BIOL 212: Test 1 (ch 1,2,3)
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 1. Microbial World, Ch 2. Bacteria, Ch 3. Eukaryal Microbes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
False Positive
an observed positive result in a sample that was expected to be negative.
False Negative
An observed negative result in a sample that was expected to be positive
Sensitivity
The limit of detectability within a test
Specificity
the limit of discrimination within a test
Control
A known entity with a predictable/known outcome
Sensitivity issue
A false negative result is always a ________ _____.
Specificity issue
A false positive is always a ________ ____.
Unknown
A sample whose outcome or value must be determined (ex. collecting microbes to be compared to the control in the future)
Ubiquity
Can be found just about everywhere
Pathogens
Organisms that are known to cause disease
Nonpathogenics
Organisms that are not known to cause disease
Opportunistic pathogen
A microorganism not ordinarily thought of as pathogenic that will cause infection when out of its normal habitat (ex. enteric bacteria)
Enteric bacteria
Infomal name for bacteria in intestinal tract
Host
An organism that serves as a habitat for another organism such as a parasite or commensal
Commensal
synergistic relationship between two organisms neither positively or negatively
mutualism
synergistic relationship between teo organisms in which both benefit the interaction
Reservoir
a nonhuman host or other site in nature serving as a perpetual source of pathogenic organism
Free-living
does not reside on or in a specific host
Date, name, temperature
What information should be labeled on the bottom petri plates? Hint: three things
Agar
What is the jello-like thing in a petri dish?
37C
Microorganisms on the fingers, nose, and mouth grow best in what temperature (C)?
25C
Microorganisms on the desk, air, soil, and leaf grow best in what temperature (C)?
Hyperthermophiles
Microbe that grows best in 65C ~ 115C
Thermophiles
Microbe that grows best 42C ~ 80C
Autoclave Sterilizers
Machine that sterilizes used petri dishes
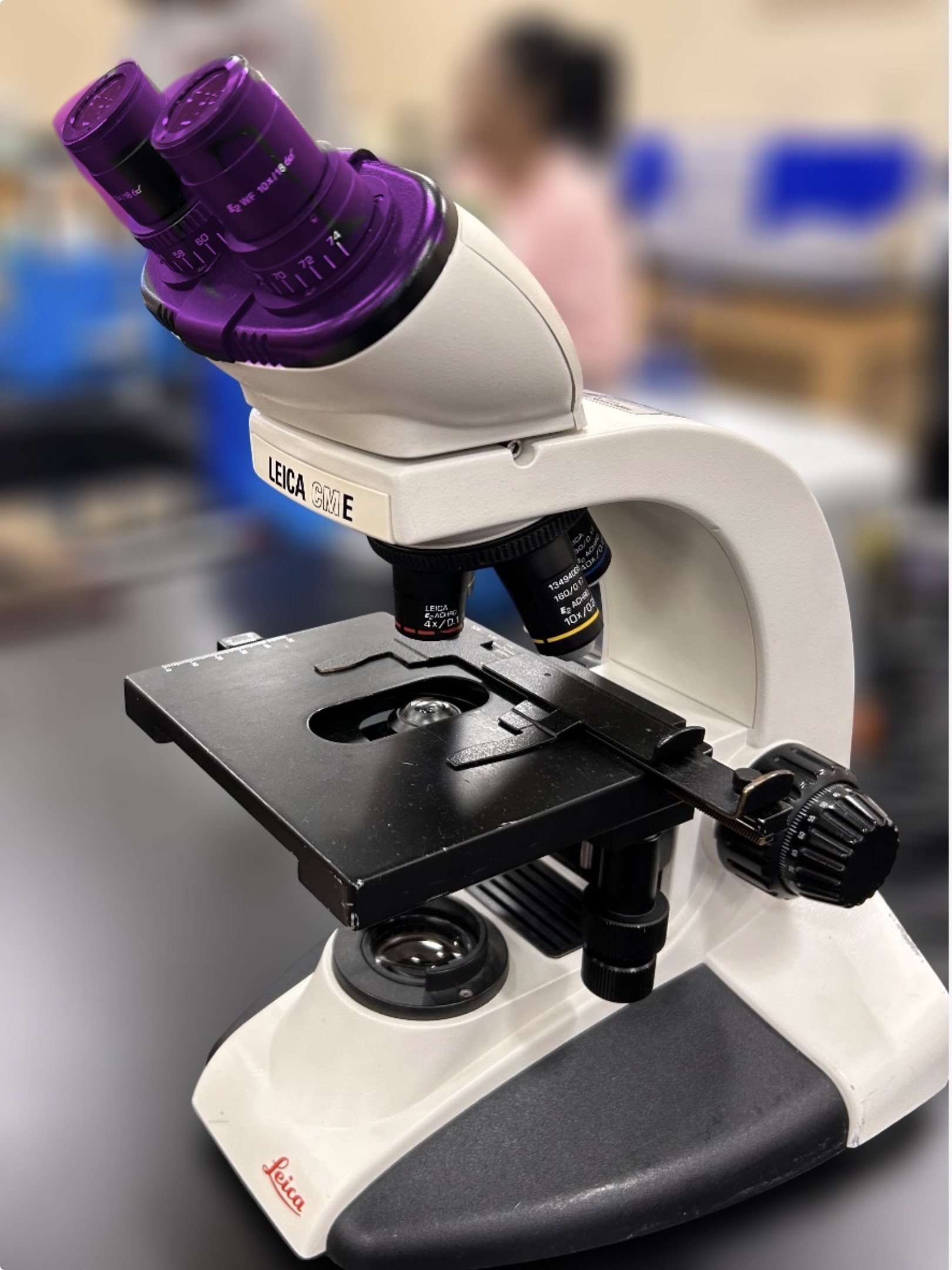
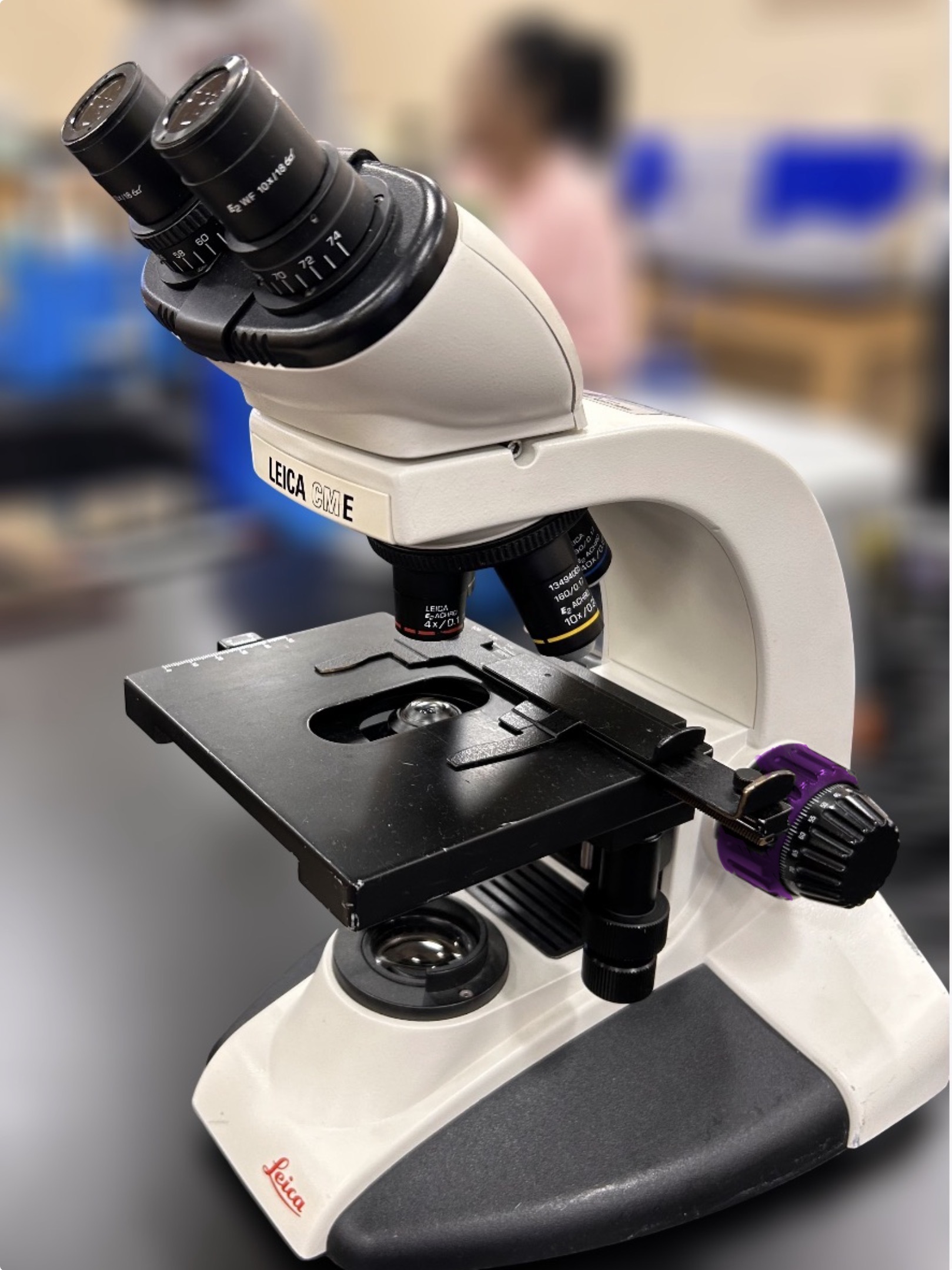
Ocular lens
Name the highlighted region.
HINT: the lens through which the microscopist looks through—-produces the virtual image by magnifying the real image

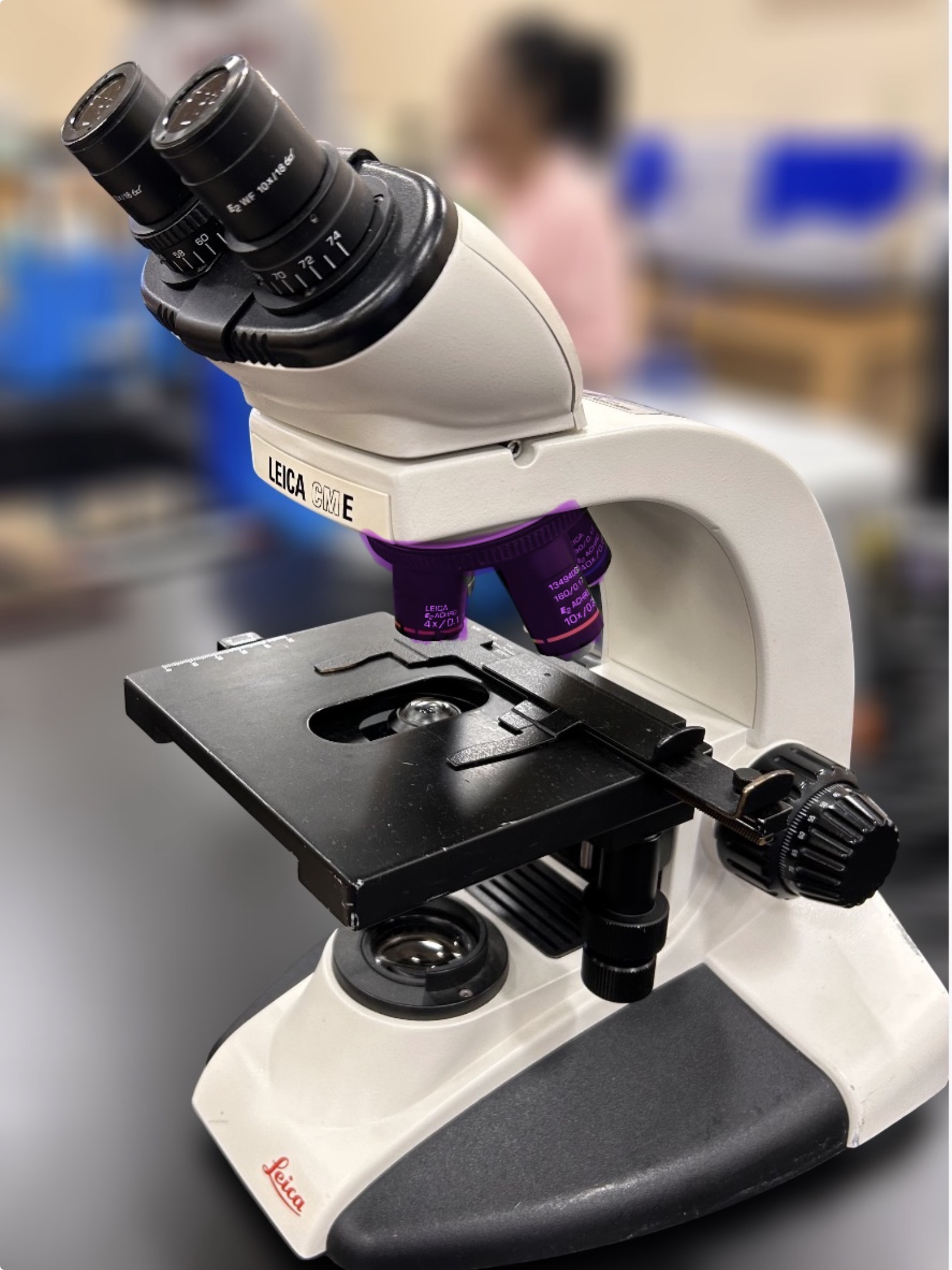
Objective lens
Name the highlighted region.
Hint: the microscope lens that first produces magnification of the specimen in a compound microscope

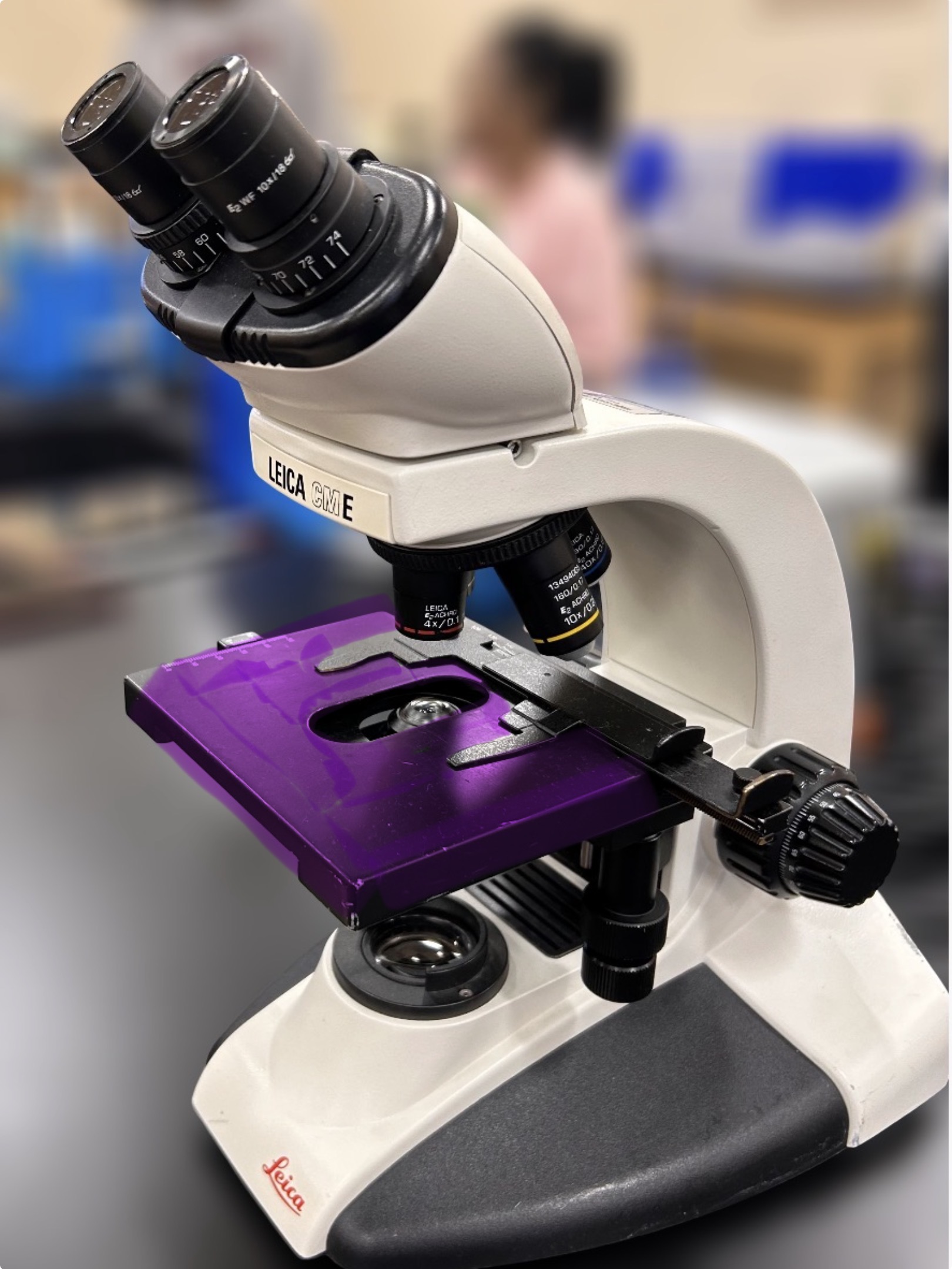
Stage
Name the highlighted region.
Hint: where the object is placed to be viewed

4x, 10x, 40x, 100x
What are the four magnifications of objective lens?
Stage clamps
Name the highlighted region.
Hint: holds the object in place.
Course focus knob
Name the highlighted region.
Hint: used to find the image

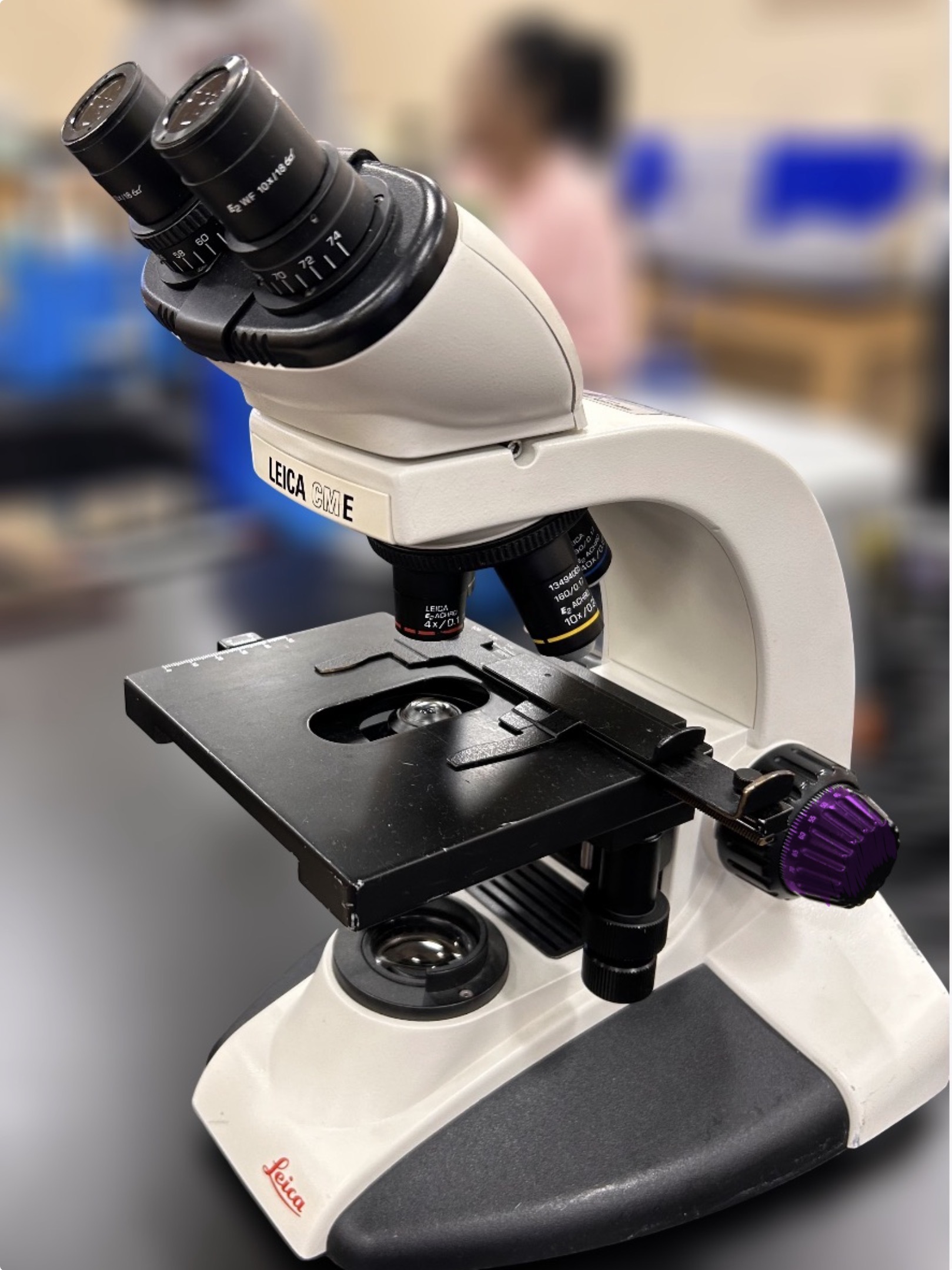
Fine focus knob
Name the highlighted region.
Hint: used to find the fine image

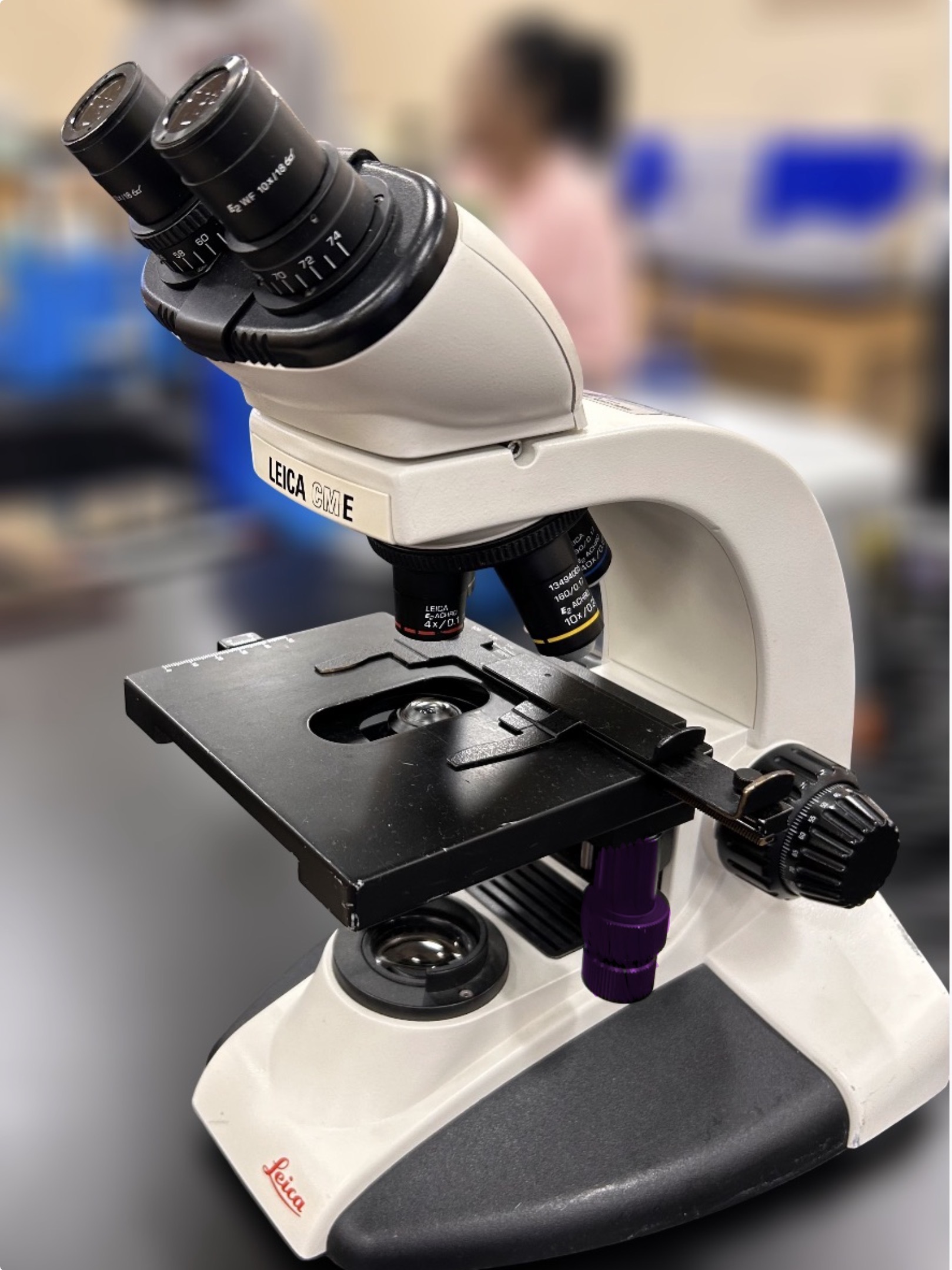
Mechanical stage adjustment knobs
Name the highlighted region.
Hint: top part moves stage front/back, bottom part moves stage left/right

Iris diaphragm
Name the highlighted region.
Hint: light should be at a minimum (closed)
Condenser
Name the highlighted region.
Hint: the lens that concentrates the light from the light source and makes illumination of the specimen more uniform.
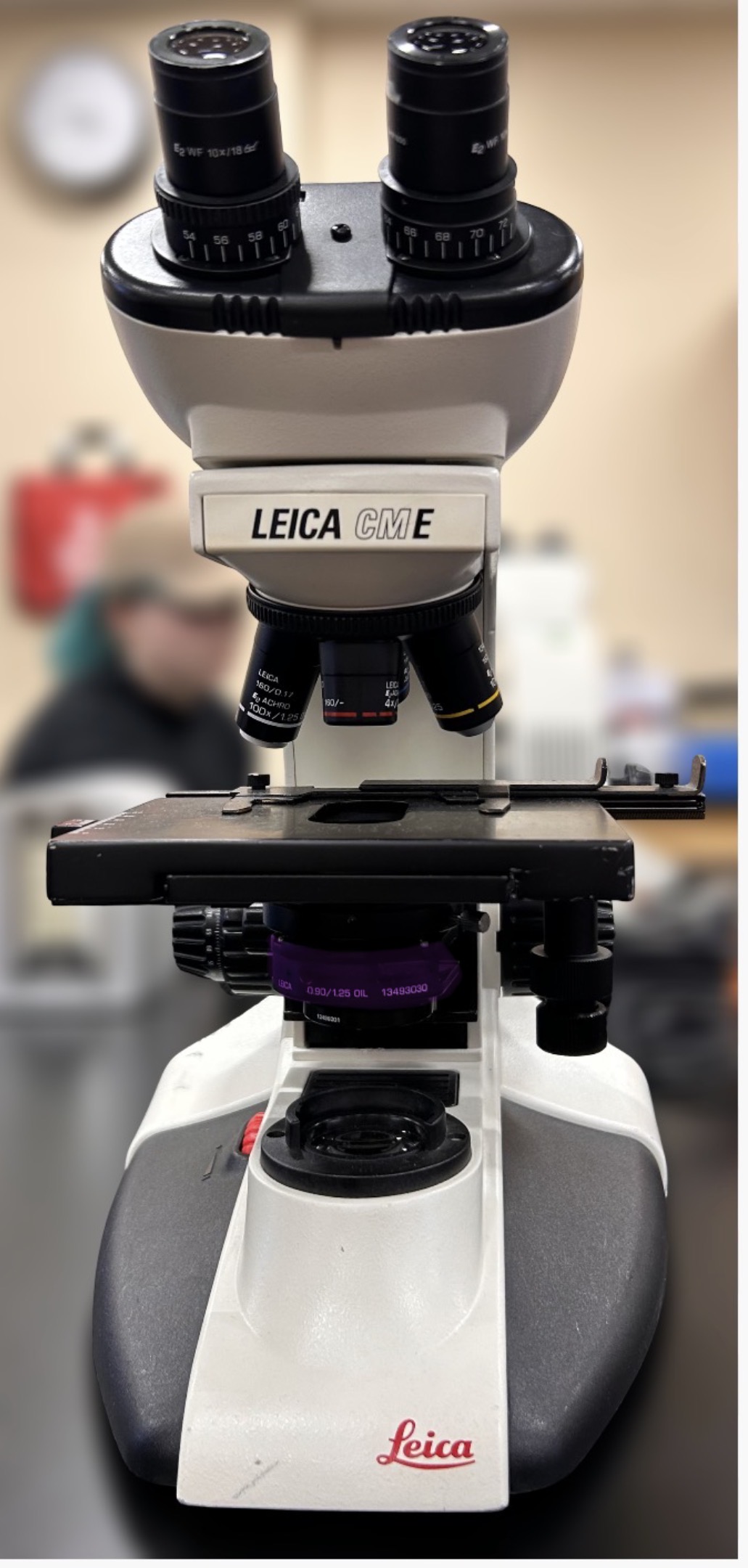

Lamp
Name the highlighted region.
Hint: shines light upwards to view image
Virtual image
Image produced when the ocular lens of a microscope magnifies the real image
Real image
Magnified image of a specimen produced from the objective lens of a microscope
Magnification object, magnification ocular
What two things are multiplied together to produce the TOTAL MAGNIFICATION?
100x
Which objective len magnification required oil immersion?
Numerical aperture
A measure of the len’s ability to capture light combing from the specimen and use it to make a image
Resolution
The clarity of an image produced by a lens
Limit of resolution
The closest two points can be together for the microscope lens to make them appear separate
Limit of resolution
What is this equation calculating?
D = wavelength (nm) / NA condenser + NA objective
Shorter
Do shorter or longer wavelengths produce a clearer image? Not including wavelengths <360nm
Bright field microscopy
What type of microscopy do we use in class?
Hint: light passes through the background unimpeded
Dark field microscopy
What type of microscopy do we NOT use in class?
Hint: uses a condenser that diminishes light that passes through the background
Phase contrast microscopy
Name the type of light microscopy that uses a contrast to view the cytoplasmic components
Fluorescence microscopy
What type of light microscopy uses fluorescent dye that emits “glow in the dark effect” with ultraviolet radiation?
400 nm to 700 nm
What is the visible wavelength of light?
Domains
A broad classification of all organisms based on the sequence of nucleotides in rRNA. Three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya
Endosymbiotic Theory
The theory whereby a primitive prokaryote was engulfed by a larger prokaryote that led to the formation of eukaryotic cells
Trophozoite
Feeding stage in the life cycle of certain protozoans
Pseudopods
Extensions of cytoplasm from amoebae that are used for movement as well as as engulfing prey
Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
Mnemonic: King Philip Came Over From Germany Swimming
Penicillium
Identify the fungi
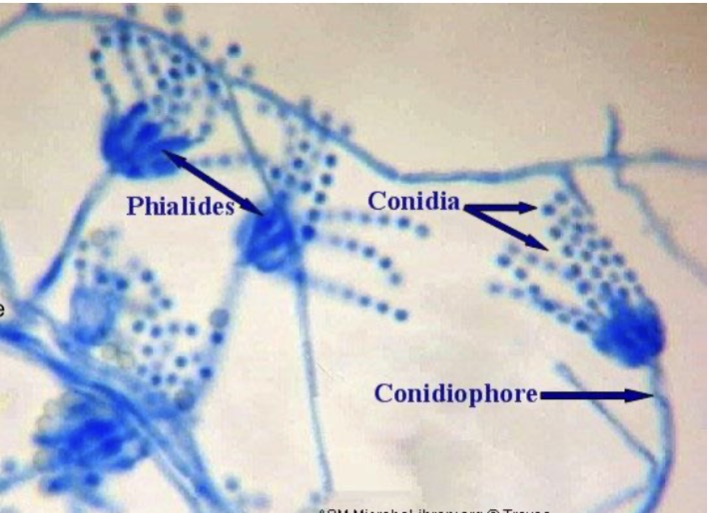
Aspergillus
Identify the fungi
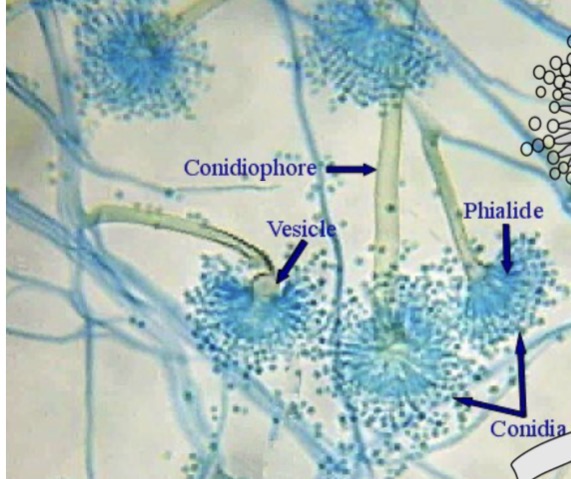
Rhizopus
Identify the fungi. Is asexual
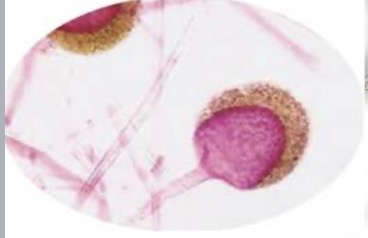
Rhizopus
Identify the fungi. Is sexual
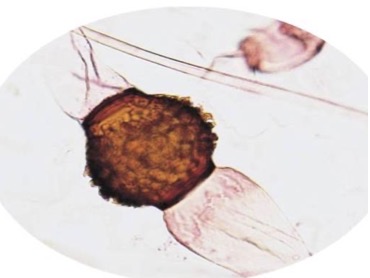
Penicillin
Identify the fungi
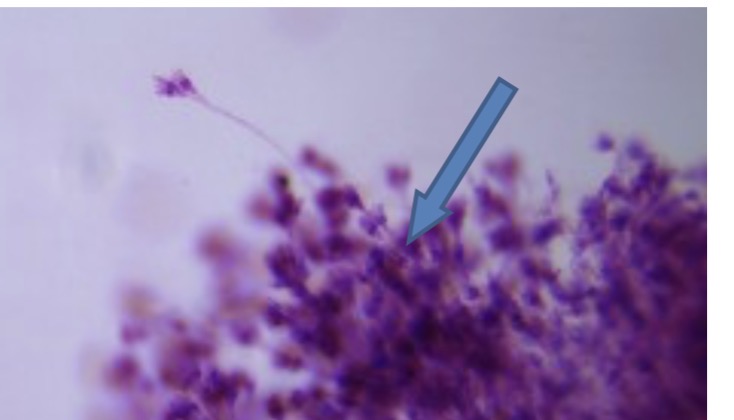
Candida albicans
Identify the fungi
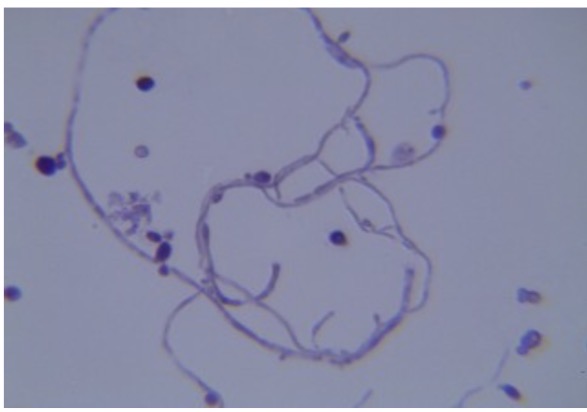
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Identify the fungi
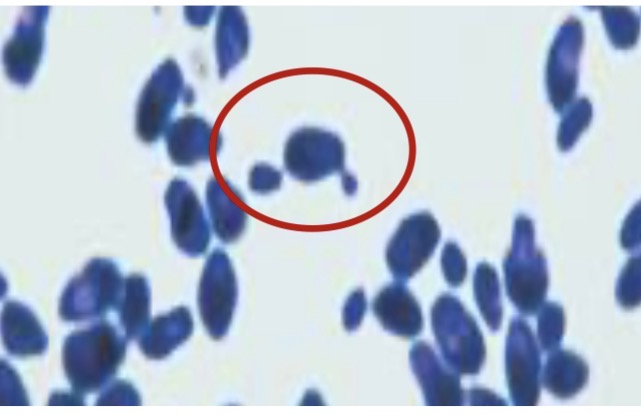
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Identify the fungi
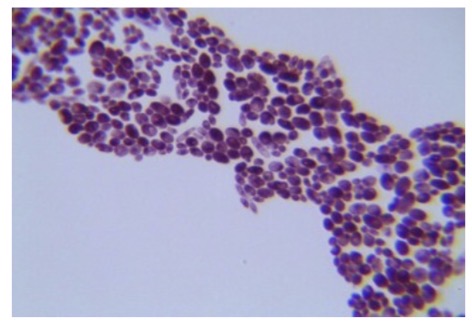
Plasmodium falciparum
Identify the alveolates. Causes malaria
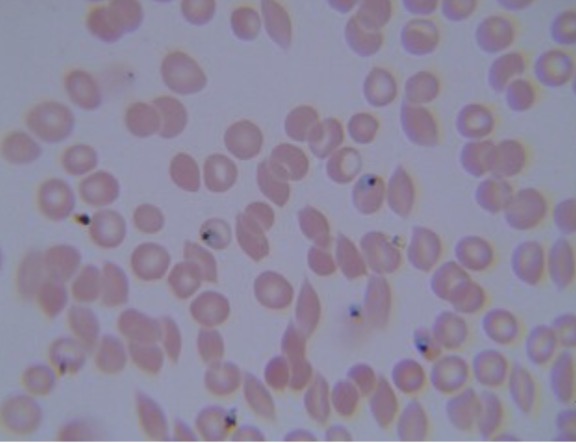
Trypanosoma cruzi
Identify the kinetoplastid. Causes Chagas’ disease
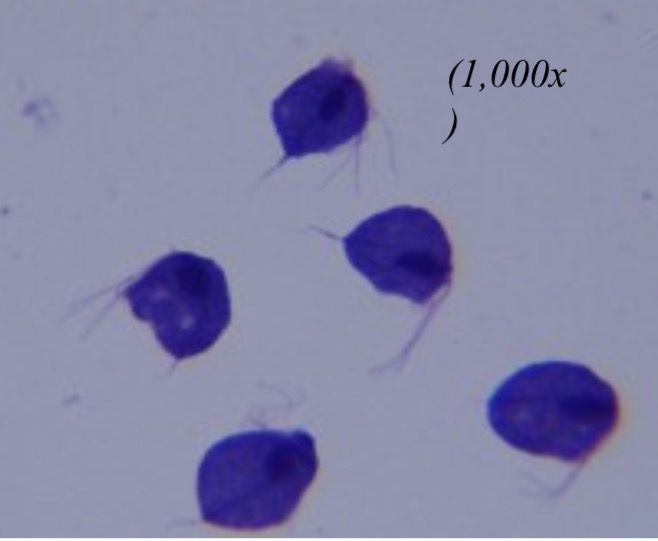
Trichomonas vaginalis
Identify the parabasalid. Is an STD
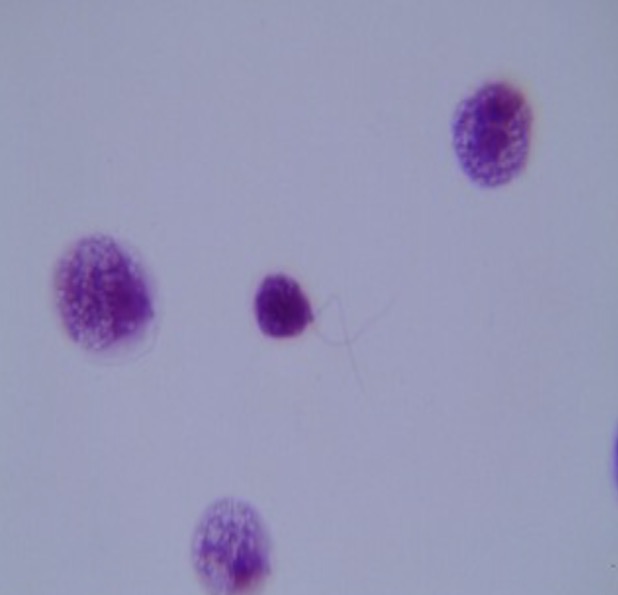
Chlamydomonas
Identify the chlorophyta
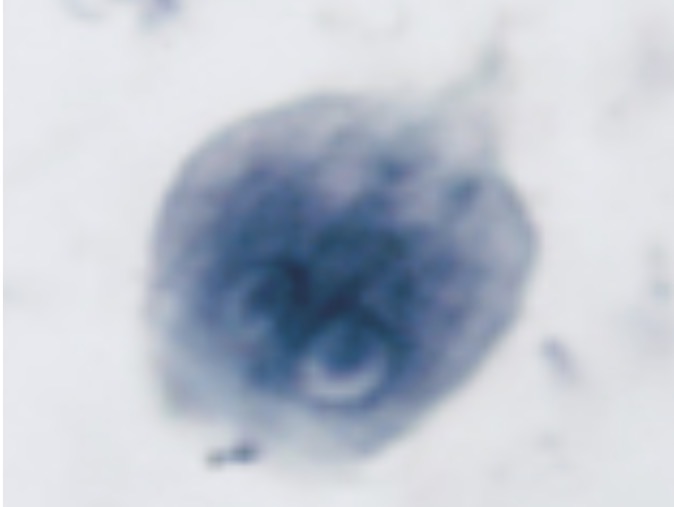
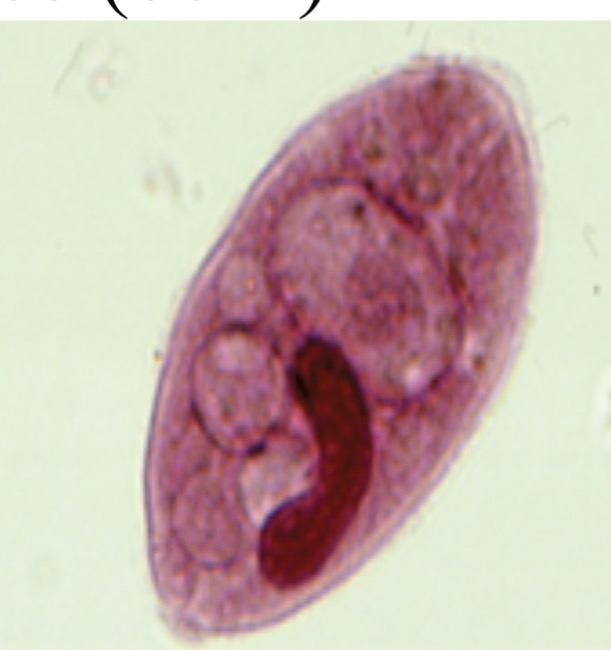
Giardia lamblia
Identify the diplomonad. Most common intentional parasitic disease affecting humans
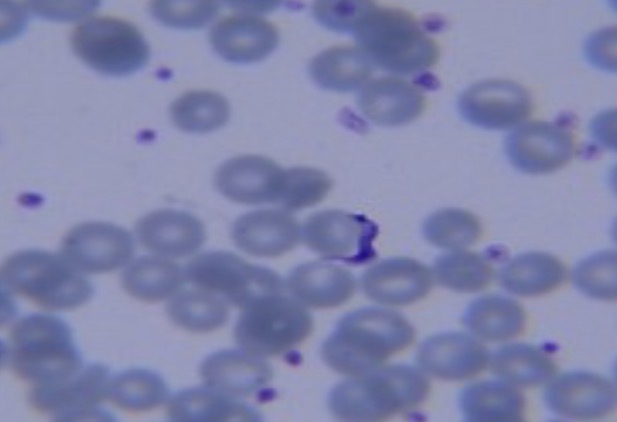
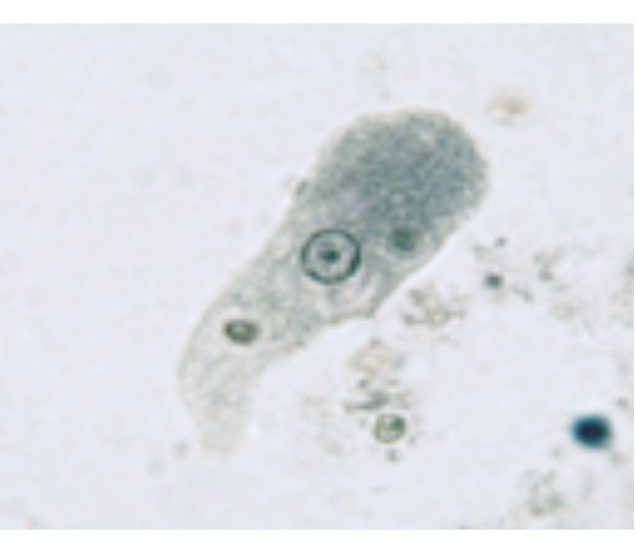
Entamoebas histolytica
Identify the entamoeba. Is parasitic and causes amoebic dysentery
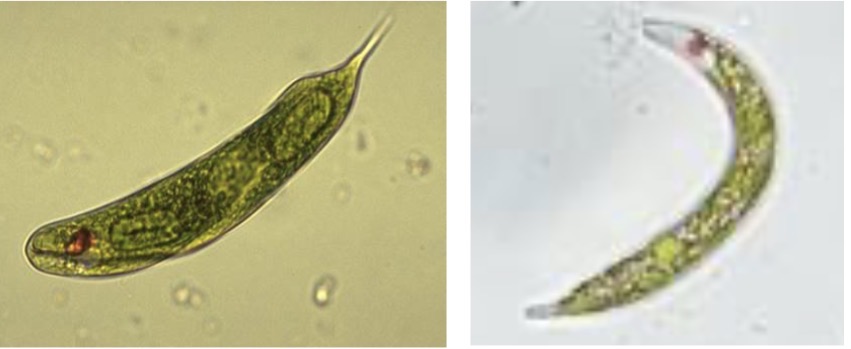
Euglena
Identify the euglenozoan
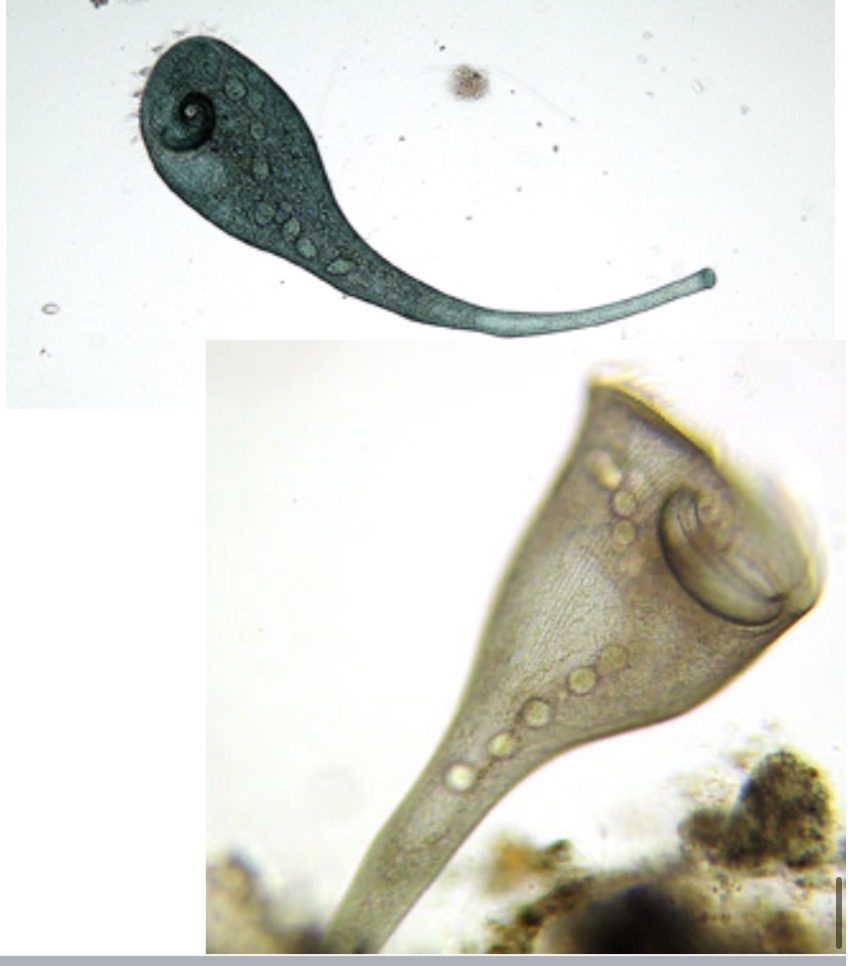
Stentor
Identify the alveotate
Balantidium coli
Identify the alveolate
Diatoms
Identify the stramenophile
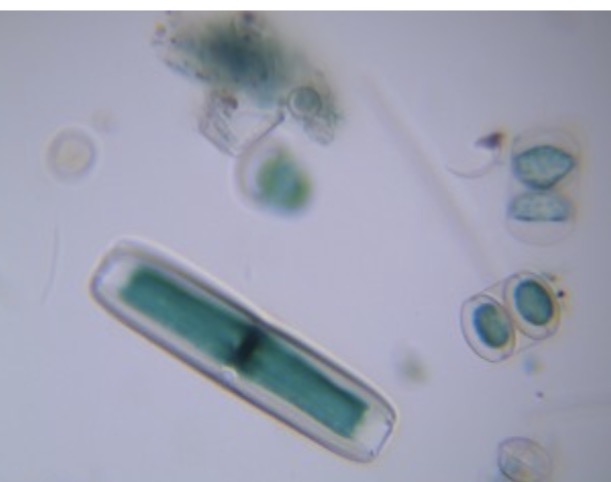
Spirogyra
Identify the charophyte
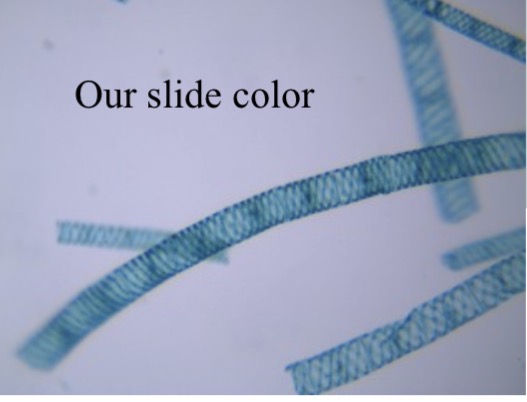
Spirogyra conjugation
Identify the charophyte
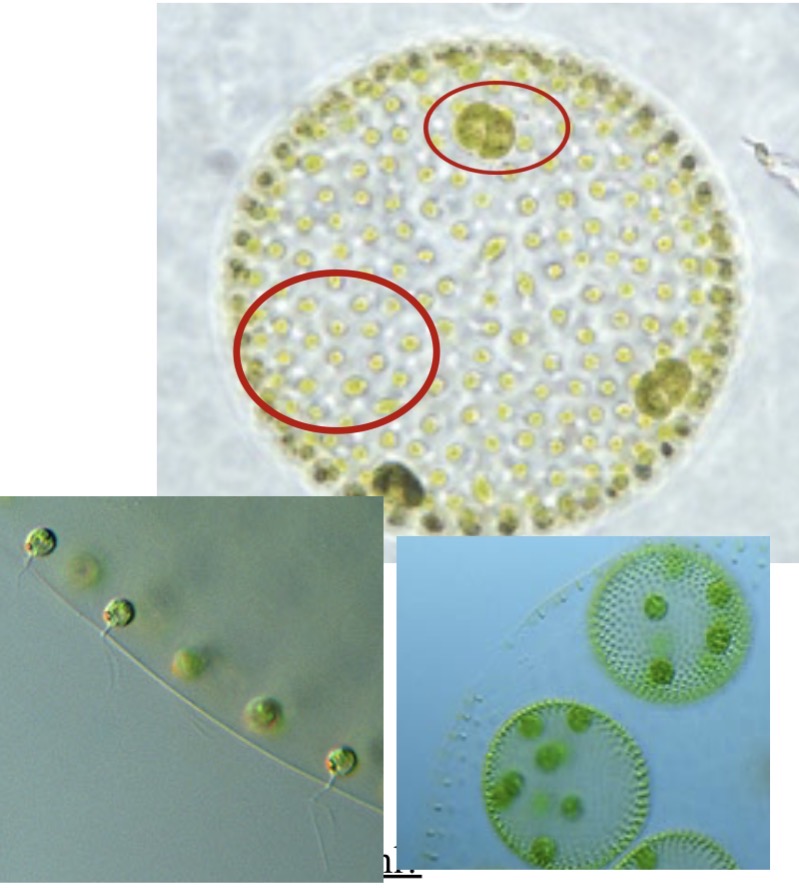
Volvox
Identify the chlorophyte
Paramecium
Identify the alveolate
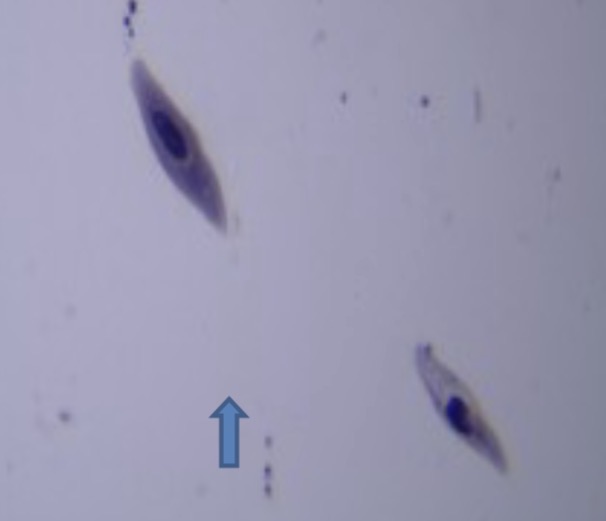
Amoeba proteus
Identify the gymnamoebas
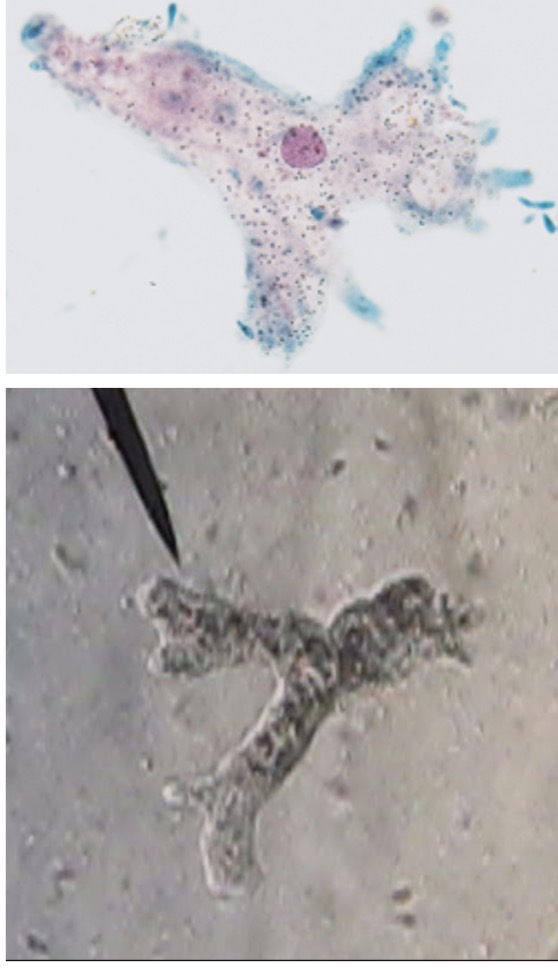
Hyphae
A filament (of filaments)of fungal cells
Yeast
Informal grouping of unicellular fungi