econ final questions
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Suppose each of 20 neighbors on a street values a streetlight at $3,000. The cost of the streetlight is $40,000. Which of the following statements is true?
a. It is not efficient to have a streetlight.
b. It is efficient for each neighbor to pay a $3,000 contribution to installing a streetlight.
c. It is efficient for the government to tax the residents $2,000 each and install a streetlight.
d. None of the answer choices are correct
c
A positive externality affects market efficiency in a manner similar to a _______.
a. common resource
b. private good
c. rival good
d. public good
d
A negative externality affects market efficiency in a manner similar to a(n) _______.
a. common resource
b. private good
c. excludable good
d. public good
a
Which of the following is an example of a common resource?
a. Tornado siren
b. Iron ore
c. A national park
d. A fireworks display
c
Which of the following are potential solutions to the problem of noise pollution near an airport?
a. Auction off noise permits to the airlines.
b. Grant rights to peace and quiet to residents near the airport so that airlines must purchase the right to make noise.
c. Regulate the amount of noise that an aircraft can make.
d. All of the answer choices are correct.
d
When markets fail to allocate resources efficiently, the ultimate source of the problem is usually _______.
a. that prices are not high enough so people overconsume
b. that property rights have not been well established
c. government regulation
d. that prices are not low enough so firms overproduce
b
Because Elaine has a family history of significant medical problems, they buy health insurance, while their friend Jerry, who has a healthier family, goes without. This is an example of ______________.
a. screening
b. adverse selection
c. moral hazard
d. signaling
b
George has a life insurance policy that pays their family $1 million if they die. As a result, they do not hesitate to enjoy their favorite hobby of bungee jumping. This is an example of _______________.
a. screening
b. signaling
c. adverse selection
d. moral hazard
d
Before selling anyone a health insurance policy, the Kramer Insurance Company requires that applicants undergo a medical examination. Those with significant preexisting medical problems are charged more. This is an example of ____________.
a. screening
b. signaling
c. moral hazard
d. adverse selection
a
Dr. Wexler displays her medical degree in her office waiting room, hoping patients will be impressed that she attended a prestigious medical school. This is an example of__________.
a. moral hazard
b. adverse selection
c. signaling
d. screening
c
If there are implicit costs of production, _______.
a. economic profit and accounting profit will be equal
b. accounting profit will exceed economic profit
c. accounting profit will always be zero
d. economic profit will exceed accounting profit
e. economic profit will always be zero
b
If a production function exhibits diminishing marginal product, its slope _______.
a. is linear (a straight line)
b. becomes steeper as the quantity of the input increases
c. becomes flatter as the quantity of the input increases
d. could be any of the answer choices
c
The marginal product of labor as production moves from employing one worker to employing two workers is _______.
a. 0
b. 20
c. 34
d. 46
e. 80
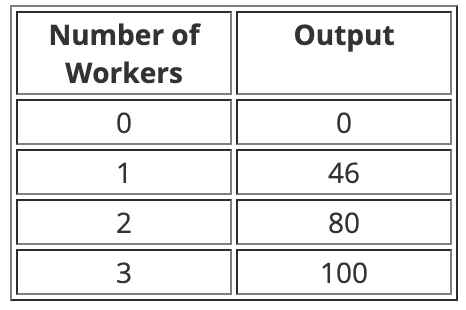
c
The production process described above shows _______.
a. increasing returns to scale
b. diminishing marginal product of labor
c. increasing marginal product of labor
d. constant marginal product of labor
e. decreasing returns to scale
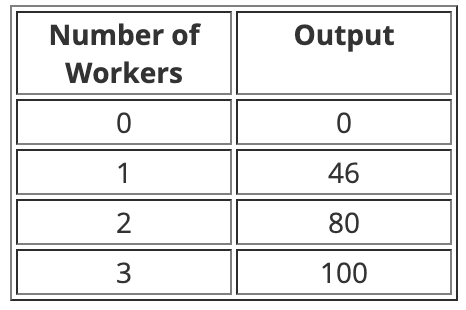
b
If marginal costs equal average total costs, _______.
a. average total costs are rising
b. average total costs are minimized
c. average total costs are maximized
d. average total costs are falling
b
If, as the quantity produced increases, a production function first exhibits increasing marginal product and later diminishing marginal product, the corresponding marginal-cost curve will _______.
a. slope downward
b. be U-shaped
c. be flat (horizontal)
d. slope upward
b
If a competitive firm is producing a level of output where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, the firm could increase profits if it _______.
a. temporarily shut down
b. maintained production at the current level
c. increased production
d. decreased production
c
When a perfectly competitive firm increases the quantity it produces and sells by 10 percent, its marginal revenue ________ and its total revenue rises by ________.
a. falls; exactly 10 percent
b. stays the same; exactly 10 percent
c. falls; less than 10 percent
d. stays the same; less than 10 percent
b
If a profit-maximizing, competitive firm is producing a quantity at which marginal cost is between average variable cost and average total cost, it will ________.
a. keep producing in the short run but exit the market in the long run
b. shut down in the short run and exit the market in the long run
c. keep producing both in the short run and in the long run
d. shut down in the short run but return to production in the long run
a
In the long-run equilibrium of a competitive market with identical firms, what are the relationships among price P, marginal cost MC, and average total cost ATC?
a. P > MC and P > ATC
b. P = MC and P = ATC
c. P > MC and P = ATC
d. P = MC and P > ATC
b
Which of the following is not a barrier to entry in a monopolized market?
a. A key resource is owned by a single firm.
b. A single firm is very large.
c. The government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce some good.
d. The costs of production make a single producer more efficient than a large number of producers.
b
When a monopolist produces an additional unit, the marginal revenue generated by that unit must be _______.
a. above the price because the output effect outweighs the price effect
b. above the price because the price effect outweighs the output effect
c. below the price because the output effect outweighs the price effect
d. below the price because the price effect outweighs the output effect
d
The profit-maximizing monopolist will choose the price and quantity represented by point _______.
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
e. none of the answer choices are correct
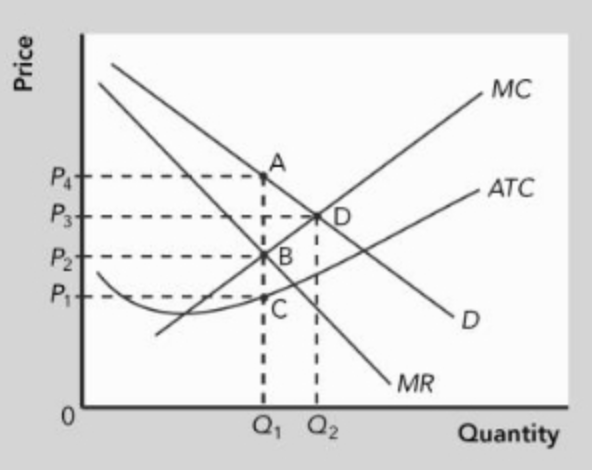
a
The profit earned by the profit-maximizing monopolist is represented by the area _______.
a. P4ABP2
b. P4ACP1
c. P4AQ10
d. P3DQ20
e. None of the answer choices are correct
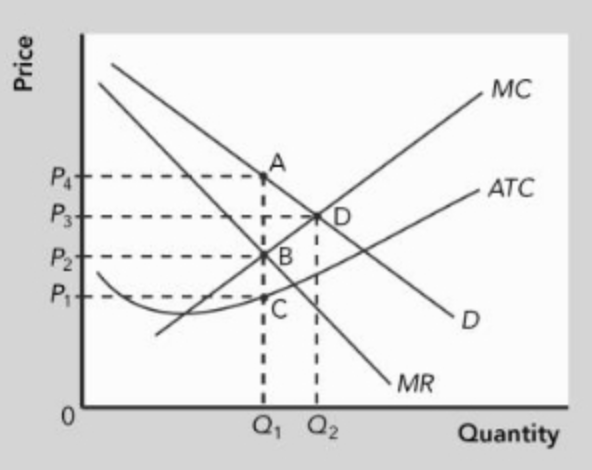
b
The monopolist's supply curve _______.
a. is the marginal-cost curve above average variable cost
b. is the marginal-cost curve above average total cost
c. is the upward-sloping portion of the average-total-cost curve
d. is the upward-sloping portion of the average variable cost
e. does not exist
e
If marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, a monopolist should _______.
a. decrease output
b. increase output
c. raise the price
d. keep output the same because profits are maximized when marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost
b
Which of the following is true regarding the similarities and differences in monopolistic competition and monopoly?
a. The monopolist faces a downward-sloping demand curve while the monopolistic competitor faces an elastic demand curve.
b. The monopolist makes economic profits in the long run while the monopolistic competitor makes zero economic profits in the long run.
c. Both the monopolist and the monopolistic competitor operate at the efficient scale.
d. The monopolist charges a price above marginal cost while the monopolistic competitor charges a price equal to marginal cost.
b
Which of the following is true regarding the production and pricing decisions of monopolistically competitive firms? Monopolistically competitive firms choose the quantity at which marginal cost equals _______.
a. marginal revenue and then use the supply curve to determine the price consistent with this quantity
b. average total cost and then use the demand curve to determine the price consistent with this quantity
c. average total cost and then use the supply curve to determine the price consistent with this quantity
d. marginal revenue and then use the demand curve to determine the price consistent with this quantity
d
Which of the following is true with regard to monopolistically competitive firms' scale of production and pricing decisions? Monopolistically competitive firms produce _______.
a. with excess capacity and charge a price above marginal cost
b. with excess capacity and charge a price equal to marginal cost
c. at the efficient scale and charge a price above marginal cost
d. at the efficient scale and charge a price equal to marginal cost
a
One source of inefficiency in monopolistic competition is that _______.
a. because price is above marginal cost, some units are not produced that buyers value in excess of the cost of production and this causes a deadweight loss
b. monopolistically competitive firms produce beyond their efficient scale
c. because price is above marginal cost, surplus is redistributed from buyers to sellers
d. monopolistically competitive firms earn economic profits in the long run
a
If oligopolists engage in collusion and successfully form a cartel, the market outcome is _______.
a. the same as if it were served by a monopoly
b. the same as if it were served by competitive firms
c. known as a Nash equilibrium
d. efficient because cooperation improves efficiency
a
Suppose an oligopolist individually maximizes its profits. When calculating profits, if the output effect exceeds the price effect on the marginal unit of production, then the oligopolist _______.
a. should exit the industry
b. has maximized profits
c. is in a Nash equilibrium
d. should produce fewer units
e. should produce more units
e
As the number of sellers in an oligopoly grows larger, an oligopolistic market looks more like a _______.
a. collusion solution
b. competitive market
c. monopoly
d. duopoly
b
When an oligopolist individually chooses its level of production to maximize its profits, it produces an output that is _______.
a. more than the level produced by a monopoly and less than the level produced by a competitive market
b. less than the level produced by a monopoly and more than the level produced by a competitive market
c. more than the level produced by either a monopoly or a competitive market
d. less than the level produced by either a monopoly or a competitive market
a
When an oligopolist individually chooses its level of production to maximize its profits, it charges a price that is _______.
a. more than the price charged by a monopoly and less than the price charged by a competitive market
b. less than the price charged by a monopoly and more than the price charged by a competitive market
c. more than the price charged by either a monopoly or a competitive market
d. less than the price charged by either a monopoly or a competitive market
b
The dominant strategy for Róza and Kyle is for _______.
a. both to be open for many hours
b. both to be open for a few hours
c. Róza to be open for many hours while Kyle is open for few hours
d. Róza to be open for few hours while Kyle is open for many hours
e. there is no dominant strategy in this prisoners' dilemma game
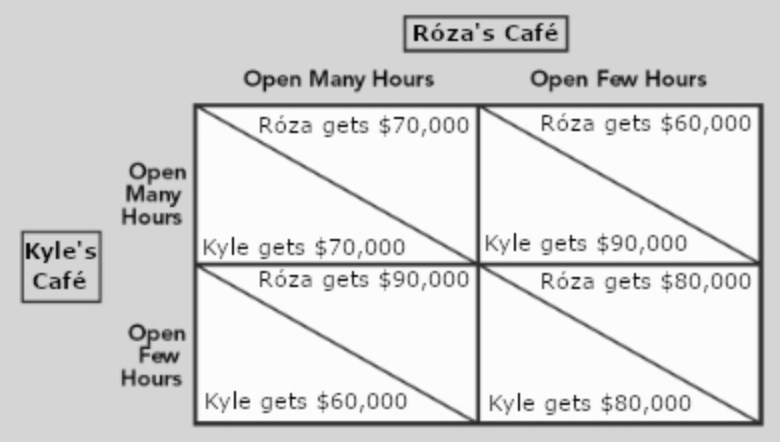
a
Suppose Róza and Kyle agreed to collude and jointly maximize their profits. If Róza and Kyle were to be able to repeatedly play the game shown earlier and they agreed on a penalty for defecting from their agreement, what is the likely outcome of the game?
a. Both are open for many hours.
b. Both are open for a few hours.
c. Róza is open for many hours while Kyle is open for few hours.
d. Róza is open for few hours while Kyle is open for many hours.
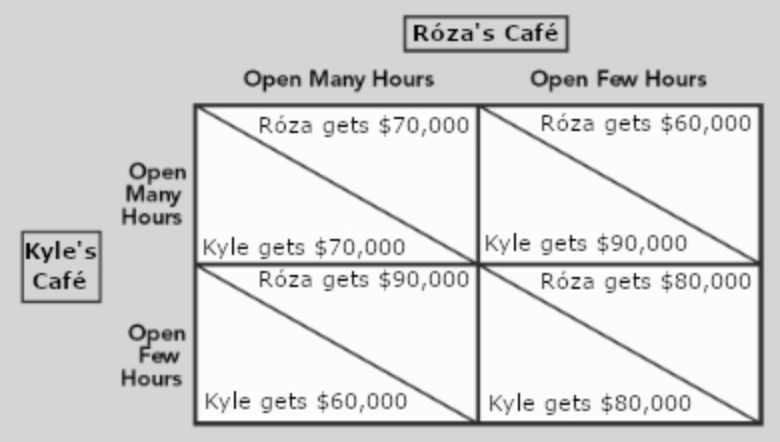
b
The prisoners' dilemma is a two-person game illustrating that _______.
a. even if cooperation is better than the Nash equilibrium, each person might have an incentive not to cooperate
b. the cooperative outcome could be worse for both people than the Nash equilibrium
c. rational, self-interested individuals will naturally avoid the Nash equilibrium because it is worse for both of them
d. even if the cooperative outcome is better than the Nash equilibrium for one person, it might be worse for the other
a
Two people facing the prisoners' dilemma may cooperate if they _______.
a. recognize that the Nash equilibrium is worse for both people than the cooperative equilibrium
b. each choose their dominant strategy
c. play the game repeatedly and expect noncooperation to be met with future retaliation
d. each realizes that the strategy they choose is not known to the other until the outcome is realized
c
The key feature of an oligopolistic market is that _________.
a. a single firm chooses a point on the market demand curve
b. each firm takes the market price as given
c. a small number of firms are acting strategically
d. each firm sells a product different from other firms
c
Kevin owns 50 acres of land. Kevin sells the land to a real estate developer who builds a subdivision with 20 houses. The land is an example of a good that is
A. both rival in consumption and excludable.
B. neither rival in consumption nor excludable.
C. excludable, but not rival in consumption.
D. rival in consumption, but not excludable.
A
The Pennsylvania Turnpike is a tolled freeway running through the state of Pennsylvania.
Motorists must pay tolls at various points along the Tumpike based on the distance they traveled on the freeway. Suppose that despite the tolls, many motorists in the urban areas use the Tumpike causing traffic to slow during peak times. What type of good would the Tumpike be classified as in this case?
A. Private good
B. Club good
C. Common resource
D. Public good
A
Under which of the following scenarios would a park be considered a common resource?
A. Visitors to the park must pay an admittance fee, but there are always plenty of empty picnic tables.
B. Visitors to the park must pay an admittance fee and frequently all of the picnic tables are in use.
C. Visitors can enter the park free of charge and there are always plenty of empty picnic tables.
D. Visitors can enter the park free of charge, but frequently all of the picnic tables are in use.
D
Who among the following is a free rider?
A. Michael listens to National Public Radio, but does not contribute to any fundraising efforts.
B. Dwight takes the commuter rail to work, but he purchases the discounted monthly passes rather than buying tickets each day.
C. Jim sends his five children to a private school rather than to the public school in his neighborhood.
D. Ryan goes to Pam's house to watch a soccer game on the local commercial television channel.
A
Six friends decide to meet at a Chinese restaurant for dinner. They decide that each person will order an item off the menu, and they will share all dishes. They will split the cost of the final bill evenly among each of the people at the table. A Tragedy of the Commons problem is likely for each of the following reasons except
A. each person has an incentive to eat as much as possible since their individual rate of consumption will not affect their individual cost.
B. there is an extemality associated with eating the food on the table.
C. when one person eats, he may not take into account how his choice affects his friends.
D. each dish would be both excludable and rival in consumption.
D
Ratings and reviews of mechanics on the Internet:
A. make it easier to avoid shady mechanics, thus reducing moral hazard.
B. raise the cost to mechanics of exploiting their adverse selection advantage.
C. make it easier for mechanics to take advantage of their information advantage.
D. completely prevents all forms of asymmetric information.
A
Some health insurance providers pay a single, set amount for the diagnosis and treatment of a specific illness. This payment scheme is meant to reduce:
A. moral hazard.
B. asymmetric information.
C. poor incentives.
D. the likelihood that doctors will prescribe too few tests to diagnose the patient.
A
A doctor who provides a second opinion knows they will not be performing any other service.
This solves moral hazard by:
A. creating less information.
B. providing the service free
C. aligning the incentives of the buyer and sellers.
D. reducing the free-rider problem.
C
An insurance company can prevent the adverse-selection death spiral by selling to groups of people such as groups of employees in a workplace. This will allow the insurance company to:
A. increase the chances that both healthy and unhealthy people will sign up for coverage.
B. increase the chances that only healthy people will sign up for coverage.
A
Taren eams a certificate in a software program that is used by professionals in the field in which Taren wants to start a career. Obtaining the certificate:
A. increases the moral hazard of hiring Taren.
B. eliminates the principal-agent problem between Taren and her employer.
C. indicates that Taren is less qualified than other candidates.
D. signals that Taren is a good candidate for the job.
D
After Napster was introduced in 1999 as a peer-to-peer file-sharing Internet service, people could cheaply distribute music. Thanks to this and other innovations (eg., YouTube), music is becoming increasingly:
A. private.
B. nonexcludable.
C. nonrival.
D. taxable.
B
Which of these is a list of rival, excludable goods ONLY?
A. a watermelon, toll highways, a private beach, a chair
B. a watermelon, cable Internet service, a private beach, a pencil, a chair
C. a watermelon, a chair, a pencil
D. online video games, a watermelon, a private beach, a pencil, a chair
C
Which of these is a list of excludable and nonrival goods ONLY?
A. cable Internet service, toll highways, public roads, soup kitchen meals
B. online video games, a private beach, toll highways, cable Internet service
C. a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads, smog reduction
D. national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction, cable Internet service
B
Which of these is a list of nonexcludable and rival goods ONLY?
A. a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads
B. online video games, a private beach, toll highways, cable Internet service
C. national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction
D. online video games, a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads
A
Which of these is a list of nonexcludable, nonrival goods ONLY?
A. national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction
B. a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads
C. online video games, a public beach, national defense, a lighthouse
D. a public beach, a lighthouse, toll highways, public roads
A
Which of these is an example of a forced rider?
A. a Canadian-American who pays taxes that help maintain the U.S. army in case of a Canadian invasion
B. someone without children who recently had to start paying a community fee for the maintenance of a new playground
C. a city resident who pays a city tax for weekly trash removal service
D. someone who dislikes the noise coming from a privately owned park and pays taxes to maintain public parks
B
An NFL game played on a satellite provider is a network is a
A. private good; public good
B. club good; common resource
C. club good; public good
D. private good; club good
D
During the Middle Ages, many villages had areas reserved for families to take their cows or sheep to graze. All families were welcome to use this land without charge. This land for grazing can be characterized as a:
A. public good.
B. private good.
C. natural resource.
D. common resource.
D
During the Holy Roman Empire, Germany's Rhine River was a major trade artery (and provided tax revenue). The numerous castles along the Rhine were toll stations, and most merchants had to travel sizable lengths of the river to arrive at their destination. Although the emperors closely guarded the right to charge a toll, local nobility would occasionally break the law and build a castle along the Rhine to charge a toll (hence the origin of the phrase "robber baron").
When possible, such "robber castles" were destroyed to prevent the tragedy of the commons. What is the commons resource here?
A. toll revenue
B. trade
C. castles
D. the Rhine
A
When new professors are hired, their job performance is monitored closely. If they meet their institution's standards, they will eventually receive tenure. After receiving tenure, professors' job performance is less closely monitored, and they become difficult to fire. Tenure thus creates
A. adverse selection.
B. a Condorcet paradox.
C. a screening problem.
D. a moral hazard problem.
D
You own an ice cream store and are concerned that an employee may be giving generous scoops to friends and relatives and smaller scoops to some other customers. This may be reducing sales.
In this example, you are the
A principal and your employee is the agent.
B. agent and your employee is the principal.
C. signaler and your employee is the screener.
D. screener and your employee is the signaler.
A
Which of the following is an example of an adverse selection problem?
A. A customer purchases four apples, two of which are bruised
B. A card shop puts its Halloween merchandise on sale on November Ist.
C. A young job applicant fails to reveal that they were fired from their last job because they were incompetent.
D. A person rents a car and then drives it less carefully and fills it with cheaper gas than they would if they owned it.
C
Which of the following events best exemplifies the concept of signaling?
A. A college student's parents, having leamed that their child is short of money, send them a check for $1,000.
B. A new company that makes high-quality bicycles at a reasonable price sends free bikes to reviewers working for bicycle magazines.
C. A grocery store maintains a policy of examining the driver's license of everyone who writes a personal check to purchase their groceries.
D. A university maintains a policy of considering for admission only those students who graduated among the top 10 percent of their high school class.
B
Bubba is a shrimp fisherman who could ear $5,000 as a fishing tour guide. Instead, he is a full-time shrimp fisherman. In calculating the economic profit of his shrimp business, the S5,000 that Bubba gave up is counted as part of the shrimp business's
A. total revenue.
B. explicit costs.
C. implicit costs.
D. marginal costs,
C
Pete owns a shoe-shine business. His accountant most likely includes which of the following costs on his financial statements?
A. Shoe polish and wages Pete could ear delivering newspapers
B. Shoe polish and rent on the shoe stand
C. Wages Pete could earn delivering newspapers and interest that Pete's money was eaming before he spent his savings to set up the shoe-shine business
D. Rent on the shoe stand and interest that Pete's money was earning before he spent his savings to set up the shoe-shine business
B
Andy gives piano lessons for S15 per hour. He also grows flowers, which he arranges and sells at the local farmer's market. One day he spends 4 hours planting $50 worth of seeds in his garden.
Once the seeds have grown into flowers, he can sell them for S150 at the farmer's market. Andy's accounting profits are
A. $100, and his economic profits are $40.
B. $100, and his economic profits are $15.
C. $40, and his economic profits are $100.
D. $15, and his economic profits are $140
A
Suppose that a "doggie day care" firm uses only two inputs: hourly workers (labor) and a building (capital). In the short rin, the firm most likely considers
A. both labor and capital to be fixed.
B. both labor and capital to be variable.
C. labor to be variable and capital to be fixed
D. capital to be variable and labor to be fixed.
C
lyana is a florist. Iyana can arrange 26 bouquets per day. She is considering hiring her husband James to work for her. Together Iyana and James can arrange 39 bouquets per day. What is James's marginal product?
A. 65 bouquets
B. 39 bouquets
C. 28 bouquets
D. 13 bouquets
D
As Bubba's Bubble Gum Company adds workers while using the same amount of machinery, some workers may be underutilized because they have little work to do while waiting in line to use the machinery. When this occurs, Bubba's Bubble Gum Company encounters
A. economies of scale.
B. diseconomies of scale.
C. increasing marginal product.
D. diminishing marginal product.
D
For a large firm that produces and sells automobiles, which of the following costs would be a variable cost?
A. The $20 million payment that the firm pays each year for accounting services
B. The cost of the steel that is used in producing automobiles
C. The rent that the firm pays for office space in a suburb of St. Louis
D. The cost of internet advertising incurred each year
B
If a fin experiences constant retums to scale at all output levels, then its long-run average total cost curve would
A. slope downward.
B. be horizontal.
C. slope upward.
D. slope downward for low output levels and upward for high output levels.
B
When a firm experiences economies of scale.
A. short-run average total cost is maximized.
B. long-run average total cost is maximized.
C. long-run average total cost decreases as output increases.
D. long-run average total cost increases as output increases.
C
Which of the following statements best reflects a price-taking firm?
A. If the firm were to charge more than the going price, it would sell none of its goods.
B. The firm has an incentive to charge less than the market price to earn higher revenue.
C. The fim can sell only a limited amount of output at the market price before the market price will fall.
D. Price-taking fins maximize profits by charging a price above marginal cost.
A
Suppose a firm in a competitive market increases its output by 30 percent. As a result, the price of its output is likely to
A. decline by 30 percent.
B. remain unchanged.
C. increase by less than 30 percent.
D. decline by more than 30 percent.
B
If Stella's Fashion Jewelry sells its product in a competitive market, then
A. the price of that product depends on the quantity of the product that Stella's Fashion Jewelry produces and sells because the finn's demand curve is downward sloping.
B. Stella's Fashion Jewelry total cost must be a constant multiple of its quantity of output.
C. Stell's Fashion Jewelry total revenue must be proportional to its quantity of output.
D. Stella's Fashion Jewelry total revenue must be equal to its average revenue.
C
Which of the following statements regarding a competitive firm is correct?
A. Because each firm faces a downward sloping demand, if a firm increases its level of output, the firm will have to charge a lower price to sell the additional output.
B. If a firm raises its price, the firm may be able to increase its total revenue even though it will sell fewer units.
C. By lowering its price below the market price, the firm will benefit from selling more units at the lower price than it could have sold by charging the market price.
D. For all firms, average revenue equals the price of the good
D
Suppose that in a competitive market the equilibrium price is S2.50. What is the marginal revenue for the last unit sold by the typical firm in this market?
A. Less than $2.50
B. More than 52.50
C. Exactly $2.50
D. The marginal revenue cannot be determined without knowing the actual quantity sold by the typical firm.
C
Tom produces commemorative t-shirts in a competitive market. If Tom decides to decrease his oufput, this will
A. increase his revenue, since the output decrease leads to a higher market price.
B. increase his revenue, since Tom's competitors will also decrease their output, so that price rises to offset the drop in Tom's output.
C. decrease his revenue, since his output has decreased and the price remains the same.
D. decrease his revenue, since the price falls as competitors increase their output to make up for his decrease in output.
C
If a competitive firm is currently producing a level of output at which marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue, then
A. a one-unit increase in output will increase the firm's profit.
B. a one-unit decrease in output will increase the firm's profit.
C. total revenue exceeds total cost.
D. total cost exceeds total revenue.
B
For a certain firm, the 100th unit of output that the firm produces has a marginal revenue of $11 and a marginal cost of $10. It follows that the
A production of the 100th unit of output increases the firm's profit by $1.
B. production of the 100th unit of output increases the firm's average total cost by $1.
C. firm's profit-maximizing level of output is less than 100 units.
D. production of the 101st unit of output must increase the firm's profit by more than $1.
A
Farmer McDonald sells wheat to a broker in Kansas City, Missouri. Because the market for wheat is generally considered to be competitive, Mr. McDonald maximizes his profit by choosing
A. to produce the quantity at which average variable cost is minimized.
B. to produce the quantity at which average fixed cost is minimized
C, the quantity at which market price is equal to Mr. McDonald's marginal cost of production.
D. the quantity at which market price exceeds Mr. McDonald's marginal cost of production by
C
Ms. Joplin sells colored pencils. The colored-pencil industry is competitive. Ms. Joplin hires a business consultant to analyze her company's financial records. The consultant recommends that Ms. Joplin increase her production. The consultant must have concluded that, at her current level of production, Ms. Joplin's
A. total revenues equal her total economic costs.
B. marginal revenue exceeds her total cost.
C. marginal revenue exceeds her marginal cost.
D. marginal cost exceeds her marginal revenue,
C
Robin owns a horse stable and riding academy and gives riding lessons for children at "pony camp." His business operates in a competitive industry. Robin gives riding lessons to 20 children per month. His monthly total revenue is $4,000. The marginal cost of pony camp is $250 per child.
In order to maximize profits, Robin should
A. give riding lessons to more than 20 children per month.
B. give riding lessons to fewer than 20 children per month.
C. continue to give riding lessons to 20 children per month.
D. We do not have enough information to answer the question.
B
The accountants hired by Forever Fitness have determined total fixed cost to be $75,000, total variable cost to be $130,000, and total revenue to be $125,000. Because of this information, in the short run, Forever Fitness should
A. shut down because staying open would be more expensive.
B. lower their prices to increase their profits.
C. stay open because shutting down would be more expensive.
D. stay open because the firm is making an economic profit.
A
Which of the following is not an example of a barrier to entry?
A. Mighty Mitch'S Mining Company owns a unique plot of land in Tanzania, under which lies the only large deposit of Tanzanite in the world.
B. A pharmaceutical company obtains a patent for a specific allergy medication.
C. A musician obtains a copyright for their original song.
D. An entrepreneur opens a popular new hair salon.
D
Bob's Butcher Shop is the only place within 250 miles that sells bison burgers. Assuming that Bob is a monopolist and maximizing his profit, which of the following statements is true?
A. The price of Bob's bison burgers will be less than Bob's marginal cost.
B. The price of Bob's bison burgers will exceed Bob's marginal cost.
C. The price of Bob's bison burgers will equal Bob's marginal cost.
D. Costs are irrelevant to Bob because he is a monopolist.
B
A movie theater can increase its profits through price discrimination by charging a higher price to adults and a lower price to children if it
A. only shows G-fated movies.
B. has no monopoly pricing power.
C. cannot easily distinguish between the tio groups of customers.
D. can prevent children from buying the lower-priced tickets and selling them to adults.
D
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A. Monopolistic competition is different from monopoly because monopolistic competition is characterized by free entry, whereas monopoly is characterized by barriers to entry.
B. Both monopolistic competition and oligopoly fall in between the more extreme market structures of competition and monopoly.
C. Monopolistic competition is different from oligopoly because each seller in monopolistic competition is small relative to the market, whereas each seller can affect the actions of other sellers in an oligopoly.
D. Both monopolistic competition and perfect competition are characterized by product differentiation.
D
Which of the following is unique to a monopolistically competitive firm when compared to an oligopoly?
A. The monopolistically competitive firm advertises.
B. The monopolistically competitive fim produces a quantity of output that falls short of the socially optimal level.
C. Monopolistic competition features many buyers.
D. Monopolistic competition features many sellers.
D
A monopolistically competitive firm chooses
A. the quantity of output to produce, but all firms in the market agree upon a single price.
B. the price, but competition in the market determines the quantity.
C. the price, but output is determined by a cartel production quota.
D. the quantity of output to produce, but the price of its output is determined by demand.
D
A monopolistically competitive firm is currently producing 23 units of output. At this level of output, the firm is charging the highest price it can at S25, has marginal revenue equal to $19, has marginal cost equal to S19, and has average total cost equal to $22. From this information we can infer that
A. the firm is currently maximizing its profit.
B. the firm is earning zero profit.
C. increasing the quantity produced will raise per-unit costs.
D. firms are likely to leave this market in the long run.
A
In monopolistically competitive markets, free entry and exit suggests that
A. the market structure will eventually be characterized by perfect competition in the long run.
B. all firms earn zero economic profits in the long run.
C. some firms will be able to eam economic profits in the long run.
D. some firms will be forced to incur economic losses in the long run.
B
Hotels in New York City frequently experience an average vacancy rate of about 20 percent (i.e., on an average night, 80 percent of the hotel rooms are full). This kind of excess capacity is indicative of what kind of market?
A. Perfect competition and monopolistic competition
B. Perfect competition only
C. Monopolistic competition only
D. Oligopoly
C
If we observe a great deal more advertising for Mucinex, an over-the-counter drug, than for a Grainger drill press, we can infer that
A. more money is spent on Mucinex than on Grainger drill presses.
B. the market for Mucinex is more highly differentiated than the market for Grainger drill presses.
C. Grainger has lower costs of production than Mucinex.
D. Mucinex operates in an oligopoly, while Grainger operates in a monopolistically competitive market.
B
A law that restricts the ability of hotels/motels to advertise on billboards outside of a resort community would likely lead to
A. no change in profits for all hotels/motels.
B. reduced efficiency of local lodging markets.
C. a request by consumers to increase the number of billboards.
D. increased price competition among hotels/motels in the community.
B
Adibok knows that it produces and sells high-quality athletic shoes. Wurkout knows that it produces and sells low-quality athletic shoes. According to the signaling theory of advertising,
A. both Adibok and Wurkout have incentives to spend large amounts of money on advertising for their athletic shoes.
B. Adibok has an incentive to spend a large amount of money on advertising for its athletic shoes, but Wurkout does not.
C. Wurkout has an incentive to spend a large amount of money on advertising for its athletic shoes, but Adibok does not.
D. neither Adibok nor Wurkout has an incentive to spend a large amount of money on advertising for their athletic shoes.
B
Suppose that Zion and Haidy are duopolists in the music industry. In May, they agree to work together as a monopolist, charging the monopoly price for their music and producing the monopoly quantity of songs. By June, each singer is considering breaking the agreement. What would you expect to happen next?
A. Zion and Haidy will determine that it is in each singer's self-interest to maintain the agreement.
B. Zion and Haidy will each break the agreement. Both singers' profits will decrease.
C. Zion and Haidy will each break the agreement. Both singers' profits will increase.
D. Zion and Haidy will each break the agreement. The new equilibrium quantity of songs will increase, and the new equilibrium price also will increase.
B
As the number of firms in an oligopoly increases,
A. the output effect decreases,
B. the oligopoly has more market power and firms earn a greater profit.
C. the price approaches marginal cost.
D, the price of the product greatly exceeds marginal cost.
C
Two suspected drug dealers are stopped by the highway patrol for speeding. The officer searches the car and finds a small bag of marijuana and arrests the two. During the interrogation, each is separately offered the following: "If you confess to dealing drugs and testify against your partner, you will be given immunity and released while your partner will get 10 years in prison. If you both confess, you will each get 5 years," If neither confesses, there is no evidence of drug dealing, and the most they could get is one year each for possession of marijuana. If each suspected drug dealer follows a dominant strategy, what should they do?
A. Confess regardless of the partner's decision
B. Confess only if the partner confesses
C. Don't confess regardless of the partner's decision
D. Don't confess only if the partner doesn't confess
A
In a prisoners' dilemma game,
A. the solution when playing the game once will be the same as the solution when the players play the game repeatedly, since agreements cannot be maintained in a prisoners' dilemma.
B. if the players play the game repeatedly, the players can achieve a higher payoff, on average, than when they play the game only once.
C. repeated play will result in a worse outcome for both players than when the game is played only once.
D. the tit-for-tat strategy in repeated play requires players to always select the opposite strategy as their opponent.
B