Equilibrium in Macroeconomics: Supply and Demand Analysis
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Equilibrium Price
Price where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
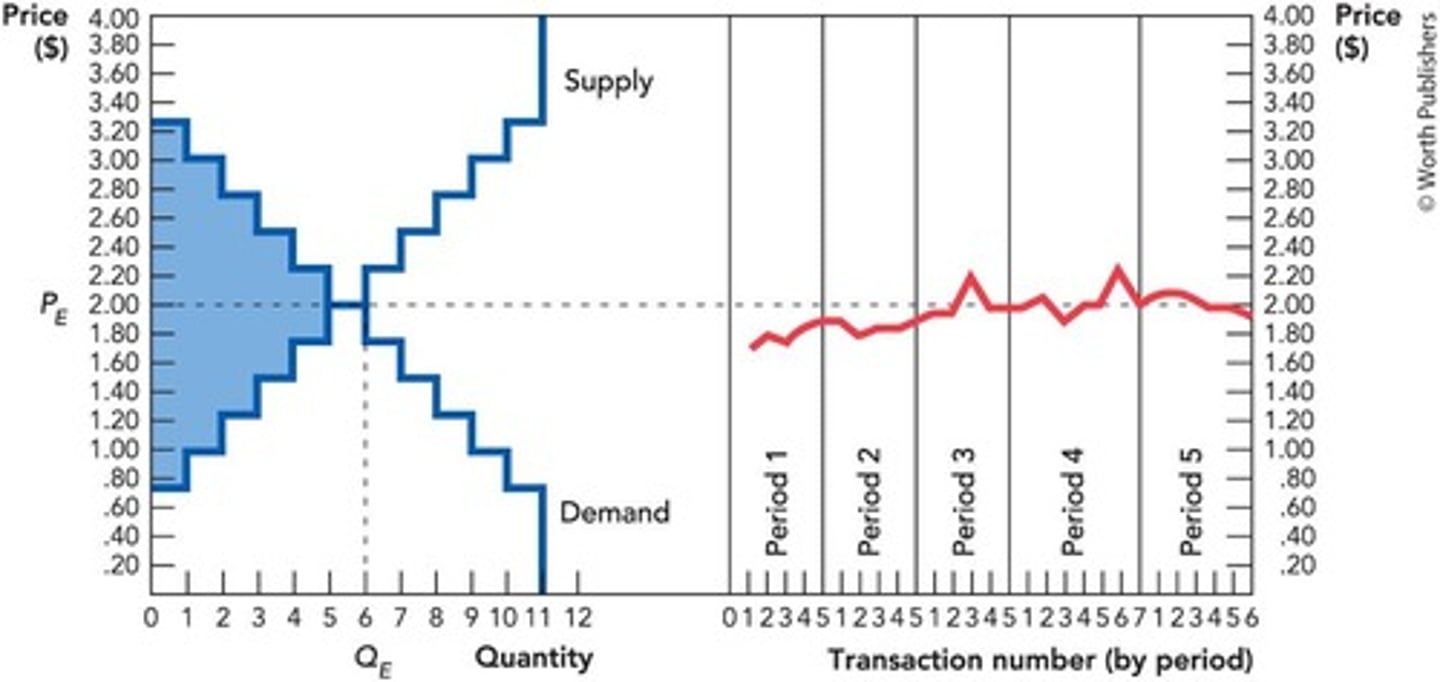
Equilibrium Quantity
Quantity exchanged at equilibrium price.
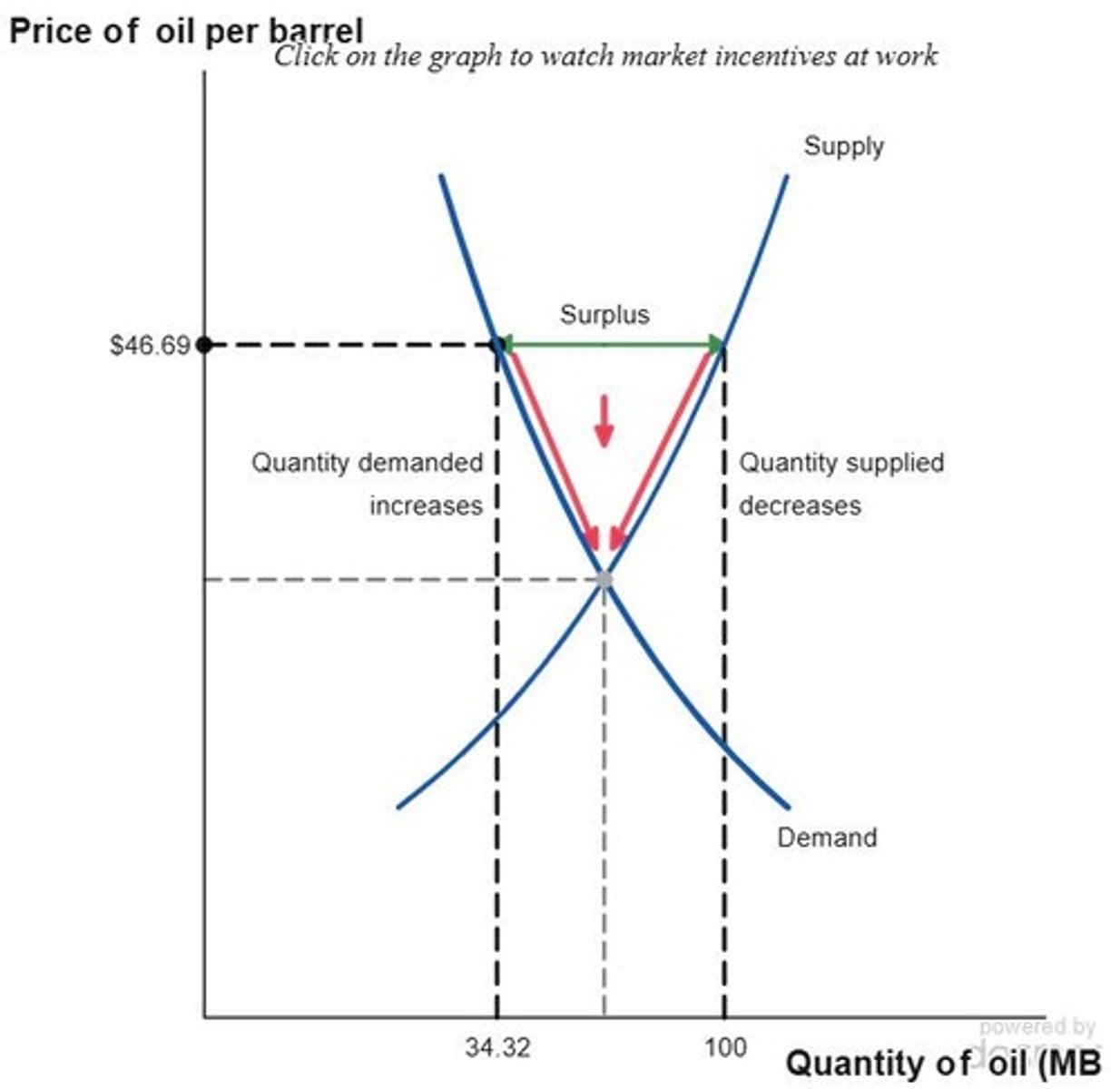
Surplus
Quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded.
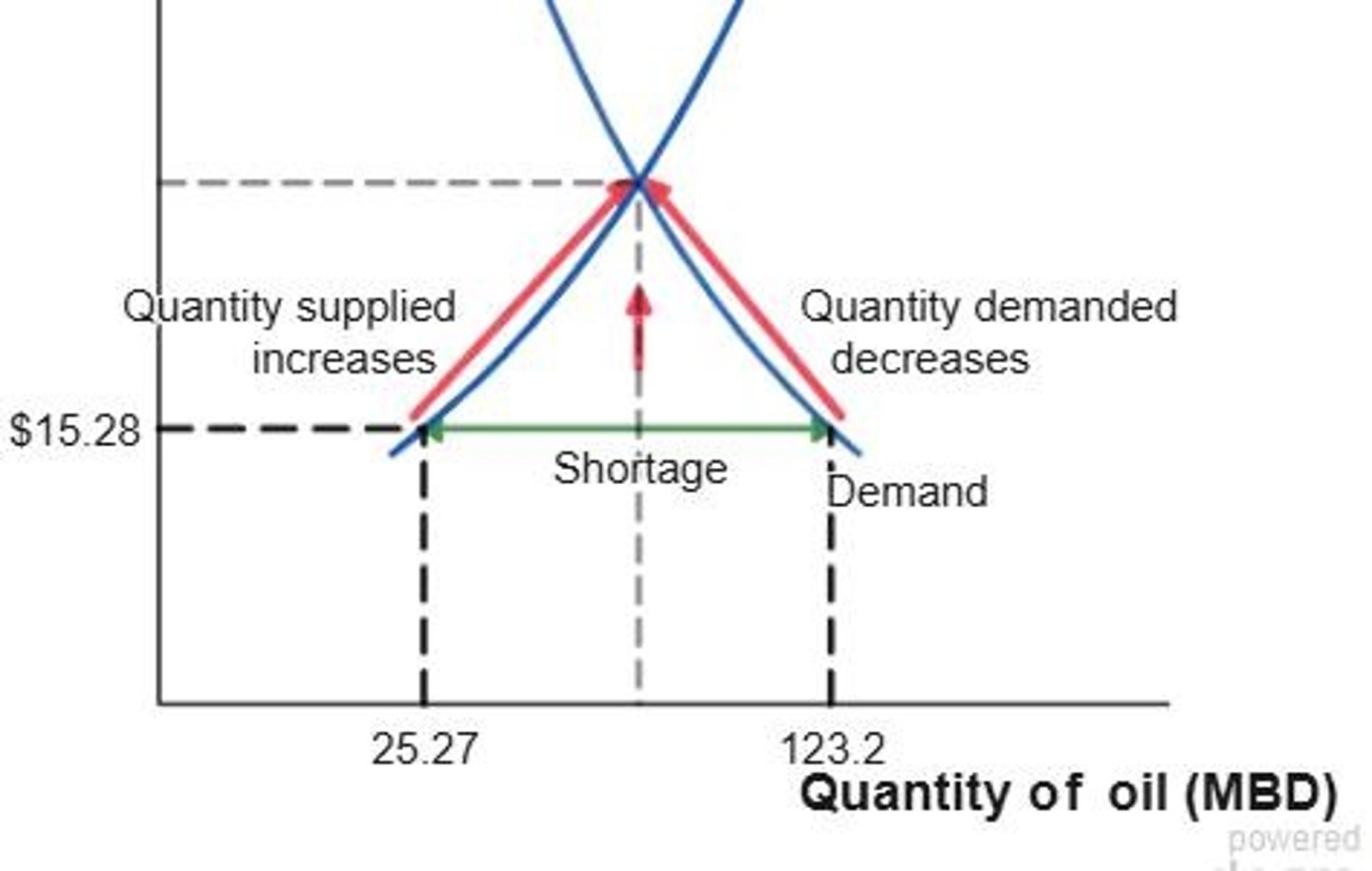
Shortage
Quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied.
Adjustment Process
Market response to changes in supply and demand.
Producer Surplus
Difference between selling price and cost of production.
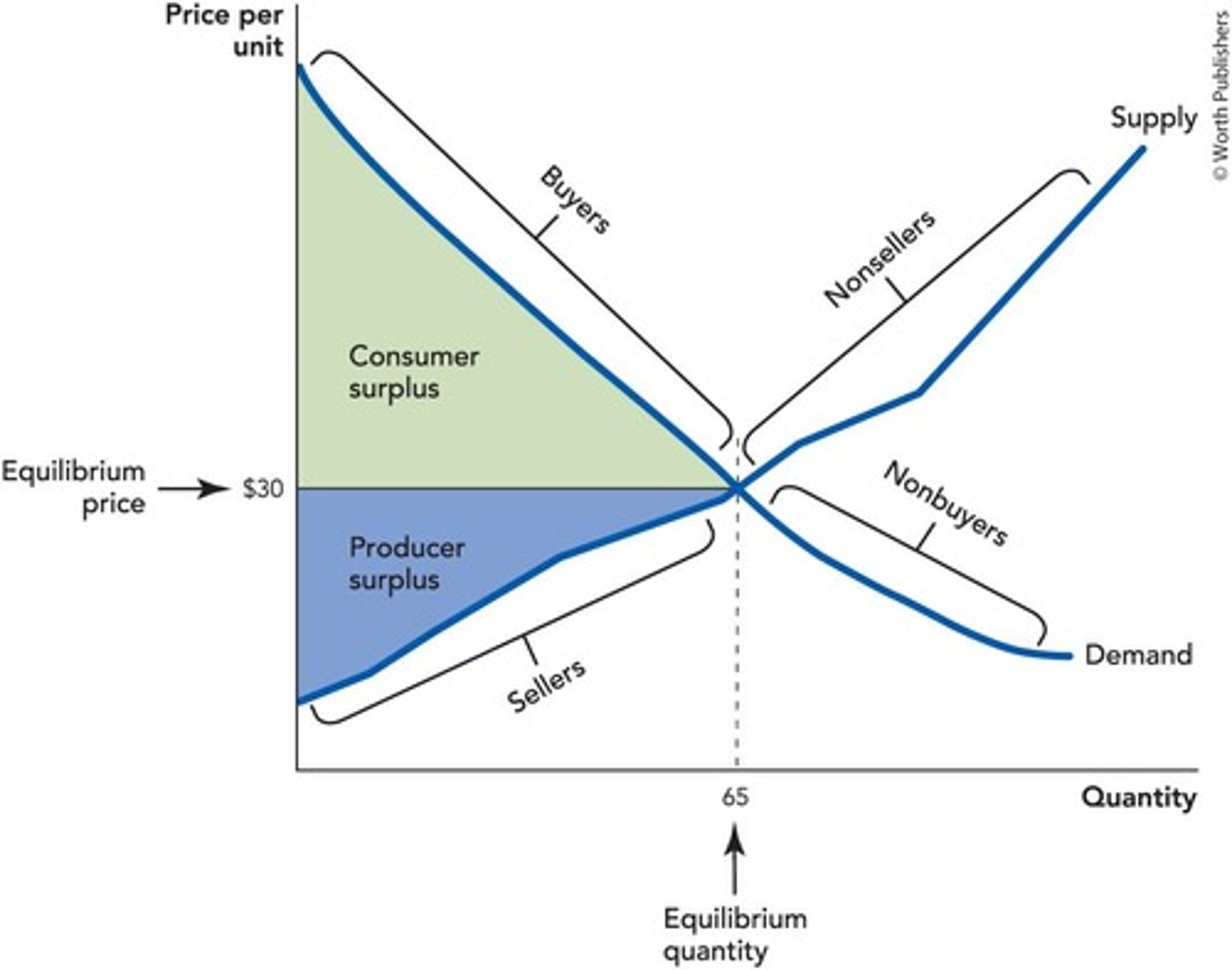
Consumer Surplus
Difference between willingness to pay and market price.
Market Forces
Economic factors that influence price and quantity.
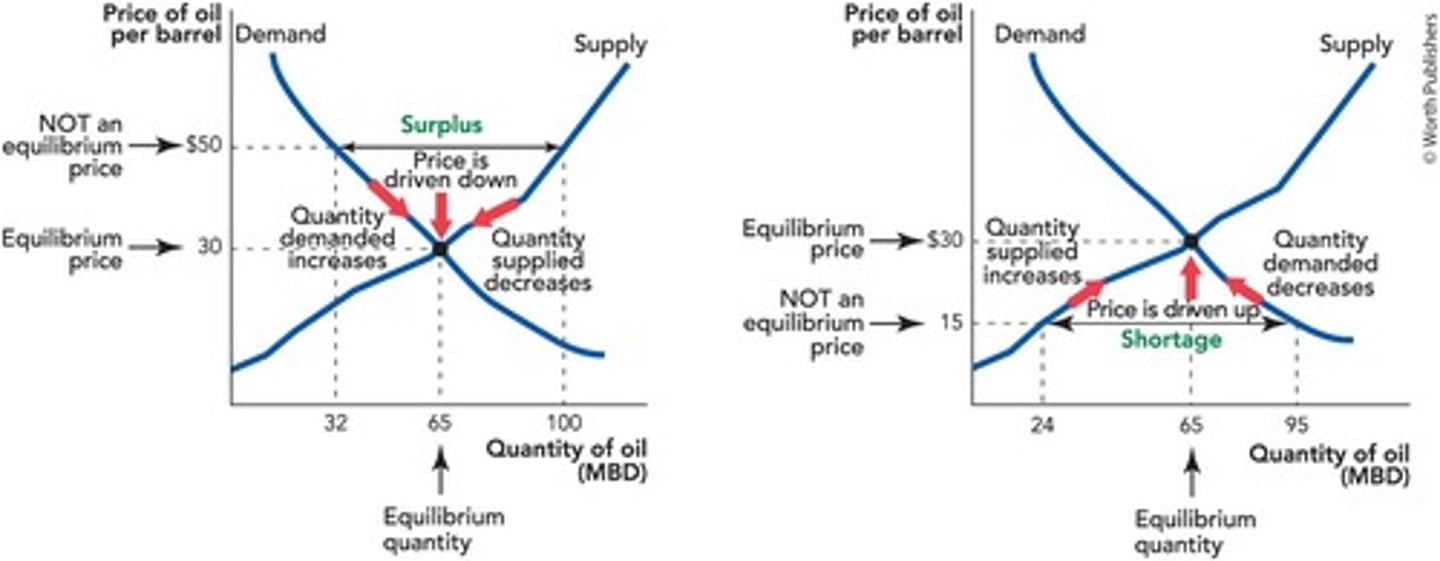
Price Decrease
Occurs when there is a surplus.
Price Increase
Occurs when there is a shortage.
Demand
Desire for a good or service at various prices.
Quantity Demanded
Amount of a good buyers are willing to purchase.

Supply
Amount of a good producers are willing to sell.
Quantity Supplied
Amount of a good available for sale at a price.
Excess Supply
Another term for surplus in the market.
Excess Demand
Another term for shortage in the market.
Incentive
Motivation for buyers or sellers to change behavior.
Price Stability
Condition where prices remain relatively constant.
Free Market
Economic system with minimal government intervention.
Laboratory Evidence
Experimental data supporting economic theories.
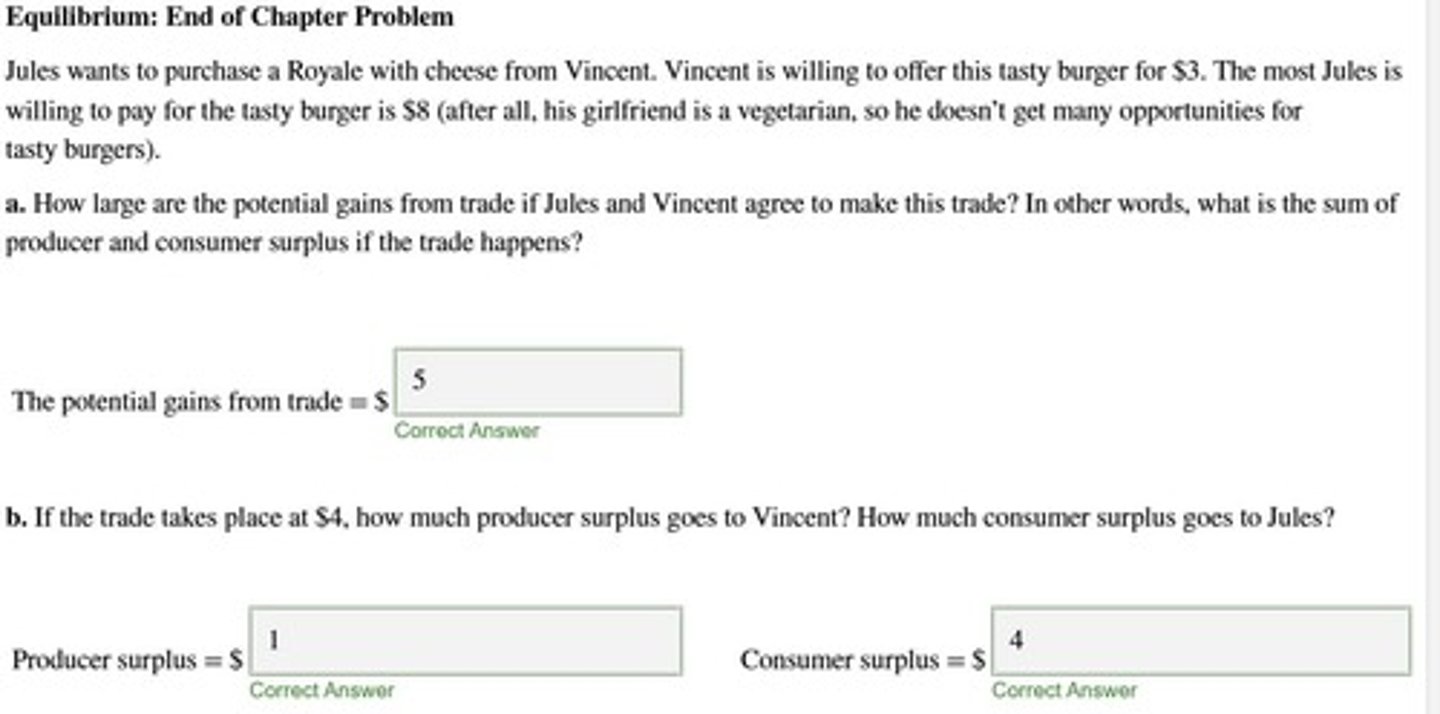
Gains from Trade
Benefits obtained from voluntary exchange.
Oil Price Understanding
Analysis of factors affecting oil pricing.
Equilibrium Quantity
Quantity at equilibrium price, no surplus or shortage.
Price Incentive
Motivation for price changes based on supply and demand.
Competition Effect
Sellers lower prices above equilibrium; buyers raise below.
Stable Equilibrium
Equilibrium price remains unchanged due to balanced demand and supply.
Buyer Behavior
Buyers buy freely at equilibrium, no price increase incentive.
Seller Behavior
Sellers sell freely at equilibrium, no price decrease incentive.
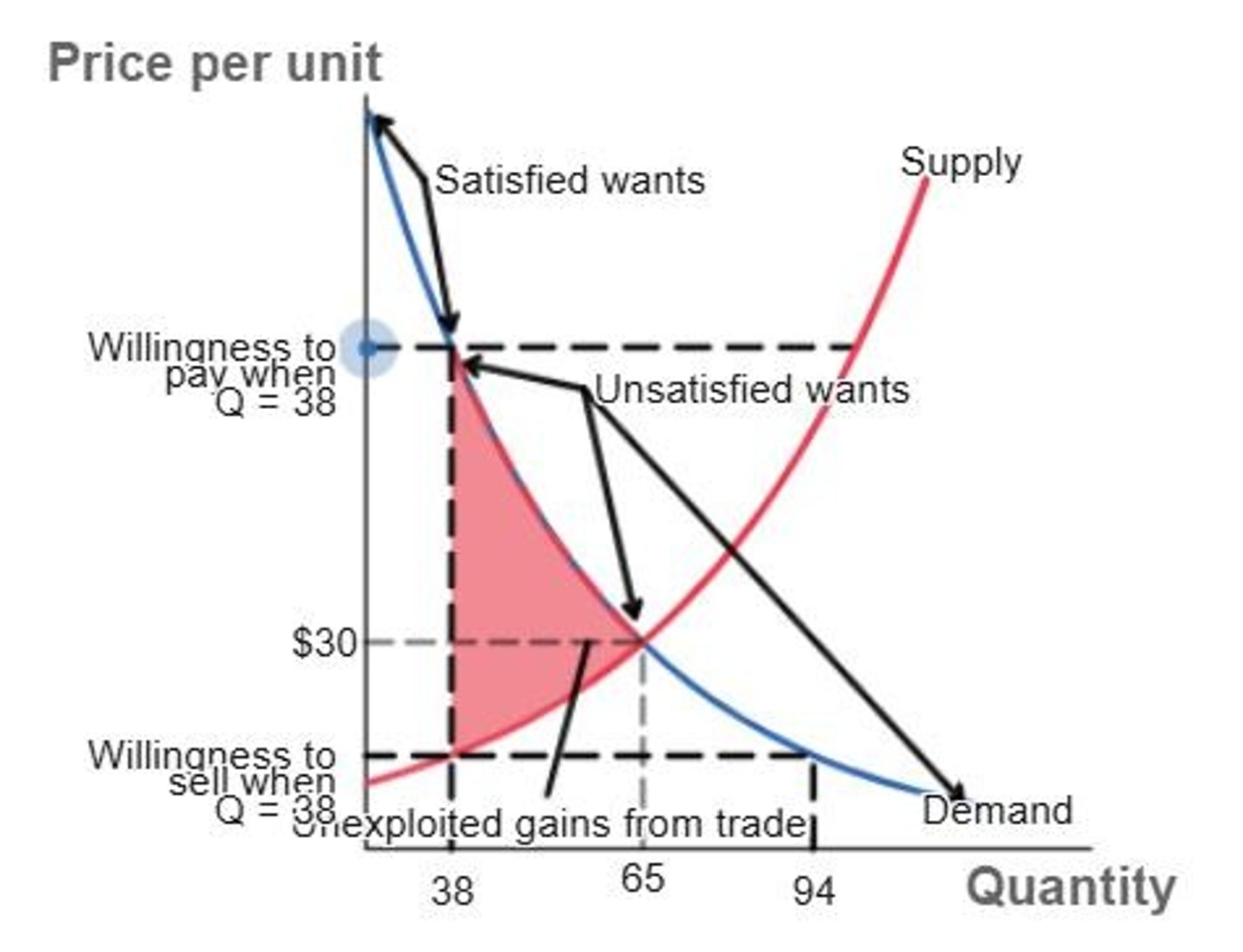
Unexploited Gains from Trade
Potential benefits when quantity is below equilibrium quantity.
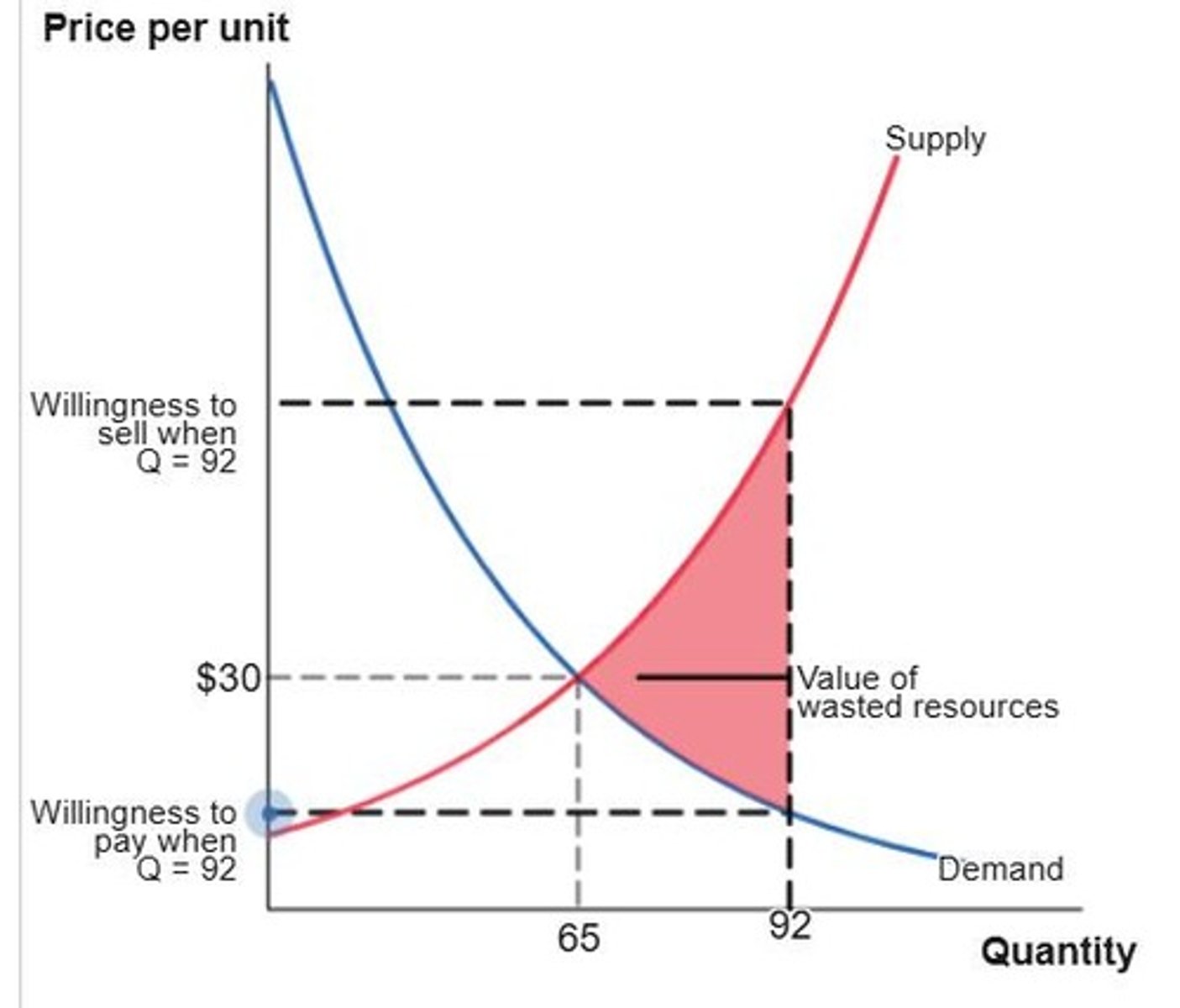
Wasted Resources
Loss incurred when quantity exceeds equilibrium quantity.
Demand Curve Value
Maximum price buyers pay at specific quantity demanded.
Satisfaction of Wants
Buyers allocate resources to highest-valued wants.
Producer Surplus
Difference between what sellers receive and minimum acceptable price.
Consumer Surplus
Difference between what buyers pay and maximum willing price.
Market Dynamics
Interaction of buyers and sellers influencing prices.
Quantity Supplied
Amount sellers are willing to sell at a given price.
Quantity Demanded
Amount buyers are willing to purchase at a given price.
Price Floor
Minimum price set by government, above equilibrium.
Price Ceiling
Maximum price set by government, below equilibrium.
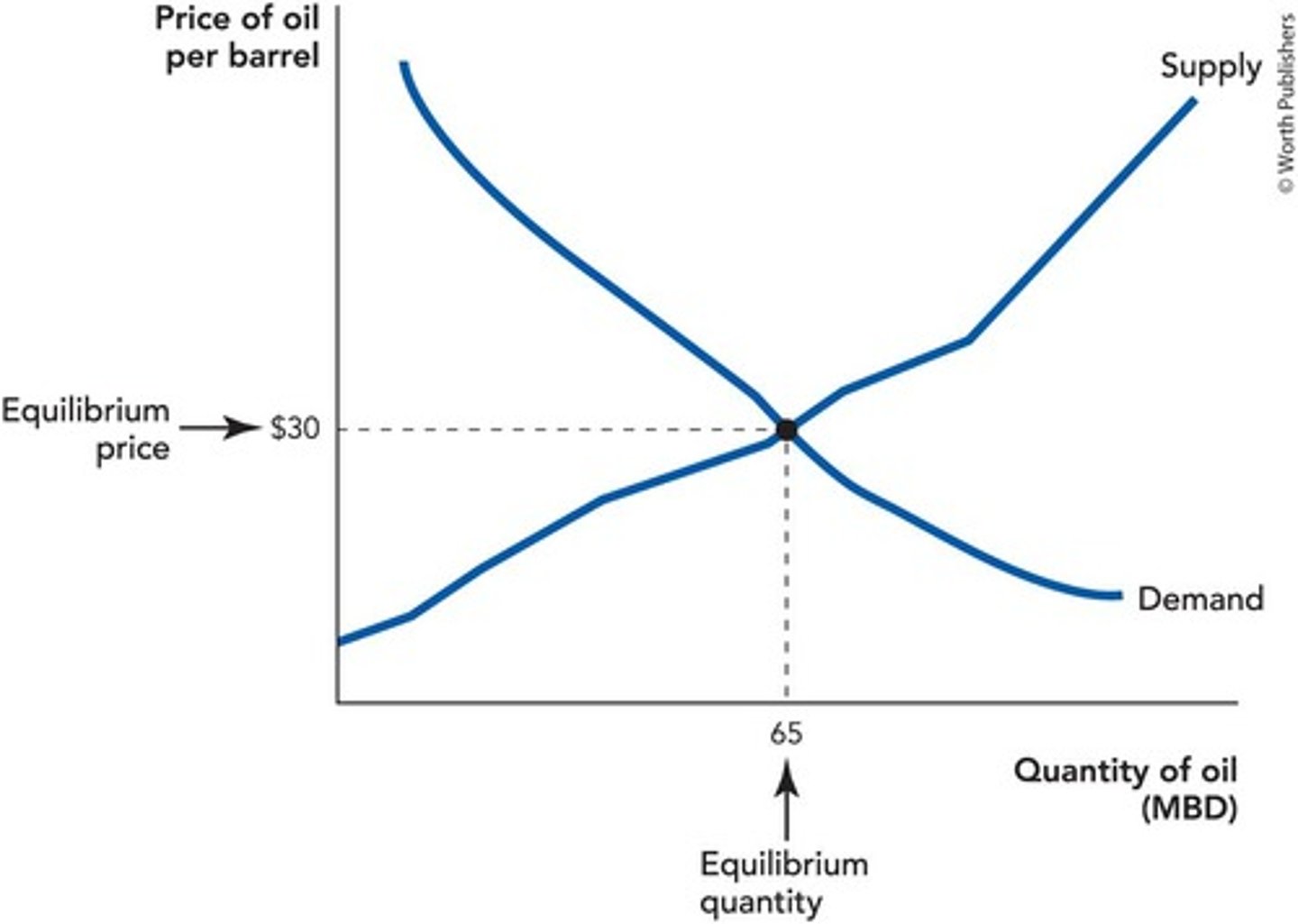
Market Equilibrium
State where supply equals demand in a market.
Trade Gains
Benefits from exchanging goods or services between parties.
Resource Allocation
Distribution of resources to meet consumer demands.
Market Efficiency
Optimal distribution of resources without waste.
Gains from Trade
Benefits achieved through voluntary exchange in markets.
Producer Surplus
Difference between selling price and production cost.
Equilibrium Price
Price where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded.
Equilibrium Quantity
Quantity sold at the equilibrium price.
Free Market
Market with minimal government intervention and regulation.
Willingness to Pay
Maximum price a buyer is ready to pay.
Lowest Cost Seller
Seller with the minimum production cost for goods.
Unexploited Gains
Potential benefits from trade not realized in the market.
Wasteful Trades
Exchanges that do not maximize total surplus.
Market Supply Curve
Graph showing quantities supplied at various prices.
Market Demand Curve
Graph showing quantities demanded at various prices.
Vernon Smith
Economist known for experimental economics and market testing.
Experimental Economics
Field studying economic behavior through controlled experiments.
Supply and Demand Model
Framework explaining price formation through supply and demand.
Bids and Offers
Proposals made by buyers and sellers in a market.
Maximum Willingness to Pay
Highest price a buyer is willing to pay.
Minimum Selling Price
Lowest price a seller is willing to accept.
Convergence to Equilibrium
Process where market prices and quantities stabilize at equilibrium.
Laboratory Experiment
Controlled study to test economic theories in practice.
Market Efficiency
Optimal allocation of resources in a free market.
Trade Periods
Segments of time during which trades are conducted.
Willingness to Pay
Maximum price buyers are willing to pay.
Lowest Costs
Minimum price suppliers are willing to accept.
Quantity Traded
Total units bought and sold in the market.
Total Surplus
Sum of producer and consumer surplus.
Equilibrium Quantity
Quantity at which supply equals demand.
Supply Curve Shift
Change in supply due to cost variations.
Demand Curve Shift
Change in demand due to external factors.
Surplus
Excess supply at a given price.
Temporary Surplus
Short-term excess supply before market adjustment.
Competition Effect
Market forces that drive prices toward equilibrium.
Technological Innovations
Advancements that lower production costs.
Old Equilibrium
Initial price and quantity before shifts occur.
New Equilibrium
Adjusted price and quantity after shifts occur.
Decrease in Supply
Reduction in quantity supplied at all prices.
Increase in Supply
Higher quantity supplied at all prices.
Decrease in Demand
Lower quantity demanded at all prices.
Increase in Demand
Higher quantity demanded at all prices.
Market Model Test
Experiment validating supply and demand principles.
Producer Surplus
Difference between selling price and cost.
Consumer Surplus
Difference between willingness to pay and price.
Supply and Demand Model
Framework explaining market behavior.
Price Adjustment
Change in price due to supply and demand shifts.
Quantity Demanded
Amount consumers are willing to buy at a price.
Supply
Amount of a good or service available for sale.
Quantity Supplied
Amount producers are willing to sell at a price.
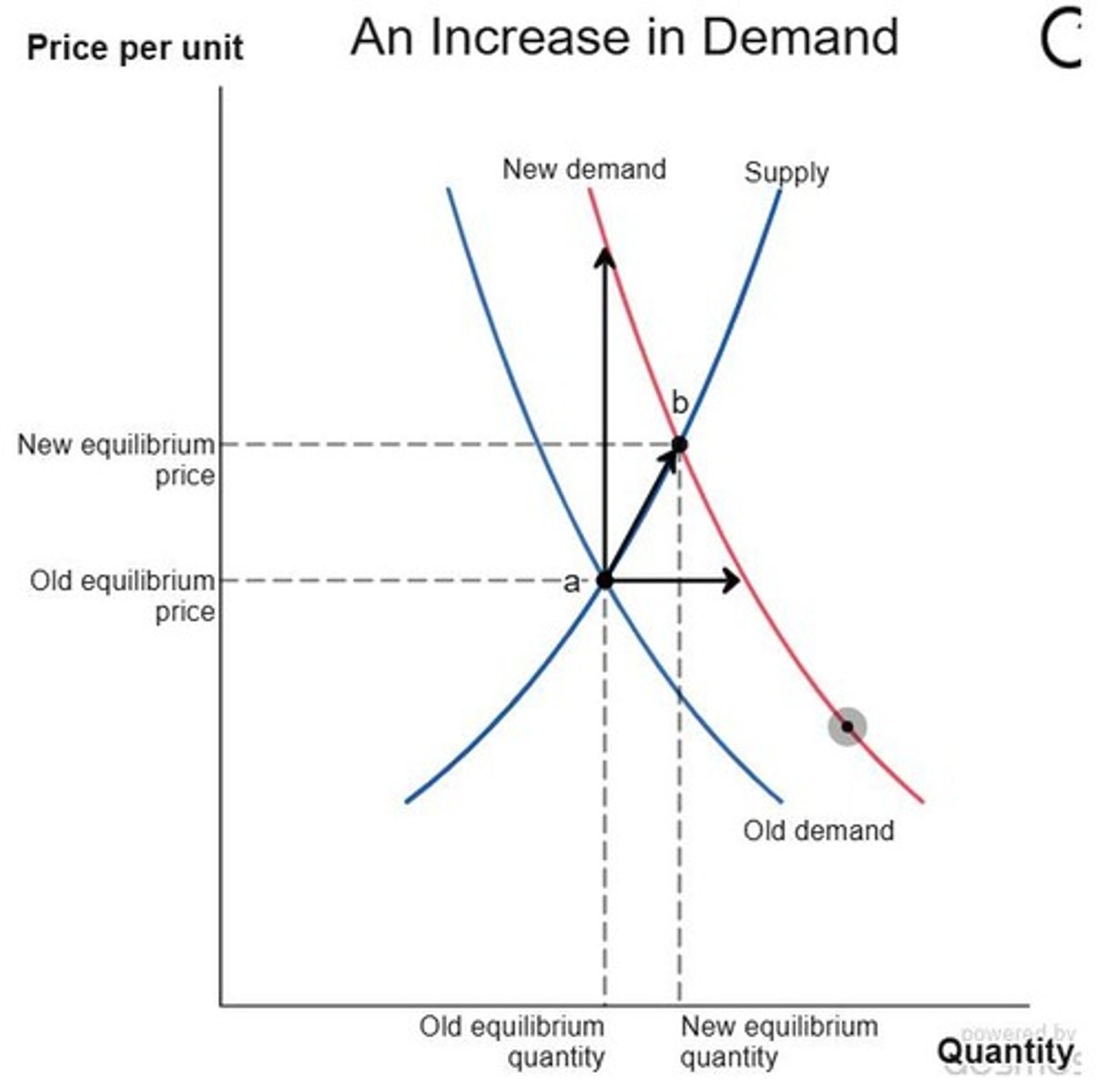
Increase in Demand
Shift of the demand curve up and right.
Increase in Quantity Demanded
Movement along the demand curve due to price change.
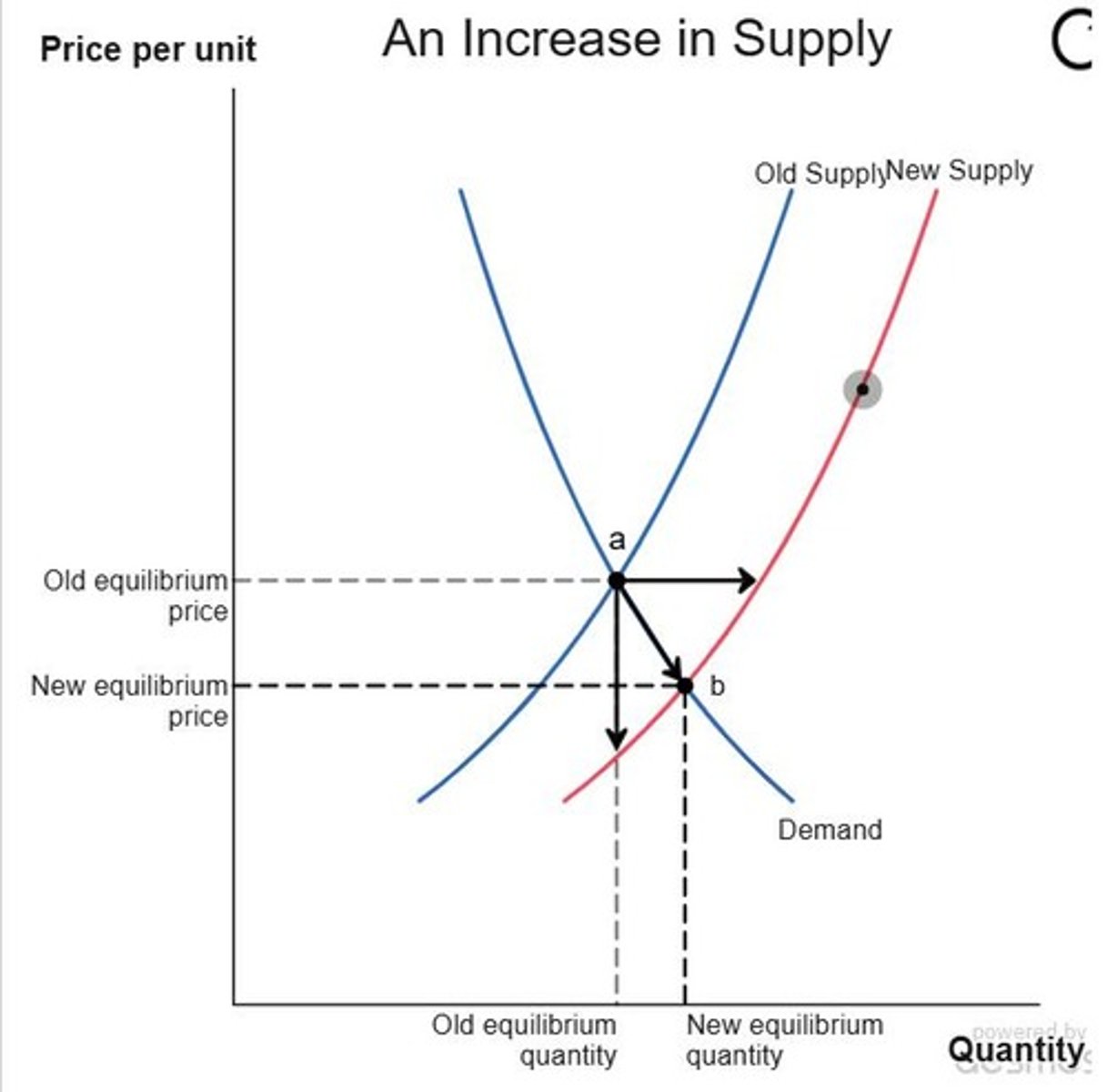
Increase in Supply
Shift of the supply curve down and right.
Increase in Quantity Supplied
Movement along the supply curve due to price change.
Market Price
Price determined by supply and demand interactions.
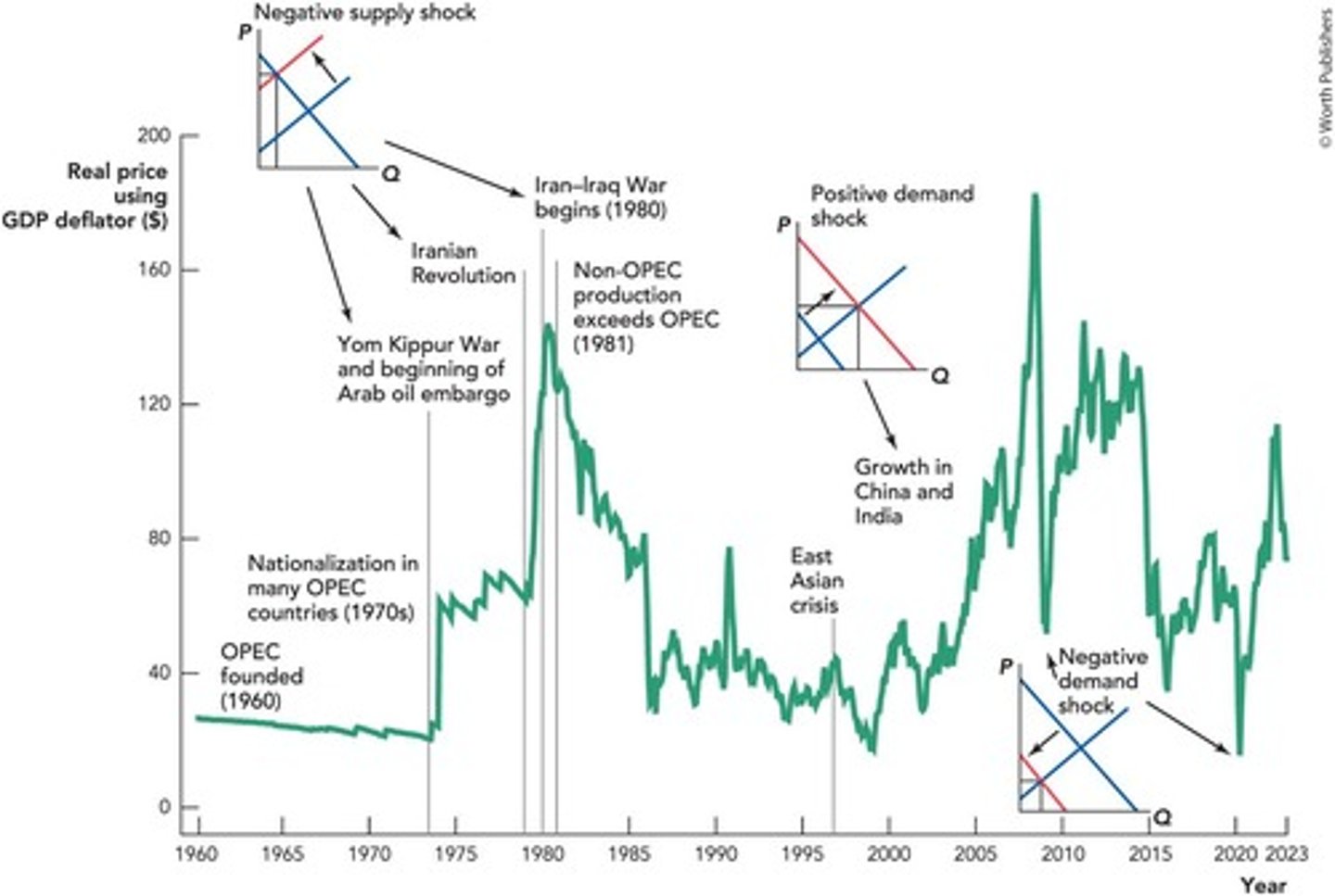
Real Price of Oil
Oil price adjusted for inflation over time.
Oil Supply Increase
Improved production techniques and discoveries boost supply.
Oil Demand Increase
Growing need for oil from early 20th century.
Competitive Conditions
Market structure where many firms compete freely.
Shifts in Demand
Changes in consumer preferences affecting demand curve.
Shifts in Supply
Changes in production costs affecting supply curve.