lec 24 - targeted therapies
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
cancer has been traditionally treated with
radiation therapy
surgery
chemotherapy - targeting proliferating cells
gardasil
vaccine that targets HPV 6,11,16,18
HPV16 and 18 cause 70% of cervical cancer and 6 and 11 cause 90% of genital warts
virus-like particle vaccine - contains purified inactive HPV proteins made in yeast cells using recombinant viral material, non-infectious
elicit strong T and B cell response - development of antibodies against HPV 6,11,16,18
herceptin
targets HER2 proteins
also erB2 - receptor tyrosine kinase, erBs are receptors for neurogulins
found on normal cells but more receptors on tumour cells as a result of gene amplification
erB2 is a monoclonal antibody stopping normal ligand so cant get growth factor and will die
normal process that RTKs and growth factors involved in
growth factors bind to the receptor tyrosine kinase intracellular domain
signal transducing proteins go to nuclear transcription factors
entry to cell cycle
growth receptor specific antibodies
many receptors expressed by cells
different antibodies can target each receotor and stop the normal ligand from binding stopping the normal signaling pathway from happening
targeted therapy for ER+ breast cancer
tamoxifen is a selective estrogen receptor (ER) modulator
it blocks the action of estrogen
binds ERs and prevents estrogen from binding
breast cancer cells that require estrogen (ER+) are therefore not able to grow
tyrosine kinase inhibitors
normally RTKs trigger downstream signalling cascades which act on cell processes such as proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and angiogenesis
many places to block
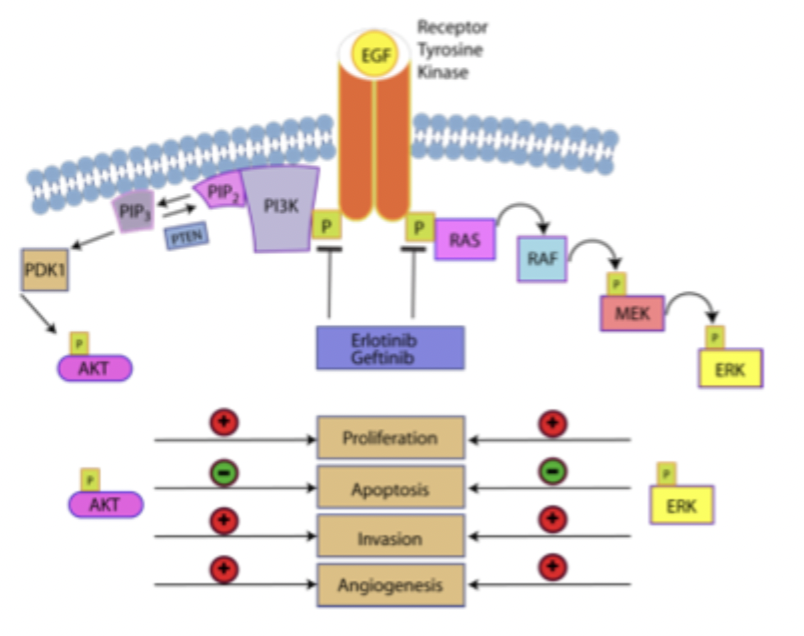
other tyrosine kinase inhibitors
MET TKIs
EGFR TKIs
IGF1R TKIs
VEGF receptor inhibitors - inhibit angiogenesis
specific pathway inhibitors
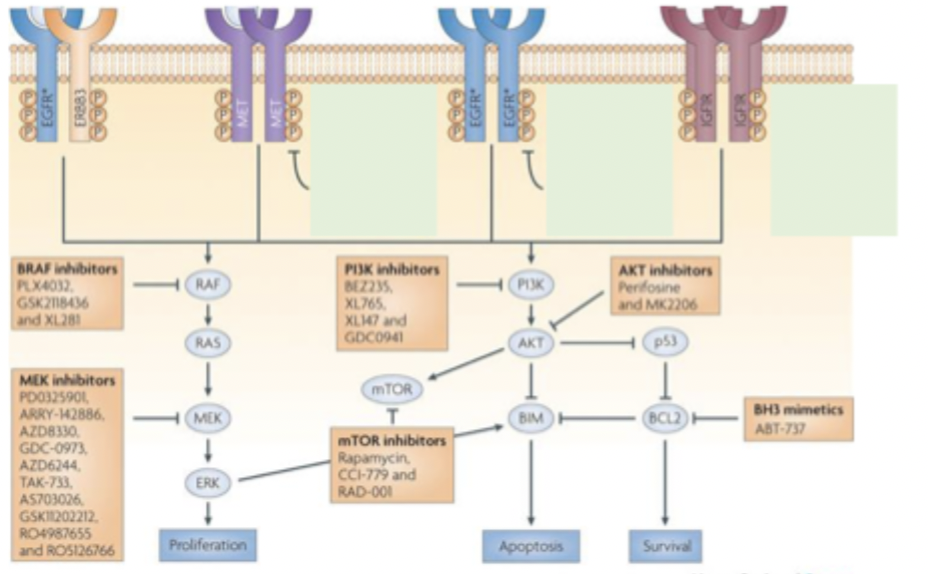
all of these steps have specific inhibitors that are there to target them but in NZ most of these are not funded - stops increased specificity of treatments
ideally would be able to target the most ideal treatment based on the patient and their specific mutation
vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors
targeting VEGF and VEGF-receptor which are upregulated in cancer
bevacizumab, sunitinib, sorafenib
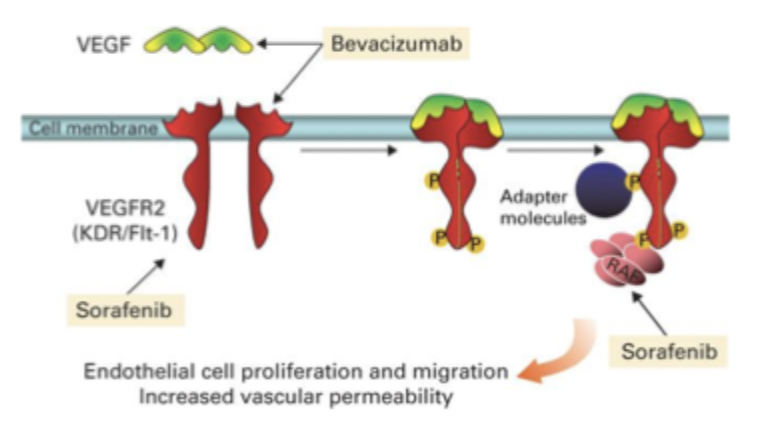
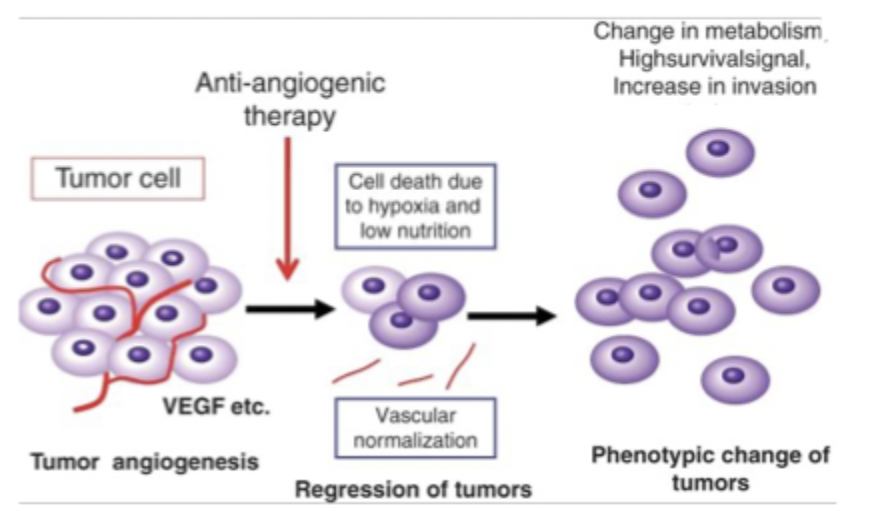
resistance
after long term therapy cells become resistent to anti-angiogenic (VEGF) treatments
change in metabolism, highsurivialsignal, increase in invasion
problems with telomerase inhibitors
stem cells have continual expression of telomerase and could theoretically be adversely affected by treatment with telomerase inhibitors
chronic myeloid leukaemia
due to translocation
encodes a constituatively expressed BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase
this leads to a creation of a fusion protein which is active in RAS, STAT and AKT pathways, all of which lead to growth factor independant proliferation and survival
medication for BCR-ABL gene
gleevec
in trials 31/31 patients showed complete remission (note as this was extended the rate dropped from 100% but still very high)
now being tested on other cancers such as melanoma
oncotype Dx breast cancer recurrence score
PCR based quantification of tumour mRNA (21 genes)
look at markers for proliferation, invasion, HER2, estrogen, reference and other to provide a score
<18 is low recurrent risk >25 is high recurrence risk
pietenpol TNBC subtyping
for cancers that dont have known receptors etc to help with clinical decisions
broader impacts of profiling cancer genomes
Idea that if we can profile tumours we can make really informed decisions about treatment and a care plan
genomic profile from tumor indicates a known vulnerability that we can target
immunotherapy
immune system DOES recognise own cancer cells
imune response is normally suppressed by cytokines secreted by the tumour
research into boosting the immune response
goal is to use this as an adjuvant therapy
the cancer immunity cycle
the development of immunity to cancer is a cyclic event
release of cancer antigens by dying cells
presentation of antigen by APCs
priming and activation of APCs and T-cells
trafficking of cytotoxic T lymphocytes
infiltration of tumour cells
recognition of cancer cells by T cells
killing of cancer cells
what are immune checkpoints
inhibitory pathways that maintain self tolerance
A way that a cancer cell will evade immune recognition
Cell expresses antigen that binds to TCR and also expresses ligand that will bind to CD1 on T cell
This makes T cell think it is a good cell so lets it proliferate
programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1)
CTLA4
mechanism of PD-1/PD-L1 therapies
tumour cells upregulate PD-L1 (ligand) that binds to PD-1 and turns T cells offso that they do not see tumour cells as non-self
anti PD therapies blocks the PD-L1/PD-1 interaction so that T cells are now able to see tumour cells as non self
pembrolizumab - plus can now treat other cancers
strategies for development of new checkpoint blockade therapies
identification of neo-antigens on tumour cells - personalised neovaccines
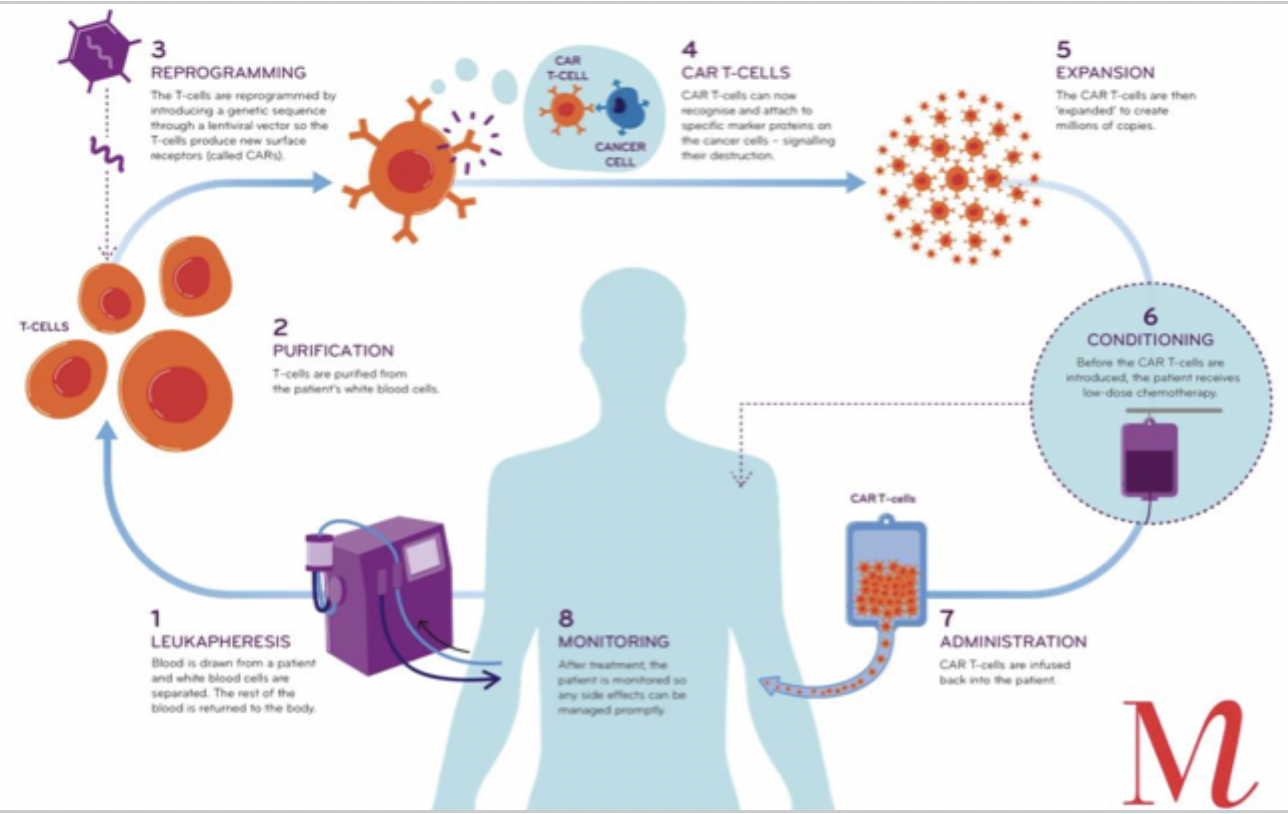
adoptive immunotherapy - modification of patient-derived CTLs to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) that bind to tumour antigens
production of CAR T-cells
drugs targeting the cancer immunity cycle
concept that drugs have been developed to target each one of the steps for the cancer immunity cycle
so lots of options to treat different cancers
epigenetics - what
modification of gene expression without altering genetic code
DNA methylation by DNA methyl transferases → gene silencing - normally CpG islands (a C followed by G at TSS 5’) are unmethylated
hypermethylation of CpG islands occurs in many cancers → gene silencing - ESR1 (estrogen response gene), BRCA1 (DNA repair genes)
histone acetylation by histone acetyltransferases
miRNA binding
types of epigenetic therapies
HDAC inhibitors
DNMT inhibitors
combination with other therapies - ESR-1 (endocrine therapy), HER2 (antibody), chemotherapy
miRNA
malignant pleural mesothelioma
80-90% of people diagnoses with MPM have been exposed to asbestos
mechanics working with brake linings
insulators
builders
20-40 year latency following inhalation
miRNA therapy for MPM
miRNAs target pathways that are known to be involved in MPM - miR-185 targets DNMT1/PTEN/Akt pathway that is normally activated in MPM (suppresses inflammation)
miR-15b is downregulated in MPM
miR-126 targets include VEGF-A which is involved in angiogenesis
hallmarks of cancer
inducing angiogenesis
resisting cell death
deregulating cellular energetics
sustaining proliferative signalling
avoiding immune destruction
evading growth suppression
enabling replicative immortality
tumour promoting inflammation
activating invasion and metastasis
genome instability and mutation