forensic psych ch.10
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
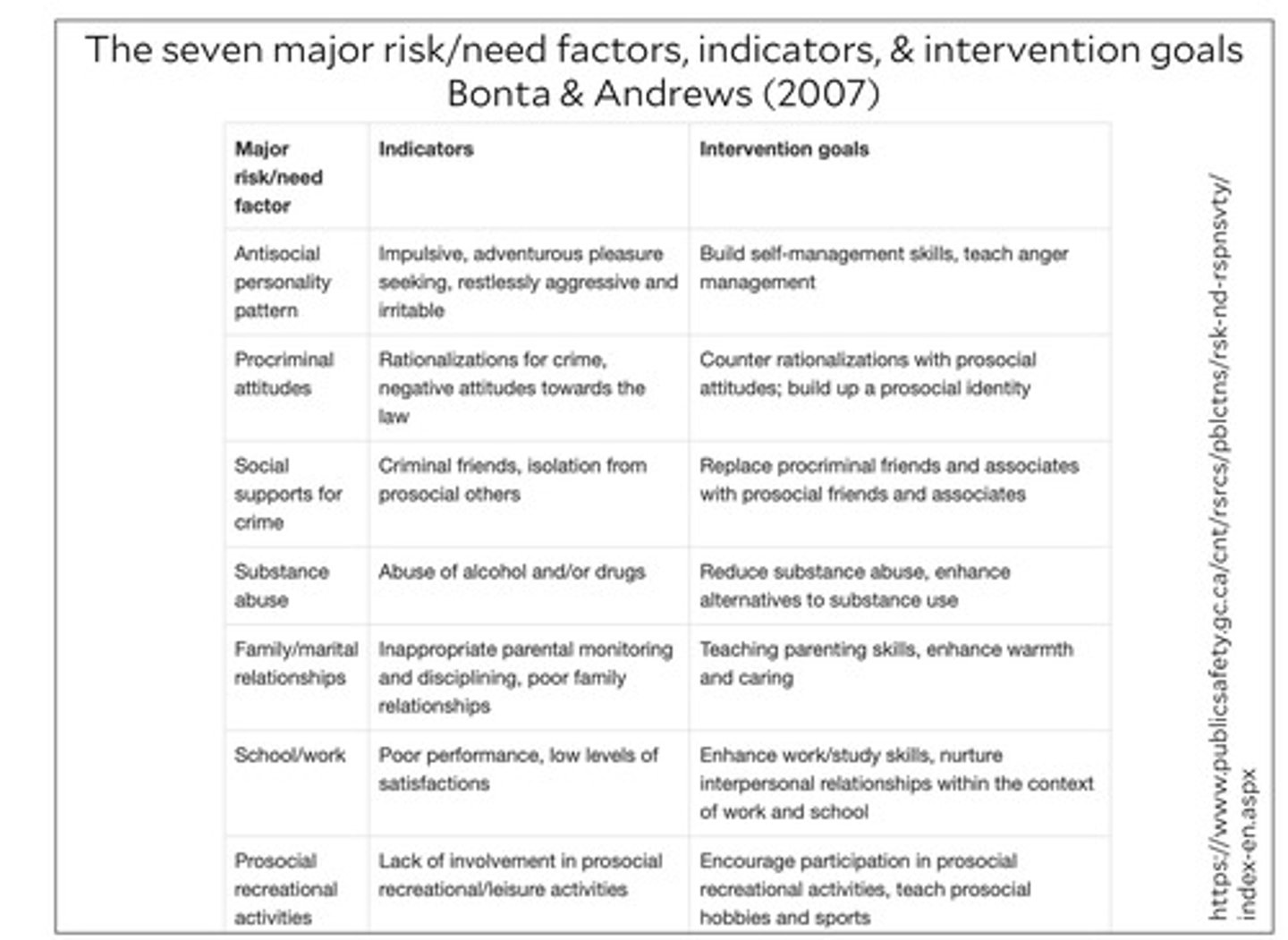
7 major risk/need factors, indicators, and interventions goals
what is risk assessment
- risk is a range
- probability may change over time
- levels of risk interact with personal, background, and situational factors
2 components of risk assessment
1) prediction -> analysis of future criminal act (reoffend)
2) management -> develop strategies to manage or reduce risk
- emphasis on violence prevention over prediction
Indeterminant sentence
eligible for parole after 20 years -> actual sentence indeterminant (could be life)
- Dangerous offender (DO)
- Long-term offender (LTO)
when does risk assessment happen?
at every major decision point in criminal proceedings
- pretrial
- sentencing
- release
prediction outcomes
predicted to not reoffend -> doesn't = true negative (correct)
predicted to not reoffend -> does -> false negative (incorrect)
predicted to reoffend -> doesn't = false positive (incorrect)
predicted to reoffend -> does = true positive (correct)
base rate problem
risk assessments = lots of false positives
- reduction of freedoms + liberties of offender (ex., longer term in prison)
unstructured clinical judgement
intuition
- Look over files
- Talk with offender
- No guidelines
Actuarial prediction
data
- risk factors based on statistical outcomes
- Likelihood number
- Removes clinician judgement
Structured professional judgement
data + intuition
- Predetermined risk factors + professional judgement
Static predictors
historical
resistant to change/can't control
past behavior/events
- age at which commit crimes, family history (exposure to violence, victim to maltreatment)
- Younger onset of criminal behavior = higher prediction rate of recidivism
Dynamic predictors
criminogenic needs
changeable/controllable
- impose restrictions/sanctions on behavior
static-99
10-item actuarial scale, scored out of 4 each (ex., young age at time of release, ever lived with intimate partner)
HCR-20
20 items, primarily static
- Combine static factors with risk management
dispositional factors
traits, tendencies, style
- demographics (age at first offence, gender)
- personality, attitudinal characteristics (criminal attitudes, impulsivity, psychopathy)
clinical factors
substance use -> direct (commit crime while on drugs) and indirect (commit crime to buy drugs)
mental disorders (especially psychoses)
contextual factors
"situational"
aspects of current environment:
- lack of social support
- access to weapons or victims
protective factors
1) prosocial involvement
2) strong social support
3) strong attachments
4) intelligence