New innovations lecture 3
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cont. Strategies & Idea Generation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Which strategy to use depends on…
– Growth Opportunity
Ansoff’s opportunity matrix!
– Protection for Innovation
Is it possible to patent?
Easy to duplicate?
– Scale of Market
Larger markets = more interesting to establish market leadership!
– Competition
Competitor analysis!
– Position in Production/ Distribution System
Position in the value-chain?
Product Platform Planning
⚫ Many firms find that it is not efficient to develop a single product.
⚫ Platform: product families that share similarities
in design, development, or production process.
– Sony: four platforms for Walkman launched 160 product variations.
– Boeing: passenger, cargo, short- and long-haul planes made from same platform.
– Ryobi: uses a single electric motor for dozens of
consumer power tools.
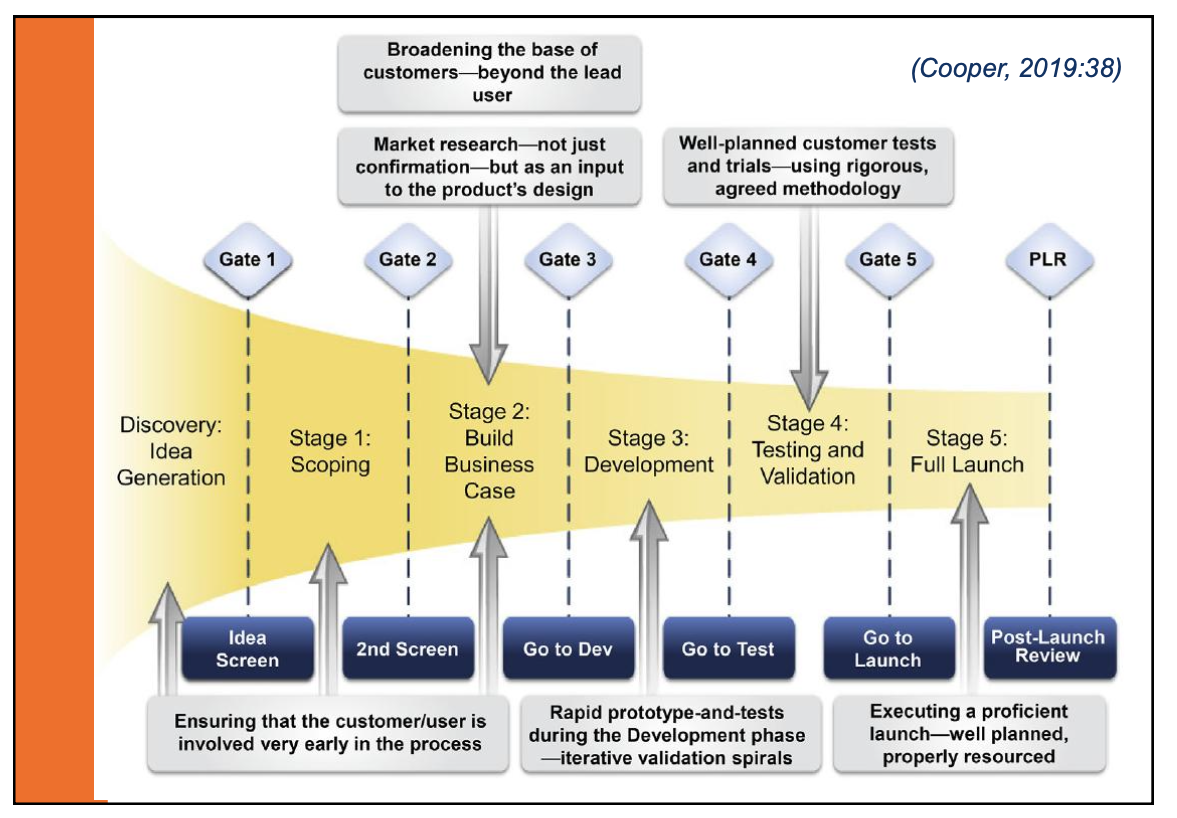
The Product Innovation Charter (PIC)
⚫ It is the new product team’s strategy.
⚫ It is for Products (not processes).
⚫ It is for Innovation (think of the definition of new
product).
⚫ It is a Charter (a document specifying the
conditions under which a firm will operate).
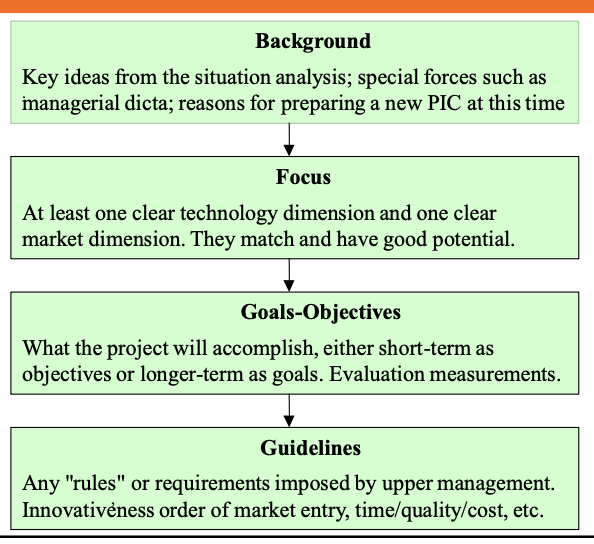
The Contents of a Product
Innovation Charter
Strategic Buckets Model for One SBU in Exxon Chemical
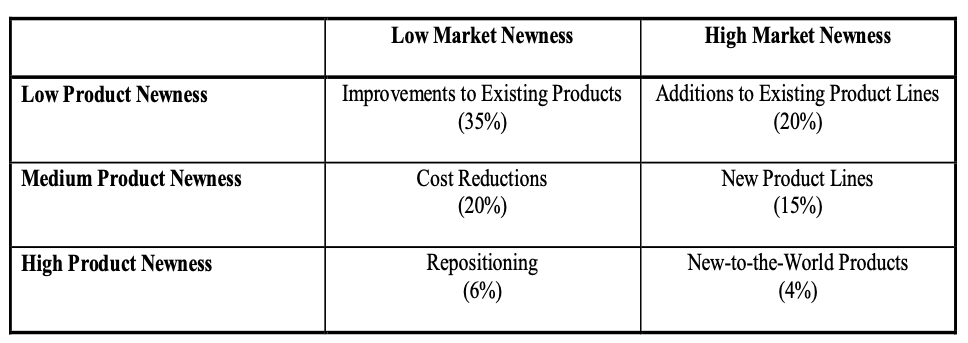
Sources of Identified Opportunities
⚫ An underutilized resource (a manufacturing
process, an operation, a strong franchise)
⚫ A new resource (discovery of a new material with many potential uses)
⚫ An external mandate (stagnant market combined with competitors’ activities)
⚫ An internal mandate (new products used to close long-term sales gap, senior management desires)
Idea generation methods
⚫ Direct search
⚫ Technological innovation Both product & process!
⚫ Exploratory user studies
⚫ Facilitating lead users E. von Hippel’s “Sources of Innovation”
⚫ Integration of technology & marketing QFD
⚫ Creativity methods…
Techniques to enhance group creativity
⚫ Brainstorming
– Brainstorming Circle
– Reverse Brainstorming
⚫ Phillips 66 group (also known as buzz groups &
free association groups)
⚫ Tear-Down
⚫ ”And Also” (also known as Idea buildning and
modification)
Divergent & Lateral Thinking
⚫ The process of developing multiple solutions to a given problem or stimulus
⚫ Characteristics
– Fluency (ability to produce ideas quickly)
– Flexibility (capacity to consider a variety of approaches simultaneously)
– Orginality (think out ideas that are different)
– Elaboration (think through the details and do it)
Delphi - method
⚫ Developed in the 50s by RAND corp.
⚫ Survey in two or more rounds
⚫ Provides the participants with the results from the previous round as input for change/discussion
⚫ Nobody looses face – done anonymously
⚫ Useful for longe-range forcasting (20-30 years)
where experts are the only source of info
⚫ (Similar to a Think Tank - more a way of organizing people)
Focus groups critique
1. 2. 3. 4. You lack knowledge about the consumer wants
You want to get responces that are BIASED by other subjects
You can effectively prevent mgmnt from generalization
You plan to follow up with research possible to generalize from
=> Use one-on-one Non Directive Interviewing J. Scott Armstrong (2001)
Idea selection
⚫ Not always easy!
⚫ How much resources is needed?
⚫ Consequences for other projects?
⚫ Predictions of future markets?
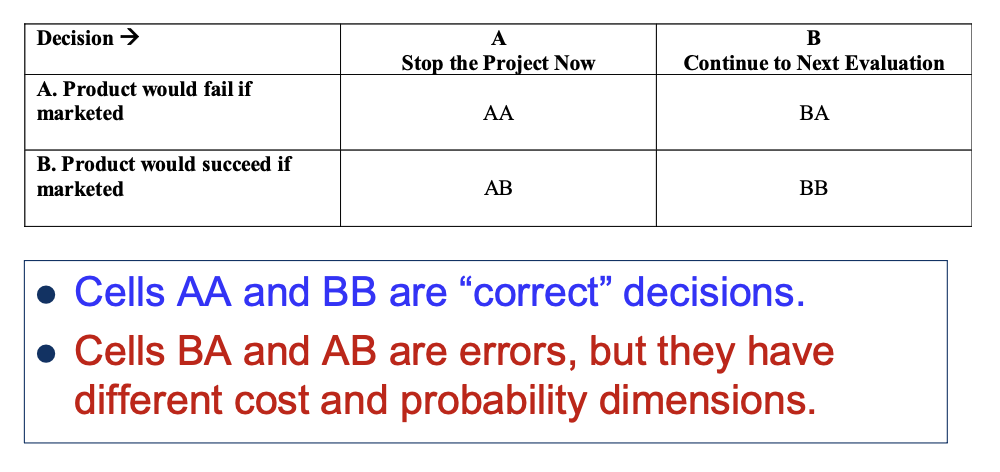
Risk/Payoff Matrix at Each Evaluation
Approaches to Idea/Project Evaluation
1. Benefit measurement models
2. Economic models
3. Portfolio selection models
4. Market research models
Open Innovation
⚫ Instigated by Henry Chesbrough in 2003
⚫ Antithesis of the traditional vertical integration
model (Internal innovation leads to internal dev.
products that are sold by the company.)
Interactive model of innovation (Fig 1.7)
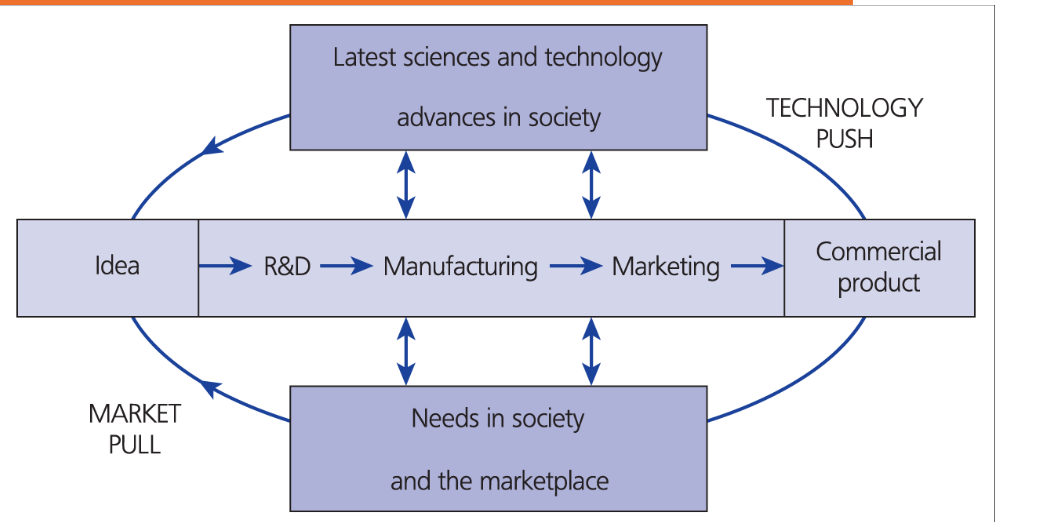
”Traditional” way of Innovation
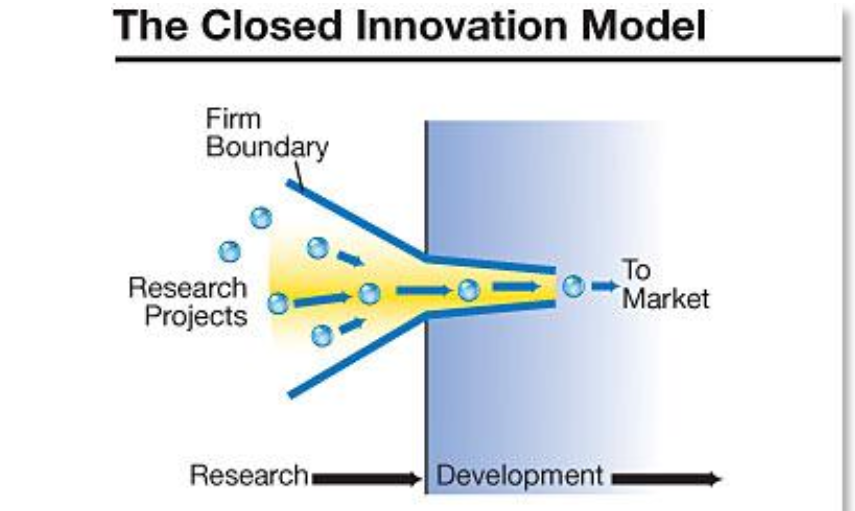
The Open Innovation way
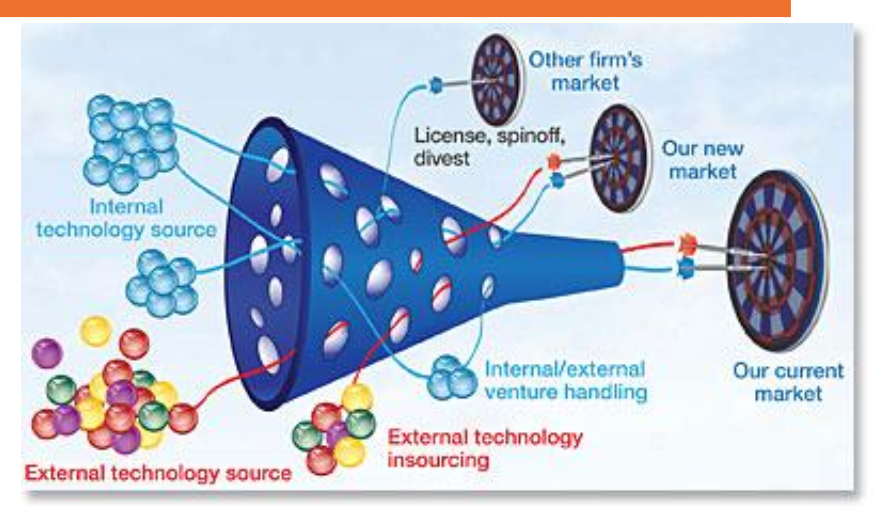
Differences closed and open
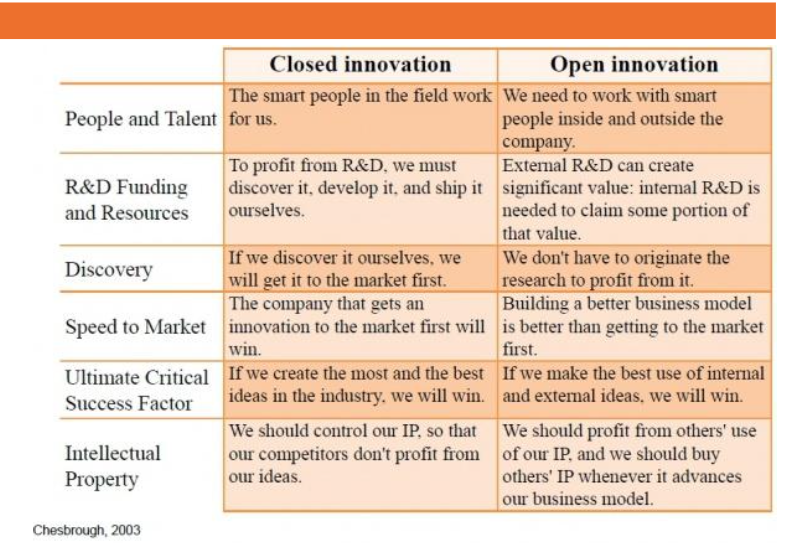
5 Steps to ”open up”
1. Become a customer or supplier to your former
internal projects
2.Let others develop your nonstrategic initiatives
3. Make your Intellectual Property (IP) work harder
for you and others
4.Grow your ecosystem, even when you are not
growing
5.Create open domains to reduce costs and to
expand participation
Different forms of open innovation by technology development business
model and IP strategy. Bogers et al. (2019)
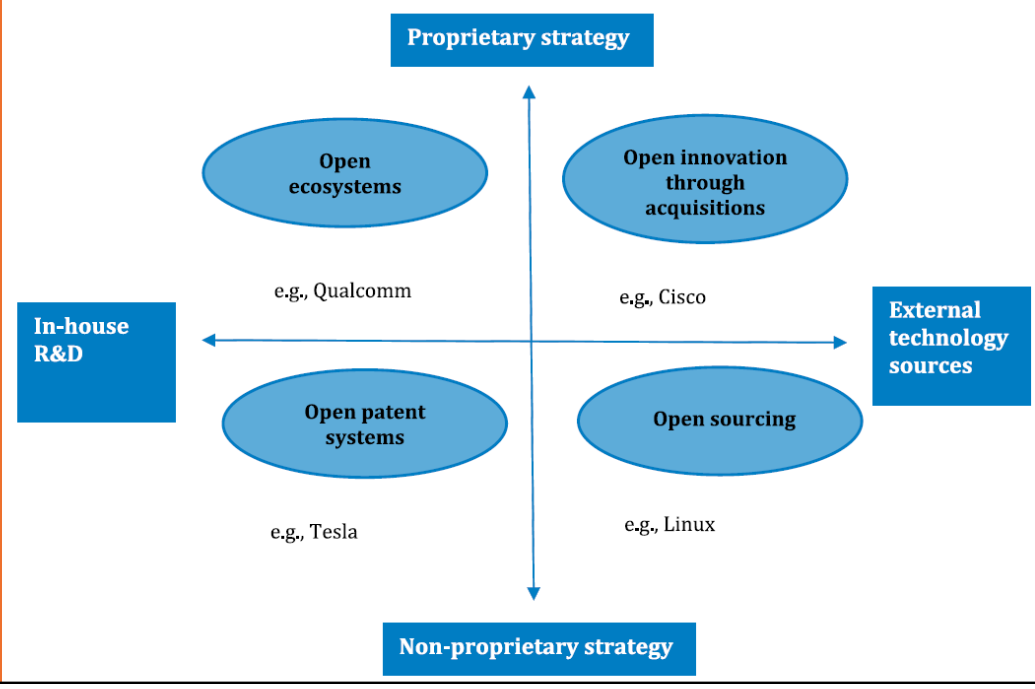
cooper 2