Selection, speciation and evolution
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what is genetic diversity
the number of different alleles of genes in a population
what 4 things cause genetic variation in a population
independent segregation
crossing over of alleles
random fusion of gametes
random mutation
define population
a group of individuals of the same species that live in the same space and can interbreed
what 4 reasons may allow an individual to have better survival chances due to their genotype
competition
predation
disease
changes in the environment
what happens to the frequency of advantageous alleles in a population over time
they increase in frequency
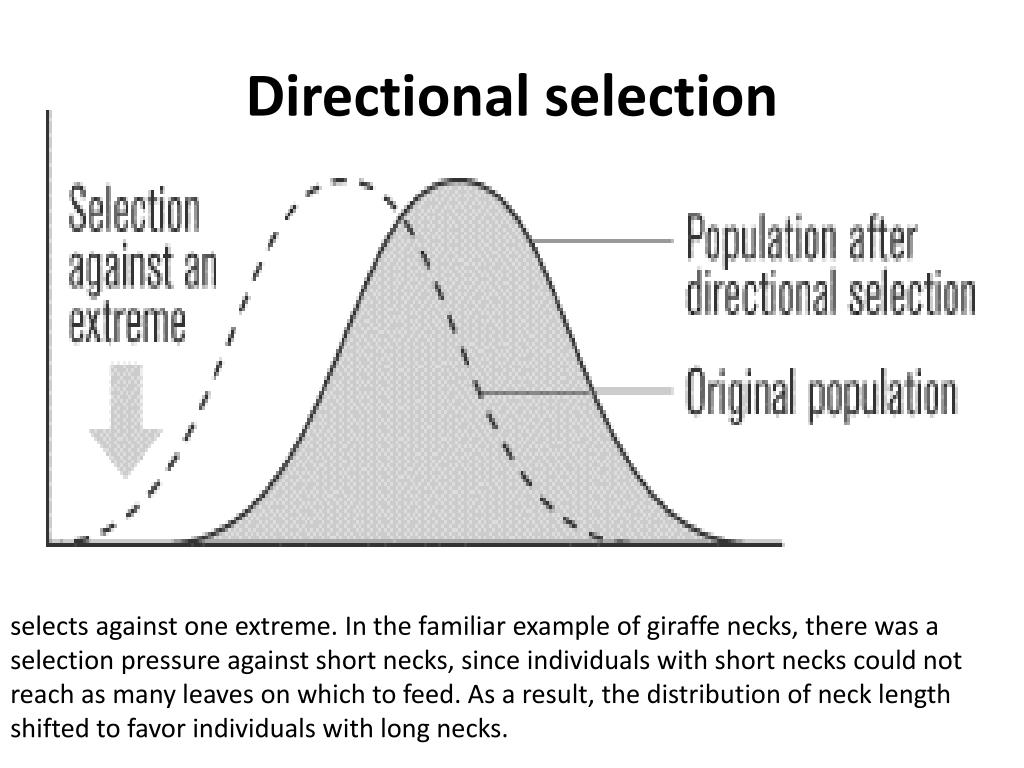
what is directional selection
where a selection pressure favours one extreme over the other extreme and moderate characteristics
what is an example of directional selection
antibiotic resistance in bacteria
how does the phenotype characteristic mean and median shift with directional selection
shifts towards the favoured extreme
what does the graph for directional selection look like
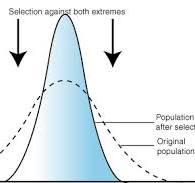
what is stabilising selection
where selection pressures favour a non-extreme median phenotype
how does the data change with stabilising selection
the mode stays the same but the mode frequency increases
name an example of stabilising sekection
birthweight
what does a graph look like for stabilising selection
name 3 difference sbetween stabilising and direvtional selection
the mode changes for direction selection but doesn’t for stabilising
the mode stays the same frequency with direction but increases with stabilising
with directional 1 extreme is at a disadvantage but with stabilising both extremes are at a disadvantage
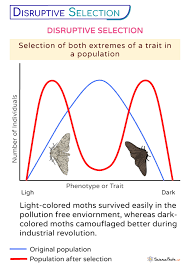
what is disruptive selection
when individuals with extreme traits are favoured over individuals in the middle of the trait distribution
describe the shape of the disruptive selection graph
a bi-modal, two peaked curve, in which the two extremes create their own curve
draw a graph for disruptive distribution
what is speciation
when new species are derived from one existing species
what is allele frequency
how often a particular allele occurs within a population
define gene pool
all of the alleles of all the individuals in a population at a given time
what is allopatric speciation
when a new species forms while geographically isolated from its parent population
what is sympatric speciation
a subset of a population forms a new species with reproductive isolation not geographic isolation
explain how geographical isolation leads to allopatric isolation
two species become reproductively isolated via geographical isolation
there is genetic variation in both populations due to random mutation of DNA
different environmental conditions create different selection pressures
natural selection occurs, and individuals with the advantageous alleles are more likely to survive and breed
different favourable alleles are passed on to offspring, and this leads to different changes in allele frequencies
eventually members of the separate population will be unable to breed successfully tto produce fertile offspring
what is polyploidy
possessing more than 2 sets of chromosomes
what can cause reproductive isolation
habitat preference
polyploidy
morphology
behaviour
explain how sympatric speciation occurs
there is no geographical isolation between the two populations
there is genetic variation within the community due to random gene mutation
this leads to reproductive isolation
different alleles of each population increase in frequency
disruptive natural selection occurs as there is a shift towards each extreme of the phenotype
eventually each species cannot interbreed to produce fertile offspring