AP Psychology Unit Seven Part 2 Vocabulary
1/49
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Sigmund Freud
Founder of psychoanalysis
Originally a medical doctor and found that his patients were suffering from an illness with psycho-logical causes
This led him to develop theories of the unconscious mind, psycho-sexual development and Psychoanalysis
Psychoanalytic Theory
Psychologist: Sigmund Freud
Behavior is due to unconscious motives and conflicts
Early childhood experiences determine personality

Unconscious Mind
-foundation for the psychoanalytic theory
-controls the phenomena of repressed feelings, automatic skills, subliminal perceptions, thoughts, habits and automatic reactions as well as possibly holding emotional complexes, phobias and desires.

Id
located in the unconscious
present at birth
Ruled by the "Pleasure Principle" and has no values, morality, or logic (animal instincts)

Ego
located in both conscious, & unconscious
Developed after birth, the self
Ruled by the "Reality Principle" and balances the id and superego by being organized, rational, and postponing gratification
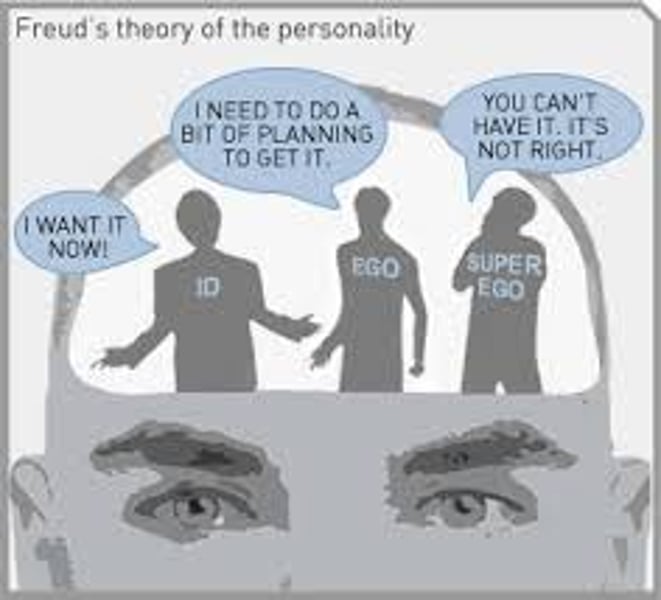
SuperEgo
located in both conscious, & unconscious
developed by age 5
Ruled by the "Morality Principle" and is the opposite of the Id because it is the internal, parental voice with rules and values

Free Association
A technique used to access the unconscious
patient freely exposes his/her ideas, impressions, etc.

Freudian Slips
Slips of the tongue that expose the unconscious

Psychosexual Development
- sequential and discontinuous stages with changing erogenous zone and conflict in each stage
if conflict is not successful resolved, the result is fixation
O.A.P.L.G (Oral, Anal, Phallic, Latency, Genital)
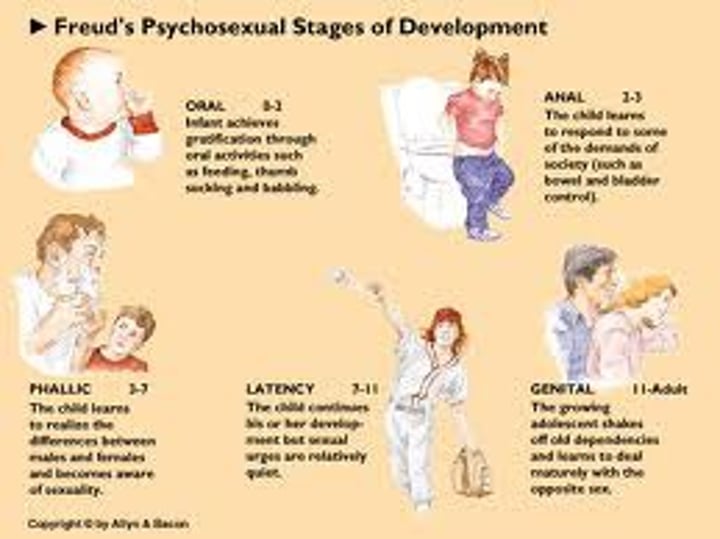
Oral stage
Age: 0-1
Erogenous Zone: Mouth
Task: Oral Activities (sucking, chewing, biting, etc)
Fixation: Smoking, Over-eating

Anal stage
Age: 1-3
Erogenous Zone: Anus
Task: Potty Training
Fixation: Anal retentive or Anal Expulsive

Latency stage
Age: 6 to puberty
Erogenous Zone: None
Task: develop relationships with same sex peers to strengthen gender identity
Fixation: doesn't occur at this stage

Phallic stage
Age: 3-5
Erogenous Zone: Genitals
Task: Gender Identity
Fixation: Narcissism, Homosexuality

Genital stage
Age: Puberty to death
Erogenous Zone: Genitals
Task: Find a hetero-sexual relationship
Fixation: doesn't occur at this stage but old conflicts will arise

Penis Envy
Freudian theory that girls become upset and scarred because because they don't have a penis and a penis is a key to being successful. Phallic Stage

Electra Complex
girls sexually desire dad and hate mom but need to resolve this in order to develop a gender identity
Phallic Stage of Psycho-sexual Development

Oedipus Complex
boys sexually desire mom and hate dad but need to resolve this in order to develop a gender identity
Phallic Stage of Psycho-sexual Development

Defense mechanisms
- extreme measures protect the ego from threats; operate unconsciously and deny, falsify, or distinct reality
- not successful coping strategies because they do not remove stressors

Neo-Freudians
Jung, Horney, Adler
Believed that Freud put too much emphasis on sex and there needed to be more emphasis on social factors

Collective unconscious
Psychologist: Carl Jung
Defined: A warehouse of "instinctive memories" passed down to each generation and all humans share
and is made up of archetypes
Archetypes
Defined: Inherited universal concepts that create the Collective Unconscious
Examples: Anima v. Animus, Mother v. Father, Persona v. Shadow, Hero v. Villain

Basic Anxiety
Psychologist: Karen Horney
anxiety that is created by being born helpless.
Most overcome this, those who don't develop neurotic personalities- aggressive, compliant, or withdrawn

Womb envy
Psychologist: Karen Horney
Defined:
women do not suffer from "penis envy" but are envious of male's superior status.
Men are envious of a women's ability to have children and therefore, they compensate with other forms of achievement.

Inferiority Complex
Psychologist: Alfred Adler
Defined: people who compensate for feelings of inferiority (feeling like they're less than other people, not as good as others, worthless, etc.) by acting ways that make them appear superior.

Projective Tests
Description: Provide ambiguous stimuli in order to trigger the projection of one's inner dynamics
Strengths: Provide lots of information
Weaknesses: highly subjective and has low reliability
Tests: Rorschach Inkblot Test, & Thematic Apperception Test (TAT), Draw a Person test

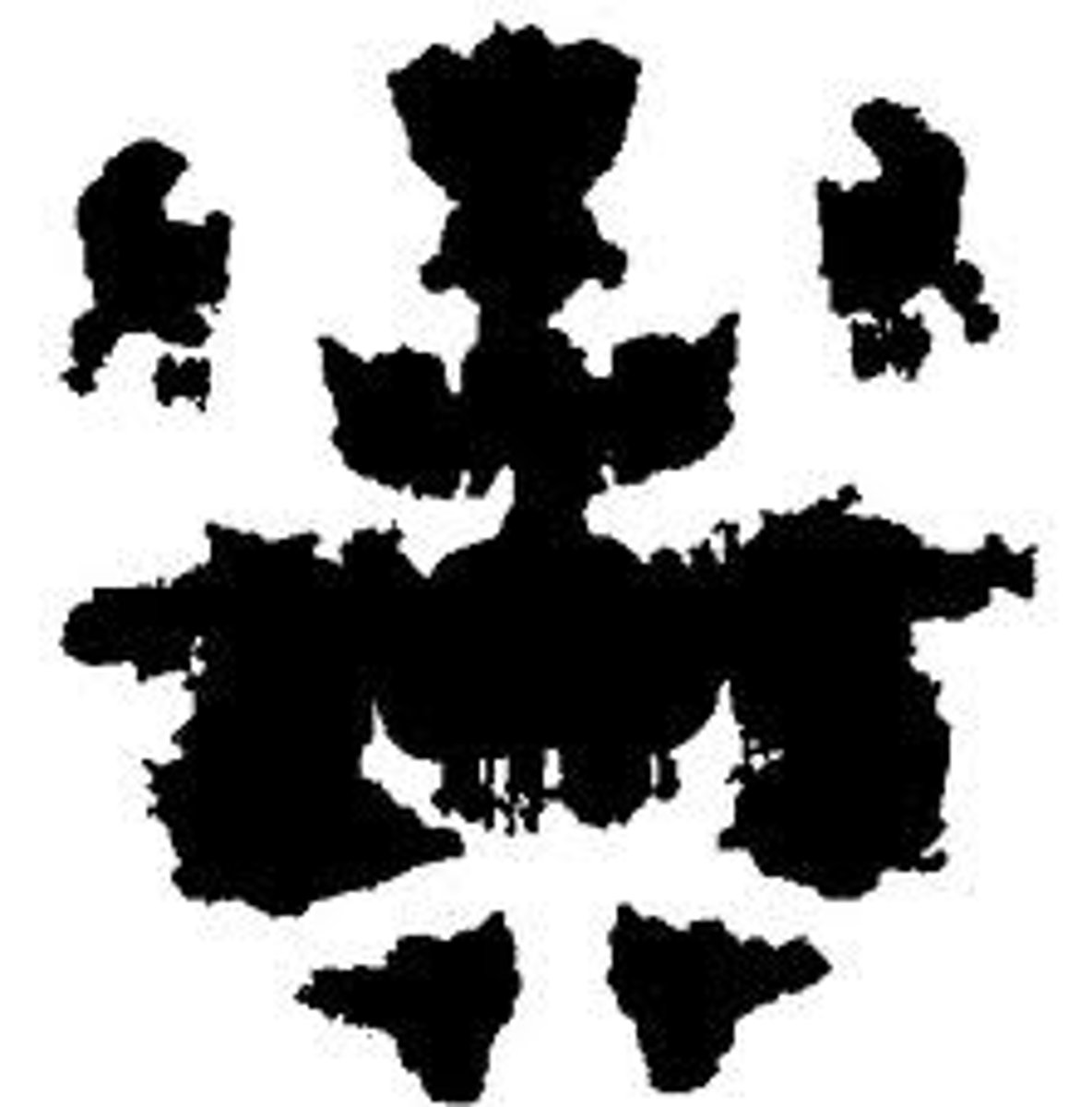
Rorschach Inkblot Test
seeks to identify people's inner feelings and conflicts by analyzing their interpretations of 10 inkblots.
Critics question the validity and reliability of the tests.

Thematic Apperception Test
people view ambiguous pictures and then make up stories about them.
Presumably, their accounts reflect their interests and inner feelings.

Humanistic Psychologists
Carl Rogers, Abraham Maslow
Description: People develop their personality by trying to reach their full potential
Strengths: model was built in a therapy setting
Weaknesses: concepts are vague and subjective, individualistic and western based and naive because it fails to appreciate the reality of our capacity for evil

Self-Concept
Psychologist: Carl Rogers
Goal: Actualizing Tendency (full potential)
Theory: A person has who they are, Real Self, and who they want to be, Ideal Self and a successful persoanlity has congruence
People need genuineness (honesty), unconditional positive regard (love), and empathy (understanding) to develop a good persoanlity

Congruence
A person's Real Self and Ideal Self can merge together
Part of Roger's Self-Concept Theory
Incongruence
When a person's Real Self and Ideal self do not match, causing anxiety.
Part of Roger's Self-Concept Theory

Unconditional positive regard
Defined: receiving acceptance, value, and love from others without requirements
Part of Roger's Self-Concept theory in which he says it is necessary to receive from others in order to develop a healthy personality

Empathy
People will try to understand one's feelings and mirror it back to them
Part of Roger's Self-Concept theory in which he says it is necessary to receive from others in order to develop a healthy personality

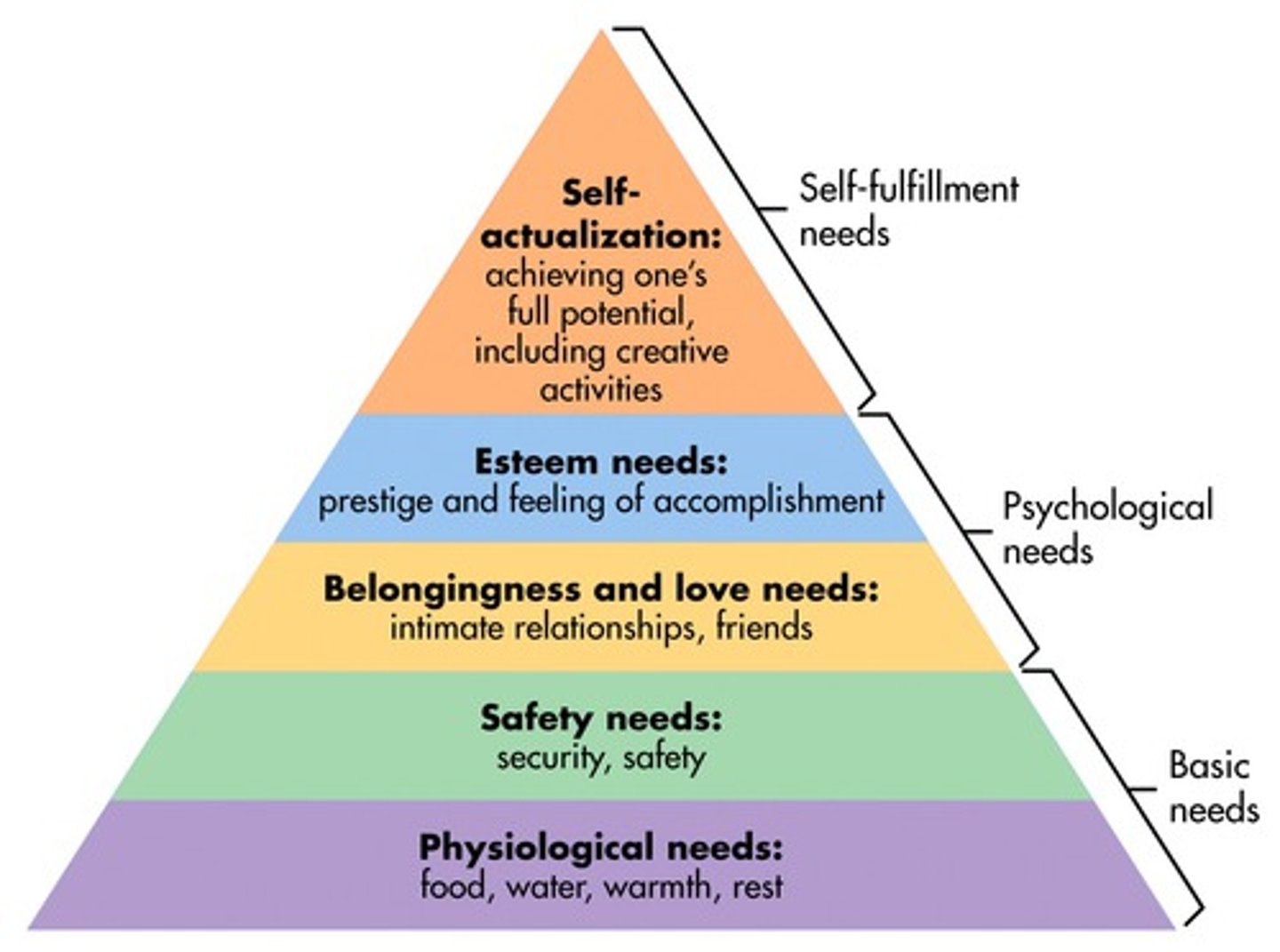
Hierarchy of Needs
Psychologist: Abraham Maslow
Description: Pyramid
Trait Theories
Description: focuses on identifying how people typically behave but does NOT explain how personality developed
Strengths: based on empirical evidence with factor analysis
Weaknesses: people might behave differently based on the situation they are experiencing
Tests: 16 Personality Factors (16 PF), 3 Dimensions, and Myers Briggs
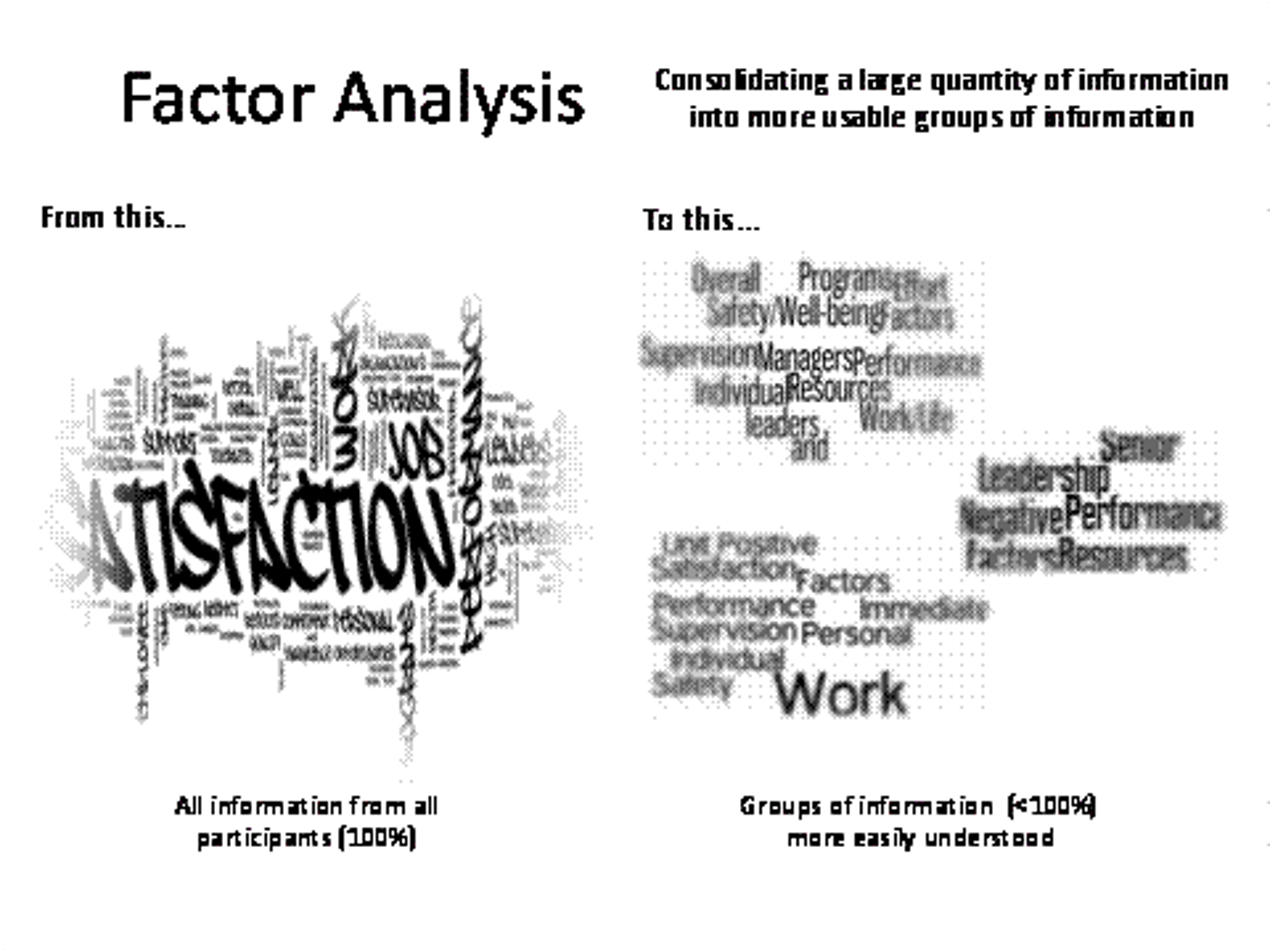
Factor analysis
- a statistical procedure that identifies common factors among groups of items, to simplify a long list of items into a small number of dimensions
-used with trait theories
Self-Report Inventories
Description: a questionnaire which is used to gauge a wide range of feelings and behaviors
Strengths: empirically derived
Weaknesses: social desirability-people can lie and manipulate the information
Tests: MMPI, CPI, 16 PF

MMPI
Most extensively researched personality inventory.
Used to assess mental health professions (police, nurses, doctors, pilots)

Big Five Trait Theory
Psychologists: McCrae and Costa
Description: OCEAN or CANOE
Significance: traits are stable in adulthood, heritability accounts for 50% of personality and can be used to predict other personal attributes
Openess
characteristics such as imagination and insight, and those high in this trait also tend to have a broad range of interests

Conscientiousness
include high levels of thoughtfulness, with good impulse control and goal-directed behaviors.

Extraversion
characterized by excitability, sociability, talkativeness, assertiveness and high amounts of emotional expressivenes

Agreeableness
includes attributes such as trust, altruism, kindness, affection and other pro-social behaviors.

Neuroticism
characterized by sadness, moodiness and emotional instability

Social Cognitive Approach to Personality
Description: Personality is influenced between the interaction of a person's traits (including their thinking) and their social context
Strengths: based on empirical evidence
Weaknesses: minimizes the importance of one's inner traits, emotions, and unconscious motives
Examples: Reciprocal Determinism, Locus of Control
Psychologists: Bandura
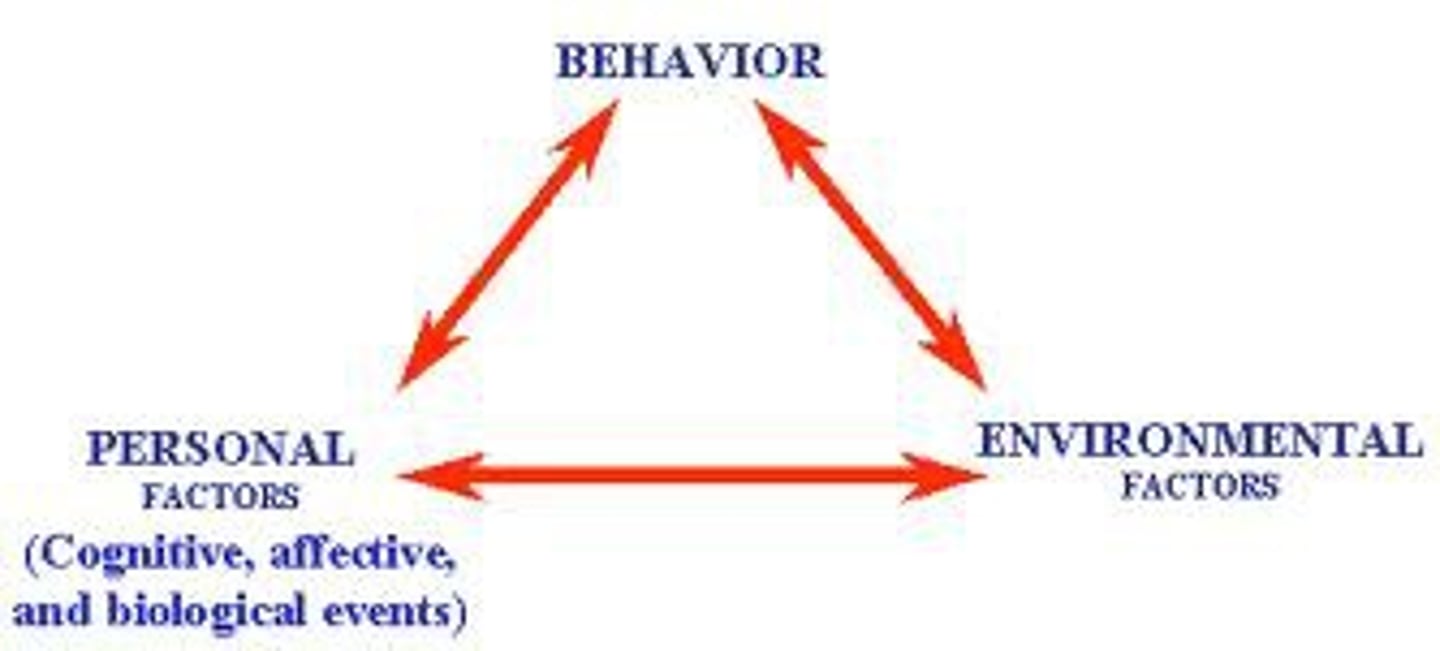
Reciprocal determinism
Psychologist: Bandura
Defined: Personality is developed by the interaction of behavioral, cognitive, and environmental factors.
How it works: Everyone has a "self-system" of skills abilities and attitudes
Self-Efficacy is what can change the system
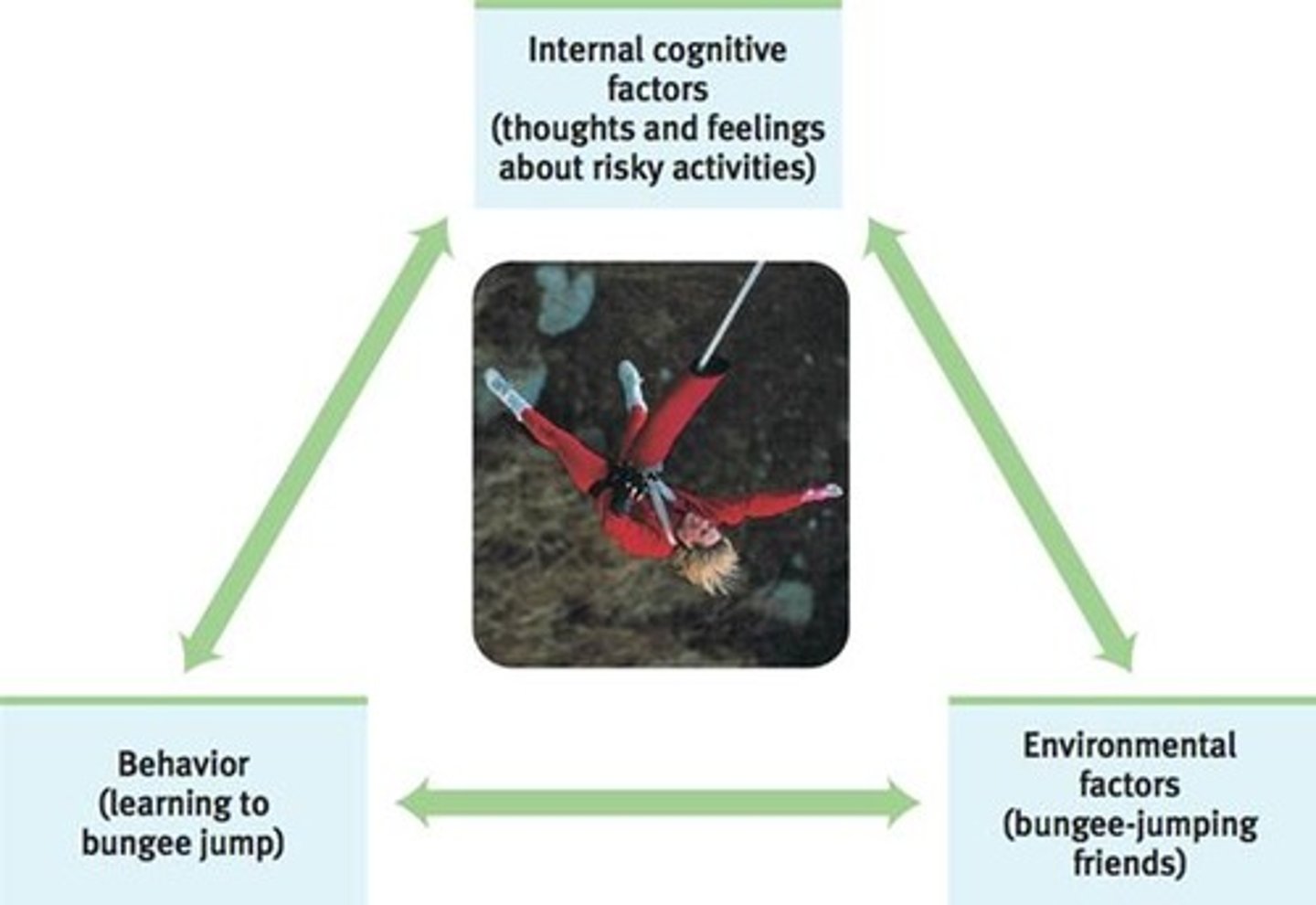
External Locus of Control
The perception that chance or outside forces beyond your personal control determine your fate
Effects: Pessimism and often learned helplesses

Internal Locus of Control
The perception that you control your own fate
Effects: Optimism
Optimism leads to longer lives with less illnesses but excessive optimism can also lead us to be blind to risks and overconfidence

Self- efficacy
Defined: the belief in your own ability to deal with different situations and accomplish specific goals
It is NOT self esteem which is your general sense of self worth
Consequences: people with high self-efficacy are able to succeed because they have an internal locus of control

Compensation
Defense Mechanism where people try to overcome feelings of inferiority in one area by striving to be superior in another area
Major part of Alfred Adler's theory
