GW PUBH 1101 Henry: Chapter 2 (Evidence-Based Public Health)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
burden of disease
occurrence of disability and death due to a disease
morbidity and mortality
disability and death
course of disease
how often the disease occurs, how likely it is to be present, what happens once it occurs; we look at rates to determine this
distribution of disease
looks at who gets the disease, location of these people, when the disease occurs, etc.; focuses on group associations, race/age/gender/SES, urban/rural, risk factors
epidemiologists
public health professionals who look at frequencies of diseases
group associations
these are investigated when epidemiologists look for disease distribution; suggest ideas/hypotheses about etiology of disease
risk indicators
this is when types of a factor occur more frequently among groups w the disease when compared to groups without the disease
artifactual
these are differences or changes in a distribution of disease are not real; could be this if there are differences/changes in interest/ability in identifying the disease or if there are differences/changes in disease definition; Ex: these types of changes can happen w new technology, new interest in detection, changes of definition like with HIV/AIDS
age adjustment
looks at age to see if that is a factor in disease development
incidence
the number of NEW cases over the total population at risk within the same time period
prevalence
when there are new AND preexisting cases within a certain time period within a population; this is typically higher than the incidence
population comparisons
ecological studies; these look at groups or a population without having information on specific individuals in the group
confounding variable
variable in a study/experiment that is never really taken into account when making the experiment, it is usually found afterwards
contributory cause
causation of a disease that is established using research studies, where the cause is associated with the effect, the cause precedes the effect, and altering the cause alters the effect
case-control studies
establish that a cause is associated with an effect for individuals; Ex: show that cigarettes and lung cancer occur together more frequently than by just chance alone
risk factor
when a factor has been shows to be associated with a certain outcome; Ex: smoking cigarettes is associated w the outcome of lung cancer
cohort studies
establish that the cause precedes the effect; these follow individuals with the cause or risk factors and those without the cause/risk factor to see who develops the effect/outcome; Ex: smokers are compared with non-smokers to see which group develops lung cancer
randomized controlled trials
establish that altering the cause alters the effect; individuals are assigned to be exposed or not exposed to the cause to see who develops the effect; Ex: some will smoke and some will not, and they will be tracked to see who develops lung cancer
efficacy
implies that an intervention is effective and it increases positive outcomes
necessary cause
a condition that must be present for the effect to occur; Ex: cigarettes are not this because some never smoke but still develop lung cancer
sufficient cause
a condition that automatically produces the effect in question; Ex: this is not cigarettes because some smoke but do not develop lung cancer
PERIE process
framework for defining/analyzing/addressing public health issues; it is circular and the cycle will repeat itself if need be
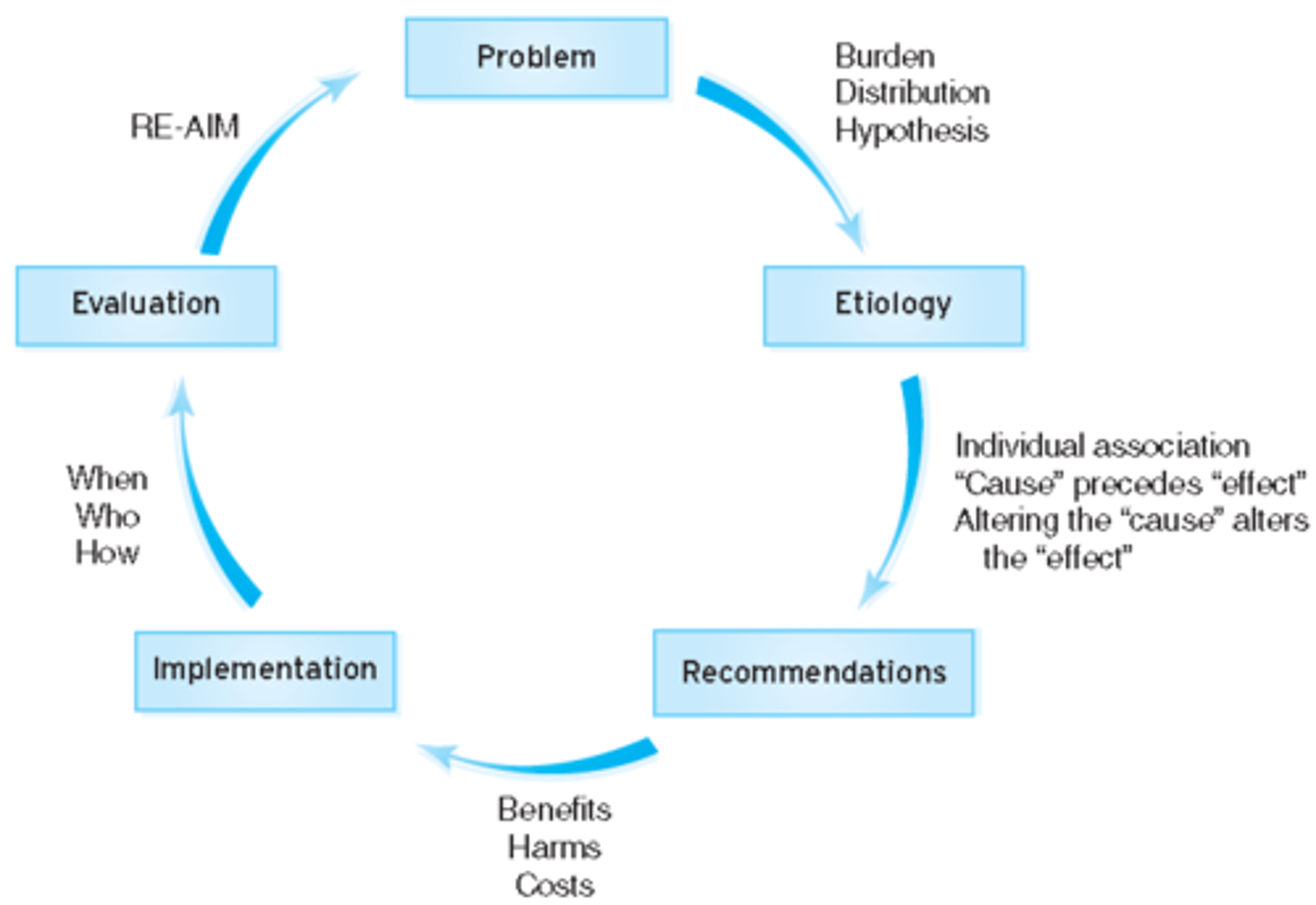
problem
P in PERIE; defining what the main health issue is that needs to be addressed
etiology
E in PERIE; what is the contributory cause? we look at the different studies to establish relationships between causes and effects for indivdiuals
recommendations
R in PERIE; works to reduce health impact; evidence-based __________ are built on evidence from intervention studies that indicate whether health outcomes will be improved; these interventions account for benefits as well as safety & harm; scored based on evidence quality
score
part of recommendations; can be good, fair, or poor; criteria for evidence-based recommendations is graded based on the quality of investigation
implementation
I in PERIE; looks at when, who, and how to intervene by focusing on the timing of disease to introduce intervention, who the intervention is for, and the type of intervention; these are done once there are strong recommendations
information intervention
intervention strategy that looks to change behavior through individual encounters, mass media, or group interactions; Ex: Truth campaign for smoking
motivation intervention
intervention strategy that looks to change behavior via incentives that are tangible rewards; Ex: student rewards for not smoking
obligation intervention
intervention strategy that looks to change behavior through laws and regulations; Ex: increasing age to purchase cigarettes, suspension of student athletes who smoke
victim blaming
could happen in motivational interventions; Ex: punishing smokers who smoke could be seen as this bc it implies that smoking is the fault of the smoker
primary interventions
type of intervention; occurs before disease onset and tries to stop disease from every occurring; Ex: yearly checkups, eye doctor
secondary interventions
type of intervention; occurs after the development of disease or when symptoms appear; Ex: pre-diabetes, testing abnormalities, pre-cancerous cells, person in cancer remission, family history for disease
tertiary interventions
type of intervention; occur after the occurrence of symptoms, is the management of disease; Ex: diagnosis of cancer and currently going through chemotherapy, diabetes type II and managing w insulin treatments
evaluation
measures how much of the problem has been eliminated by the interventions, looks at what problem remains; we want to publish this data and if it succeeds w another population, or want the intervention to be adapted to fit different groups
RE-AIM framework
relatively new method of intervention evaluation; reach effectiveness, adoption, implementation, maintenance; used in clinician work/clinic settings