Lecture 2: SHOULDER: SCAPULAR, DELTOID AND GLENOHUMERAL JOINT REGIONS
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Which joint has the widest range of motion in the body?
Glenohumeral (shoulder) joint
What articulates with the glenoid cavity?
Head of the humerus
Why is the shoulder joint prone to injury?
Shallow glenoid cavity → high mobility → low stability
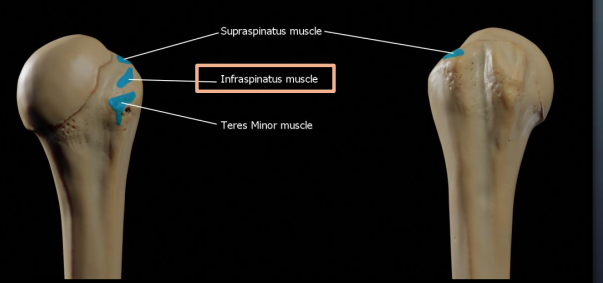
Which muscle attaches to the supraspinous fossa?
Supraspinatus
Which muscle attaches to the infraspinous fossa?
Infraspinatus
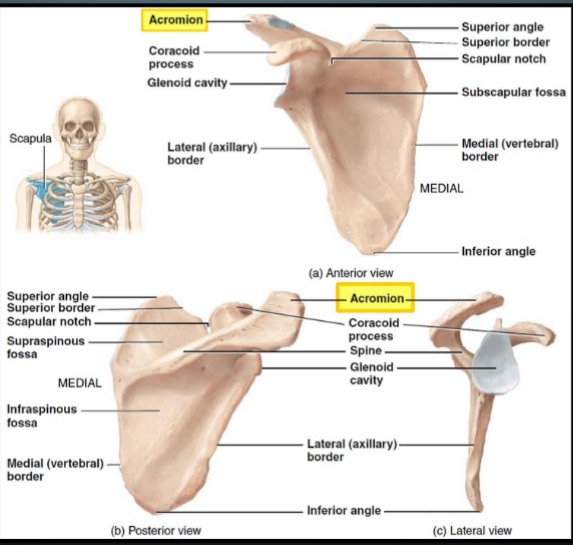
Which joint involves the acromion?
Acromioclavicular (AC) joint
Where is the supraspinous fossa located?
Posterior scapula, above the spine, does not cover ribs
Where is a bursa typically found?
Between bony features to reduce friction during movement
Where is the scapular notch visible?
Both anterior and posterior views
Where does rhomboid minor insert?
Root (medial end) of the spine of the scapula
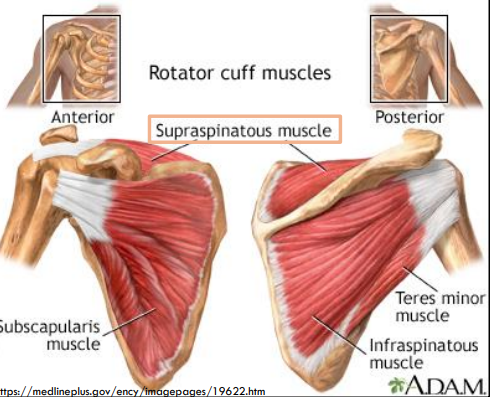
What muscles make up the rotator cuff?
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor, Subscapularis
What is the primary function of the rotator cuff?
Stabilizes the shoulder while allowing wide range of motion
What is the primary action of supraspinatus?
Initiates shoulder abduction (0–15°)
Which muscle takes over abduction after 15°?
Deltoid
Where does the supraspinatus tendon pass?
Under the acromion
Why is supraspinatus commonly injured?
Compression under acromion due to narrow subacromial space
What spinal levels form the brachial plexus?
C5–T1
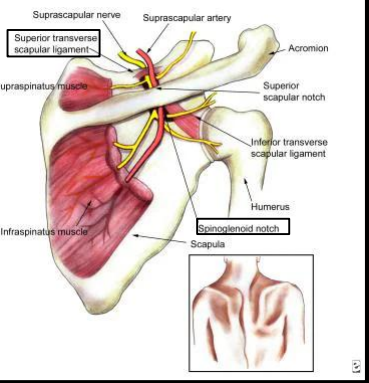
What nerve innervates supraspinatus?
Suprascapular nerve
Where does the suprascapular nerve originate?
Brachial plexus (C5–C6)
What passes through the suprascapular notch?
Nerve under, artery over (“Army over Navy”)
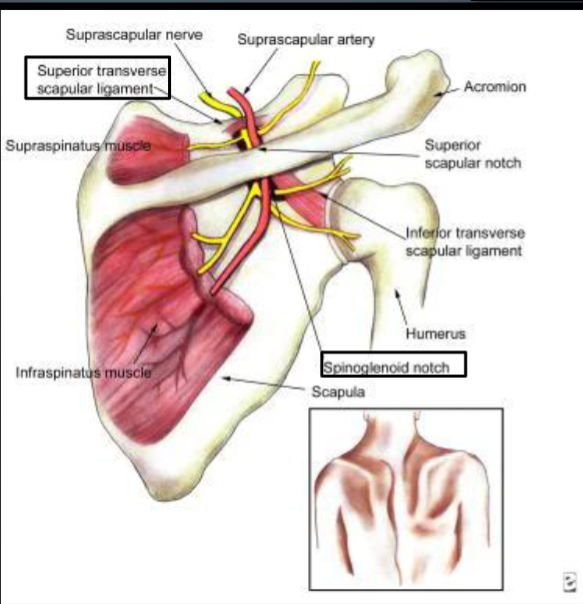
What passes through the spinoglenoid notch?
Suprascapular nerve (supplies infraspinatus)
Is the deltoid a rotator cuff muscle?
No
What nerve innervates the deltoid?
A: Axillary nerve
What muscles does the axillary nerve innervate?
Deltoid and teres minor
Where is the axillary nerve most at risk?
Surgical neck of the humerus
What is a clinical sign of axillary nerve injury?
Loss of shoulder abduction and flattened shoulder contour
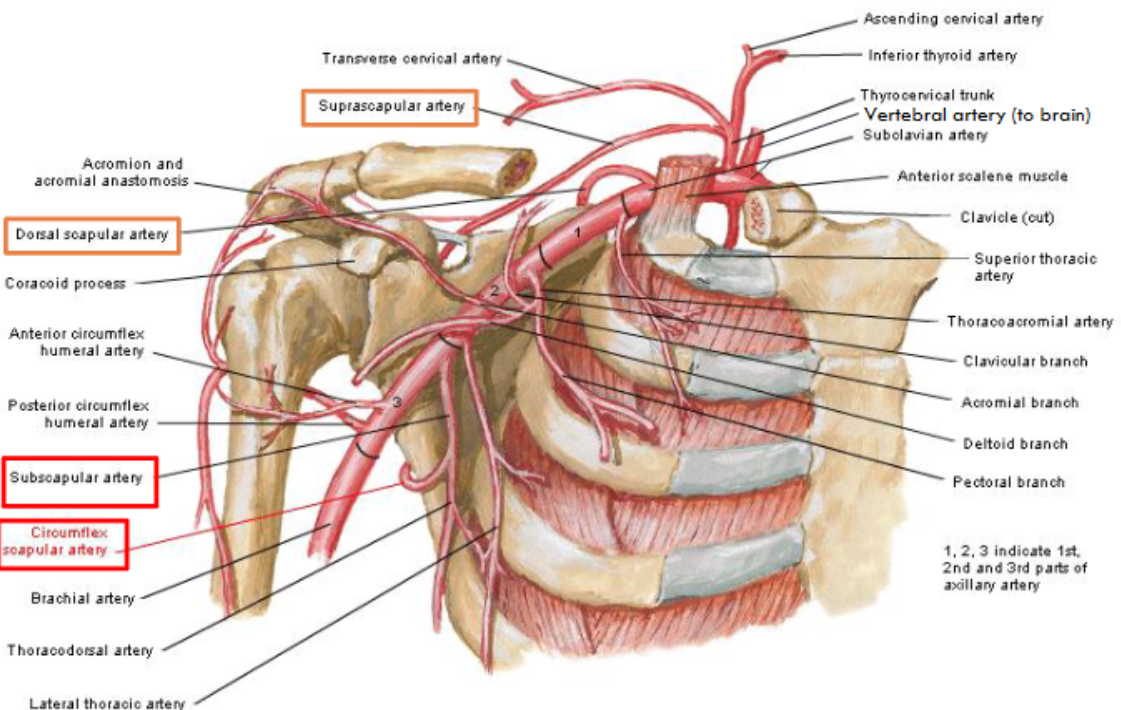
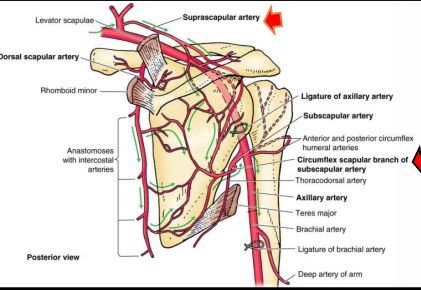
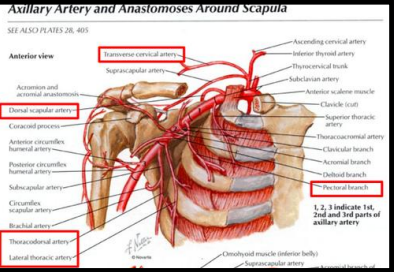
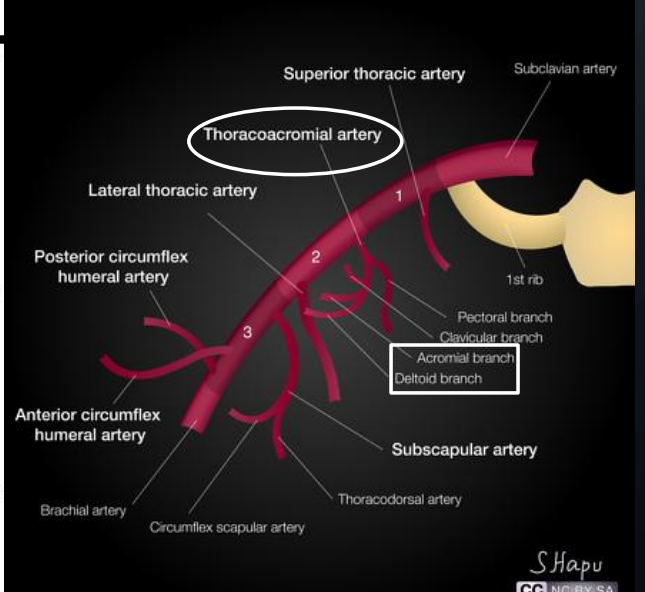
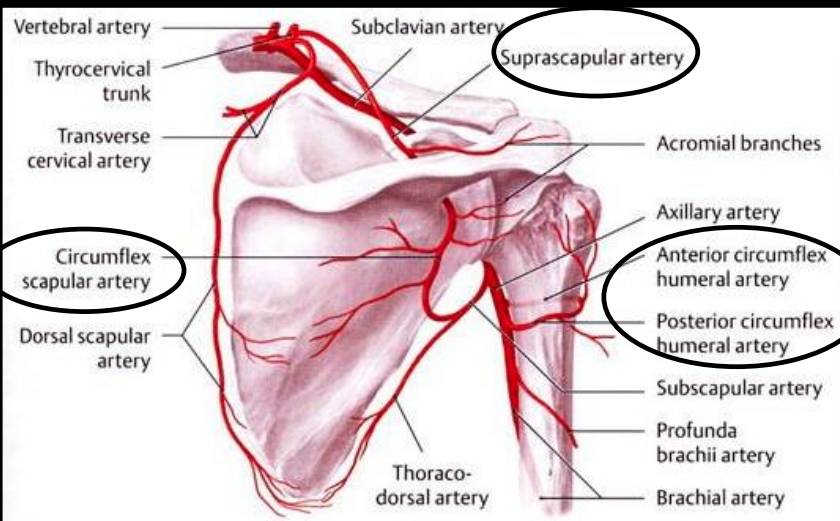
What artery gives rise to many shoulder branches?
Subclavian artery
What are the branches of the thoracoacromial artery?
Clavicular, Acromial, Pectoral, Deltoid (CAPD)
Which arteries supply the scapula?
Suprascapular, dorsal scapular, subscapular, circumflex scapular arteries
What is scapular anastomosis?
Network of arteries supplying the scapula that maintains blood flow if one artery is blocked
What movement do all rotator cuff muscles assist with?
Circumduction
Scapular Region
What are the rotator cuff muscles?
1. Supraspinatus m.
2. Infraspinatus m.
3. Teres minor m.
4. Subscapularis m.
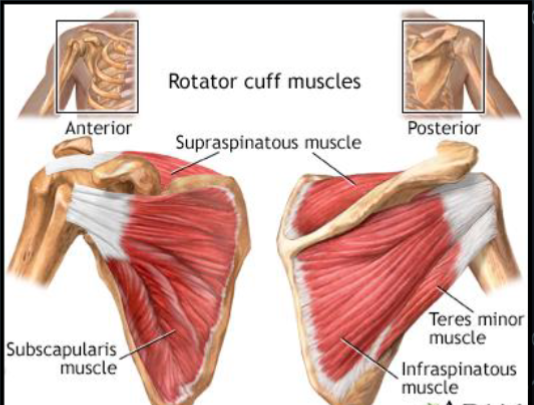
What is the role of the rotator cuff muscles?
Main Role: Provide dynamic stabilization of thehumeral head within the glenoid fossa.
Allow a wide range of motion
Brachial Plexus (C5-T1)
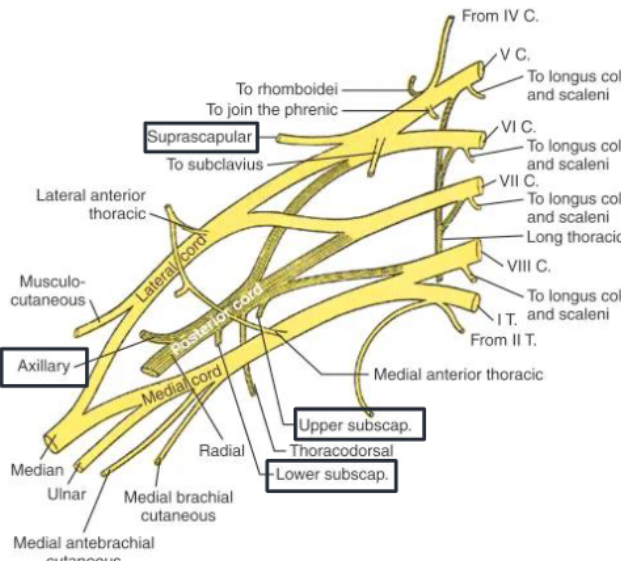
Subclavian and Axillary Arteries
Where is the supraspinatus muscle located in relation to trapezius?
Deep to the trapezius muscle
What is the origin of the supraspinatus muscle?
Supraspinous fossa of the scapula
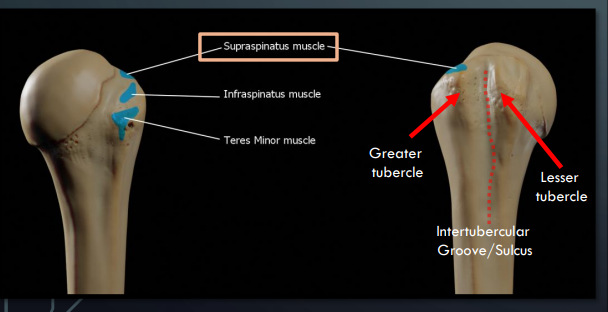
What is the insertion of the supraspinatus muscle?
Greater tubercle of the humerus
What is the primary action of the supraspinatus muscle?
Abduction of the arm
What secondary action does supraspinatus perform at the shoulder?
Pulls the head of the humerus medially toward the glenoid cavity
What nerve innervates the supraspinatus muscle?
Suprascapular nerve (C5–C6)
What artery supplies the supraspinatus muscle?
Suprascapular artery
Where is the infraspinatus muscle located?
Occupies a major part of the posterior scapula
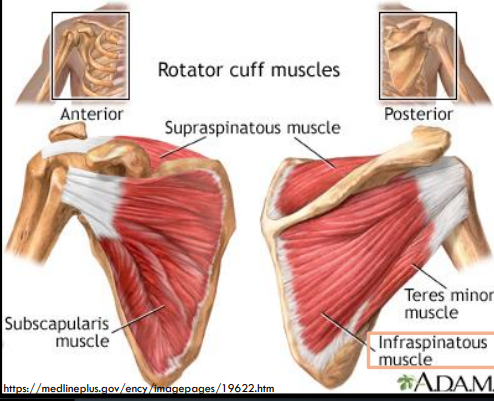
What is the origin of the infraspinatus muscle?
Infraspinous fossa of the scapula
What is the insertion of the infraspinatus muscle?
Greater tubercle of the humerus
What is the primary action of the infraspinatus muscle?
Primary external rotator of the arm when abducted
What stabilizing function does infraspinatus provide?
Stabilizes the humeral head in the glenoid cavity
What nerve innervates the infraspinatus muscle?
Suprascapular nerve (C5–C6)
What arteries supply the infraspinatus muscle?
Suprascapular artery and circumflex scapular artery
Where is the teres minor muscle located?
Extends between the scapula and the head of the humerus
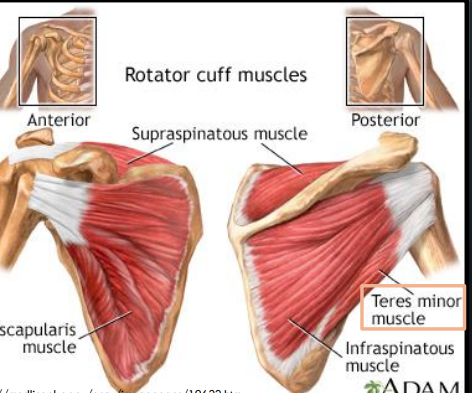
What is the origin of the teres minor muscle?
Lateral border of the scapula
What is the insertion of the teres minor muscle?
Greater tubercle of the humerus
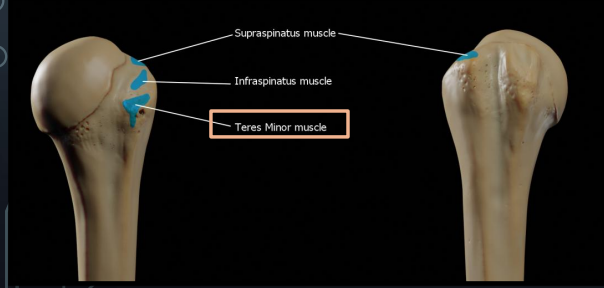
What is the action of the teres minor muscle?
Assists with external rotation when the arm is adducted
What nerve innervates the teres minor muscle?
Axillary nerve (C5–C6)
What arteries supply the teres minor muscle?
Suprascapular artery and dorsal scapular artery
Where is the subscapularis muscle located
Subscapular fossa of the scapula
What is the origin of the subscapularis muscle?
Subscapular fossa of the scapula
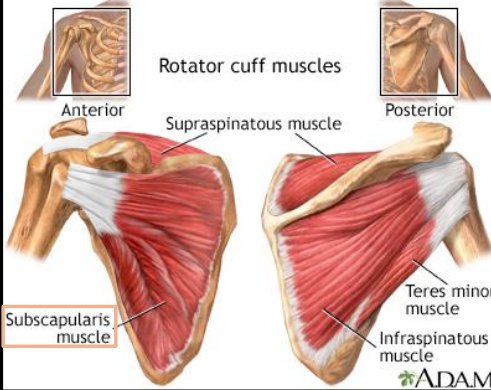
What is the insertion of the subscapularis muscle?
Lesser tubercle of the humerus
What is the primary action of the subscapularis muscle?
Internal rotation of the arm
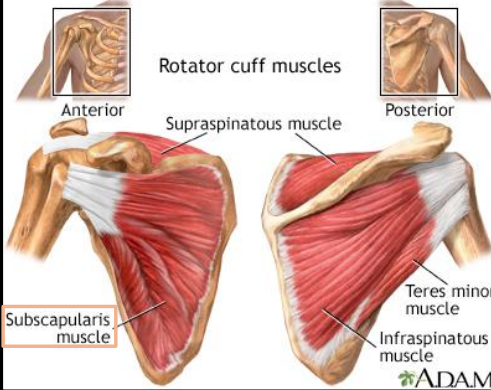
What stabilizing role does subscapularis provide?
Stabilizes the humeral head in the glenoid cavity
What nerve innervates the subscapularis muscle?
Subscapular nerve (C5–C6)
What arteries supply the subscapularis muscle?
Subscapular artery and suprascapular artery
What causes most rotator cuff injuries?
Progressive wear and tear of rotator cuff tendons
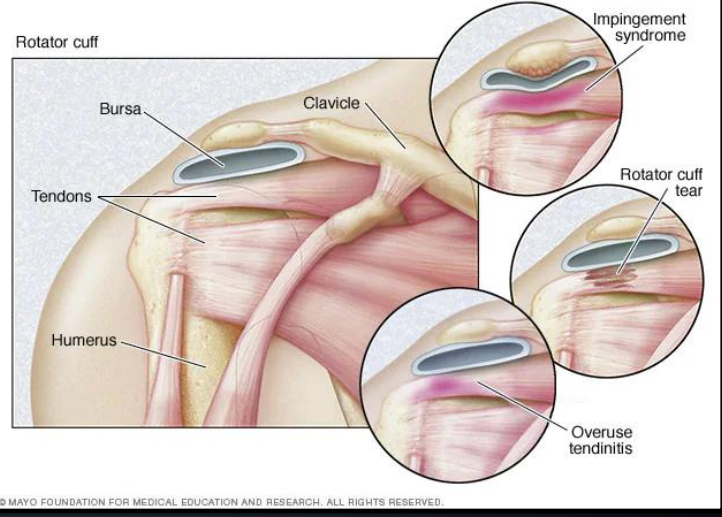
How does age affect rotator cuff injury risk?
Risk increases with age
What activities commonly contribute to rotator cuff injuries?
Repetitive overhead movements
How are rotator cuff injuries managed?
Physical therapy or surgical intervention
What bony landmarks does the deltoid muscle span?
Clavicle, acromion, and spine of the scapula
What is the origin of the clavicular (anterior) part of the deltoid?
Lateral one-third of the clavicle
What are the origins of the clavicular (anterior), acromial (middle), and spinal (posterior) parts of the deltoid?
Clavicular (anterior): Lateral one-third of the clavicle
Acromial (middle): Acromion
Spinal (posterior): Spine of the scapula
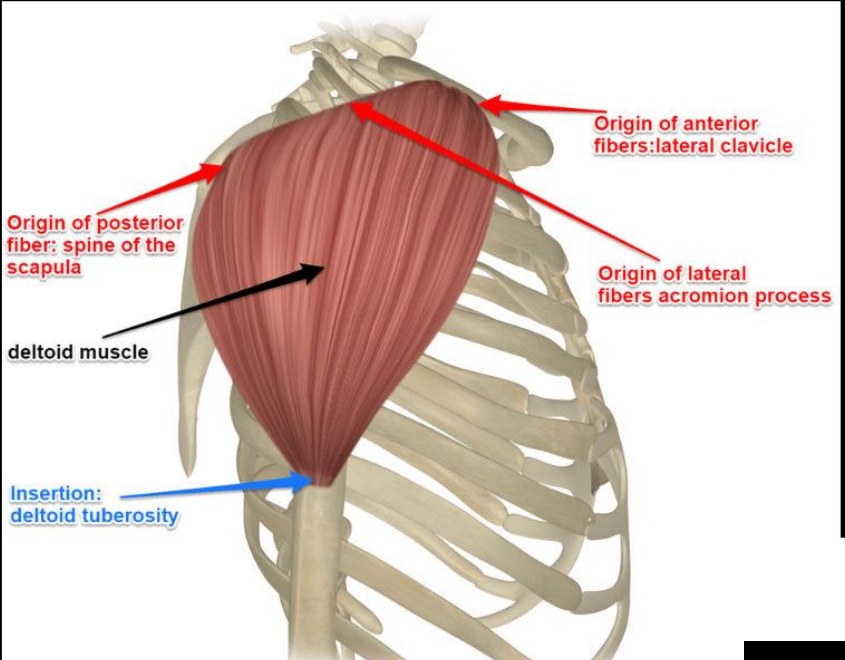
What is the insertion of the deltoid muscle?
Deltoid tuberosity of the humerus
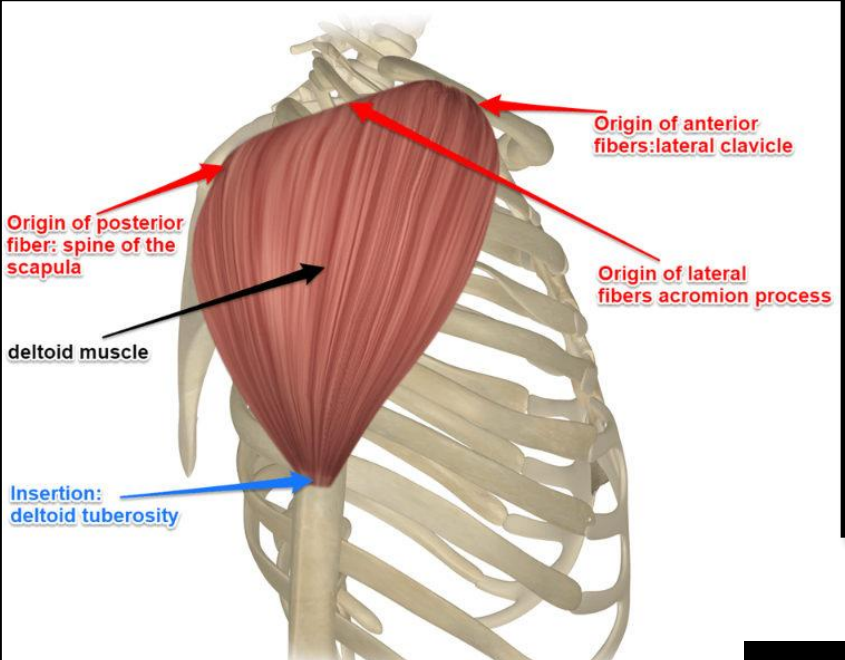
What is the action of the clavicular (anterior) deltoid fibers?
Flexion and internal rotation of the arm
What is the action of the acromial (middle) deltoid fibers?
Abduction of the arm beyond the initial 15°
What is the action of the spinal (posterior) deltoid fibers?
Extension and external rotation of the arm
What nerve innervates the deltoid muscle?
Axillary nerve (C5–C6)
What arteries supply the deltoid muscle?
Deltoid and acromial branches of thoracoacromial artery, subscapular artery, anterior and posterior circumflex humeral arteries
What type of joint is the glenohumeral joint?
True synovial ball-and-socket (diarthrodial) joint
True synovial ball-and-socket (diarthrodial) joint
Upper extremity to the trunk (axial skeleton)
What bones form the glenohumeral joint?
Head of the humerus and glenoid fossa of the scapula
: What movements are allowed at the glenohumeral joint?
Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, internal rotation, external rotation, circumduction
What type of cartilage covers the articular surfaces of the glenohumeral joint?
Hyaline cartilage
How is the glenoid fossa described anatomically?
Shallow, pear-shaped pit
Why is the glenohumeral joint incongruent?
Glenoid fossa concavity is less acute than humeral head convexity
What structure deepens the glenoid fossa?
Glenoid labrum
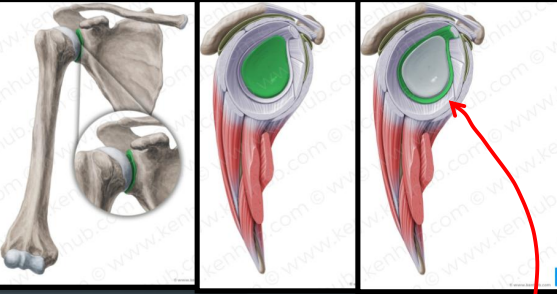
What is the composition of the glenoid labrum?
Fibrocartilage
What is the functional trade-off of the glenohumeral joint design?
Wide range of motion with reduced stability
What ligaments make up the glenohumeral ligaments?
Superior, middle, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments
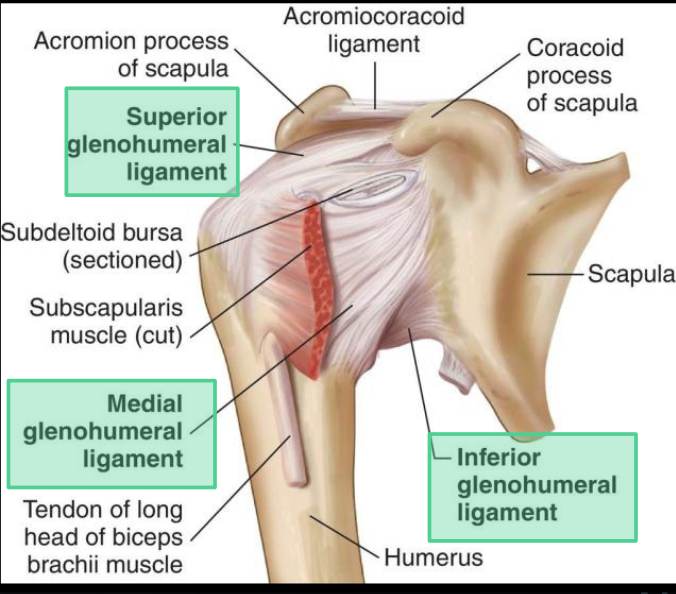
What is the function of the glenohumeral ligaments?
Stabilize the shoulder and prevent dislocation
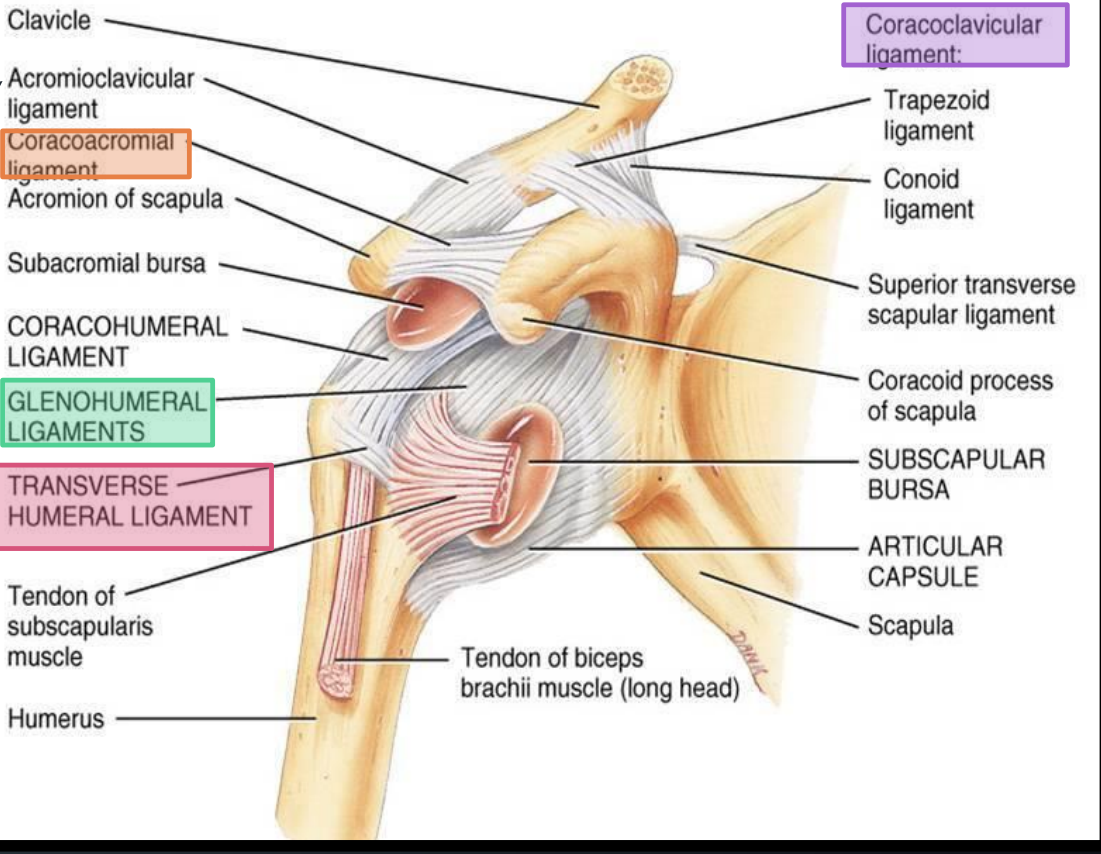
What does the coracoacromial ligament connect?
Coracoid process to acromion
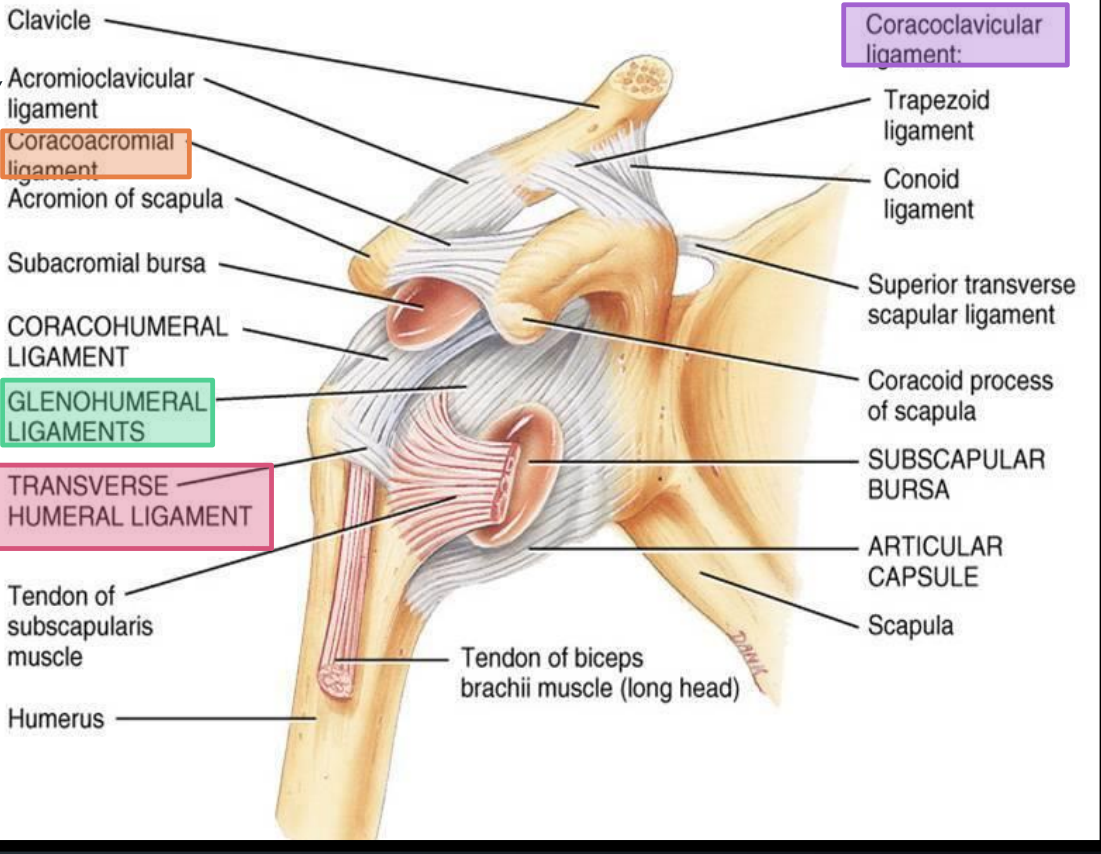
What ligaments make up the coracoclavicular ligaments?
Trapezoid and conoid ligaments
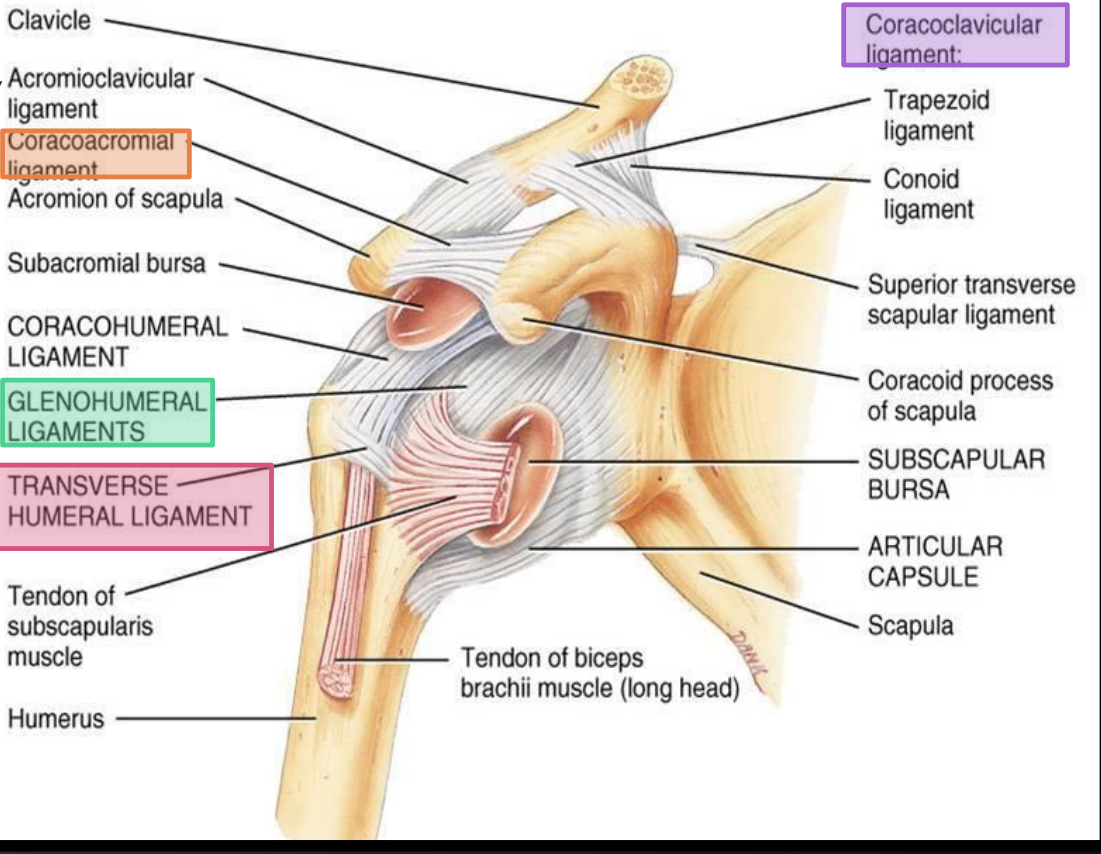
What bones do the coracoclavicular ligaments connect?
Clavicle to coracoid process of the scapula
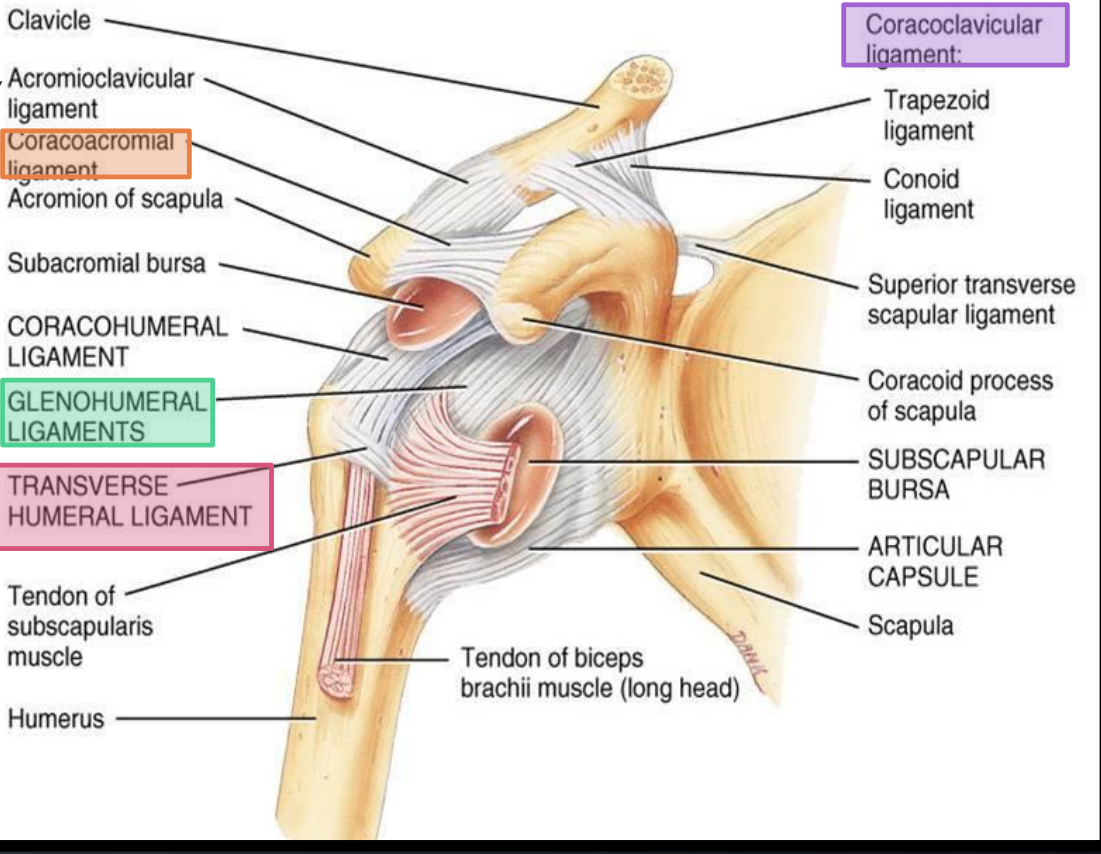
What is the function of the coracoclavicular ligaments?
Prevent vertical displacement of the scapula relative to the clavicle
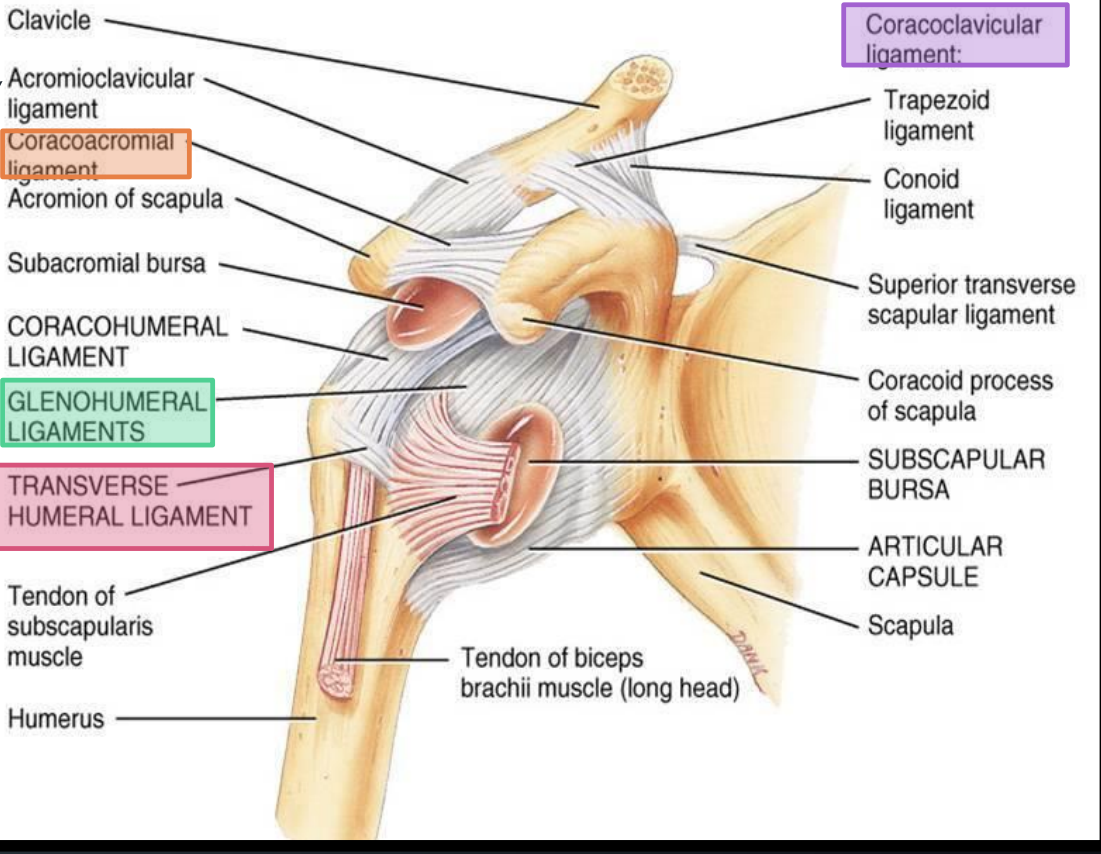
What injury commonly results from rupture of the coracoclavicular ligaments?
Acromioclavicular joint dislocation
What is the function of the transverse humeral ligament?
Holds the tendon of the long head of biceps brachii in the bicipital groove
Between which structures does the bicipital groove lie?
Greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus
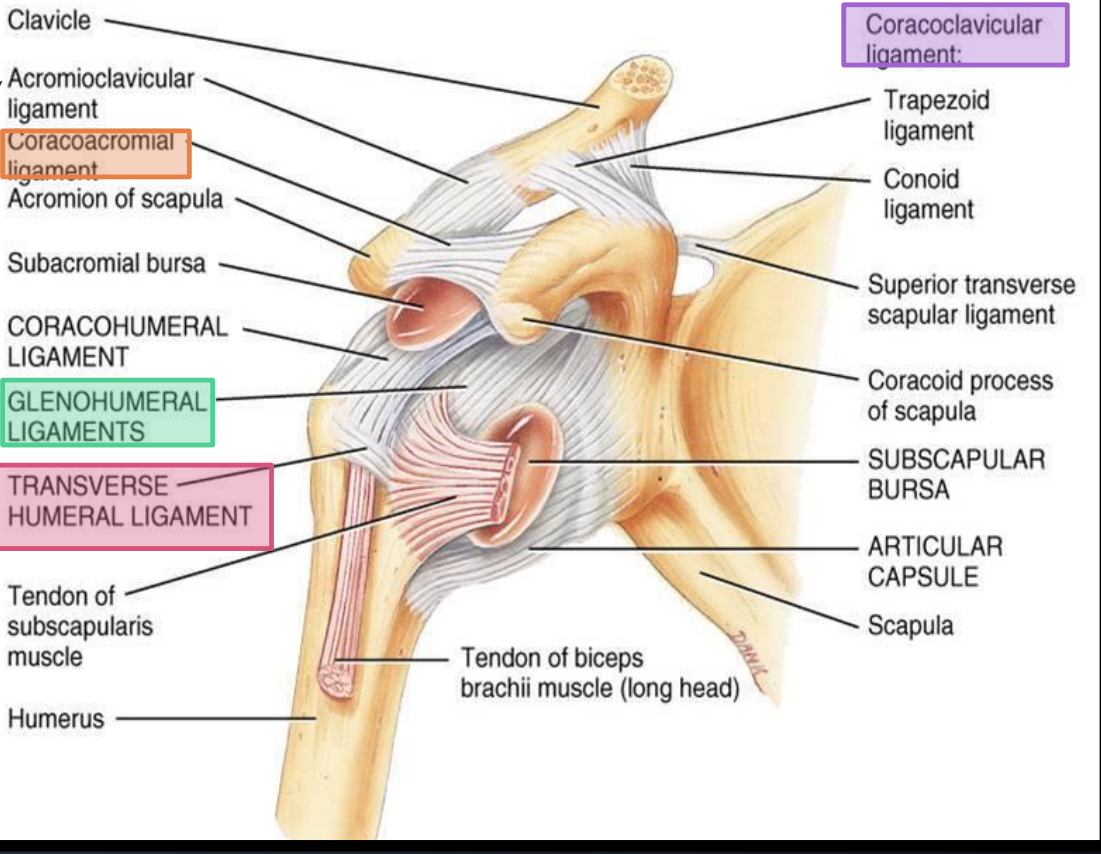
What nerves innervate the glenohumeral joint?
Subscapular nerve, axillary nerve, lateral pectoral nerve, suprascapular nerve
What arteries supply the glenohumeral joint?
Anterior circumflex humeral, posterior circumflex humeral, circumflex scapular, suprascapular arteries
Action of the glenohumeral joint?
Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, external/lateral rotation, internal/medial rotation and circumduction
What are common causes and risk factors for shoulder impingement syndrome?
Repetitive overhead motions, bone spurs/bony growths, inflammation or swelling reducing subacromial space
How do posture and aging affect shoulder impingement syndrome?
Poor posture increases risk; age-related wear and tear increases risk