Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
The functional portions of the pituitary gland are the…
neurohypophysis and adenohypophysis
Which hormone is sometimes given to women to induce labor?
oxytocin
What role does oxytocin play in lactation?
ejection of milk
Oxytocin is responsible for
causing contractions of uterine smooth muscle during labor.
Which gland is located in the sella turcica?
pituitary (hypophysis)
Which of the following will inhibit the secretion of growth hormone?
Growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH)
Chronic hypersecretion of growth hormone as a child would result in…
gigantism
Which of the following characteristics is associated with hyposecretion of thyroid hormones?
Weight gain
Which of the following is involved in the regulation of thyroid hormone levels?
Thyroid-stimulating hormone from the anterior pituitary
The endocrine glands located on top of the kidneys are the _________ glands.
adrenal
Which of these hormones is NOT secreted by the adrenal cortex?
Norepinephrine
Which of the following glands is both an endocrine gland and an exocrine gland?
Pancreas
A _________ hormone stimulates the secretion of other hormones from the target tissues.
tropic
pituitary gland
secretes at least nine hormones that regulate numerous body functions and other endocrine glands
endocrine gland attached to the hypothalamus by the infundibulum; also called hypophysis
posterior pituitary
develops from the floor of the brain and consists of the infundibulum and the neurohypophysis
anterior pituitary
develops from the roof of the mouth
hypothalamus
regulates pituitary gland activity through neurohormones and action potentials
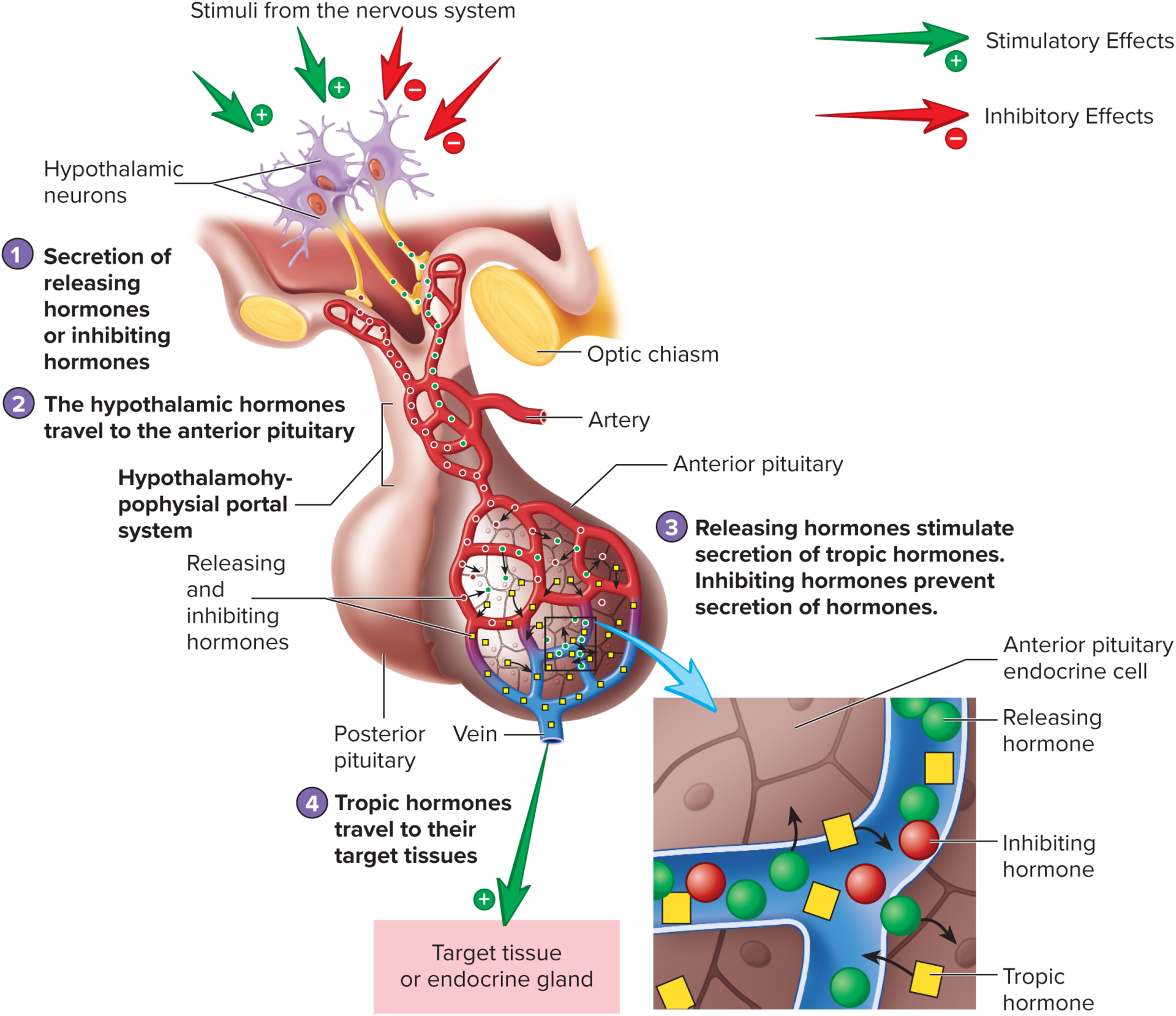
hypothalamohypophysial portal system
connects the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary
neurohormones
produced in hypothalamic neurons
through the portal system, these inhibit or stimulate hormones production in the anterior pituitary
move down the axons of the tract and are secreted from the posterior pituitary
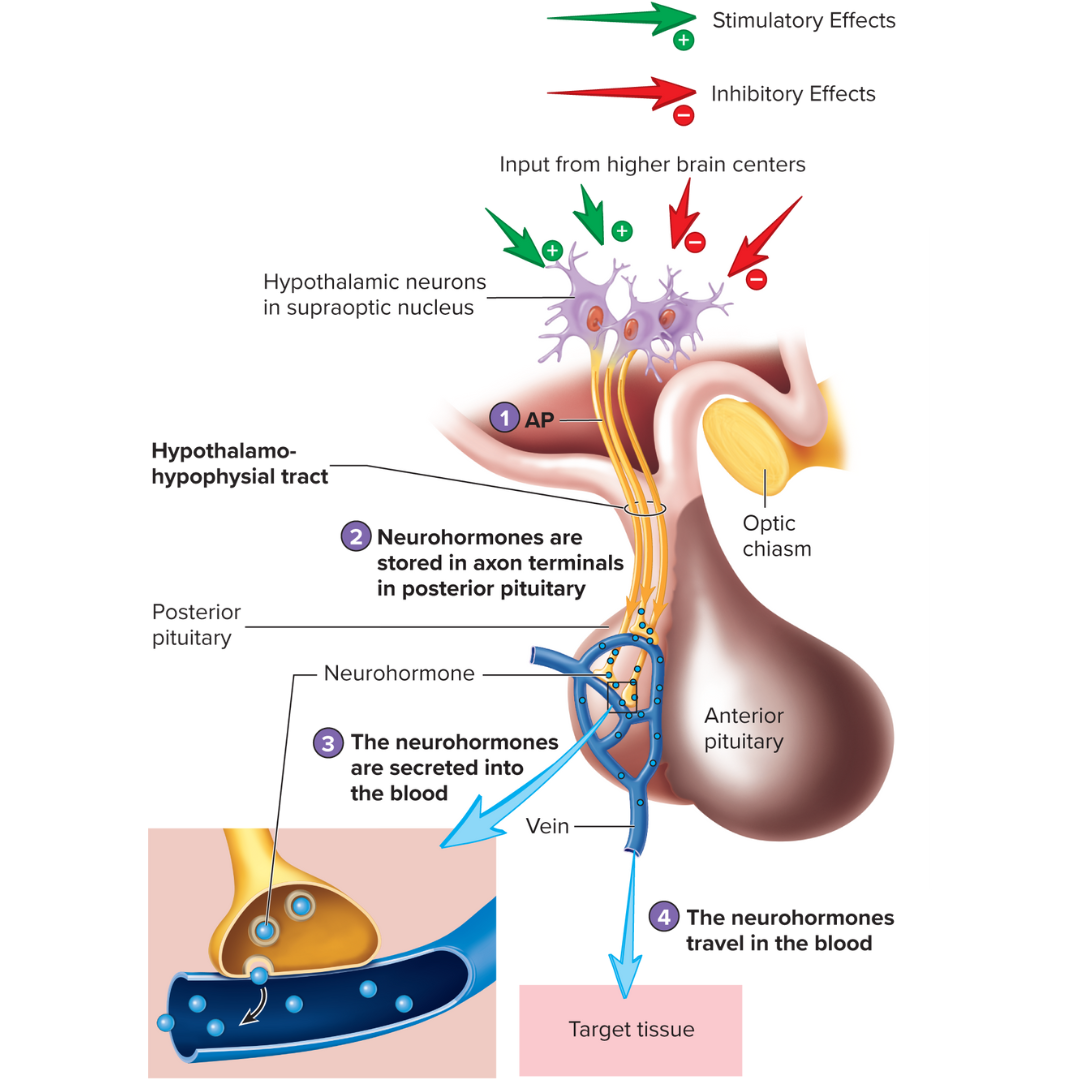
hypothalamohypophysial tract
connects hypothalamus and posterior pituitary
Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
Hormones of the Hypothalamus
Structure: peptide
Target Tissue: anterior pituitary cells that secrete growth hormone
Response: increased growth hormone secretion
Growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH), or somatostatin
Hormones of the Hypothalamus
Structure: small peptide
Target Tissue: anterior pituitary cells that secrete growth hormonr
Response: decreased growth hormone
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
Hormones of the Hypothalamus
Structure: small peptide
Target Tissue: anterior pituitary cells that secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone
Response: increased thyroid-stimulating hormone secretion
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
Hormones of the Hypothalamus
stimulates ACTH release; low blood glucose levels and stress stimulate this hormone’s' secretion
Structure: peptide
Target Tissue: anterior pituitary cells that secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone
Response: increased adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
Hormones of the Hypothalamus
Structure: small peptide
Target Tissue: anterior pituitary cells that secrete luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone
Response: increased secretion of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone
Dopamine (prolactin-inhibiting hormone, PIH)
Hormones of the Hypothalamus
Structure: amino acid derivative
Target Tissue: anterior pituitary cells that secrete prolactin
Response: decreased prolactin secretion
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Hormones of the Posterior Pituitary
promotes water retention by the kidneys
Structure: small peptide
Target Tissue: kidneys
Response: increased water reabsorption (less water is lost in the form of urine)
Oxytocin
Hormones of the Posterior Pituitary
promotes uterine contractions during delivery and causes milk letdown in lactating females
Structure: small peptide
Target Tissue: uterus; mammary glands
Response:
GH
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary
stimulates gorwth in most tissues and regulates metabolism. regulated by GHRH and somatostatin
Structure: protein
Target Tissue: most tissues
Response: increased growth in tissues
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary
description
Structure: glycoprotein
Target Tissue: thryoid gland
Response: increased thyroid hormone secretion
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary
stimulates cortisol secretion from the adrenal cortex and increases skin pigmentation
Structure: peptide
Target Tissue: adrenal cortex
Response: increased glucocorticoid hormone secretion
Lipotropins
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary
cause lipid breakdown
Structure: peptides
Target Tissue: adipose tissues
Response: increased lipid breakdown
β (beta) endorphins
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary
plays a role in analgesia
Structure: peptides
Target Tissue: Brain, but not all target tissues are known
Response: analgesia in the brain; inhibition of gonadatropin-releasing hormone secretion
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary
increases skin pigmentation
Structure: peptide
Target Tissue: melanocytes in the skin
Response: increase melanin production in melanocytes to make the skin darker in color; memory functions in the CNS
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary
Structure: glycoprotein
Target Tissue: ovaries; testes
Response: ovulation and progesterion production in ovaries; testosterone synthesis and support for sperm cell production in testes
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary
Structure: glycoprotein
Target Tissue: follicles in ovaries; seminiferous tubules in males
Response: follicle maturation and estrogen secretion in ovaries; sperm cell production in testes
prolactin
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary
Structure: protein
Target Tissue: ovaries and mammary glands in females
Response: milk production in lactating females
tropic hormones
many hormones from the anterior pituitary gland are this type of hormone
stimulate the secretion of other hormones from the target tissues
control the growth of target tissues
thyroid gland
one of the largest endocrine glands
located anterior neck
composed of two lateral lobes connected by median tissue mass (isthmus)
synthesizes and secretes three hormones: triiodothyronine, tetraiodothyronine, and calcitonin
Thyroid hormones (T3 & T4) secreted by thyroid follicles
Hormones of the Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
Structure: amino acid derivative
Target Tissue: most cells of the body
Response: increased metabolic rate; increased protein synthesis; essential for normal growth and maturation
calcitonin secreted by parafollicular cells
Hormones of the Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
Structure: peptide
Target Tissue: bone
Response: decreased rate of breakdown of bone by osteoclasts; prevention of a large increase in blood Ca2+ levels
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Hormones of the Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
increases bone breakdown and blood calcium levels
Structure: peptide
Target Tissue: bone, kidneys, small intestine
Response: increased rate of breakdown of bone by osteoclasts; increased reabsorption of Ca2+ in the kidneys; increased absorption of Ca2+ from the small intestine; increased vitamin D3 synthesis; increase blood Ca2+ levels
mechanism of action and the effects of T3 and T4 in the body
transported in the blood bound to thyroxine-binding globulin as well as other plasma proteins
bind with nuclear receptor molecules and initiate new protein synthesis
affect nearly every tissue in the body and increase metabolism in many tissues
TRH and TSH regulate T3 and T4 secretion
calcitonin
an increase in blood calcium levels stimulates [term] secretion by parafollicular cells
decreases blood calcium and phosphate levels by inhibiting osteoclasts
parathyroid glands
four glandular masses embedded in the posterior surface of the thyroid gland
epinephrine (80%); norepinephrine (20%)
Hormones of the Adrenal Medulla
Structure: amino acid derivatives
Target Tissue: heart, blood, vessels, liver, adipose cells
Response: increased cardiac output; increased blood flow to skeletal muscles and the heart; preparation for physical activity
mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)
Hormones of the Adrenal Cortex
acts on the kidneys to increase sodium and to decrease potassium and hydrogen levels in the blood
Structure: steroids
Target Tissue: kidney
Response: increased Na+ reabsorption and K+ and H+ excretion; enhanced water reabsorption
glucocorticoids (cortisol)
Hormones of the Adrenal Cortex
Structure: steroids
Target Tissue: most tissues
Response: increased protein and lipid breakdown; increased glucose production; inhibition of immune response and decreased inflammation
androgens
Hormones of the Adrenal Cortex
Structure: steroids
Target Tissue: many tissues
Response: of minor importance in males; in females, development of some secondary sex characteristics, such as axillary and pubic hair
zona glomerulosa
Outer layer of the adrenal cortex that secretes aldosterone.
zona fasciculata
Middle layer of the adrenal cortex that secretes cortisol.
zona reticularis
Inner layer of the adrenal cortex that secretes androgens and estrogens.
pancreatic islets
the endocrine portion of the pancreas
each [term portion] is composed of alpha cells, beta cells, and delta cells, which each secrete their own different hormones
Alpha (α) cells
Hormones of the Pancreas
Hormone: glucagon
Structure: peptide
Target Tissue: primarily liver
Response: increased breakdown of glycogen for release of glucose into the blood; increased production of new glucose
Beta (β) cells
Hormones of the Pancreas
Hormone: insulin
Structure: peptide
Target Tissue: especially liver, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue
Response: increased uptake and use of glucose and amino acids
Delta (ẟ) cells
Hormones of the Pancreas
Hormone: somatostatin
Structure: peptide
Target Tissue: alpha and beta cells (some somatostatin is produced in the hypothalamus)
Response: inhibition of insulin and glucagon secretion
insulin
Hormones of the Pancreas
target tissue: liver, adipose tissue, muscle, and the satiety center in the hypothalamus
effects: increases the uptake of glucose and amino acids by cells for energy production
secretion:
increases because of elevated blood glucose levels, an increase in some amino acids, parasympathetic stimulation, and GI hormones
decreases because of sympathetic stimulation
glucagon
Hormones of the Pancreas
target tissue: mainly the liver
effects: causes breakdown of glycogen and lipids for use as an energy source
secretion: stimulated by low blood glucose levels, certain amino acids, and sympathetic stimulation
somatostatin
Hormones of the Pancreas
inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion
testosterone
Hormones of the Testes
Structure: steroid
Target Tissue: most cells
Response: aids in spermatogensis, development of genitalia, maintenance of functional reproductive organs, secondary sex characteristics, and sexual behavior
inhibin
Hormones of the Reproductive Organs
Structure: polypeptide
Target Tissue: anterior pituitary gland
Response: inhibits FSH secretion
estrogen
Hormones of the Ovaries
Structure: steroid
Target Tissue: most cells
Response: aids in uterine and mammary gland development and function, maturation of genitalia, secondary sex characteristics, sexual behavior, and menstrual cycle
progesterone
Hormones of the Ovaries
Structure: steroid
Target Tissue: most cells
Response: aids in uterine and mammary gland development and function, maturation of genitalia, secondary sex characteristics, and menstrual cycle
relaxin
Hormones of the Ovaries
Structure: polypeptide
Target Tissue: connective tissue cells
Response: increases the flexibility of connective tissue in the pelvic area, especially the symphysis pubis