Photosystems and Light Reactions in Photosynthesis: Structure, Function, and Electron Flow
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
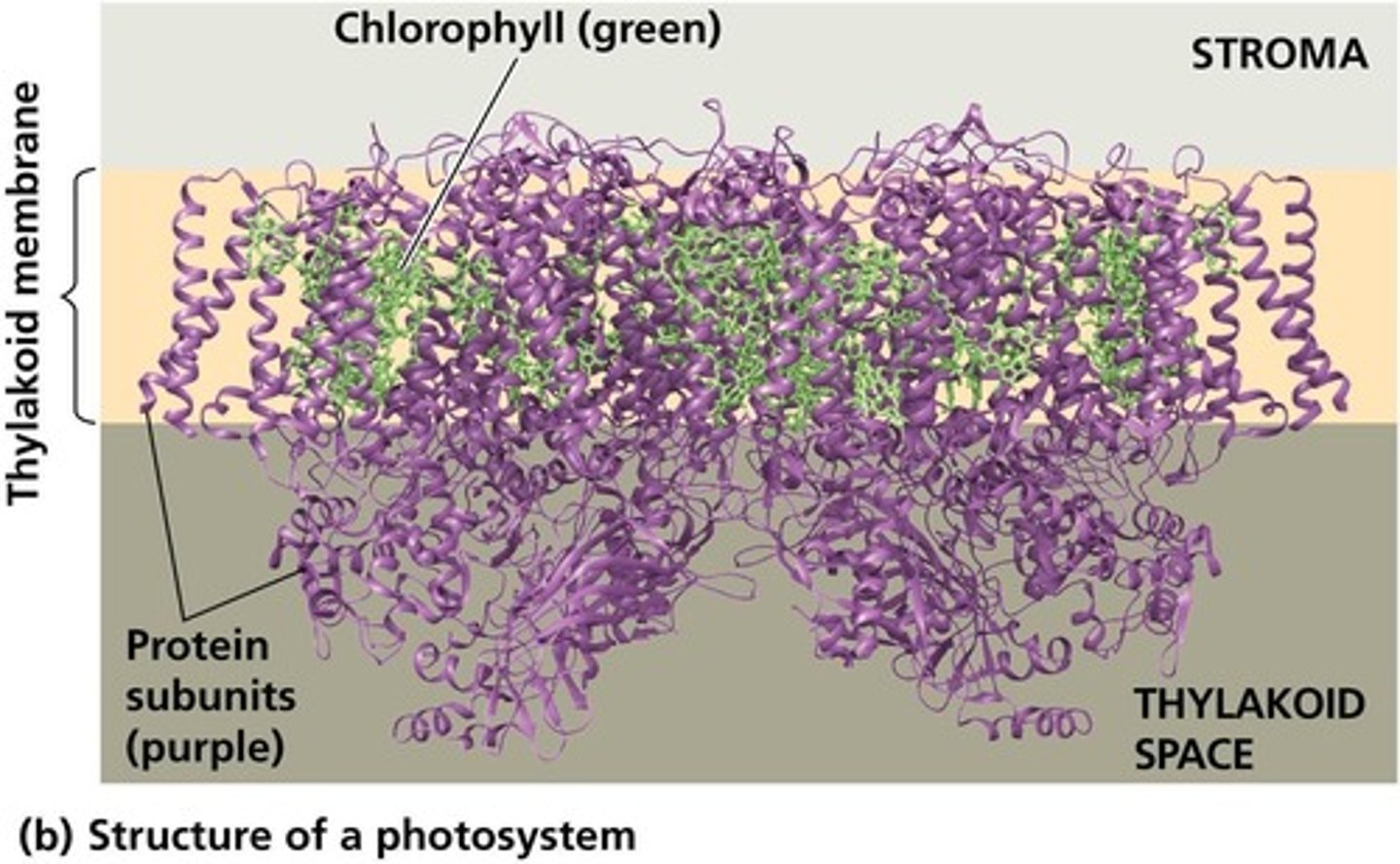
What are photosystems composed of?
Chlorophyll molecules, small organic molecules, and proteins organized into complexes in the thylakoid membrane.
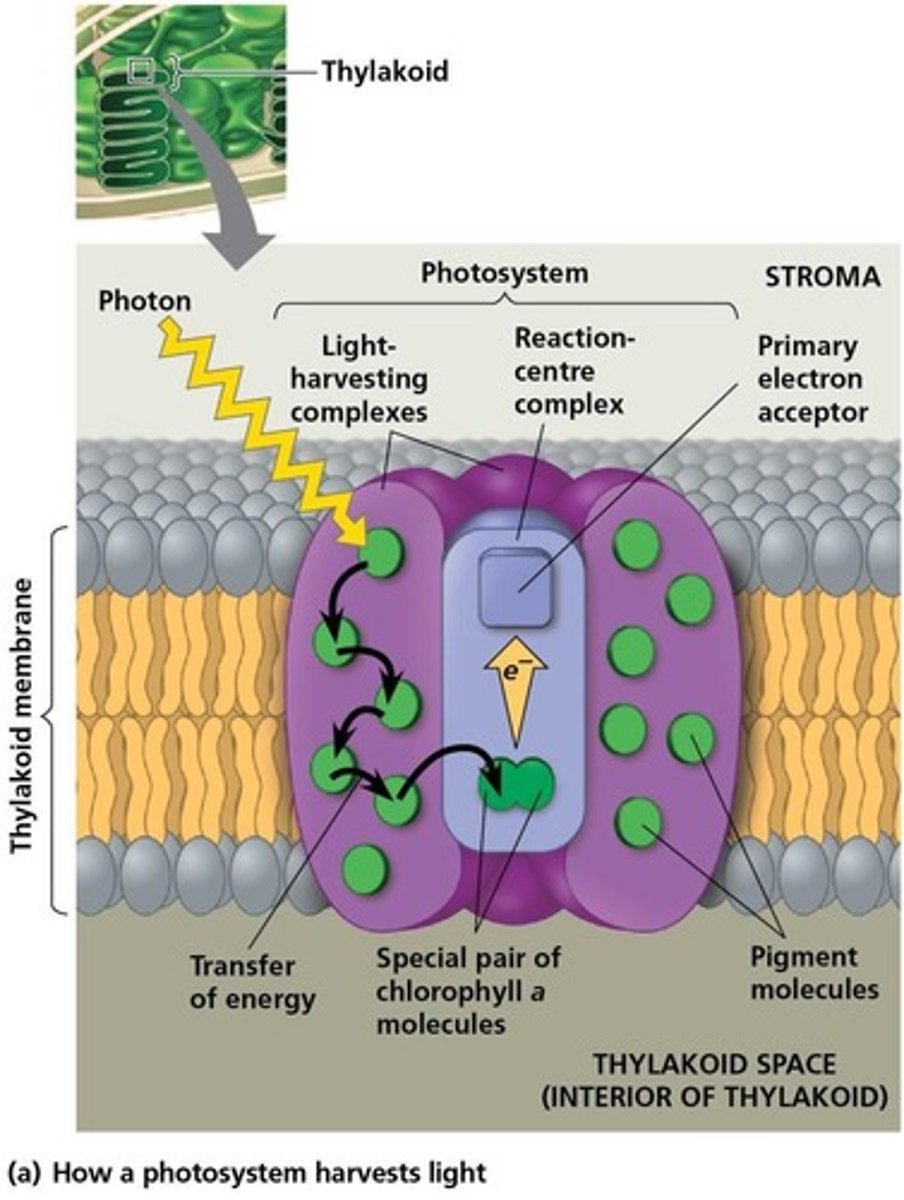
What is the function of light-harvesting complexes?
They transfer the energy of photons to the reaction-center chlorophylls.
What are the two types of photosystems found in thylakoid membranes?
Photosystem II (PS II, P680) and Photosystem I (PS I, P700).
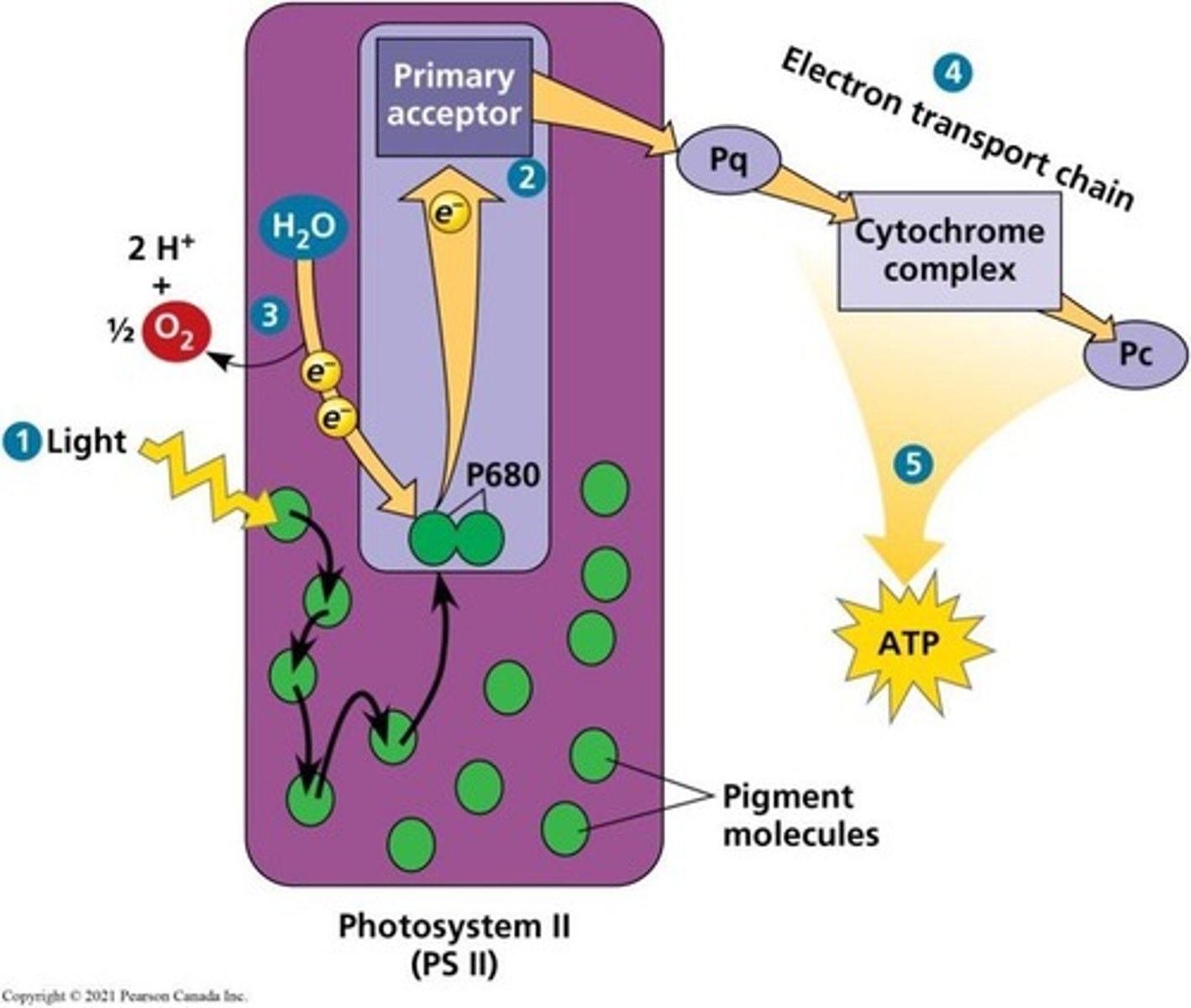
What is the primary role of PS II in the light reactions?
PS II functions first and is involved in generating ATP and NADPH.
Why is PS II named as such?
It was discovered second, despite functioning first in the light reactions.
What wavelength of light does PS II (P680) absorb best?
680 nm wavelengths of light.
What wavelength of light does PS I (P700) absorb best?
700 nm wavelengths of light.
What are the two possible routes for electron flow in the light reactions?
Linear (non-cyclic) and cyclic electron flow.
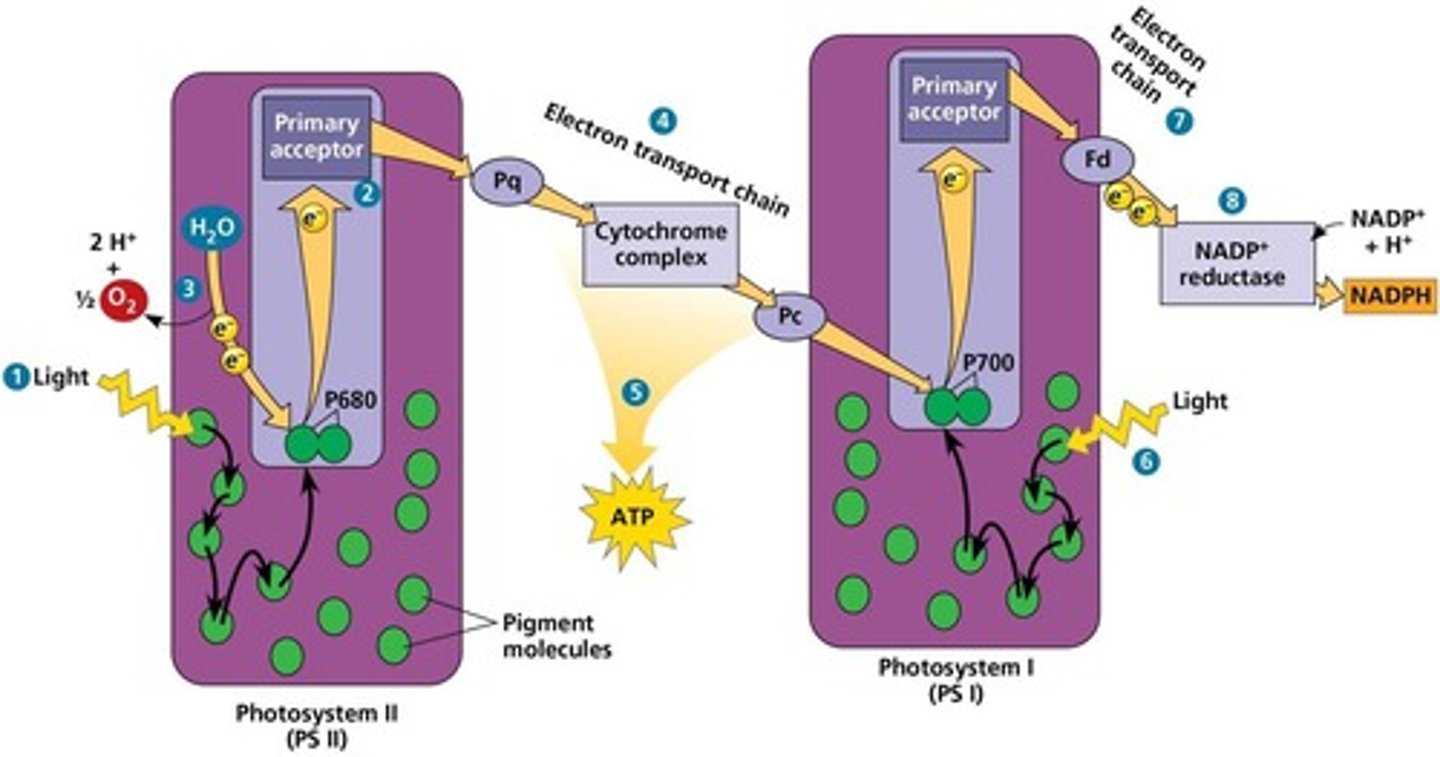
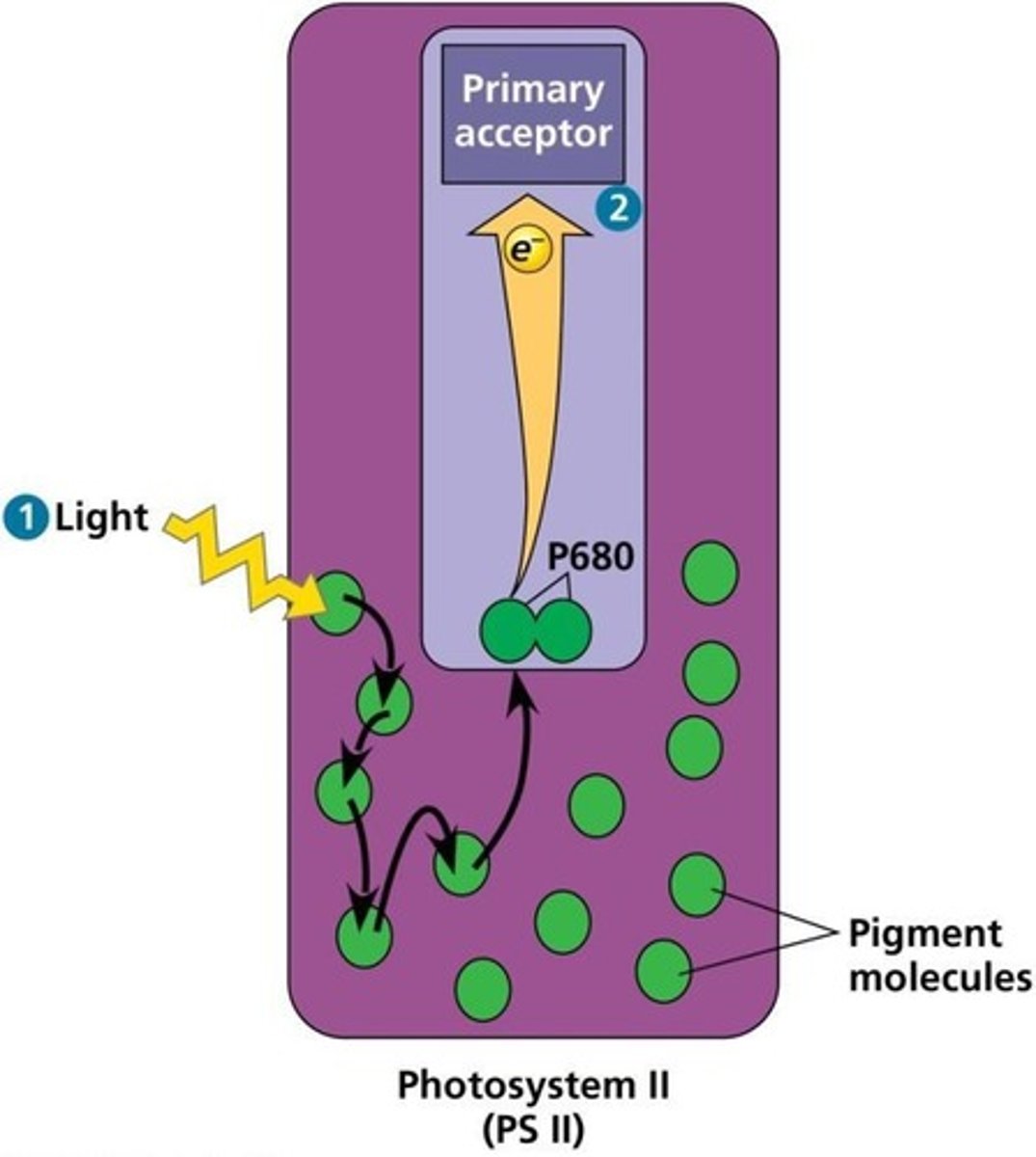
What is the first step of the light reactions in photosystems?
A photon of light is absorbed by a pigment of PS II, and energy is transferred to P680.
What happens to P680 after it absorbs light?
An excited electron is transferred from P680 to the primary electron acceptor, generating P680+.
How is P680+ restored after losing an electron?
Electrons from water (H2O) are transferred to P680+, reducing it back to P680 and releasing O2 as a by-product.
What is the role of the electron transport chain (ETC) in linear electron flow?
It facilitates the transfer of electrons from PS II to PS I and helps generate a proton gradient for ATP synthesis.
What occurs when the photoexcited electron falls down the ETC?
Energy released is used to move protons across the thylakoid membrane, generating a proton gradient.
What happens to P700 in PS I during the light reactions?
P700 becomes P700+ when it loses an electron, which is then replaced by an electron from PS II.
What is the final step in linear electron flow?
Electrons are transferred from ferredoxin (Fd) to NADP+, reducing it to NADPH, catalyzed by NADP+ reductase.
What is the significance of NADPH in photosynthesis?
NADPH provides high-energy electrons for the Calvin cycle and helps maintain the proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane.
What is the by-product of water splitting during the light reactions?
Oxygen (O2) is released as a by-product.
What is the role of chlorophyll a in photosystems?
Chlorophyll a is the key light-harvesting pigment that participates directly in the light reactions.
What is the primary electron acceptor in photosystems?
It is a molecule that accepts excited electrons from the reaction center chlorophylls.
What does the term 'cyclic electron flow' refer to?
An alternative pathway of electron flow that does not produce ATP but recycles electrons within PS I.
What is the main outcome of linear electron flow?
The generation of ATP, NADPH, and oxygen during the light reactions.
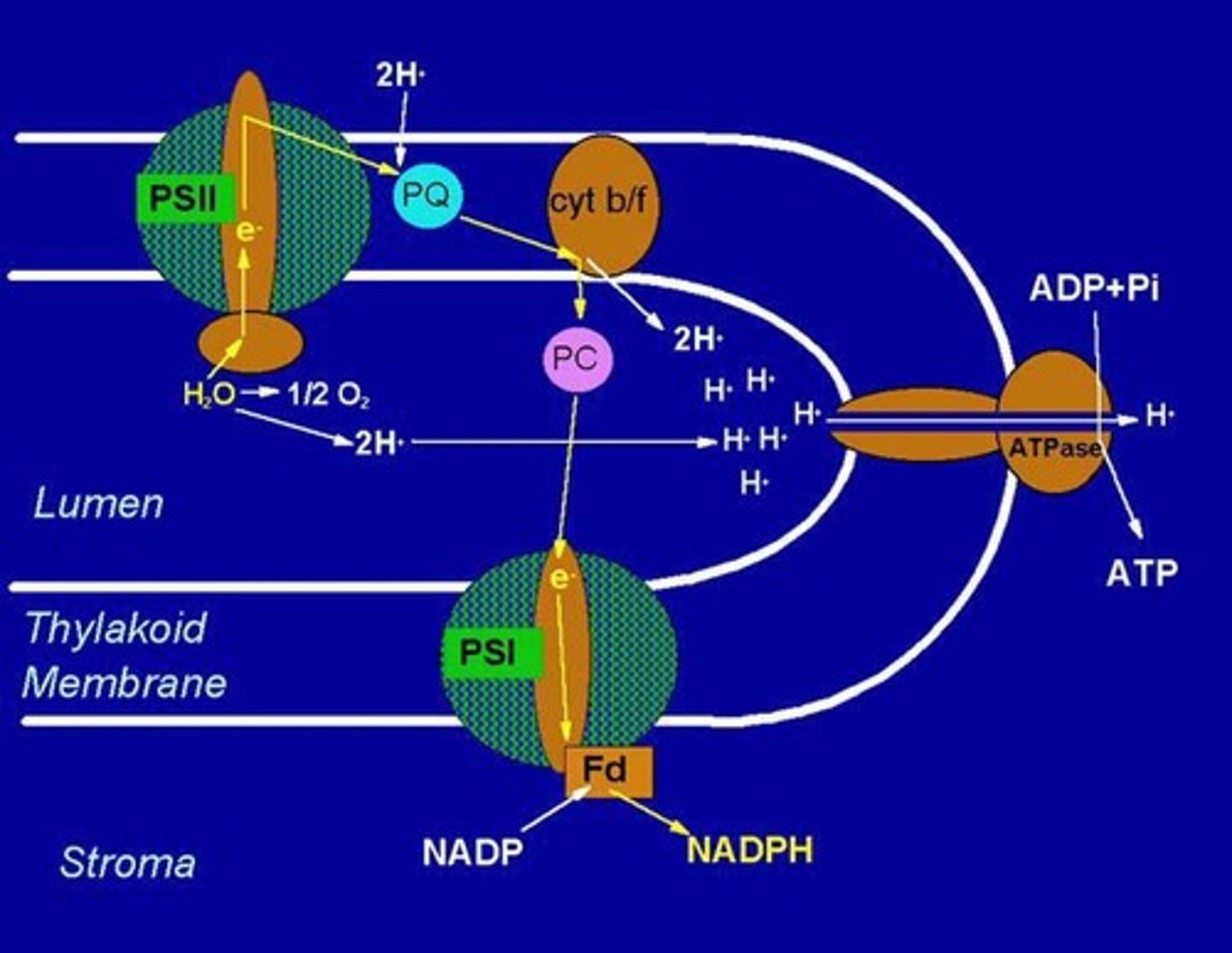
What is the significance of the proton gradient generated during linear electron flow?
It drives ATP synthesis through ATP synthase in the thylakoid membrane.
What happens to the energy of photons absorbed by photosystems?
The energy is transferred to reaction-center chlorophylls, initiating the light reactions.
Where does cyclic electron flow occur?
In the thylakoid membrane.
What is the role of PSII in cyclic electron flow?
PSII is not involved; electrons cycle back from ferredoxin (Fd) to PSI.
What is the reaction center of PSI?
P700 reaction center.
What does cyclic electron flow produce?
ATP, but not NADPH or O2.
Why does cyclic electron flow satisfy the Calvin cycle's needs?
It generates more ATP than NADPH.
What is chemiosmosis?
The movement of ions (H+) across a semi-permeable membrane down their electrochemical gradient.
What powers ATP synthesis during chemiosmosis?
The diffusion of H+ ions from the thylakoid space to the stroma.
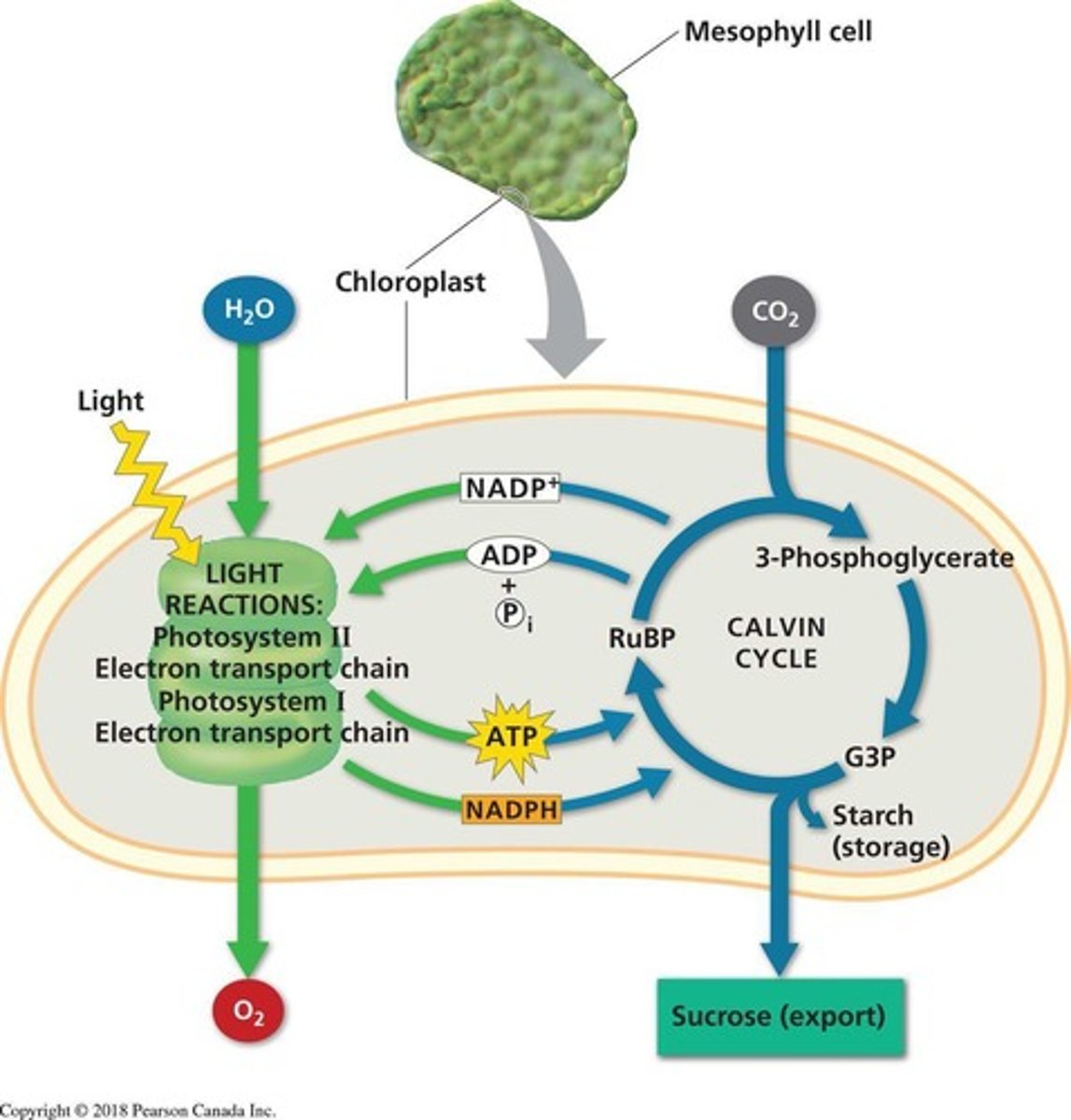
What is the main function of the Calvin cycle?
To use ATP and NADPH to reduce CO2 to sugar.
Who discovered the Calvin cycle?
James Bassham, Andrew Benson, and Melvin Calvin.
What is the first organic product of carbon fixation in C3 plants?
3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA).
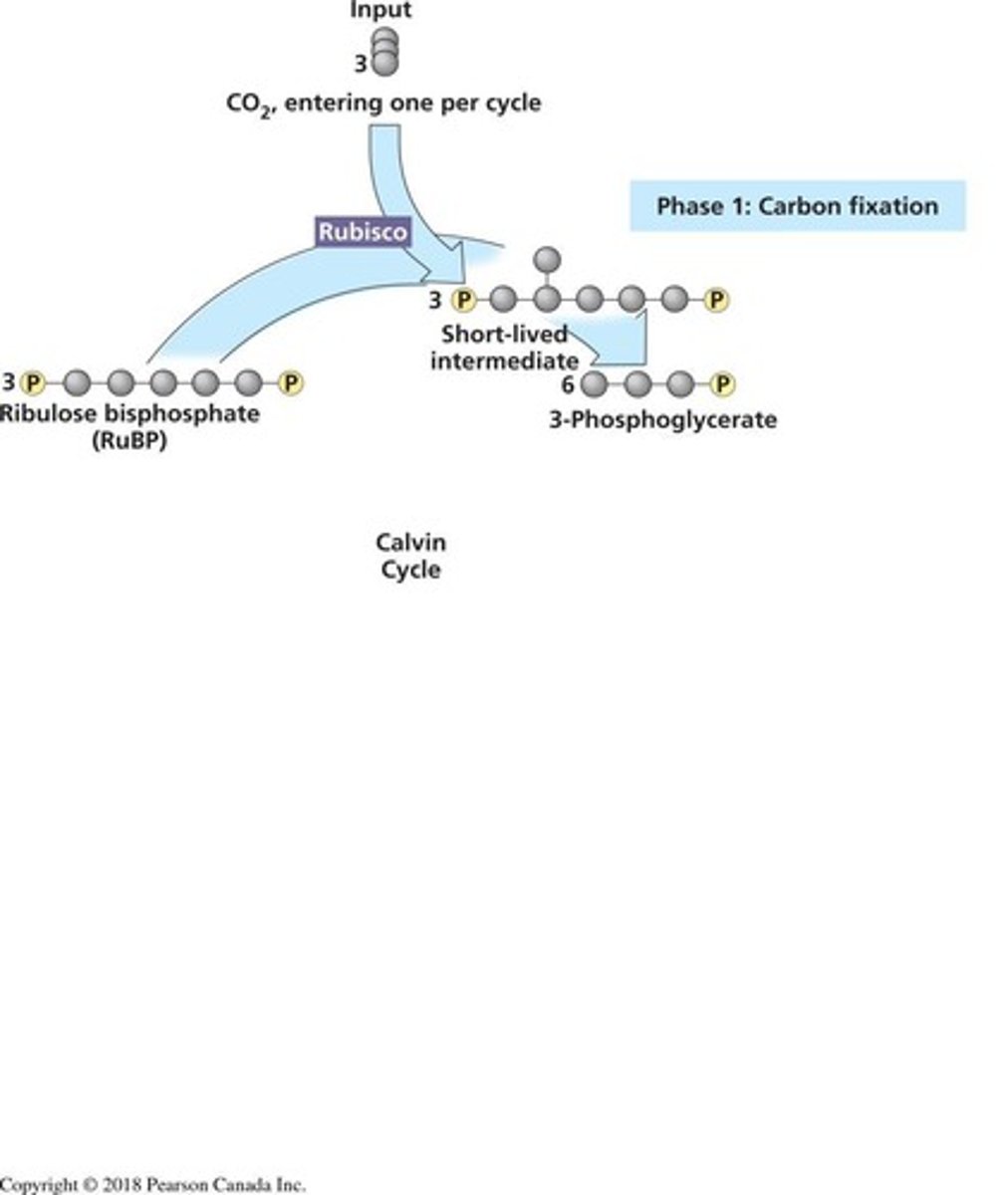
What enzyme catalyzes the fixation of CO2 in the Calvin cycle?
RuBisCO.
What are the three phases of the Calvin cycle?
1. Carbon fixation, 2. Reduction, 3. Regeneration of RuBP.
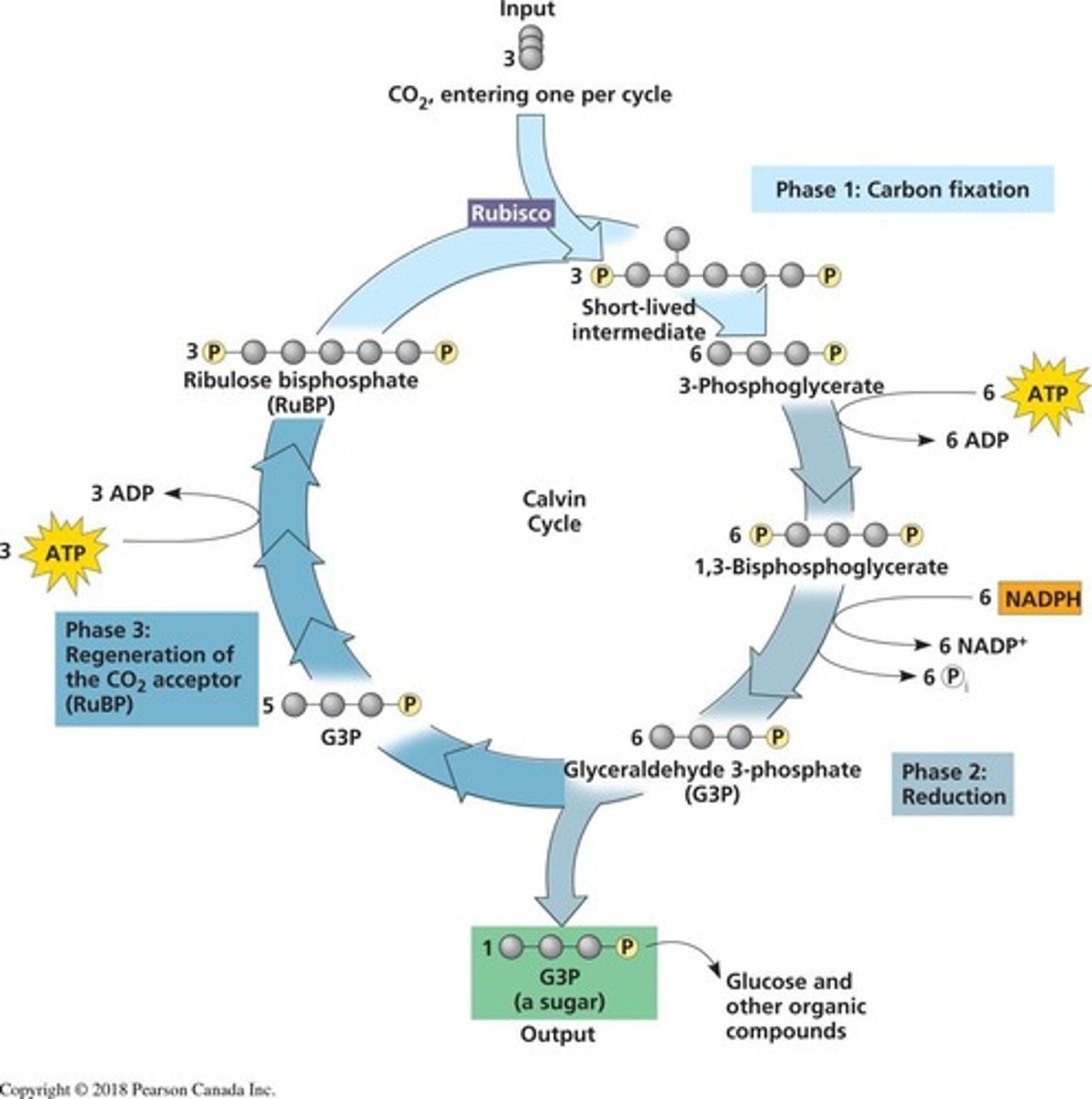
What happens during the carbon fixation phase of the Calvin cycle?
CO2 is added to RuBP to form two molecules of 3-PG.
What is the output of the reduction phase in the Calvin cycle?
A 3-carbon phosphorylated sugar called dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP or G3P).
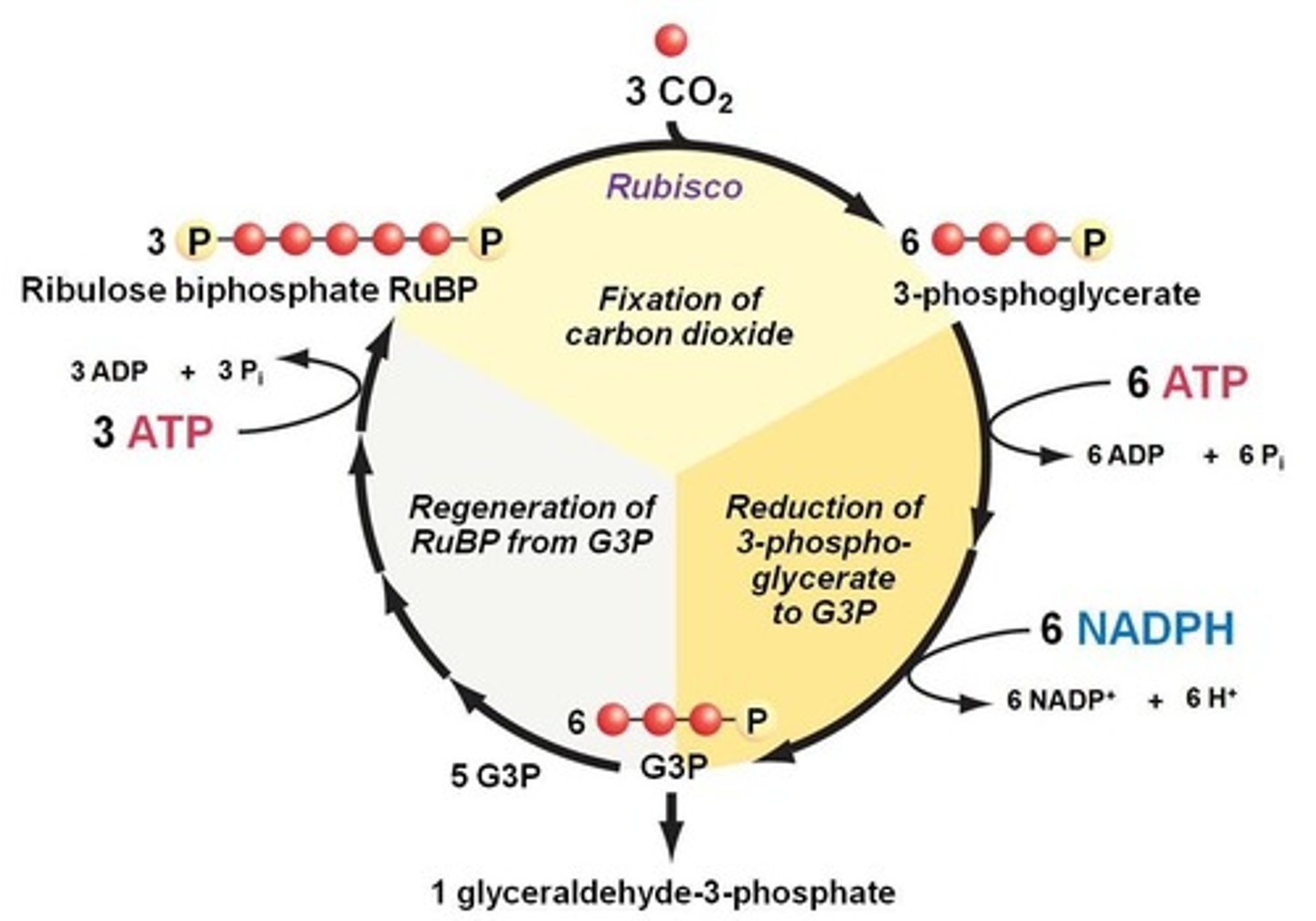
How many CO2 molecules are fixed to produce one G3P in the Calvin cycle?
Three CO2 molecules are fixed.
What is regenerated in the third phase of the Calvin cycle?
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP).
How many ATP and NADPH are used to produce one glucose in the Calvin cycle?
18 ATP and 12 NADPH.
What is photophosphorylation?
The addition of phosphate (Pi) to ADP to form ATP.
What is the significance of cyclic electron flow in certain organisms?
It may be the only means of generating ATP during photosynthesis in organisms like purple sulfur bacteria.
What role does cyclic electron flow play in protecting cells?
It may protect cells from intense light-induced damage.
What is the net gain of the Calvin cycle after three turns?
One G3P molecule is produced.
What type of plants primarily utilize the Calvin cycle?
C3 plants, such as rice, wheat, and soybean.
What is the main output of the Calvin cycle that can exit the chloroplast?
G3P, which can be converted to sugars or starch.