bio practicum #1
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
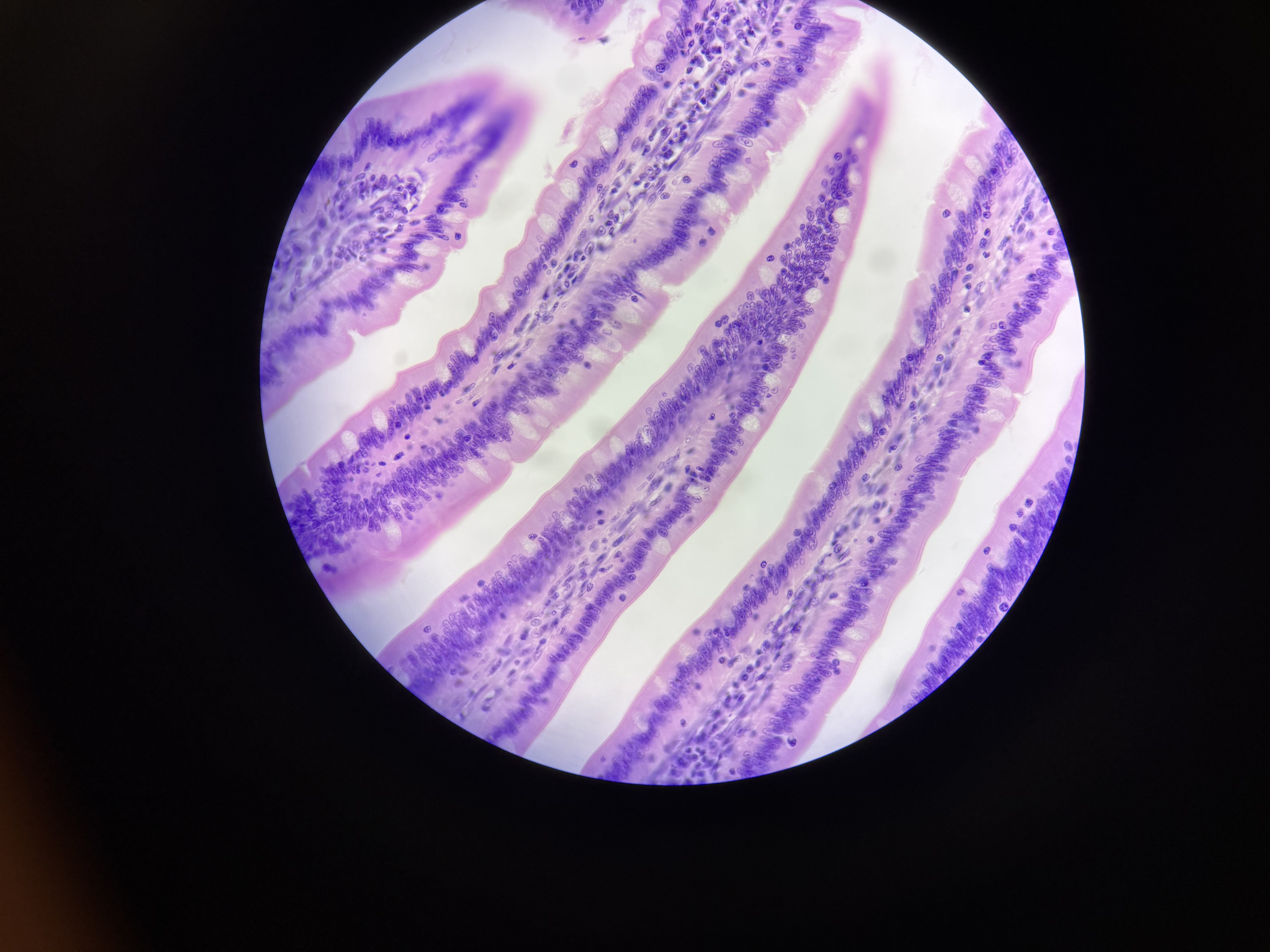
stratified squamous epithelial
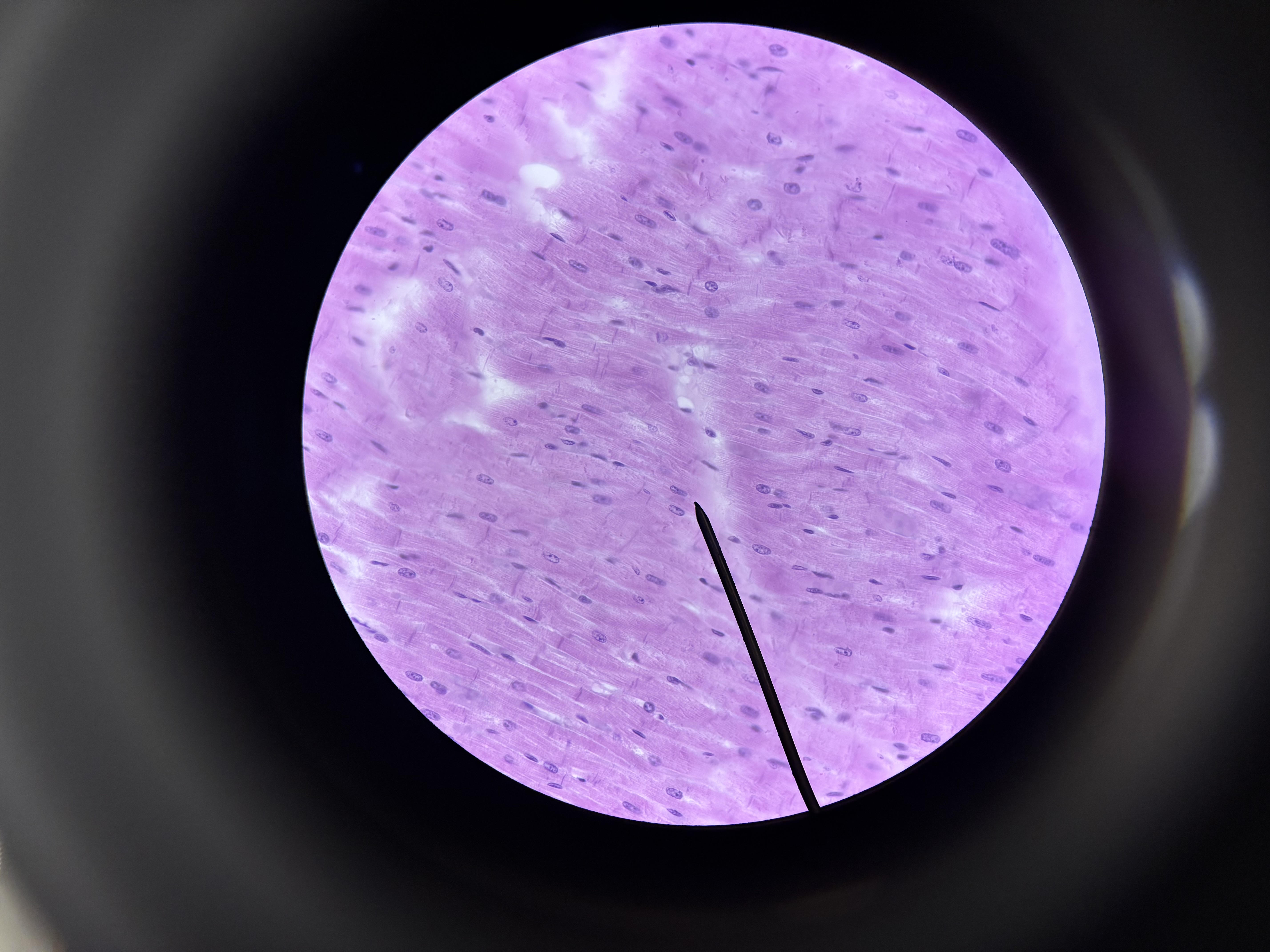
smooth muscle
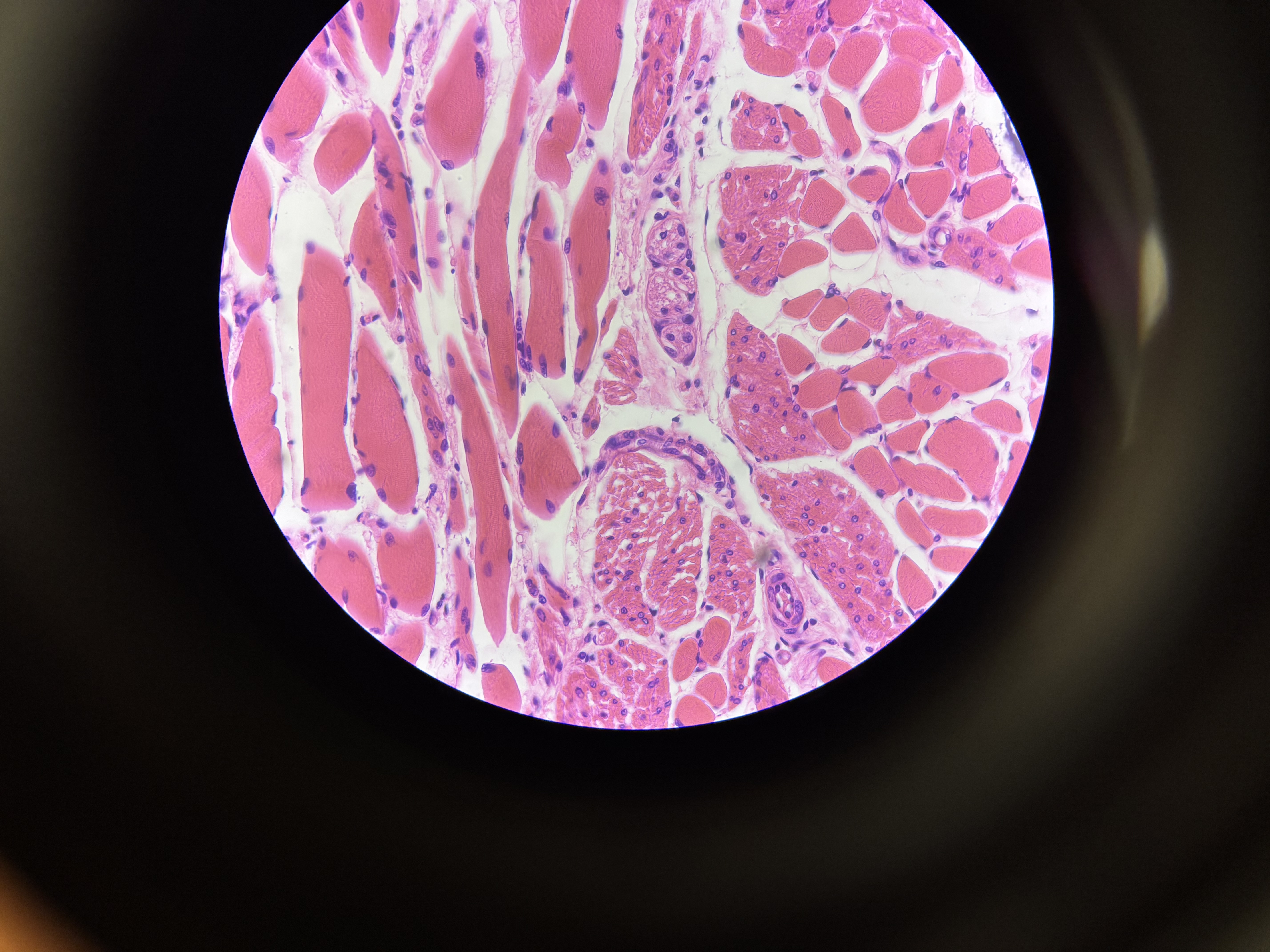
cardiac muscle
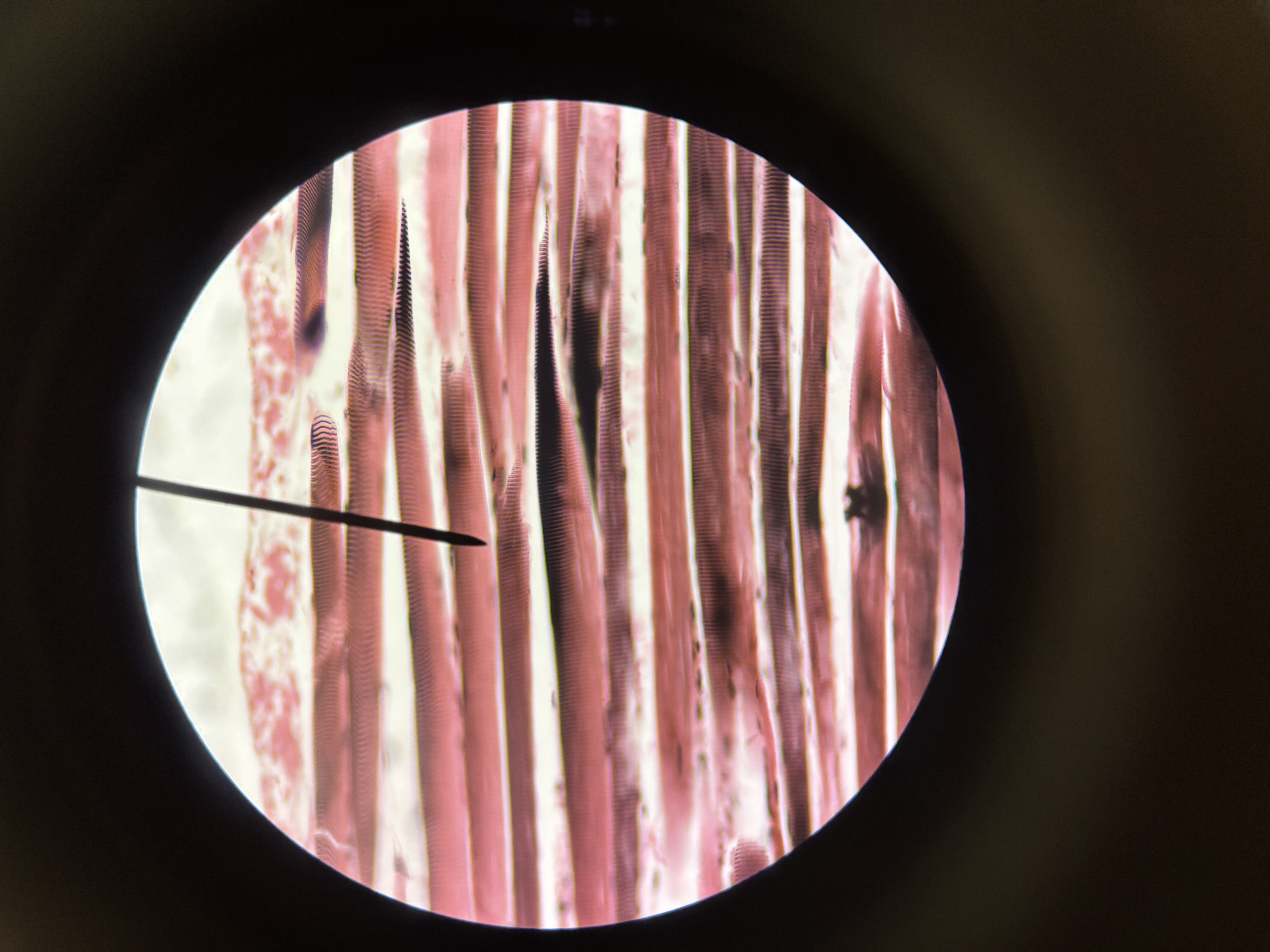
skeletal muscle
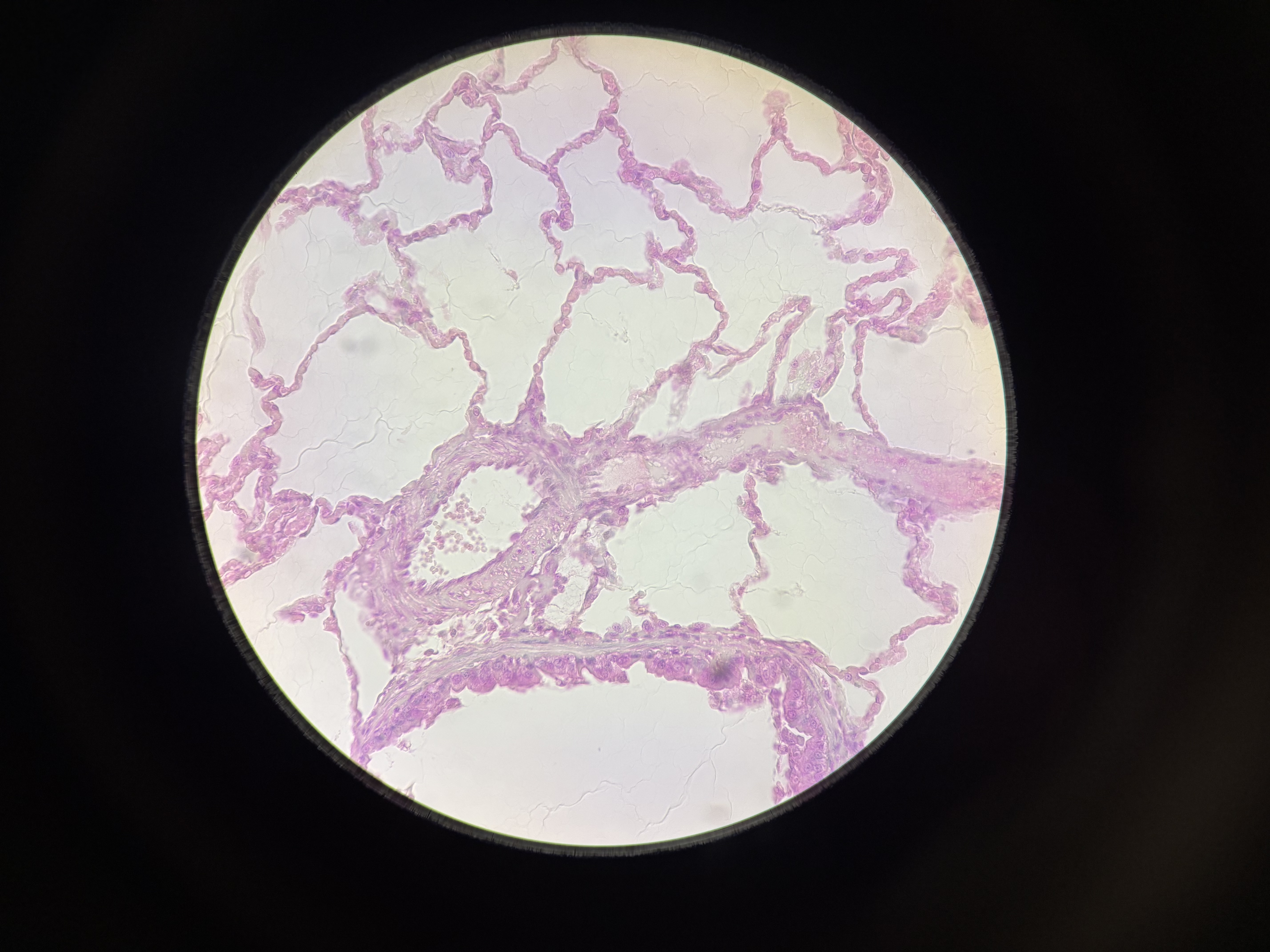
simple squamous epithelial
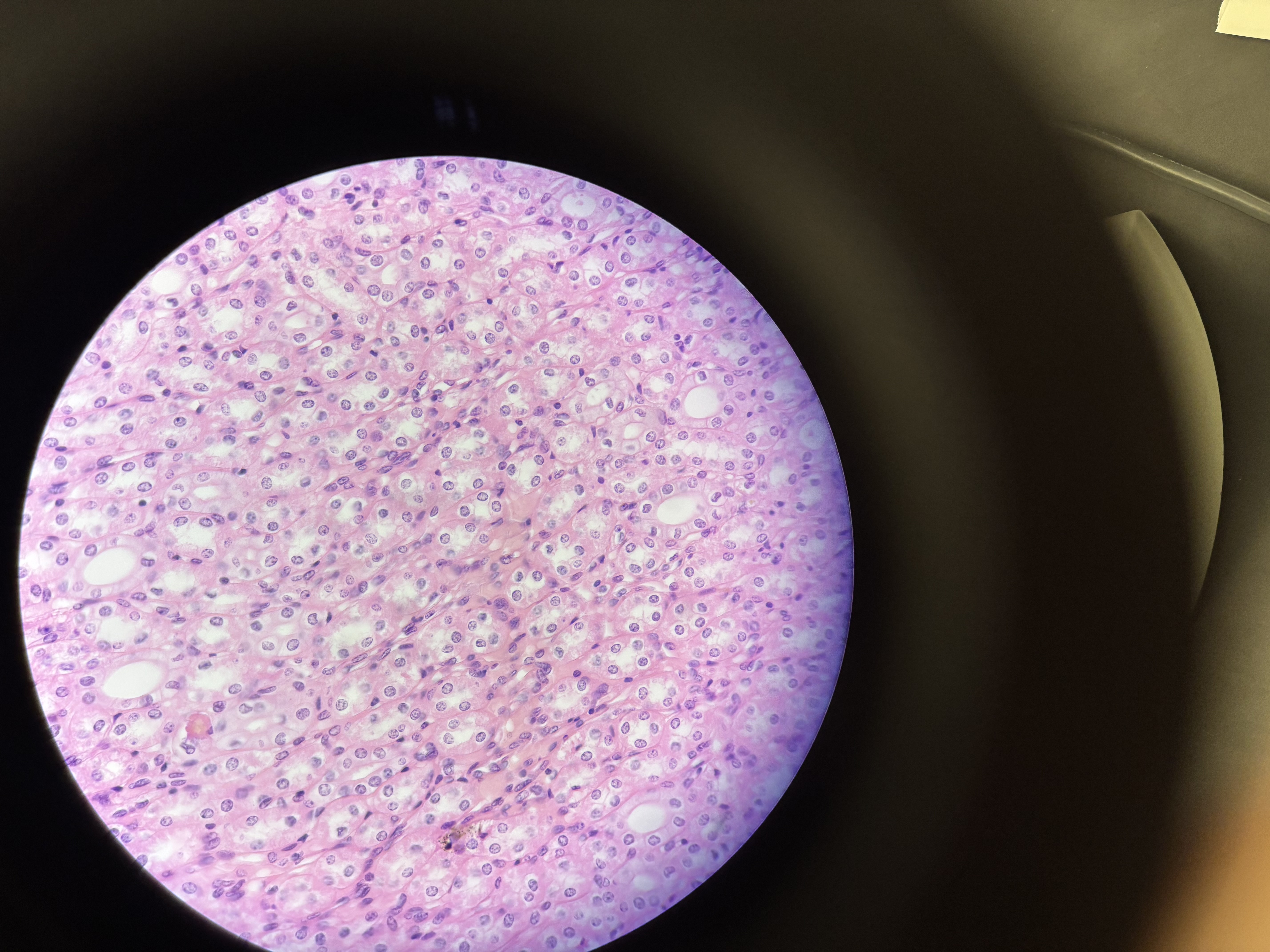
simple cuboidal epithelial
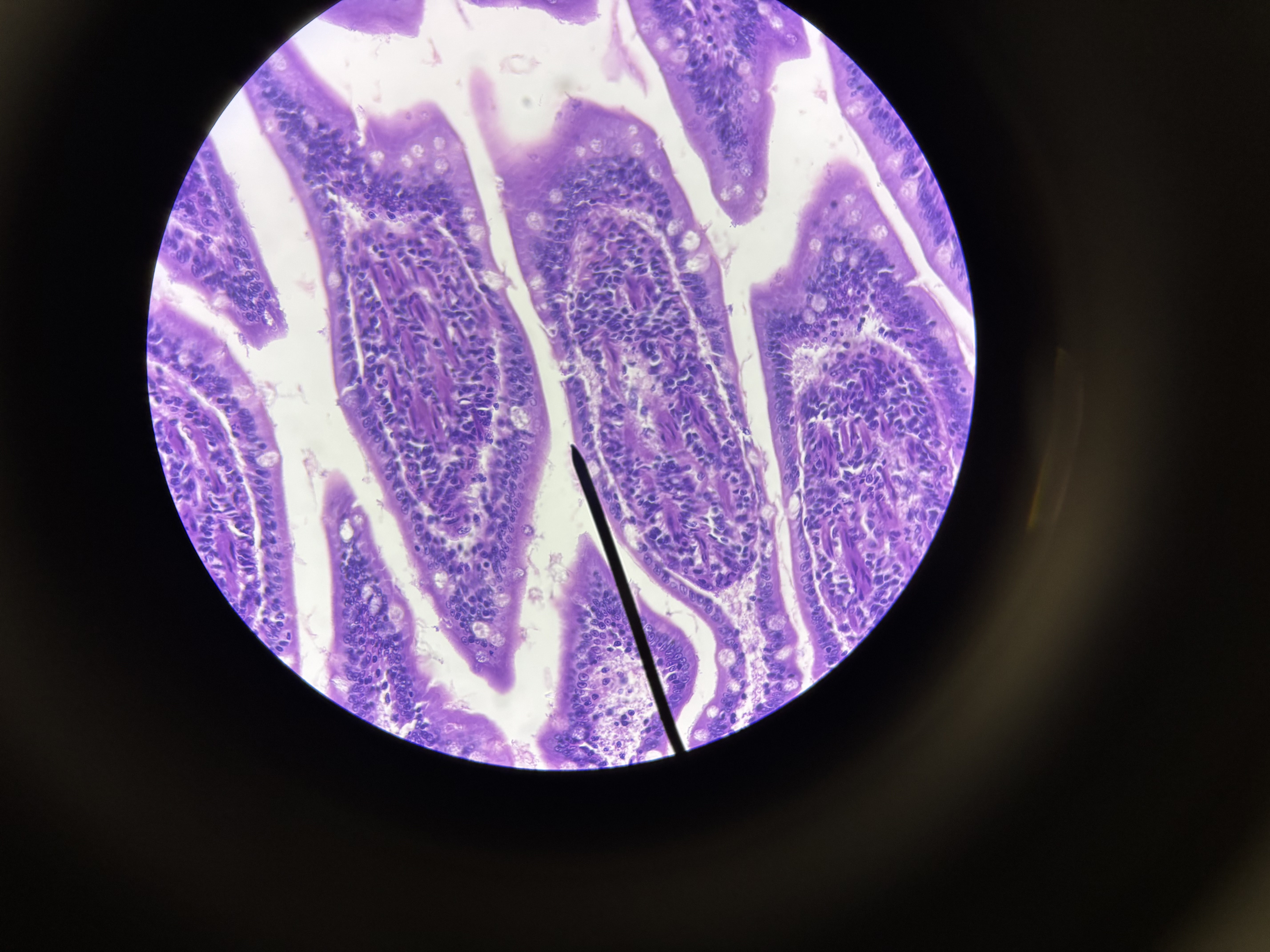
simple columnar epitheleal
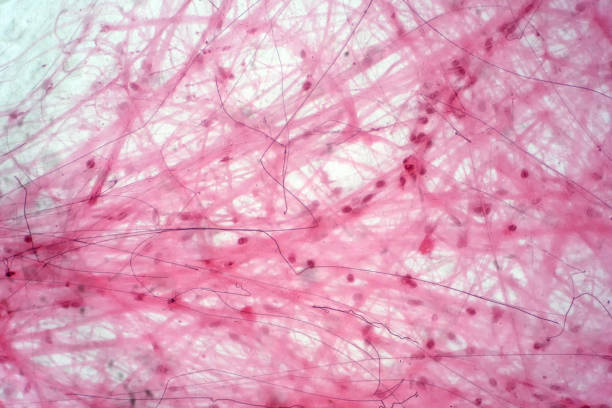
loose connective tissue
endoderm
innermost layer of the three primary germ layers
ectoderm
outermost layer of the three primary germ layers in the embryo
mesoderm
middle layer of the primary germ layers
specific tissue types derived from endoderm
epithelial
where is epithelial tissue derived from endoderm found
lining of airways and the lumen of digestive tract
specific tissue types derived from ectoderm
epithelial and nervous
specific location of epithelial tissue derived from ectoderm
epidermis of the skin
specific location of nervous tissue derived from ectoderm
brain and spinal cord
specific tissue types derived from mesoderm
epithelial, muscle, and connective
specific location of epithelial tissue derived from mesoderm
lining of the body cavity
specific location of muscle tissue derived from mesoderm
skeletal muscles, heart, walls of digestive tract
specific location of connective tissue derived from mesoderm
bones, cartilage, blood
epithelial tissues (general)
closely connected cells with no visible intercellular space
basal end
end where epithelial tissue is attached to another tissue
apical end
free end, not attached to anything
simple squamous epithelium location
lining of body cavities
simple squamous epithelium function
covering surfaces, allowing for diffusion (of gases) and filtration (of fluids)
simple squamous epithelium structural characteristics
flat, scaly, single layer
simple cuboidal epithelium location
kidney tubules/ducts, glands
simple cuboidal epithelium function
protection and secretion (ex. hormones)
simple cuboidal epithelium structural characteristics
cube shaped, single layered
simple columnar epithelium location
lining cavities and tracts (digestive system, respiratory tract)
simple columnar epithelium function
secretion, absorption, protection, transportation
simple columnar epithelium structural characteristics
tall narrow cells, single layer
stratified squamous epithelium location
skin and esophagus lining
stratified squamous epithelium function
protection from damage
stratified squamous epithelium structural characteristics
multiple layers, scaly cells
hydra body symmetry
radial
hydra body cavity
acelomates
planarian body symmetry
bilateral
planarian body cavity
acoelomate
earthworm body symmetry
bilateral
earthworm body cavity
coelomate
grasshopper body symmetry
bilateral
grasshopper body cavity
coelomate
hydra digestive system-complete or incomplete?
incomplete/closed, one opening for food and waste
planarian digestive system-complete or incomplete?
incomplete/closed, one opening for food and waste
earthworm digestive system-complete or incomplete?
complete, gut w/ mouth and anus, closed system
grasshopper digestive system-complete or incomplete?
incomplete, open
hydra circulatory system
no true circulatory system
planarian circulatory system
no true circular system, rely on diffusion for gas exchange and nutrient transport
earthworm circulatory system
closed system with blood vessels and aortic arches (act as heart)
grasshopper circulatory system
open system, “blood” aka hemolymph moves through interconnected sinuses to deliver nutrients and hormones
hydra respiratory system
gas exhange by simple diffusion, oxygen is absorbed from water and co2 released through epidermis
planarian respiratory system
no respiratory system, gas exhange by diffusion
earthworm respiratory system
gas exchange via cutaneous respiration
grasshopper respiratory system
spiracles allow air to enter and leave respiratory system, lead to tracheal tubes that deliver oxygen to cells and tissues
hydra reproductive system
both asexual (budding, bud detaches from parent) and sexual (under stress conditions, some hermaphroditic)
planarian reproductive system
asexual (transverse fission/regeneration) or sexual (hermaphroditic or cross fertilization)
grasshopper reproductive system
sexual reproduction (female has ovipositor)
earthworm reproductive system
sexual (cross fertilization), hermaphrodites
hydra excretory system
diffusion into water directly from cells
planaria excretory system
flame cells, tubules and excretory pores
earthworm excretory system
nephridia remove metabolic waste products (act as kidneys)
grasshopper excretory system
malpighian tubules function like kidneys, filter waste and deposit it in hindgut
“eyes” of the planaria
eyespots
expanded regions lateral to anterior end in planaria
auricles
what takes in food for the planaria (in digestive tract)
pharynx
planaria- what does food pass from pharynx to that distributes nutrients
intestinal diverticula
nephridia-earthworm
coiled tubes appearing in the coelom, remove waste from body cavity
typhlosole-earthworm
large flap of tissue extending to lumen, increases surface area for absorption and digestion
where is dorsal blood vessel earthworm
above intestine
clitellum
big band in earthworms, functions in reproduction
prostomium
earthworms, small lobe located above the mouth
vas deferens
earthworm, male parts, male genetical pores
nephridiopores
pores that earthworms excrete waste by
does self fertilization occur in earthworms
no
order of earthworm digestive tract
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, crop, gizzard, stomach-intestine
what does the crop do
food storage, white and soft
what does the gizzard do
grinding food, hard
order of everything visible in the earthworms
pharynx, seminal vesicles, crop, gizzard, intestine (dorsal blood vessel on top)
what are inside seminal vesicles
testes
job of seminal receptacles
recieve sperm from mating partner
aortic loops
(hearts) pump blood through blood vessel
job of the pharynx
pump to ingest food
ocelli
3 tiny simple grasshopper eyes
labrum
grasshopper upper lip structure, used to hold food
mandibles
jaw like structures, used to chew food
maxillae
segmented extensions with a sensory function used to cut, taste and chew food
labium
lower lip, holds food while it is being chewed
ovipositor
fish tail looking thing on female grasshoppers, lets them deposit eggs into ground
spiracles
tiny pores to help grasshoppers breathe air
order of what you can see inside grasshopper
brain, esophagus, crop, gizzard, gastric ceca, stomach, Malpighian tubules, large intestine, small intestine (heart is on top)
Malpighian tubules
help eliminate out waste
do grasshoppers have lungs
no they have spiracles instead
does hemolymph play a role in gas exchange
no
loose connective tissue location
between different tissues (skin and bone)
loose connective tissue function
holding tissues together
loose connective tissue structure
extracellular matrix, fibers, cells
skeletal muscle location
attached to skeleton
skeletal muscle function
voluntary contraction