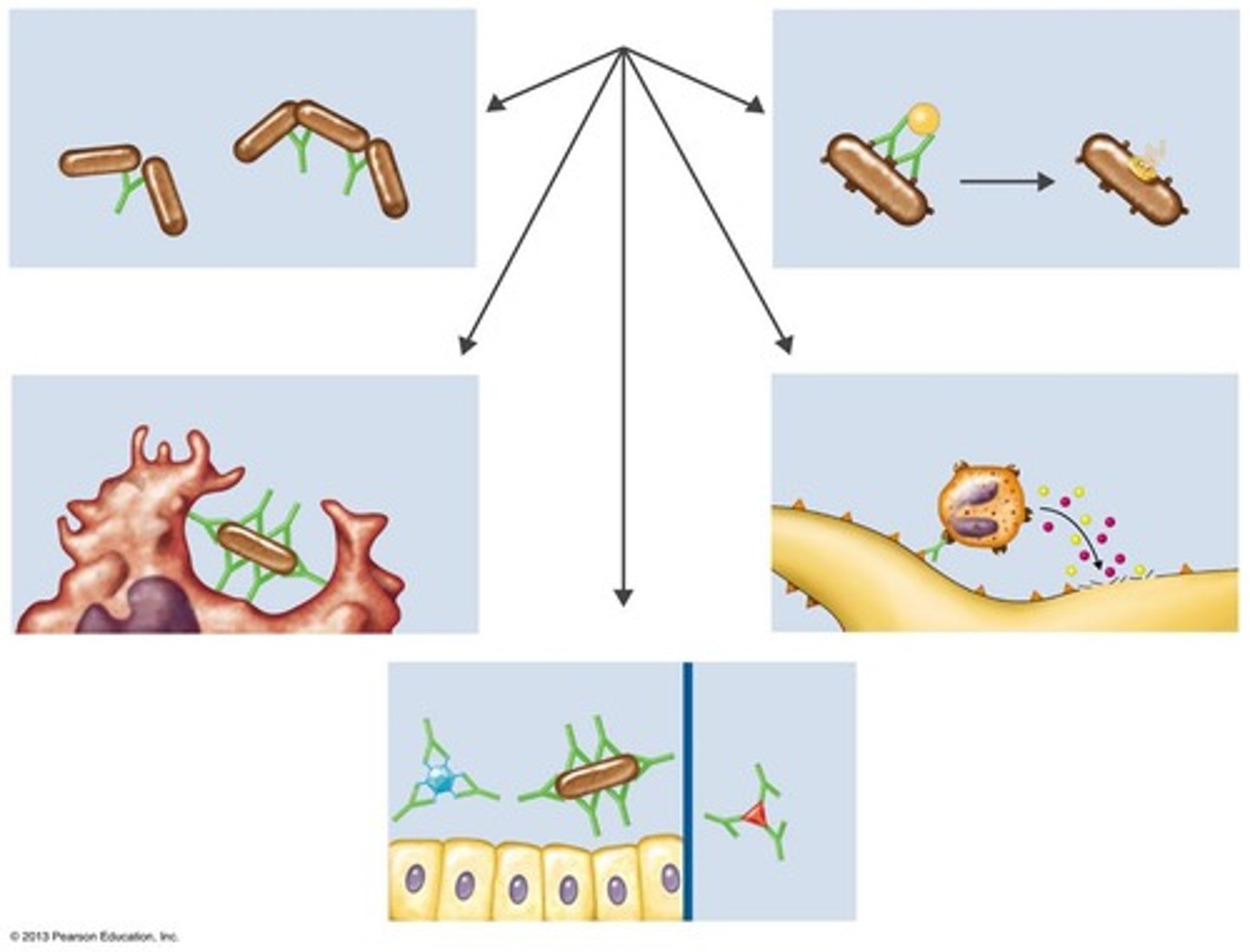
Opsonization
Coating antigen with antibody enhances phagocytosis.
Neutralization
Blocks adhesion of bacteria and viruses to mucosa.
T-independent antigens
Do not require TH; stimulate B-cell to make antibodies., Requires antigen w/repeating units (polysaccharides)
T-dependent Antigen Pathway
1. Antigen Entry
2. Antigen Recognition by B cell; a B cell binds to the antigen using its B cell receptor (BCR). -specific to one epitope on the antigen.
3. Antigen Processing by the B Cell, The B cell internalizes the antigen, breaks it into fragments, and presents a piece of it on MHC Class II on its surface.
4. Helper T Cell (CD4⁺) Recognition, a CD4⁺ helper T cell (previously activated by an APC) recognizes the antigen-MHC II complex on the B cell, the T cell binds to it using its T cell receptor (TCR).
5.The helper T cell releases cytokines to fully activate the B cell.
6. B Cell Clonal Expansion and Differentiation, activated B cell divides and becomes:
Plasma cells → make and secrete specific antibodies, Memory B cells → provide long-term immunity
7. Class Switching and Affinity Maturation, with T cell help, B cells switch antibody classes (from IgM to IgG, IgA, or IgE), also undergo affinity maturation to produce stronger-binding antibodies
T-dependent antigens
Require interaction of T-cell receptor with MHC II on B-cell.
Clonal deletion
Eliminates harmful (autoimmune) B-cells.
Memory B-cells
Same receptor, preserved for later encounter with antigen.
Antibody Types
Different classes of antibodies with distinct functions and properties.
B-cells
Express immunoglobulin receptors (BCR) for specific antigens.
Activated B cells
Differentiate into plasma cells or memory B-cells.
Immunoglobulin receptors
Receptors on the B cell surface that recognize and attach to antigens, which are then internalized and processed.
T helper cell (TH)
A type of T cell that recognizes the complex of MHC class II and antigen fragment, leading to its activation and production of cytokines.
B-cell Development
The process through which stem cells differentiate into mature B cells, each bearing surface immunoglobulins against a specific antigen.
Plasma cells
B cells that secrete antibodies into circulation.
T-cells
Major players in cell-mediated immune response that require antigen binding to surface receptors for activation.
Memory T-cells
T cells that retain the same receptor to respond to the same antigen in future encounters.
Helper T-cells (CD4+)
T cells that secrete cytokines to stimulate other immune cells.
Cytotoxic lymphocytes (CD8+)
T cells that directly destroy host cells infected by intracellular pathogens.
T-cell Receptor (TCR)
A receptor that recognizes and binds specific antigen fragments presented in the context of MHC.
Costimulatory molecule
A molecule required to activate T cells that have not previously encountered an antigen.
Antigen-presenting cell (APC)
A cell that encounters and ingests a microorganism, processes the antigen, and presents it on MHC molecules.
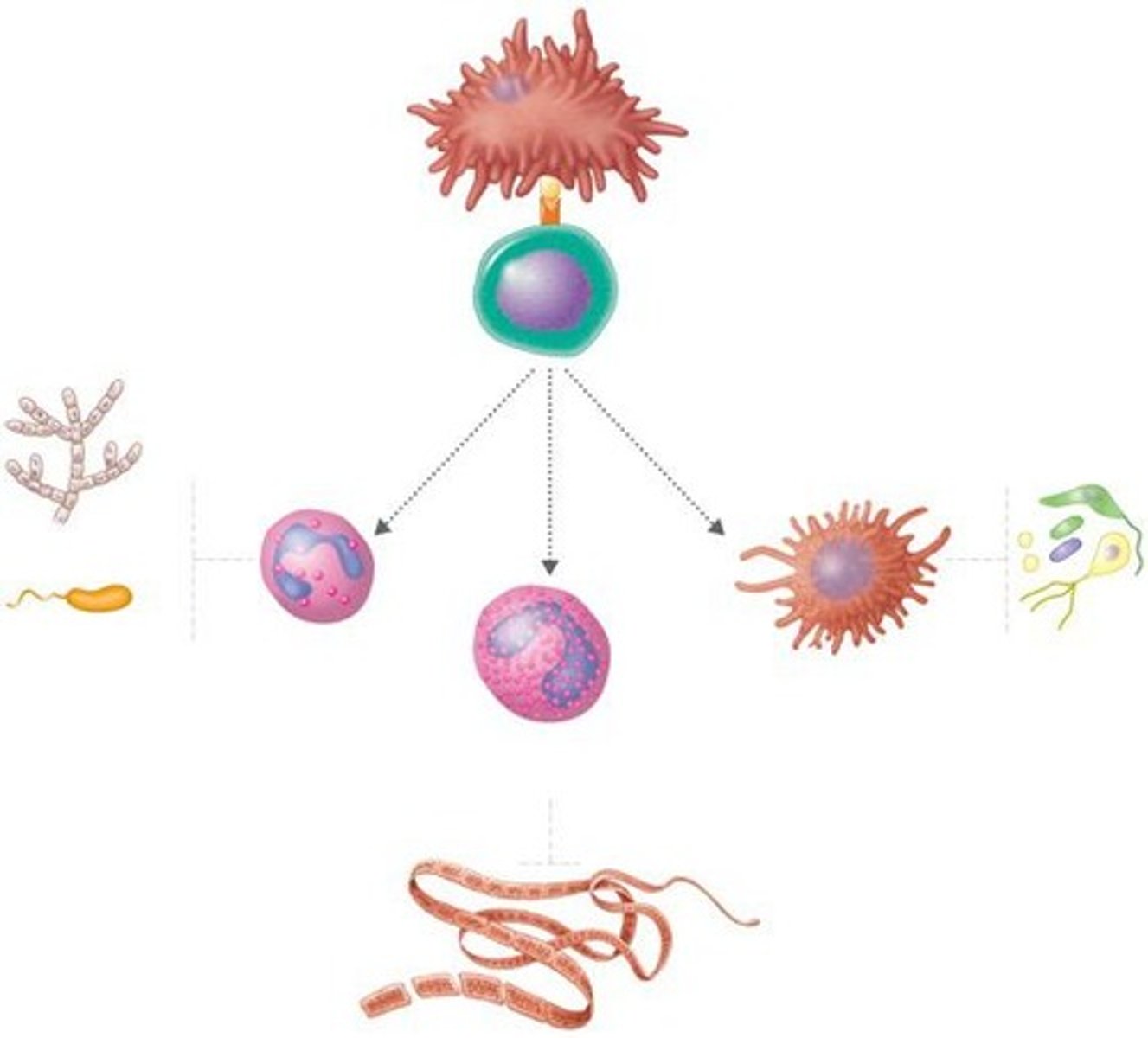
TH17 cells
A subtype of T helper cells that secrete cytokines promoting inflammatory responses and recruiting neutrophils.
TH1 cells
A subtype of T helper cells that play an important role in cellular immunity.
Nucleated cell
A cell that contains a nucleus and can present antigens via MHC molecules.
Exogenous antigens
Antigens that are presented on MHC class II molecules by APCs, including dendritic cells and B-cells.
Activated T cells
T cells that have proliferated and can activate B cells, cytotoxic T lymphocytes, and macrophages.
Antigen fragments
Short peptides derived from antigens that are presented on MHC molecules.
Microorganism carrying antigens
An organism that presents antigens which can be recognized by T cells.
IL-17
A cytokine involved in the immune response.
IFN-γ
A cytokine that activates immune cells and enhances their ability to kill pathogens.
TH2 cells
A subset of T helper cells that produce IL-4 and are important in allergic responses.
Fungi
A type of organism that can be targeted by the immune system.
Extracellular bacteria
Bacteria that exist outside of host cells.
Neutrophil
A type of phagocyte that plays a key role in the immune response.
Macrophage
A type of antigen-presenting cell that engulfs and digests pathogens.
Intracellular bacteria and protozoa
Pathogens that live inside host cells.
Mast cell
A cell that plays a role in allergic responses by producing IgE.
Basophil
A type of white blood cell involved in inflammatory reactions.
Eosinophil
A type of white blood cell that combats large parasites and is involved in allergic responses.
Helminth
A type of large parasite that can be targeted by eosinophils.
T Cytotoxic cells (CD8+)
T cells that recognize endogenous antigens on MHC I and induce apoptosis in infected cells.
T cell receptors
Molecules on T cells that recognize specific antigens presented by MHC molecules.
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs)
Activated CD8+ T cells that kill virus-infected or cancer cells.
Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity
A mechanism where antibodies direct immune cells to kill large parasites.
Antibody titer
The amount of antibody present in serum.