3.2.1.1 Structure of Eukaryotic Cells
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
eukaryotic cell
-DNA is contained in a nucleus and contains membrane-bound specialised organelles
-also means ‘true nucleus’
FEATURES + FUNCTIONS -cell-surface membrane
-’fluid mosaic’ phospholipid bilayer with extrinsic and intrinsic proteins embedded
functions = isolates cytoplasm from extracellular environment, is selectively permeable so controls transport of substances in and out of cell
-nucleus
surrounded by nuclear envelope - a double membrane
this has nuclear pores - allows molecules to enter and exit
contains nucleoplasm and histone proteins which wind around DNA as there is lots of it
contains nucleolus - manufactures ribosomal RNA and assembles ribosomes
contains chromosomes - consists of chromatin (protein-bound linear DNA) - controls protein synthesis
functions = stores genetic information, where DNA replication occurs, production of mRNA
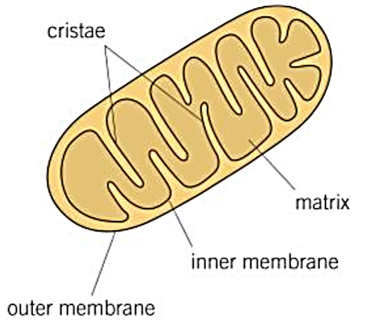
-mitochondria
-has a double membrane (outer and inner), where inner is folded to form cristae (provides large surface area), inside the inner is matrix (contains enzymes, circular mitochondrial DNA and ribosomes)
function = site of aerobic respiration to produce ATP
-chloroplast
-surrounded by a double membrane, contains thylakoids (membrane-bound flattened discs) which contain chlorophyll, when stacked they form granum, contains stroma (fluid filled matrix), contains circular DNA, ribosomes and starch grains
function = site of photosynthesis to convert solar energy to chemical energy
exocytosis
the process of how proteins are exported from cells
-golgi apparatus
-consists of cisternae (stack of membrane-bounded, flattened sacs in cytoplasm)
functions = modifies proteins or triglycerides from rER for exocytosis, often adds proteins to triglycerides or carbohydrates to proteins to form glycoproteins
-once modified, they are packaged into golgi vesicles which transport them and fuse with the cell membrane and secrete the proteins by exocytosis
-lysosomes
-membrane-bound organelle that releases hydrolytic enzymes
functions = digests the contents of phagosomes from phagocytosis, destroys worn-out organelles, release enzymes by exocytosis
-ribosomes
-formed of protein and RNA and are free in the cytoplasm or attached to the ER
-eukaryotes contain 80S ribosomes
function = site of protein synthesis - large subunit: joins amino acids, small subunit: contains mRNA binding site
-rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER)
-consists of cisternae (stack of membrane-bounded, flattened sacs in cytoplasm) and has ribosomes attached to its surface
function = site of protein synthesis and transport to golgi apparatus
-smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER)
-has no ribosomes on its surface
function = site of lipid and carbohydrate synthesis and also transport
-cell wall
-only in plant and fungi cells
-consists of polysaccharides = in plant, it consists of cellulose microfibrils and in fungi, it consists of chitin, has a middle lamella (thin layer that acts as boundary between adjacent cell walls)
functions = provides mechanical support and protection, prevents cell from bursting
-cell vacuole
-only in plant cells
-a sac bounded by a single membrane (tonoplast) containing cell sap (mineral salts, pigments, organic acids, etc)
functions = stores waste products, has low water potential so controls turgidity of cell, pigments can attract pollinators
complex multicellular organisms
-eukaryotic cells become specialised for specific functions
-specialised cells organised into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems