Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1-3 Test
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Responsiveness, Growth, Reproduction, Movement, Metabolism
5 areas of life that work together to maintain homeostasis
anatomy
"cutting open"; structure
physiology
another greek word; function
gross anatomy
what can be seen and studied with the naked eye
microscopic anatomy
use of microscopes, with limitations
chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
levels of organization
homeostatic regulation
the body's adjustments to changes that help preserve homeostasis
negative feedback
a response to a stimulus "corrects" the situation
positive feedback
stimulus produces a response that re-enforces that stimulus
integumentary system
protects against environmental hazards; helps control body temperature
nervous system
directs immediate response to stimuli, usually by coordinating the activities of other organ systems
digestive system
processes food and absorbs nutrients
urinary system
eliminates excess water, salts, and waste products
reproductive system
produces sex cells and hormones
muscular system
allows for locomotion; provides support; produces heat
skeletal system
provides support; protects tissues; stores minerals; forms blood
lymphatic system
defends against infection and disease, returns tissue fluid to the bloodstream
cardiovascular system
transports cells and dissolved materials, including nutrients, wastes, and gases
respiratory system
delivers air to sites where gas exchange can occur between the air and circulating blood
endocrine system
directs long-term changes in activities of other organ systems
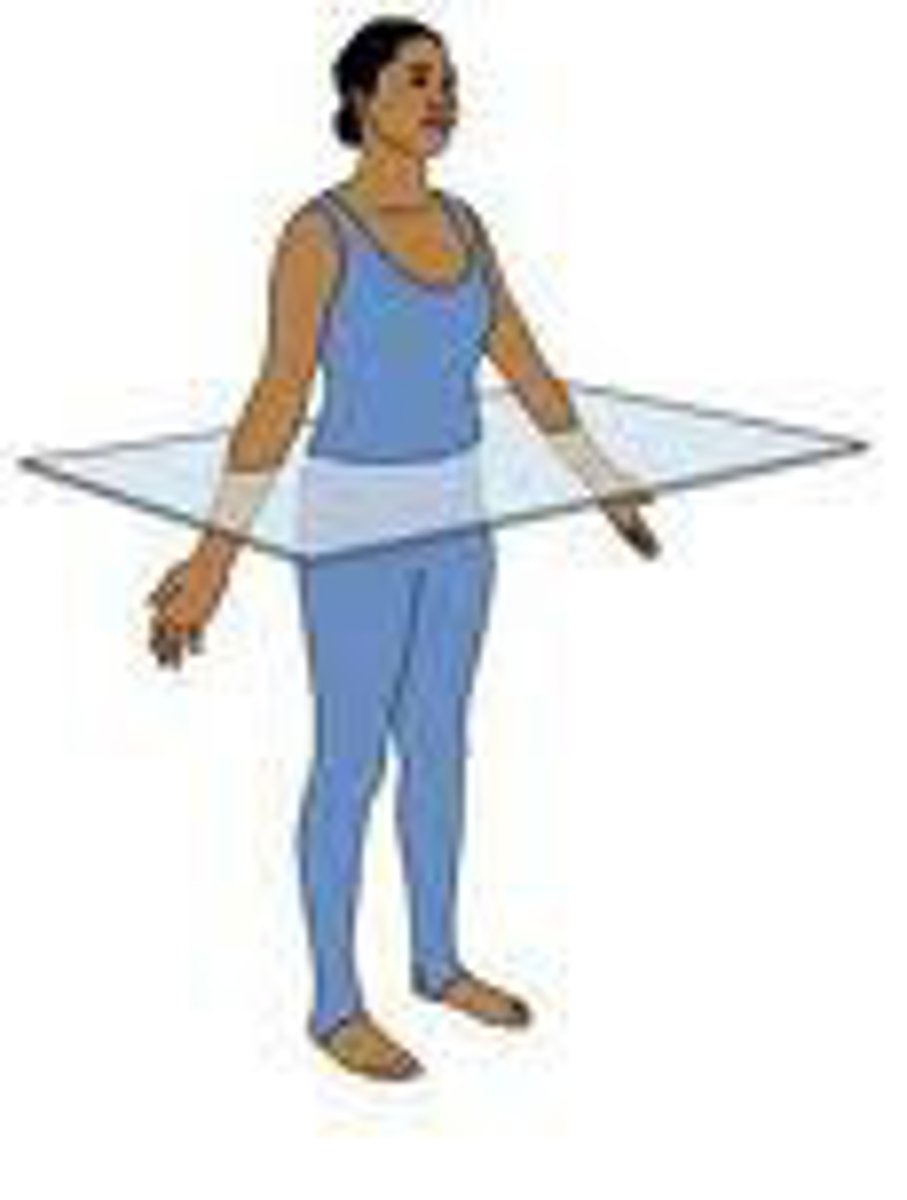
transverse plane
(cross section) divides into superior and inferior
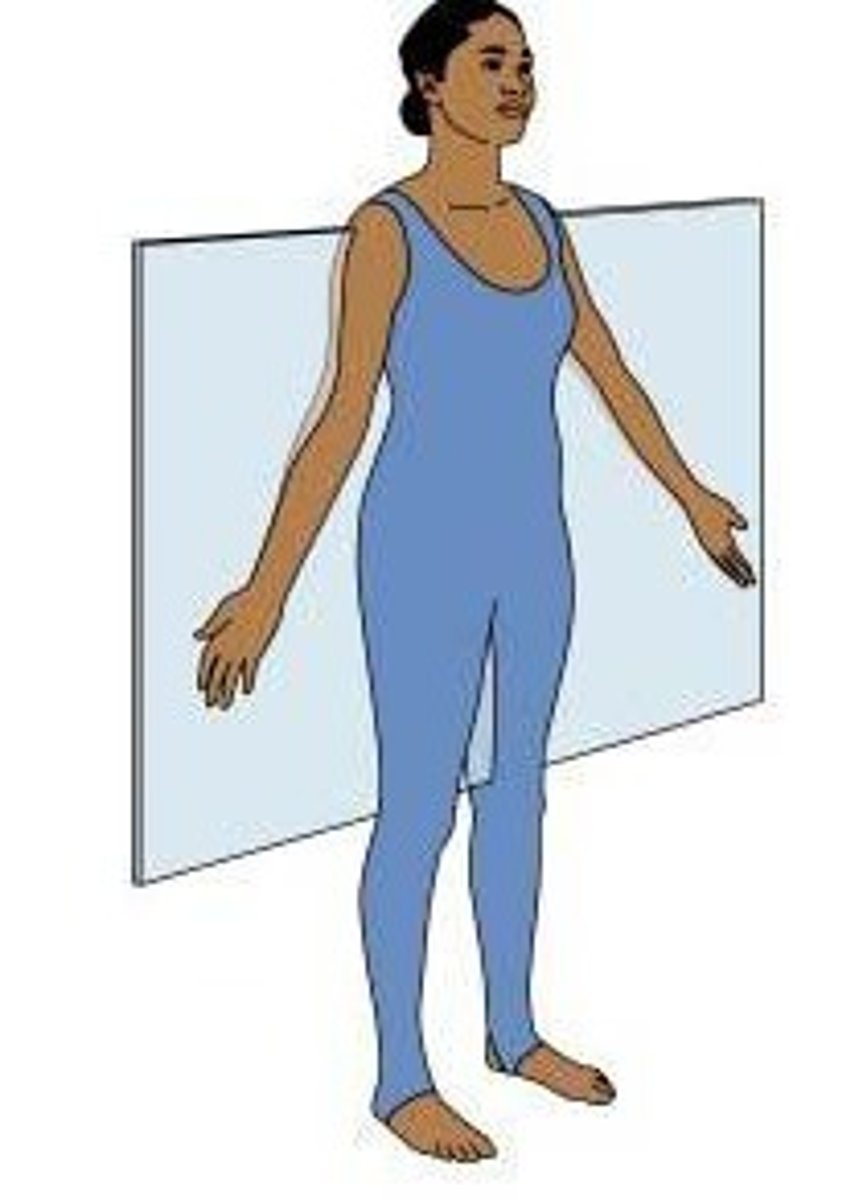
frontal plane
(coronal) divides into anterior and posterior
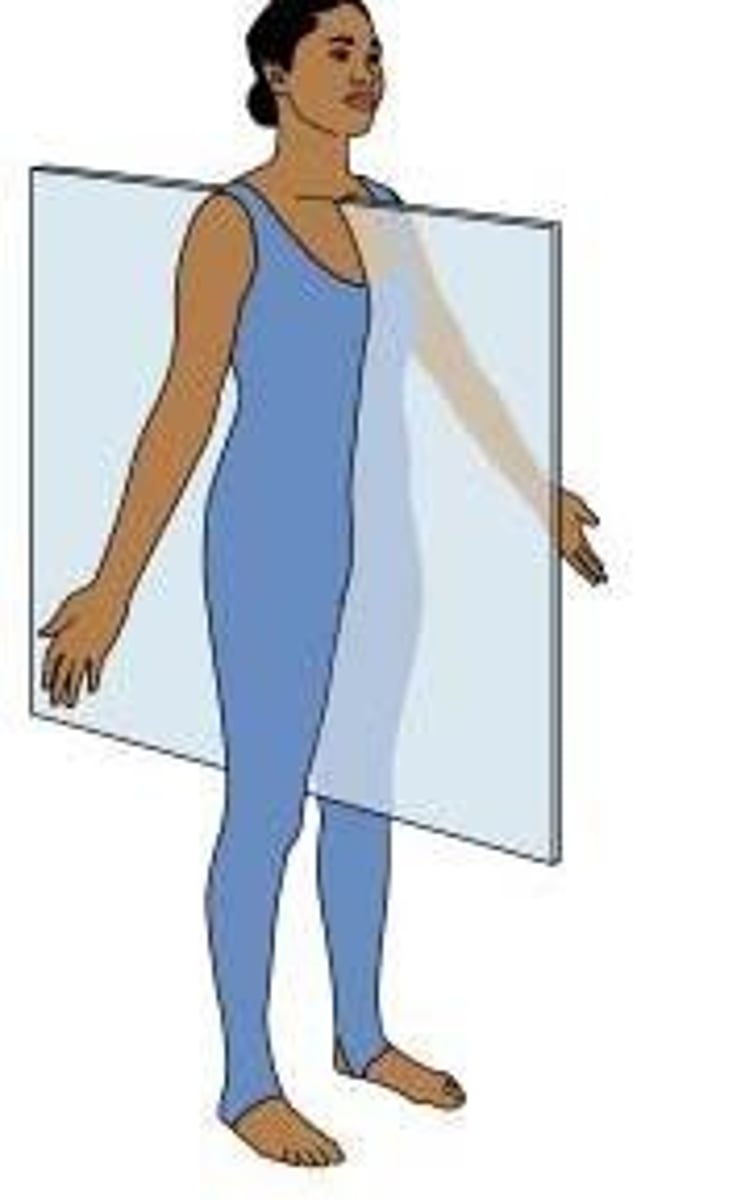
sagittal plane
cuts into left and right
ventral body cavity
diaphragm divides cavity into thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity
abdominopelvic
abdominal cavity, pelvic cavity
thoracic
pericardial cavity, pleural cavities
isotopes
if an element contains a different number of neutrons
covalent bond
molecules that are formed from the sharing of electrons in the outer shell
ionic bond
bonds formed by a reaction of anions and cations (non-metal and metal)
hydrogen bond
formed from hydrogen bonds of one molecule and adjacent molecules
decomposition reaction
AB to A + B
synthesis reaction
A + B to AB
enzymes
substances that accelerate chemical reactions and lower the activation energy
equilibrium
A state of balance
activation energy
the energy required for a reaction to occur
polar molecules
a molecule in which the centroid of the positive charges is different from the centroid of the negative charges.
excellent solvent; high heat capacity; chemical reactions
properties of water
acids
react in solution and increase the number of hydrogen ions
bases
rect in solution and decrease the number of hydrogen ions
proteins
Chains of amino acids
carbohydrates
Compound containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in the approximate ratio of C:2H:O (e.g., sugars, starches, and cellulose); Great for stored energy
lipids
A group of organic compounds composed mostly of carbon and hydrogen including a proportionately smaller amount of oxygen; are insoluble in water, and serve as a source of stored energy
nucleic acids
Macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus
phospholipids
A lipid made up of a glyerol joined to two fatty acids and a phosphate group; has two hydrophobic tails and a polar, hydrophilic head
cells are the building blocks of all plants and animals; cells are the smallest functioning units of life; cells are produced through the division of preexisting cells; each cell maintains homeostasis
cell theory
passive transport
does not require energy - diffusion, osmosis, filtration, facilitated diffusion
active transport
requires energy - carrier-mediated transport
diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
filtration
A process that separates materials based on the size of their particles.
exchange pumps
Carrier proteins that move ions with counter transport.
vesicular transport
Movement of material between organelles in the eukaryotic cell via membrane-enclosed vesicles.
endocytosis
A process in which a cell engulfs extracellular material through an inward folding of its plasma membrane.
exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
isotonic
Having the same solute concentration as another solution.
hypertonic
having a higher osmotic pressure than a comparison solution
hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
chromosome structure
chromosome structure
DNA tightly coiled around histone proteins to form nucleosomes. Nucleosomes are coiled to form coils, then coiled further to form supercoils.
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
genetic code
collection of codons of mRNA, each of which directs the incorporation of a particular amino acid into a protein during protein synthesis
transcription
DNA to RNA (nucleus)
translation
RNA to Protein (ribosomes)
central dogma
DNA - RNA - proteins
interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
mitosis
A process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells conventionally divided into five stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Mitosis conserves chromosome number by equally allocating replicated chromosomes to each of the daughter nuclei.
cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
cell membrane
provides isolation, protection, sensitivity, and support; controls entrance/exit of materials
inorganic compounds
do not contain carbon or hydrogen
organic compounds
carbon and hydrogen atoms primarily
cytosol
distributes materials by diffusion
cytoskeleton
provides strength and support; enables movement of cellular structures and materials
centrioles
essential for movement of chromosomes during cell division
ribosomes
synthesize proteins
proteasomes
break down and recycle damaged or abnormal intracellular proteins
endoplasmic reticulum
synthesizes secretory producers; provides intracellular storage and transport
rough ER
packages newly synthesized proteins
smooth ER
synthesizes lipids and carbohydrates
Golgi apparatus
stores, alters, and packages secretory products; forms lysosomes
lysosomes
remove damaged organelles or pathogens within cells
peroxisomes
catabolize fats and other organic compounds; neutralize toxic compounds generated in the process
mitochondria
produce 95% of the ATP required by the cell
nucleus
controls metabolism; stores and processes genetic information; controls protein synthesis
nucleolus
synthesizes RNA and assembles ribosomal subunits
exergonic reaction
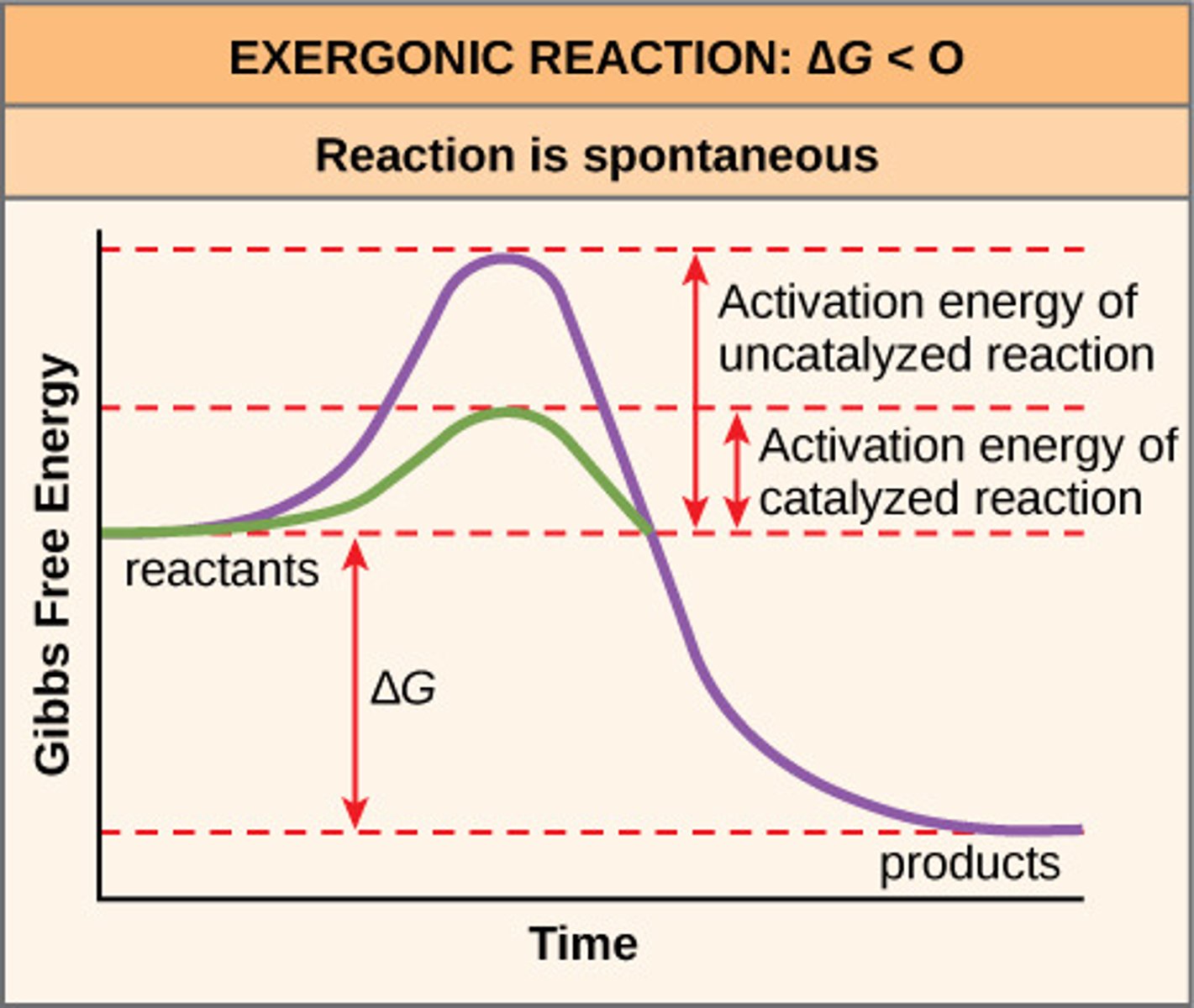
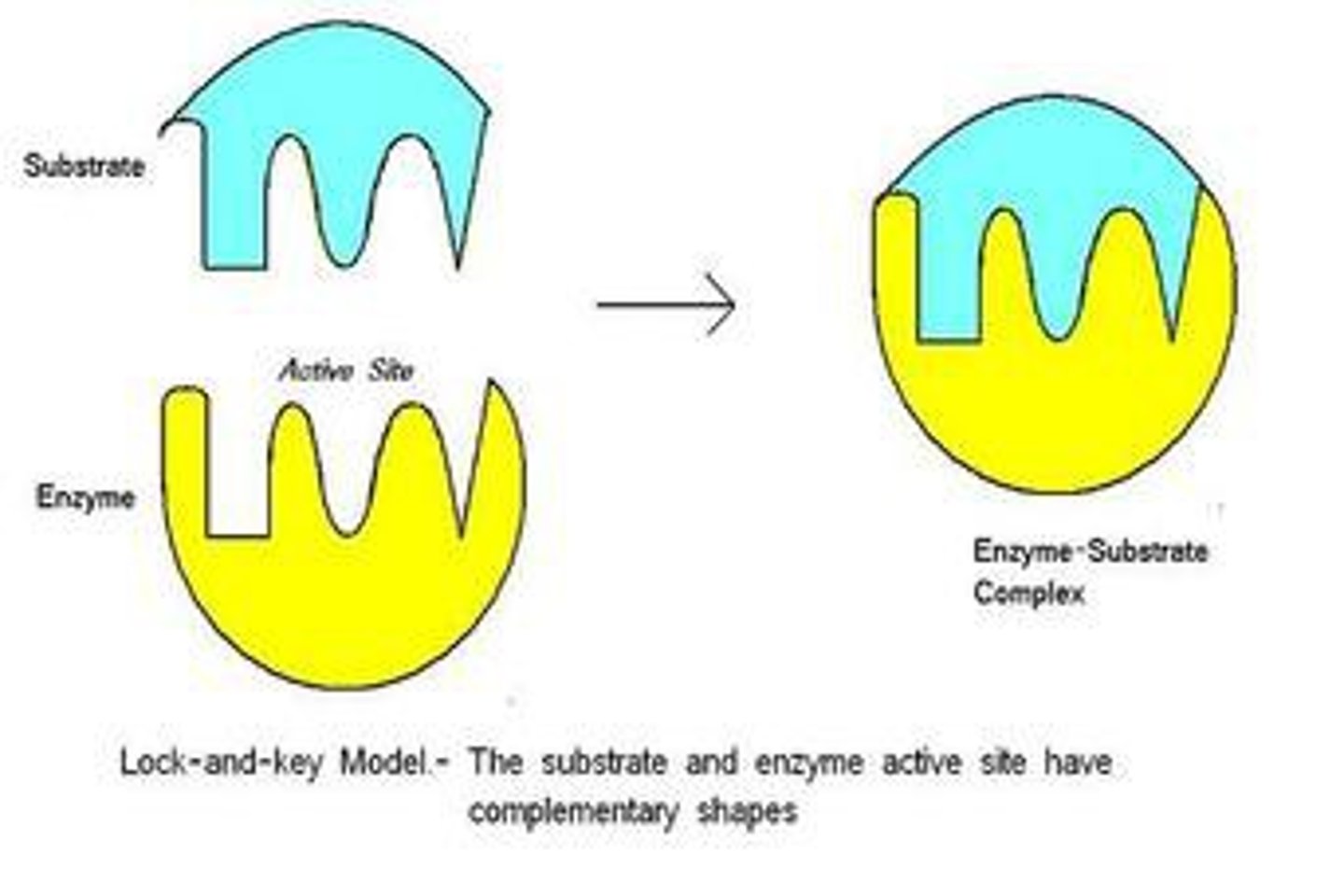
enzyme-substrate complex
active sites connect with substrates
A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s).
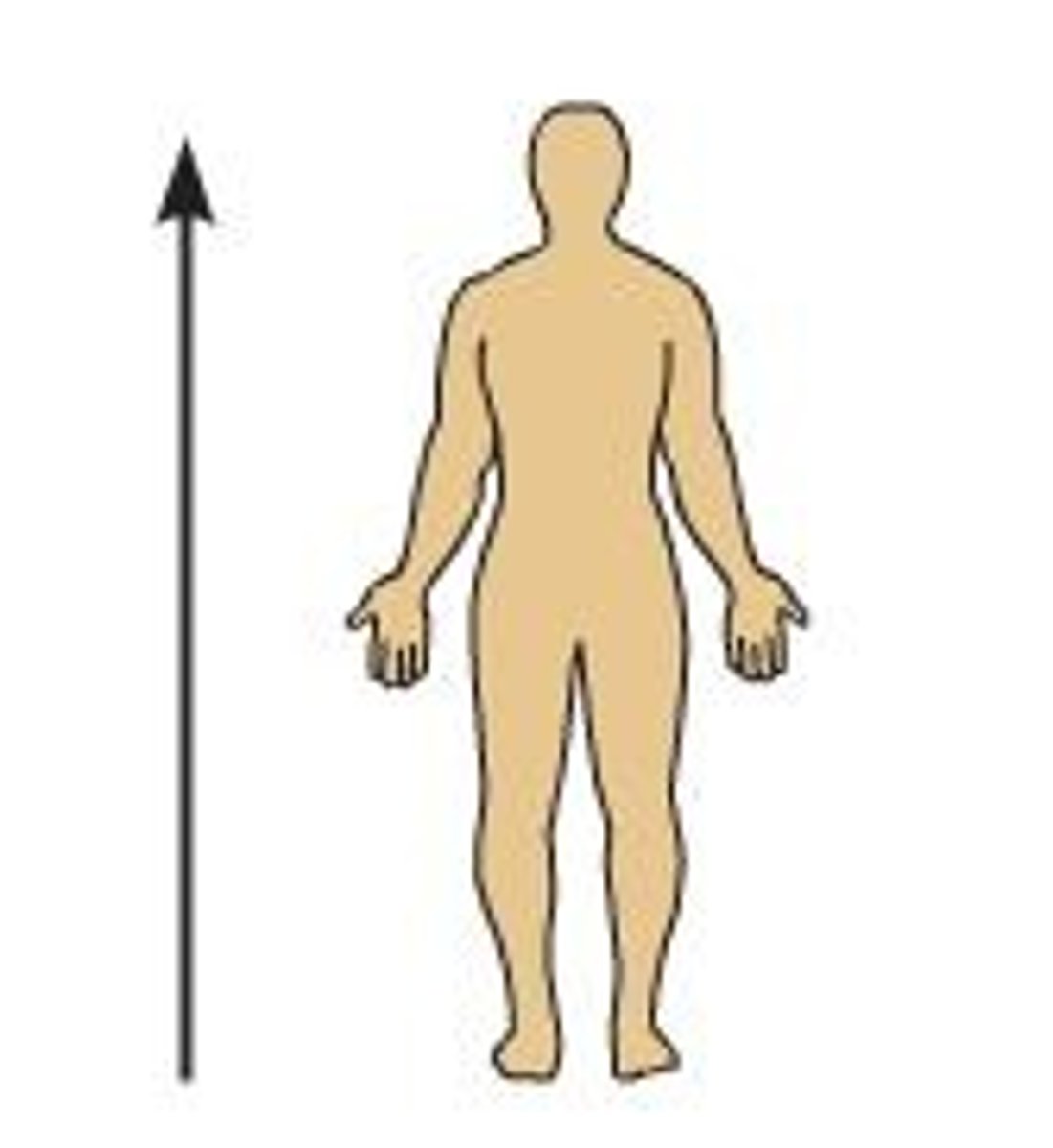
superior
toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above
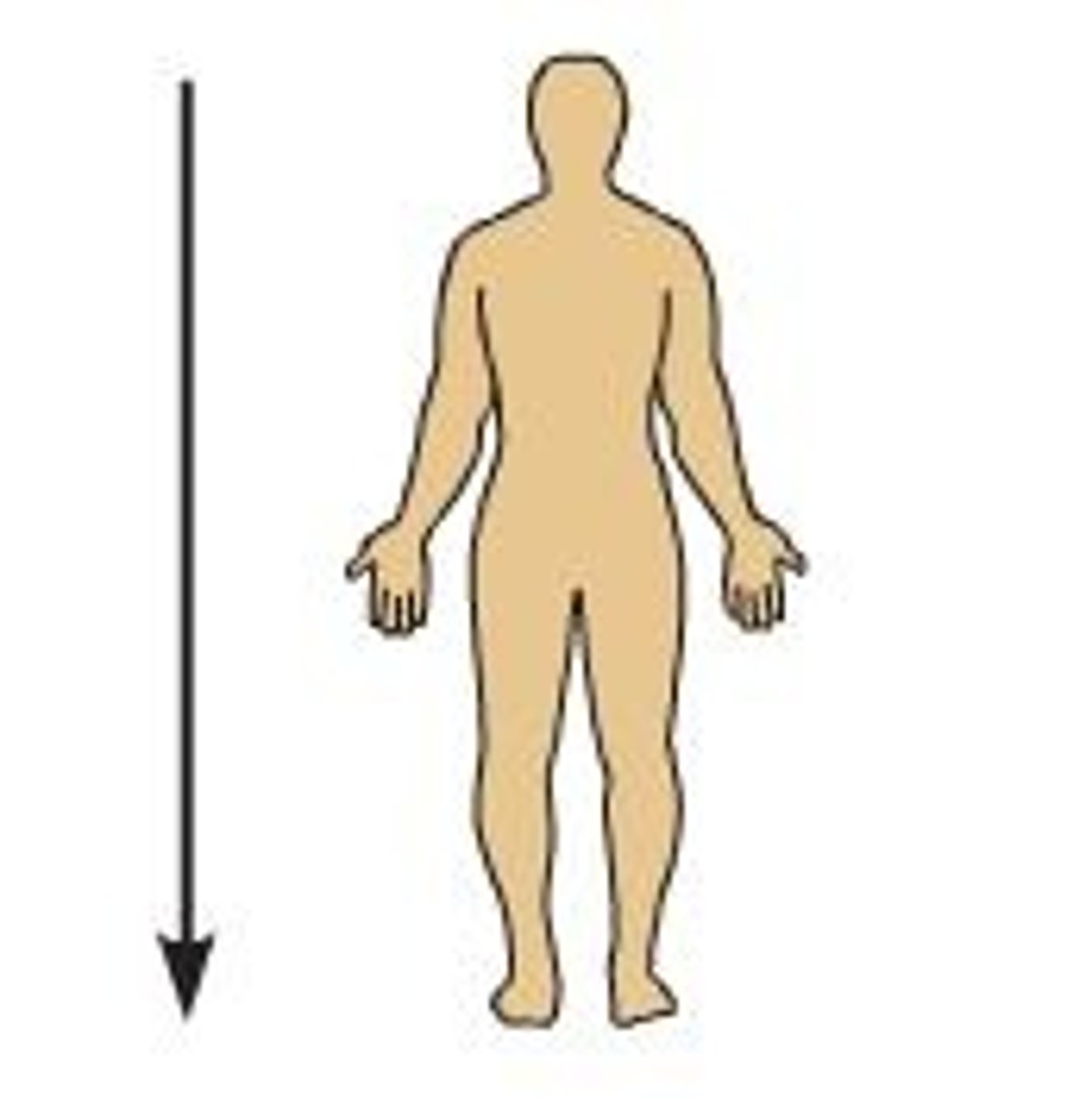
inferior
away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure of the body; below
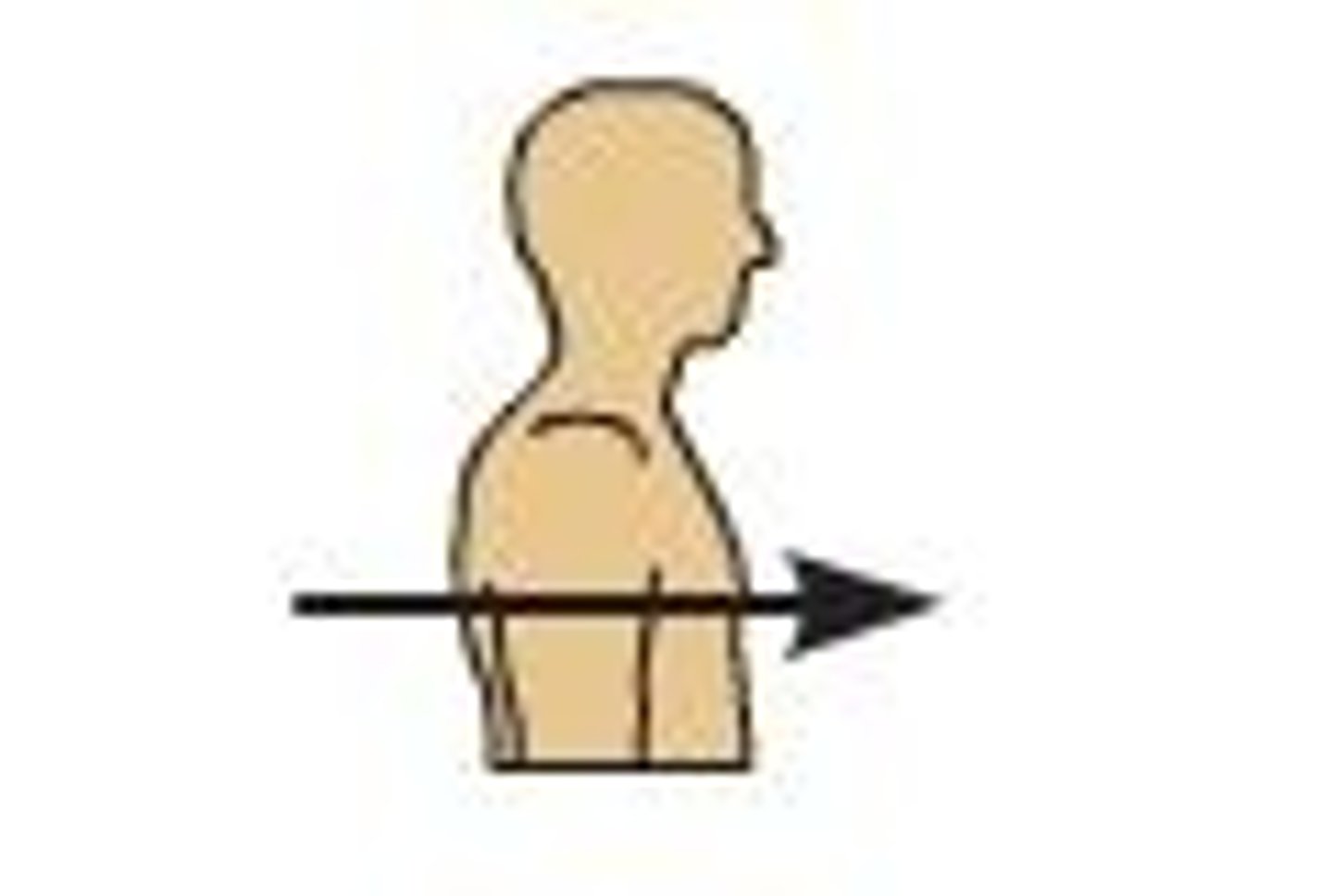
anterior
toward or at the front of the body; in front of
dorsal
toward or at the back of the body; behind
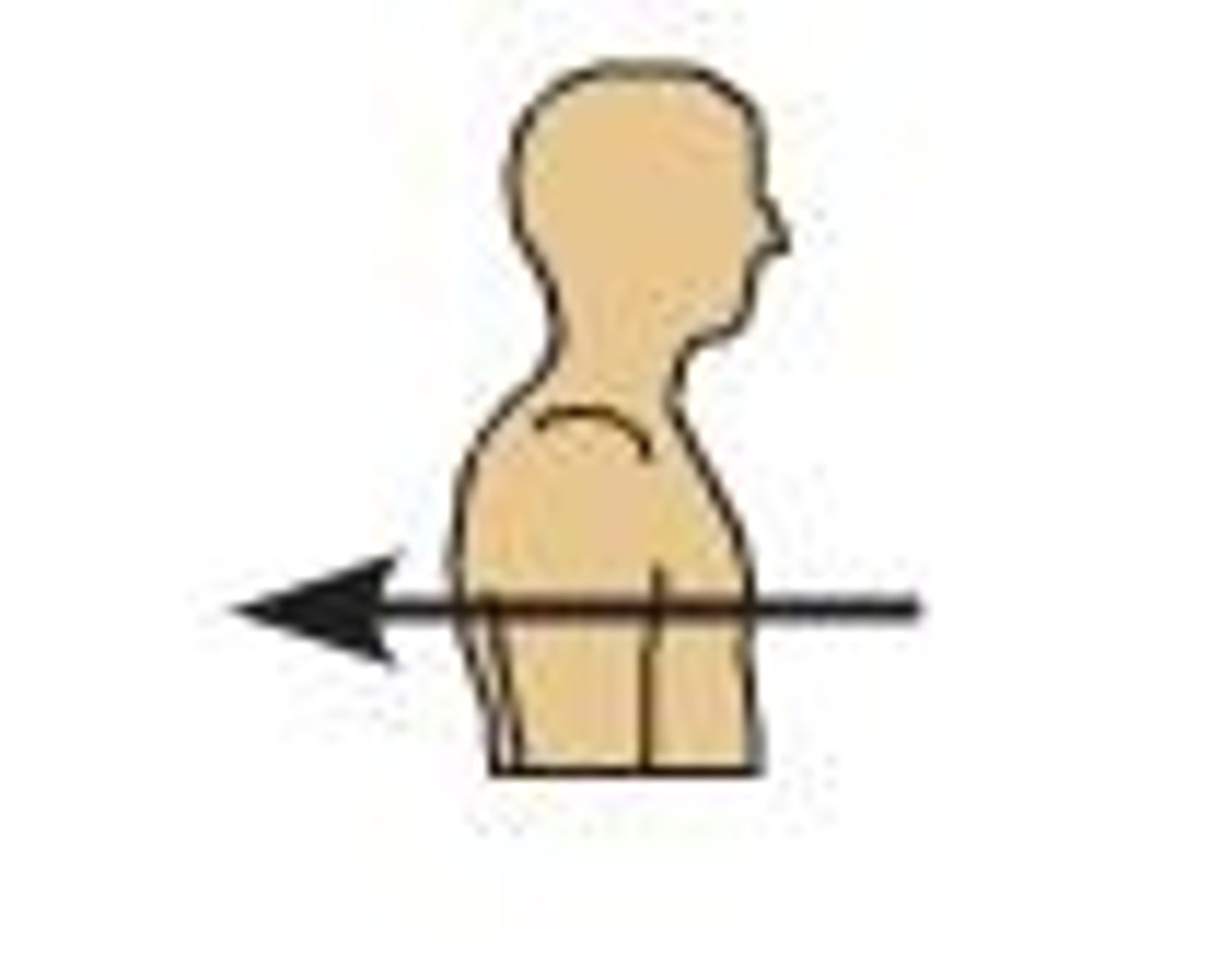
medial
toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of
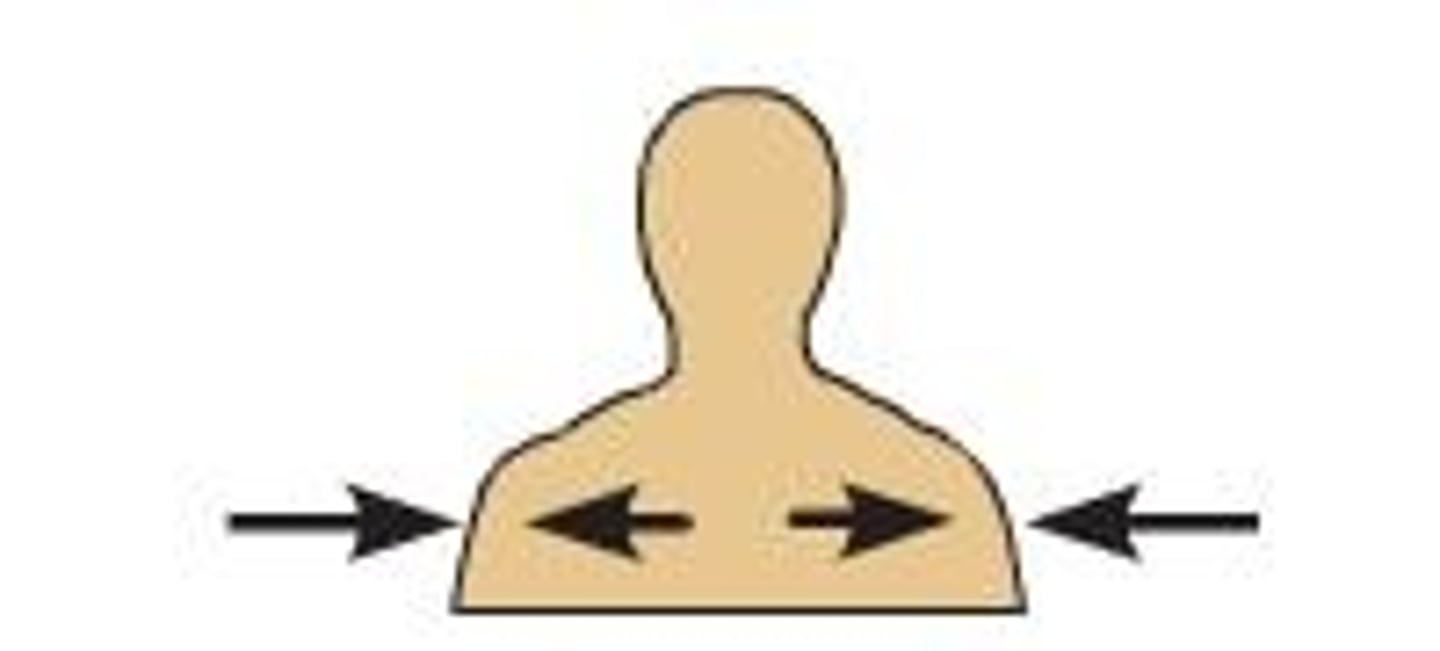
lateral
away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of
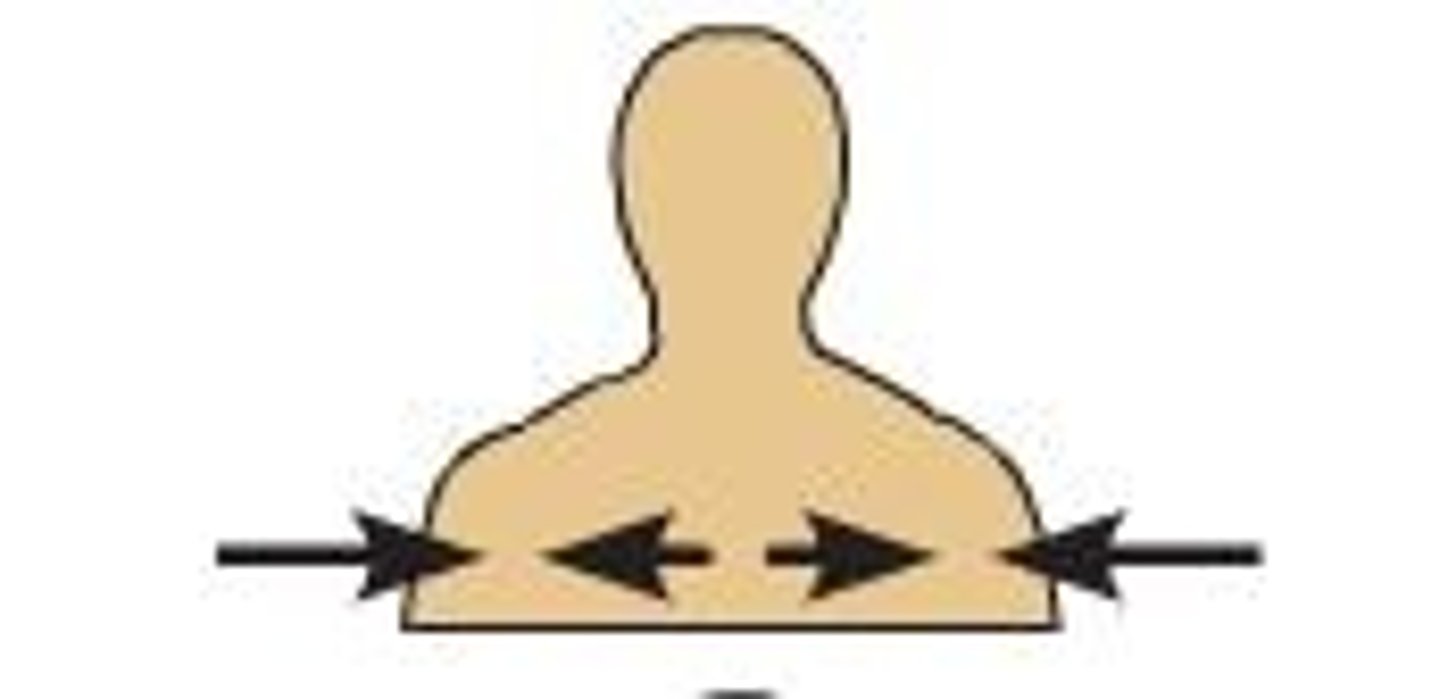
intermediate
between a more medial and a more lateral structure
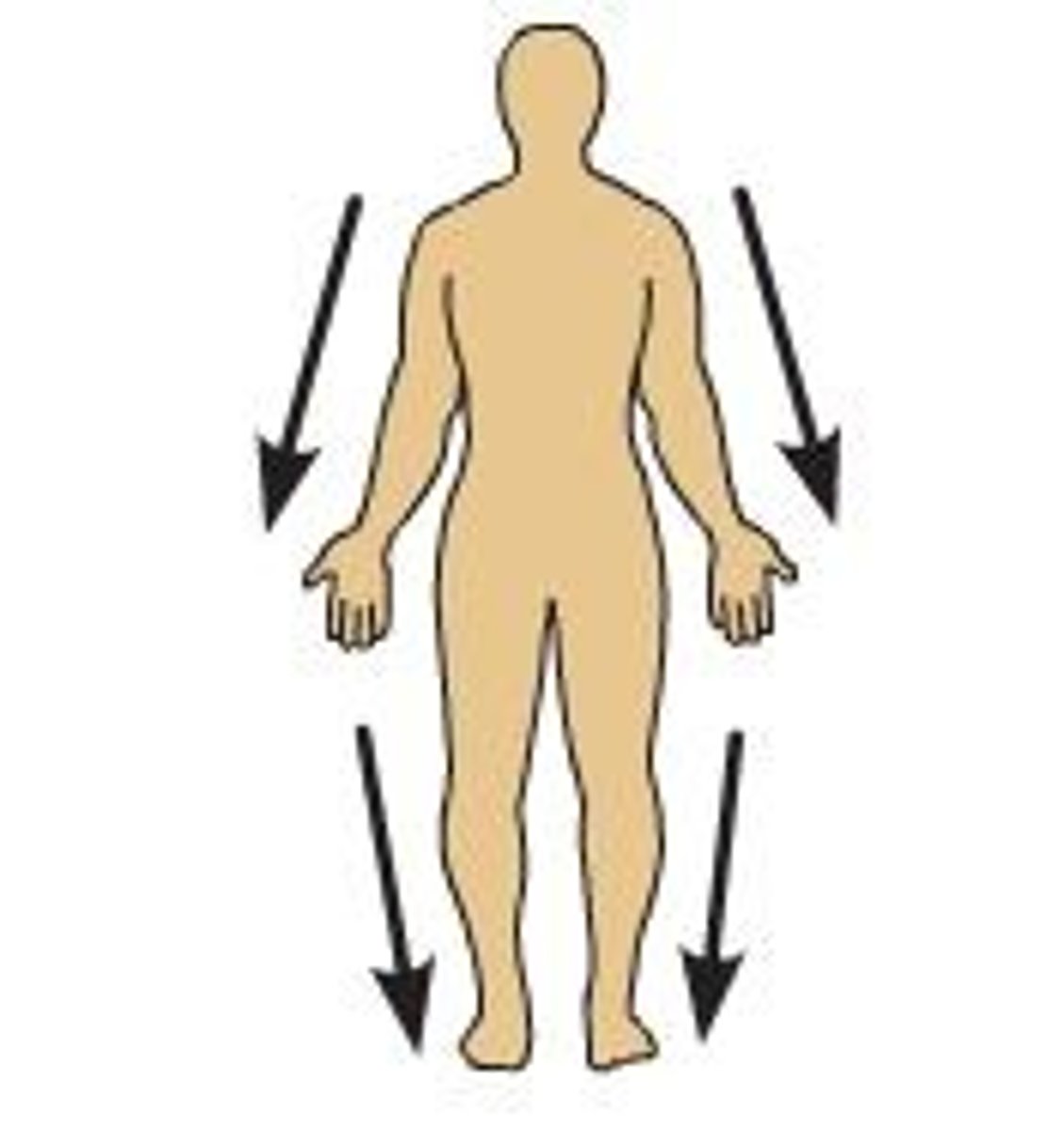
distal
farther from the origin of a body part of the point of attachment of a limb to the trunk of a body
superficial
toward or at the body surface
deep
away from the body surface; more internal