Unit 1 - Biological Basis - AP Psychology
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Somatic Nervous System
Voluntary Movement
Autonomic Nervous System
Involuntary organs (heart, lungs)
Sympathetic Nervous System
Fight/flight response
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Rest after the fight/flight response, calms the body
Neuron Dendrites
Receive incoming neurotransmitters
Neuron Axon
Action potential travels down this
Neuron Synapse
Gap b/w neurons
Neuron Myelin Sheath
Speeds up the Action Potential down the axon; protects the axon
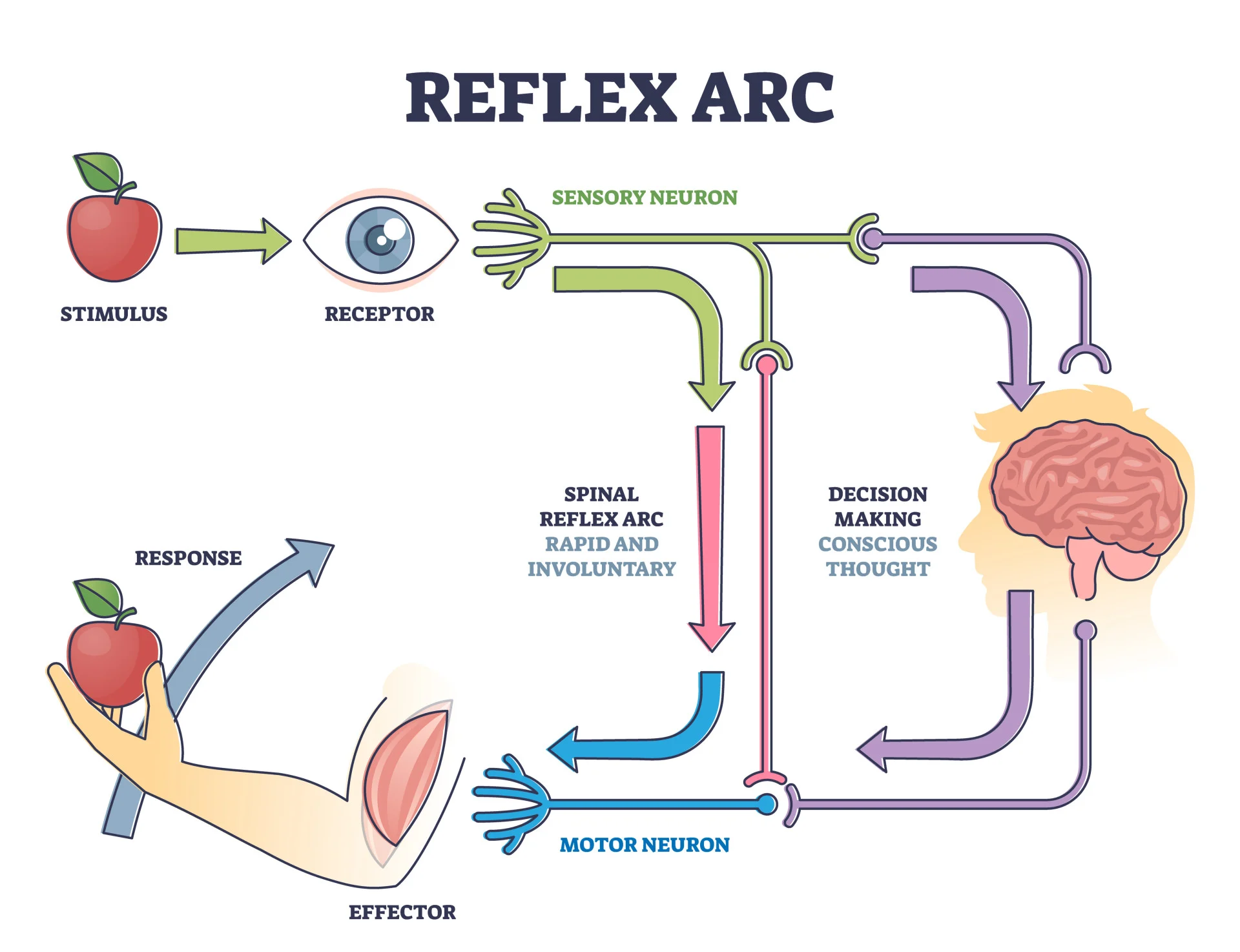
Sensory Neurons
Receive sense signals from environment - sends signals to brain
Motor Neurons
Signals to move - send signals from the brain
Interneurons
Cells in spinal cord/brain responsible for reflex arc
GLIA Cells
Support cells that give nutrients and clean up around neurons
Depolarization
Charge of neuron briefly swaps from negative to positive; triggers the action potential.
Refractory Period
Neuron must rest & reset before it can send another action potential
GABA (neurotransmitter)
Major inhibitory NT
Glutamate (neurotransmitter)
Major excitatory NT
Serotonin (neurotransmitter)
Moods, emotions, sleep - in amygdala
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Memory & movement - in hippocampus
Norepinephrine (neurotransmitter)
Sympathetic NS - too little association w/ depression
Endorphins (neurotransmitter)
Decreases pain
Substance P. (Neurotransmitter)
Pain regulation (abnormality increases pain & inflammation)
Leptin (hormone)
Makes you full
Ghrelin (Hormones)
Makes you hungry
Agonist
Drug that mimics neurotransmitters
Antagonist
Drug that blocks a neurotransmitter
Reuptake
Unused neurotransmitters are taken back up into the sending neuron
Depressants
Decrease Nervous System activity
Stimulants
Increase nervous system activity
Hallucinogens
Hallucinations & altered perceptions
Opioids
Relieves pain
Cerebellum
A brain structure that plays a key role in motor control, coordination, and balance.
Brainstem/Medulla
The part of the brain that controls vital life functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Reticular Activating System
A network of neurons in the brainstem that regulates wakefulness, arousal, and attention.
Cerebral Cortex
The outer layer of the brain, involved in higher brain functions such as thought, perception, and decision-making.
Amygdala
A small, almond-shaped structure in the brain that plays a key role in processing emotions, particularly fear and pleasure.
Hippocampus
A critical brain structure involved in the formation of new memories and learning, as well as spatial navigation.
Hypothalamus
Reward and pleasure center, as well as homeostasis, eating behaviors, and links to the endocrine system
Thalamus
Relay center for all but smell
Pituitary Gland
Master gland that regulates hormones and controls other endocrine glands.
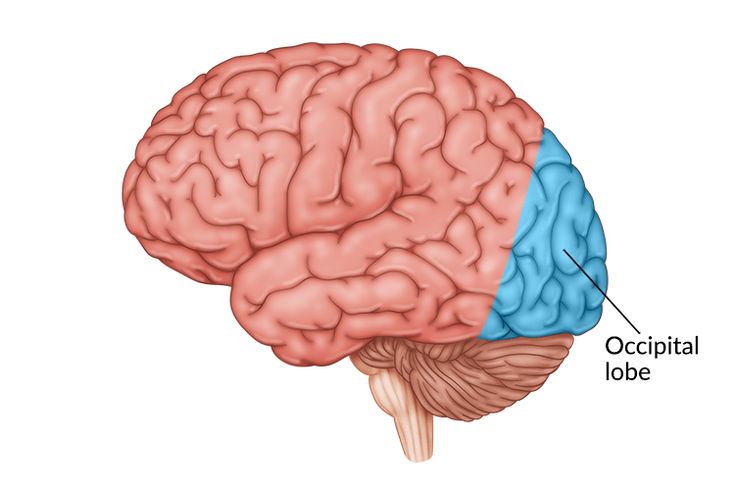
Occipital Lobe
Vision
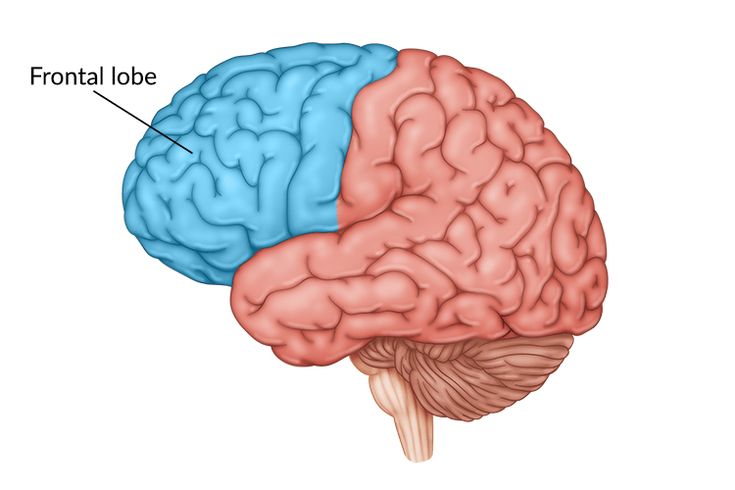
Frontal Lobe
Decision making, planning, judgement, movement, personality, language, executive function
Prefrontal Cortex
Front of frontal lobe — executive function
Motor Cortex
Back of frontal lobe - map of our motor receptors — controls skeletal movement
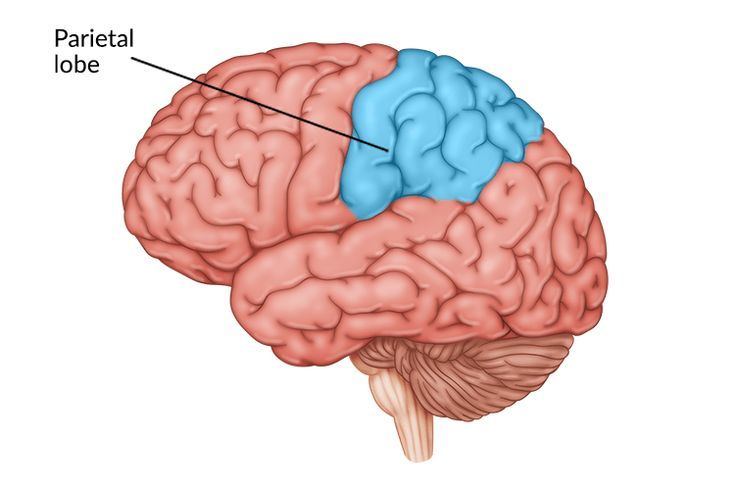
Parietal Lobe
Sensations and touch — controls association areas
Somatosensory Cortex
Map of our touch receptors
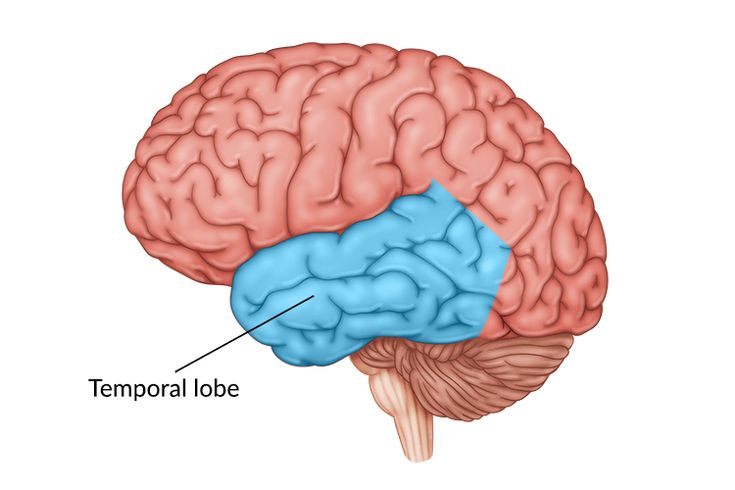
Temporal Lobe
Hearing and face recognition, language
Association areas
receive input from multiple areas/lobes to integrate info
Broca’s Area (Left hemisphere)
Inability to produce speech
Wernicke’s Area (Left hemisphere)
Can’t comprehend speech
Corpus Callosum
Bundle of nerves that connects the 2 hemispheres — sometimes severed in patients with severe seizures/split-brain patients
Brain Plasticity
Brain changes via damage and through experience
Endocrine System
System of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream, regulating various bodily functions.
Pituitary gland
The master gland of the endocrine system, which regulates growth and controls other glands by releasing hormones.
Brain Scan — EEG
Shows broad brain activity through electrical output
Brain Scan - fMRI
Shows brain activity in specific regions; measures oxygen
Multiple sclerosis
Destruction of Myelin sheath, disrupts APs, causes impaired mobility/paralysis
Myasthenia gravis
Acetylcholine blocked, APs disrupted, causes poor motor control/paralysis
Prosopagnosia
Face blindness — damage to occipital and/or temporal lobe
Epilepsy/Seizures
Caused by too much or too little glutamate/GABA
Evolutionary Psychology
Study how natural selection influences behavior
Heredity (nature)
How genes influence your behavior
Environment (nurture)
How outside situations influence your behavior (school)
Genetics (twin/adoption studies)
Identical twin will have a higher % of also developing a disease
Environment (twin/adoption studies)
Identical twins raised in different environments show differences
Central Nervous System
Brain & Spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
Rest of the NS — relays to Central NS
Reflex Arc
Important stimuli skips the brain & routes through the spinal cord for immediate reactions (hand on a hot flame)
Neurons Fire w/ an Action Potential
Ions move across membrane, sends an electrical charge down the axon
Resting Potential
Neuron maintains a -70mv charge when not doing anything
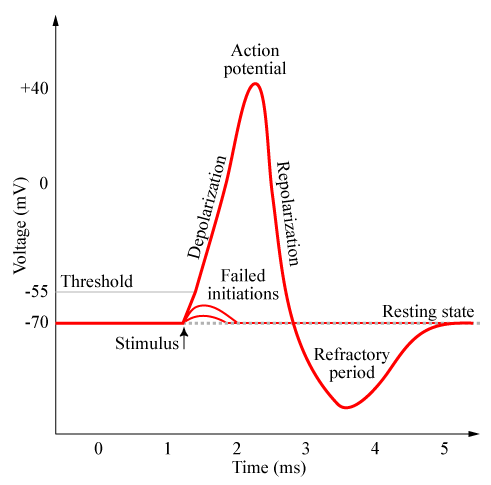
Threshold of Depolarization
Stimulus strength must reach this point to start the AP
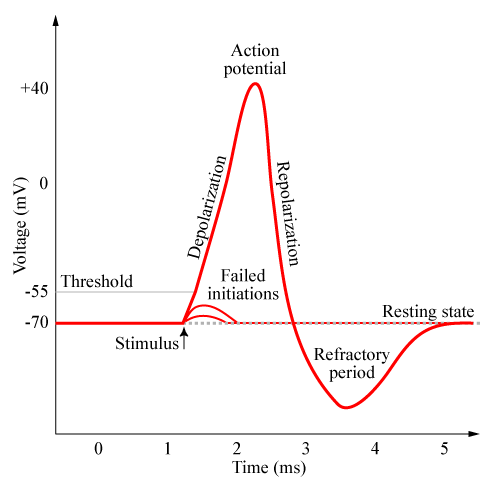
All or nothing principle
Stimulus must trigger the AP past its threshold, but does not increase the intensity or speed of the response
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals released in synaptic gap, received by neurons. Classified as excitatory or inhibitory
Dopamine
Reward (short term) & fine movement — in hypothalamus, associated with addictions
Oxytocin
Love, bonding, childbirth, lactation
Hormones
If not in the nervous system, it’s a hormone
Adrenaline
Fight or flight
Melatonin
Sleep & drowsiness
Tolerance
Needing more of a drug to achieve the same effects
Addiction
Must have it to avoid withdrawal symptoms
Withdrawal
Symptoms associated with sudden stoppage
Split-brain experiments
Image shown to right eye processed in left hemisphere — Patient can say what they saw
Imagine shown to left eye processed in right hemisphere — Patient cannot say what they saw
Lesion
Destruction of brain tissue
Blindsight
Caused by lesions to primary visual cortex, people can “see” (i.e. catch a ball, etc) despite being blind — evidence for association areas
Broca’s aphasia
Damage to Broca’s area — stuttered speech
Wernicke’s aphasia
Damage to Wernicke’s — jumbled speech
Phantom limb pain
Pain from a limb that is no longer there (amputated) — caused by brain plasticity
Alzheimers
Destruction of acetylcholine in hippocampus, memory loss