High Yield Core
1/539
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
540 Terms
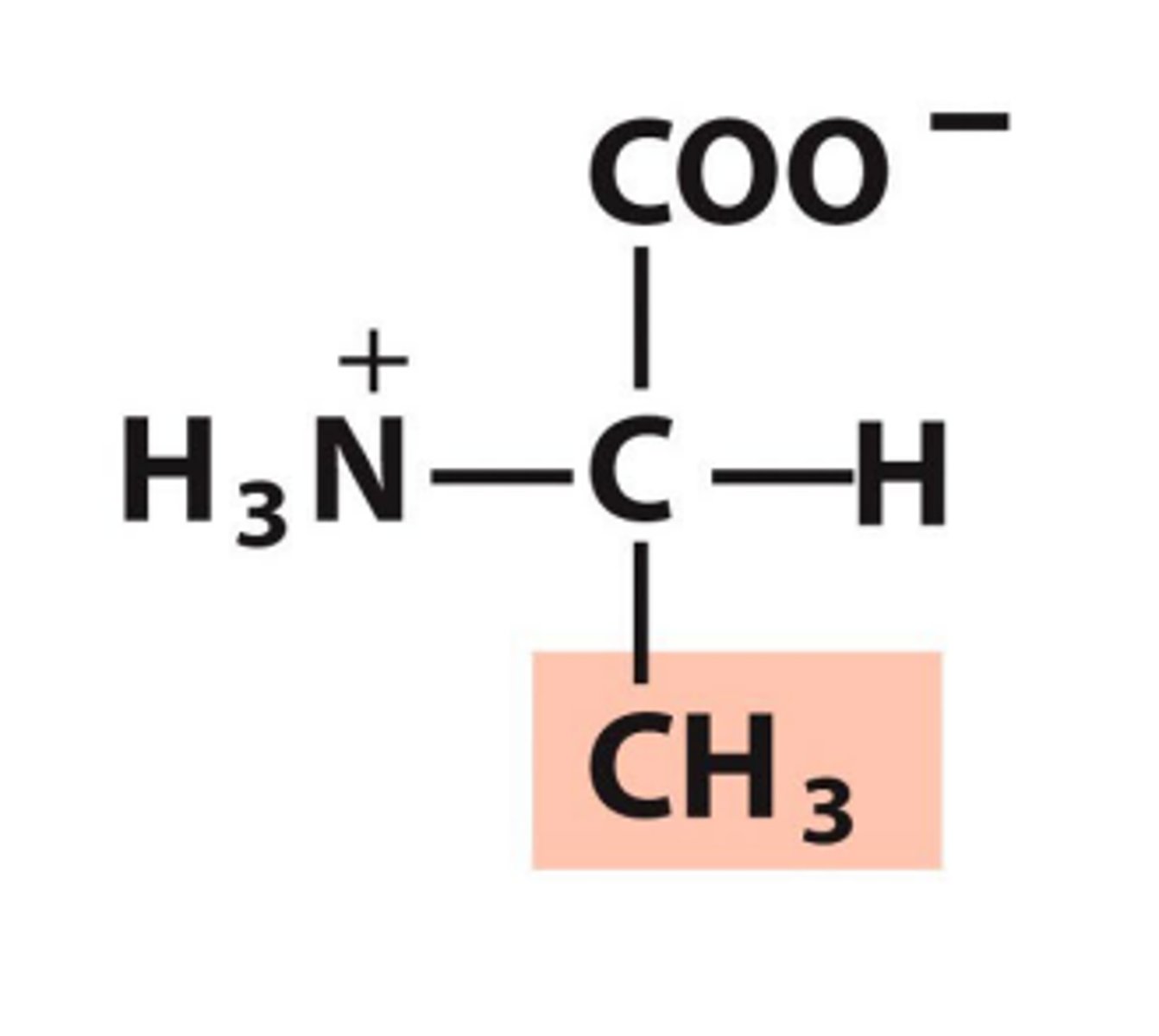
Alanine, Ala, A
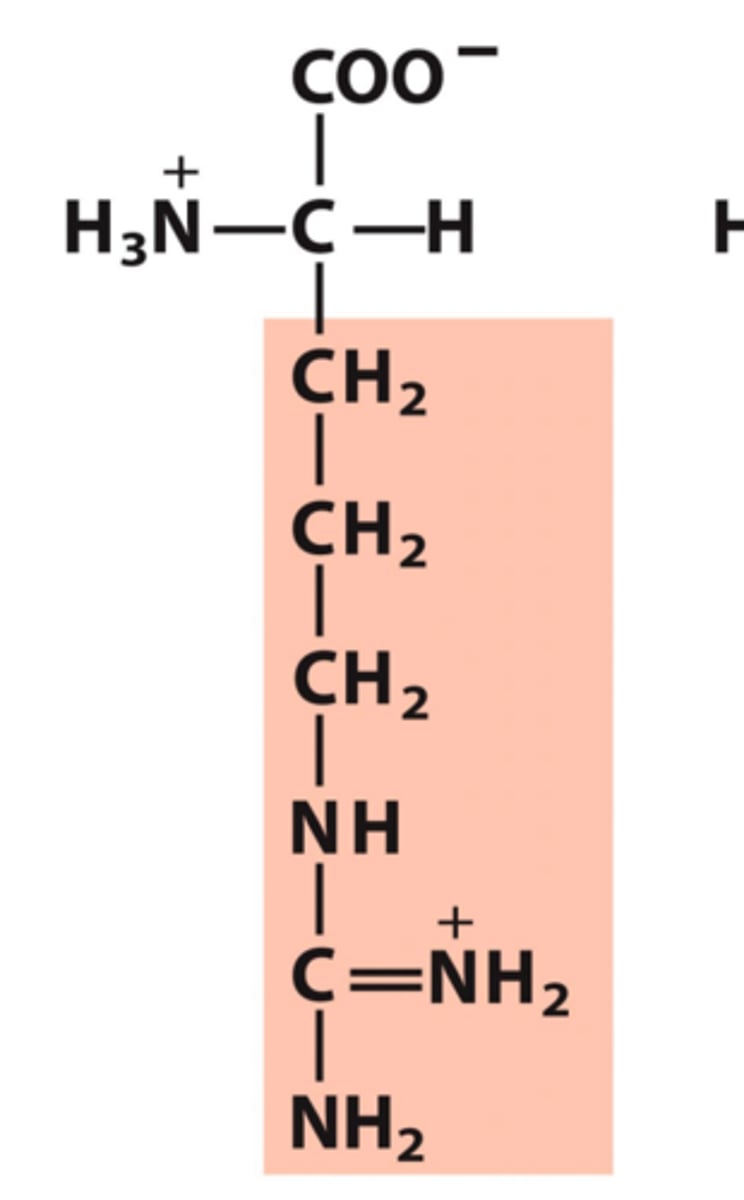
Arginine, Arg, R
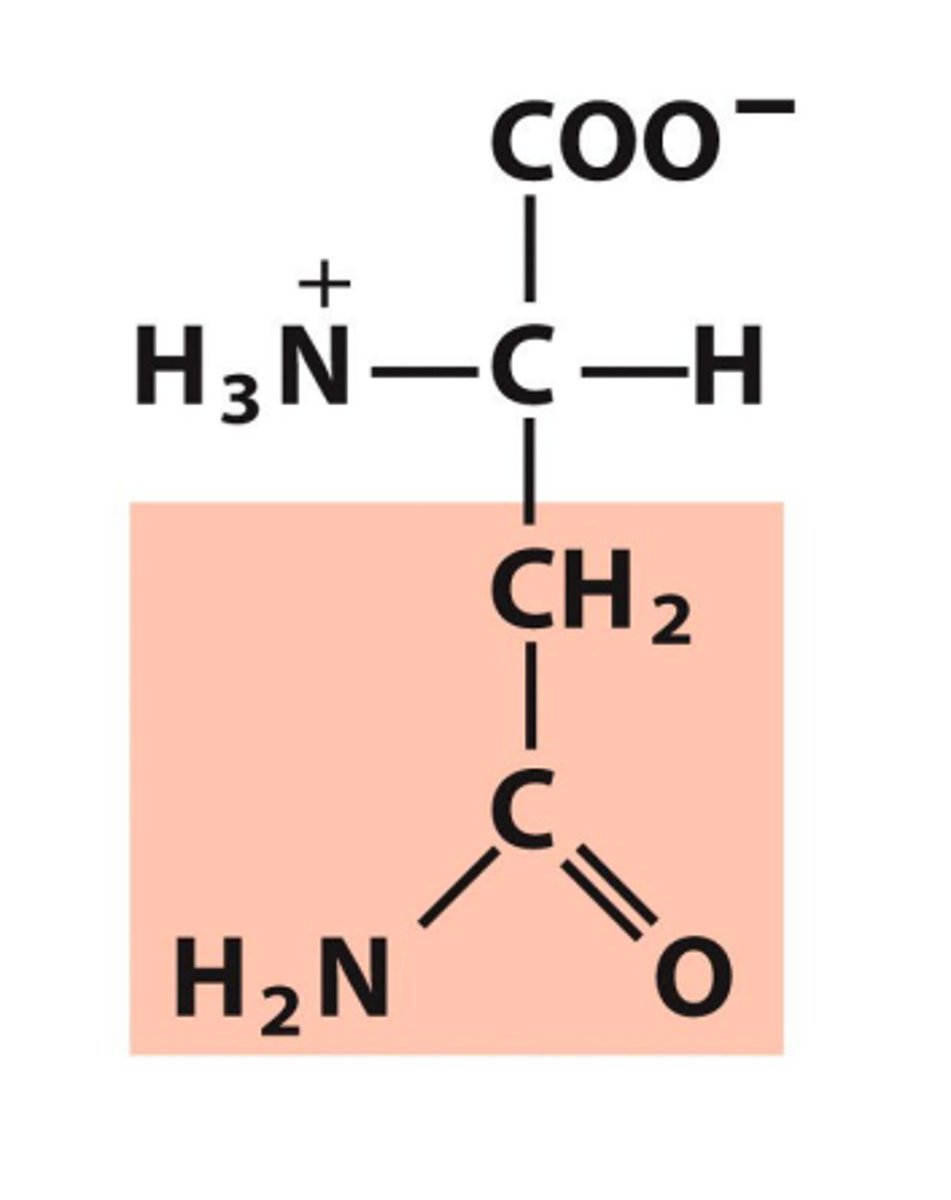
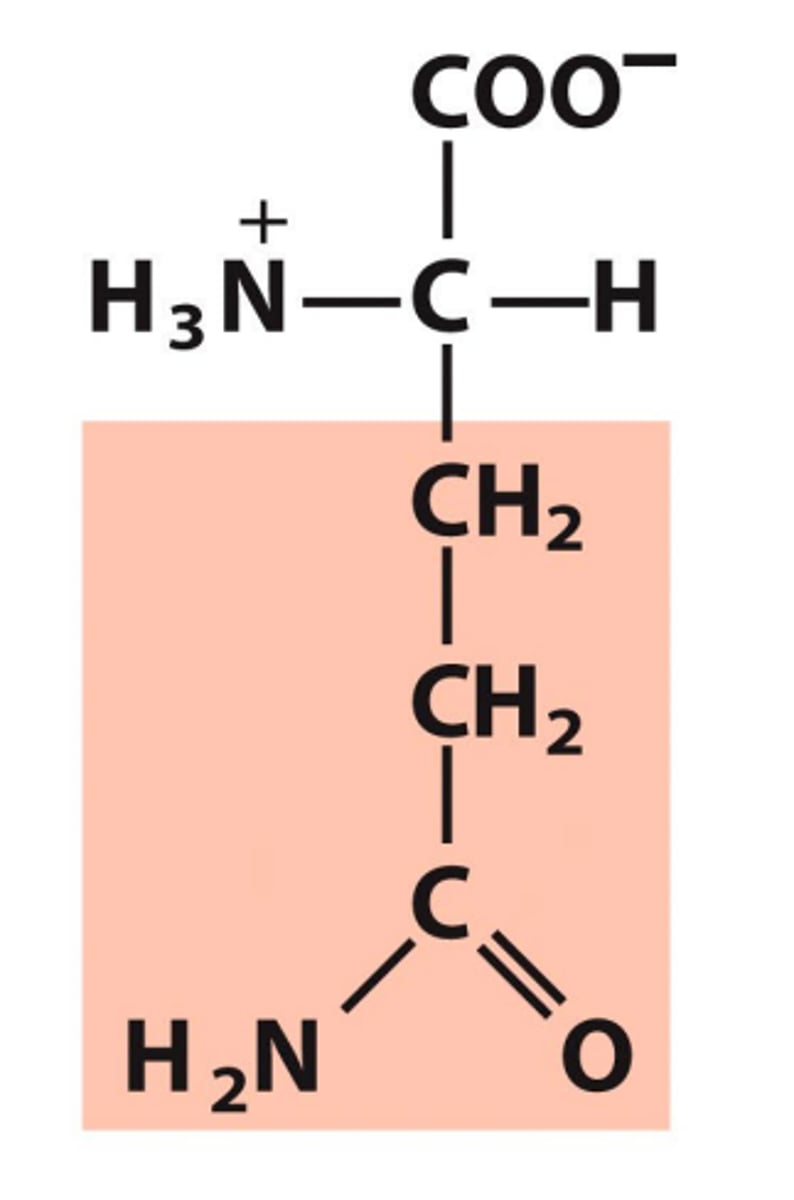
Asparagine, Asn, N
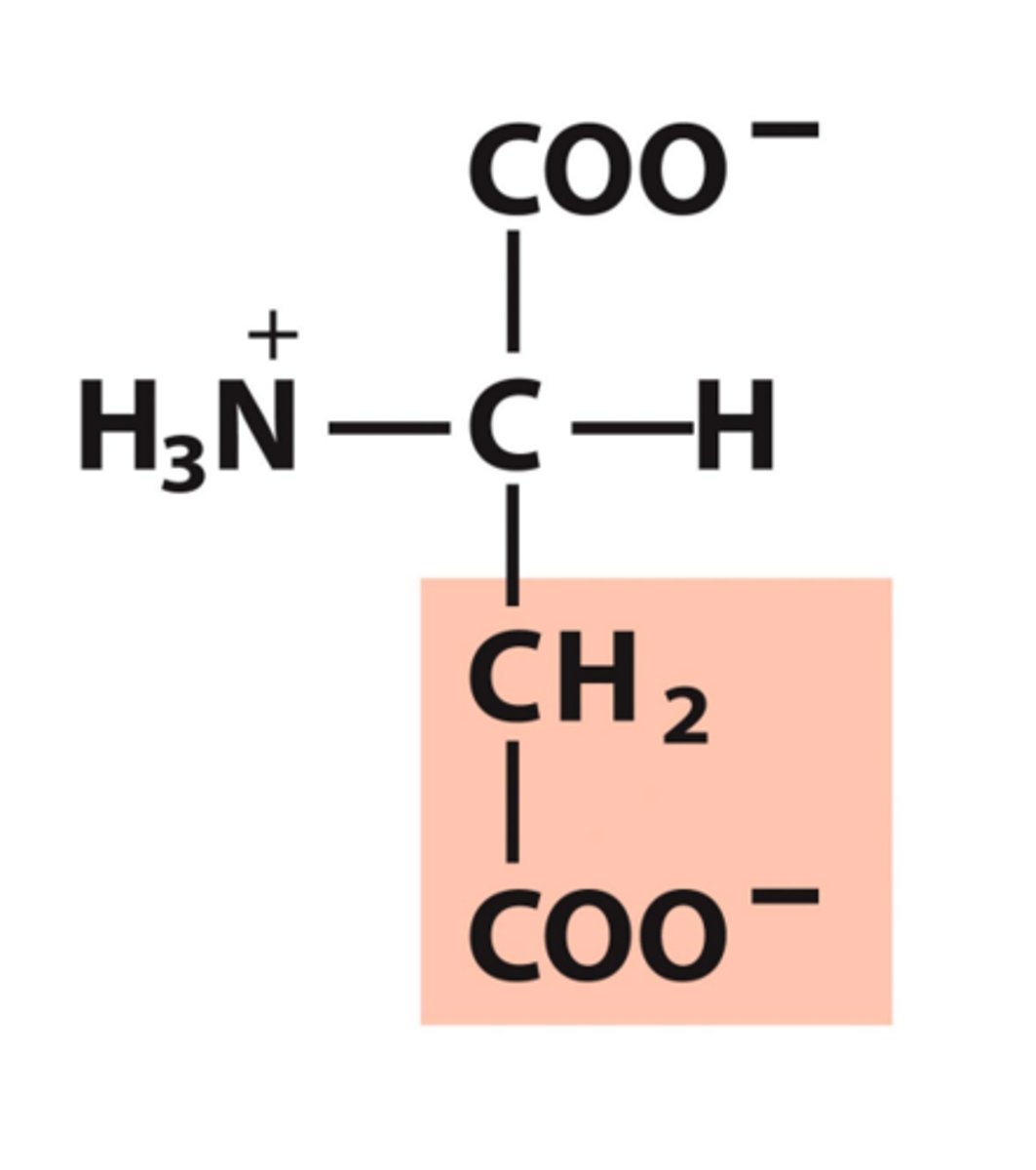
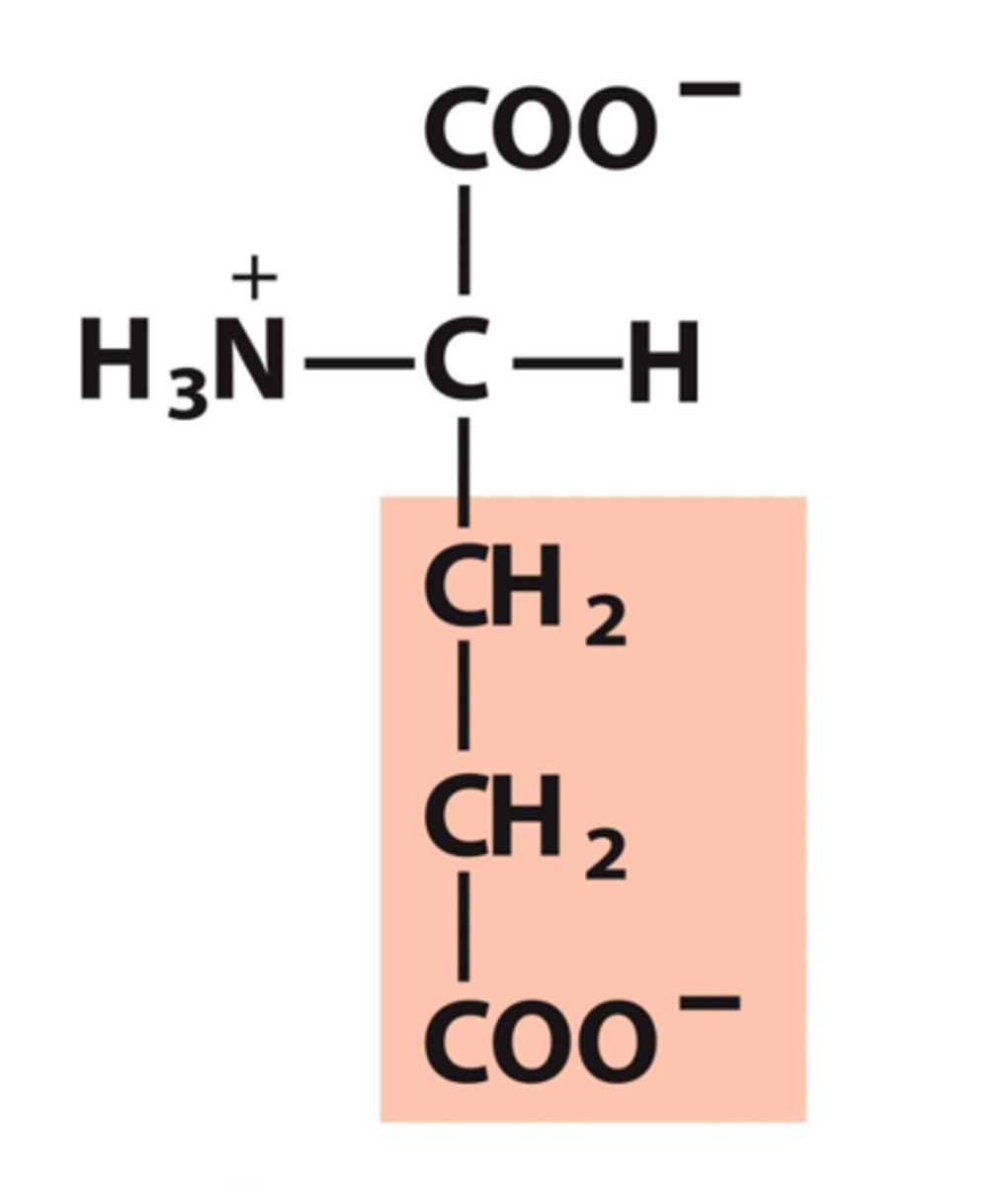
Aspartate, Asp, D
Cysteine, Cys, C
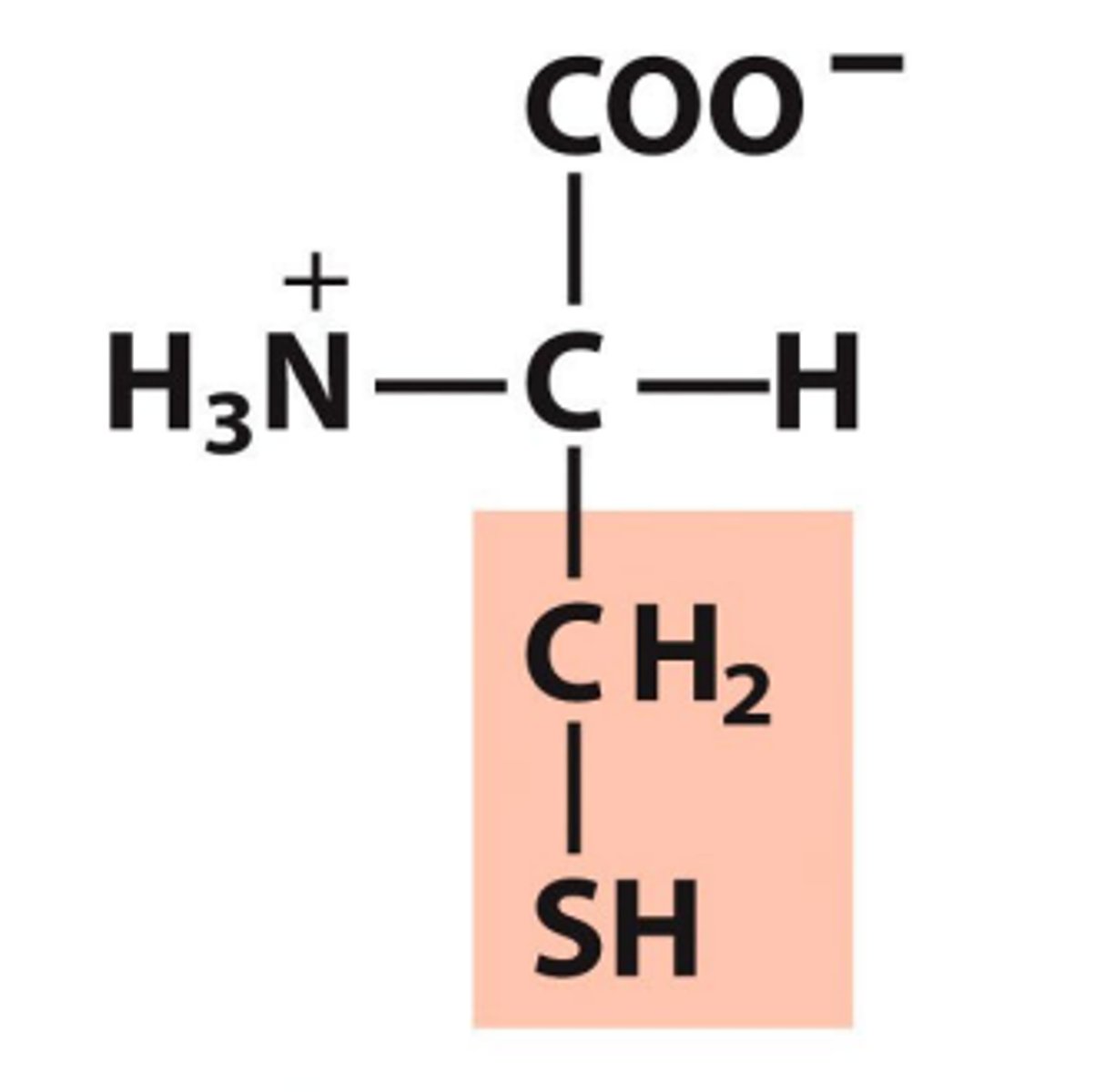
Glutamate, Glu, E
Glutamine, Gln, Q
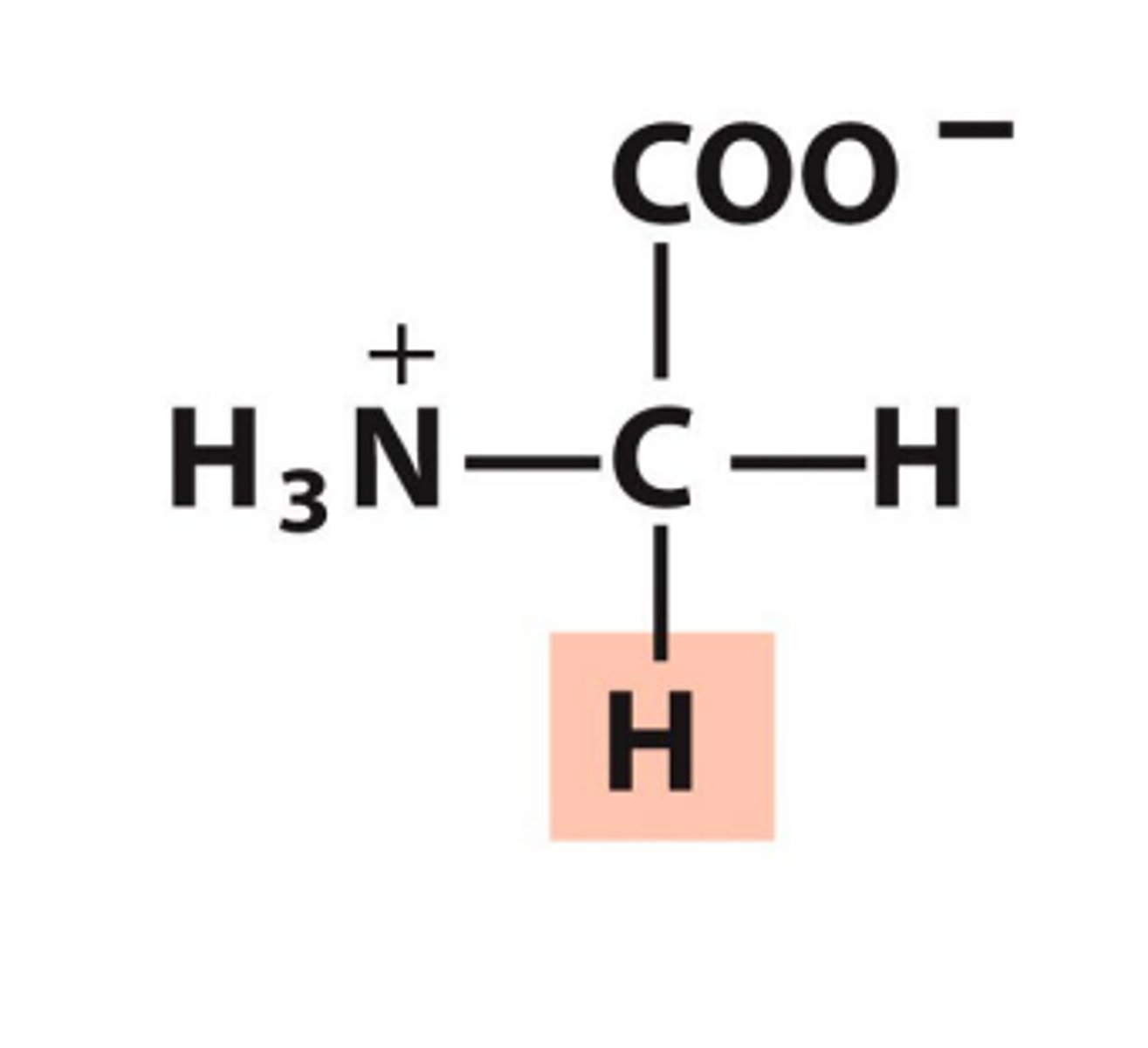
Glycine, Gly, G
Histidine, His, H
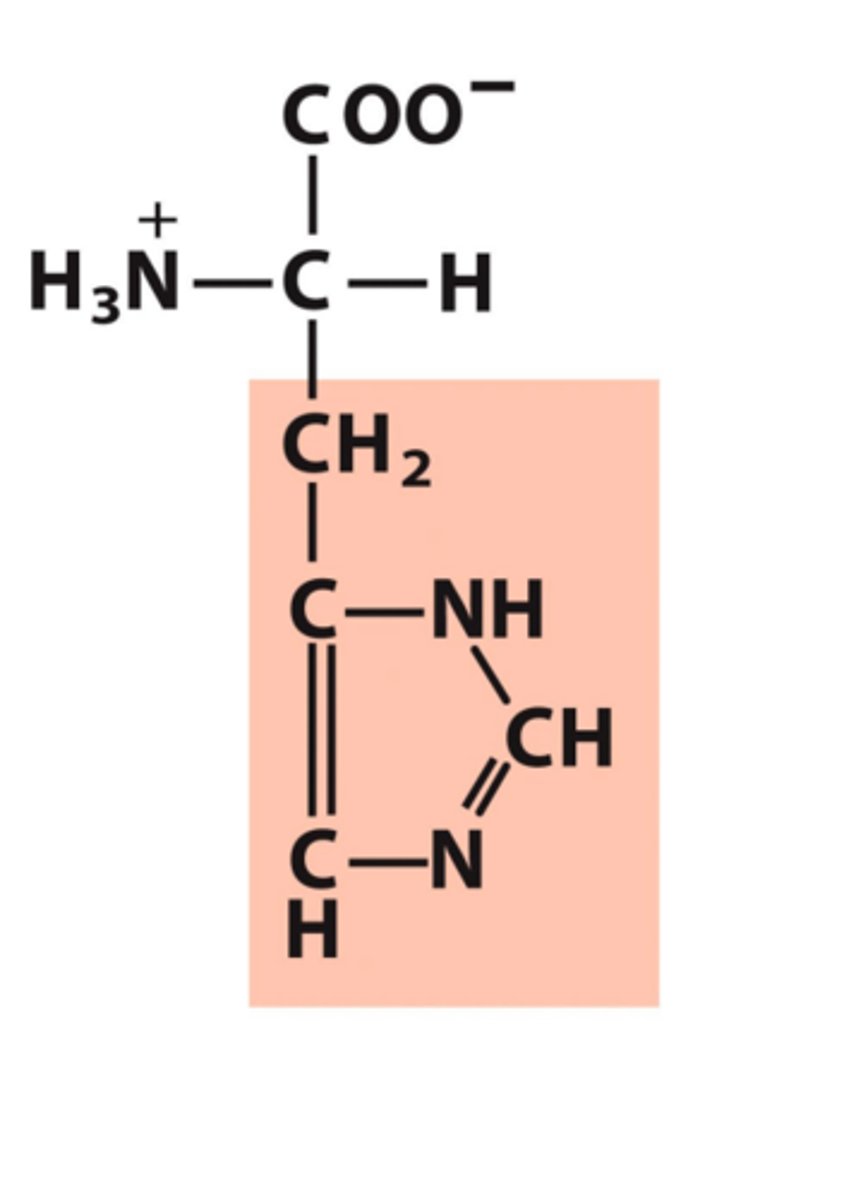
Isoleucine, Ile, I
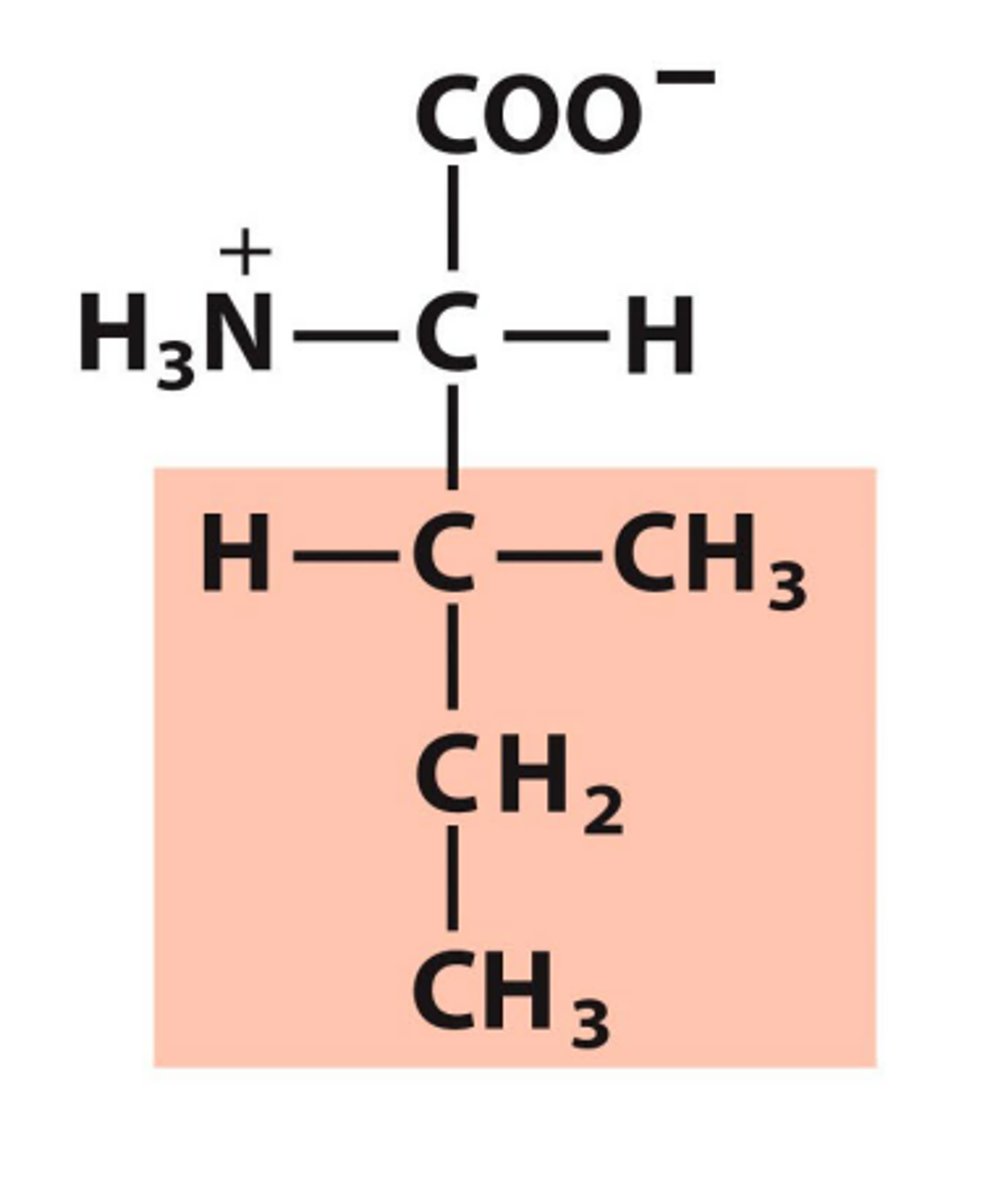
Leucine, Leu, L
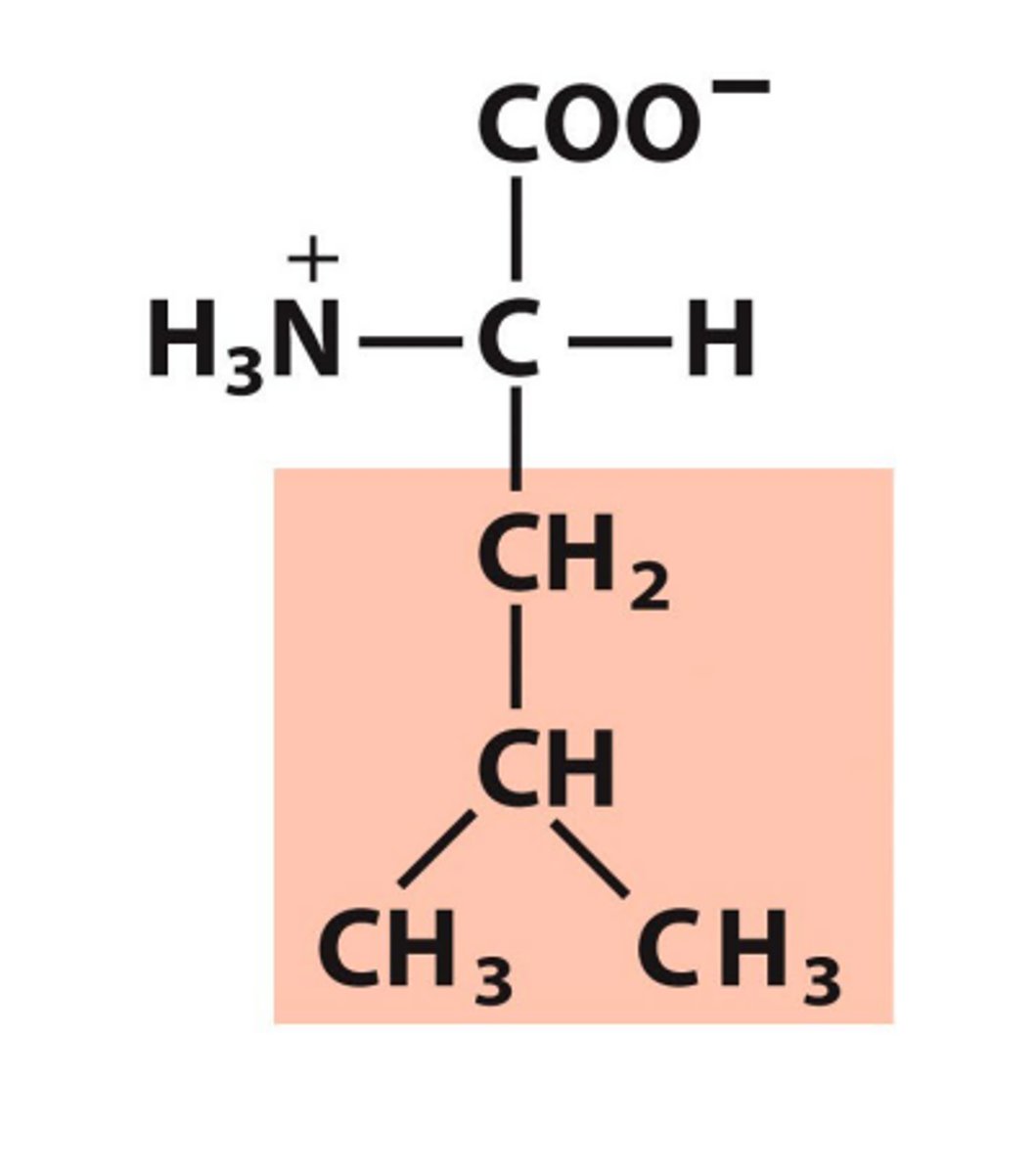
Lysine, Lys, K
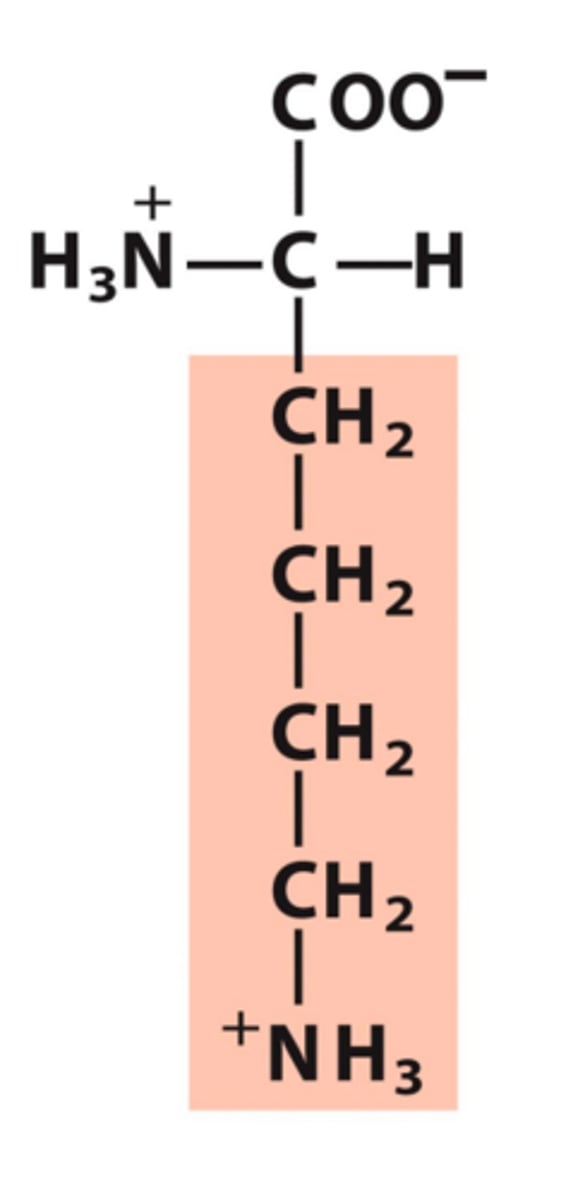
Methionine, Met, M
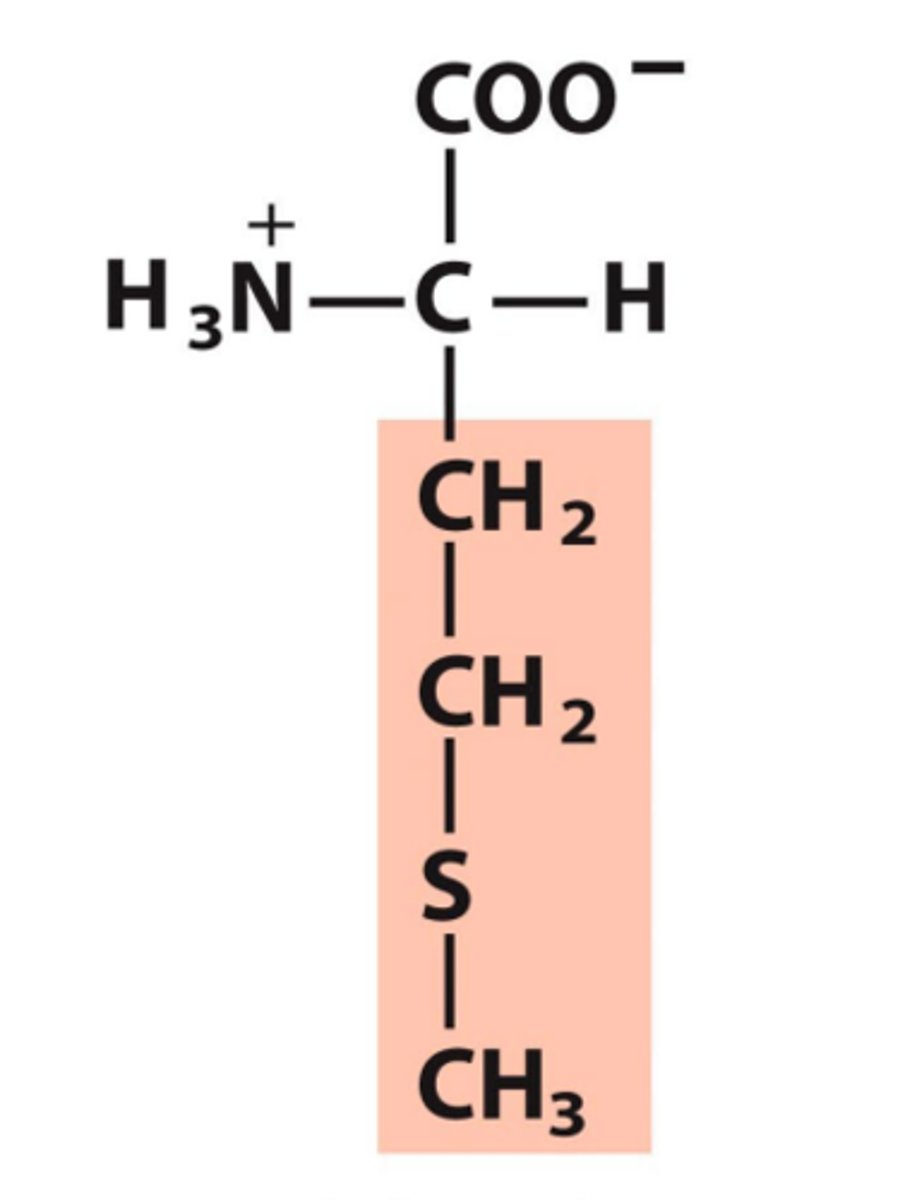
Phenylalanine, Phe, F
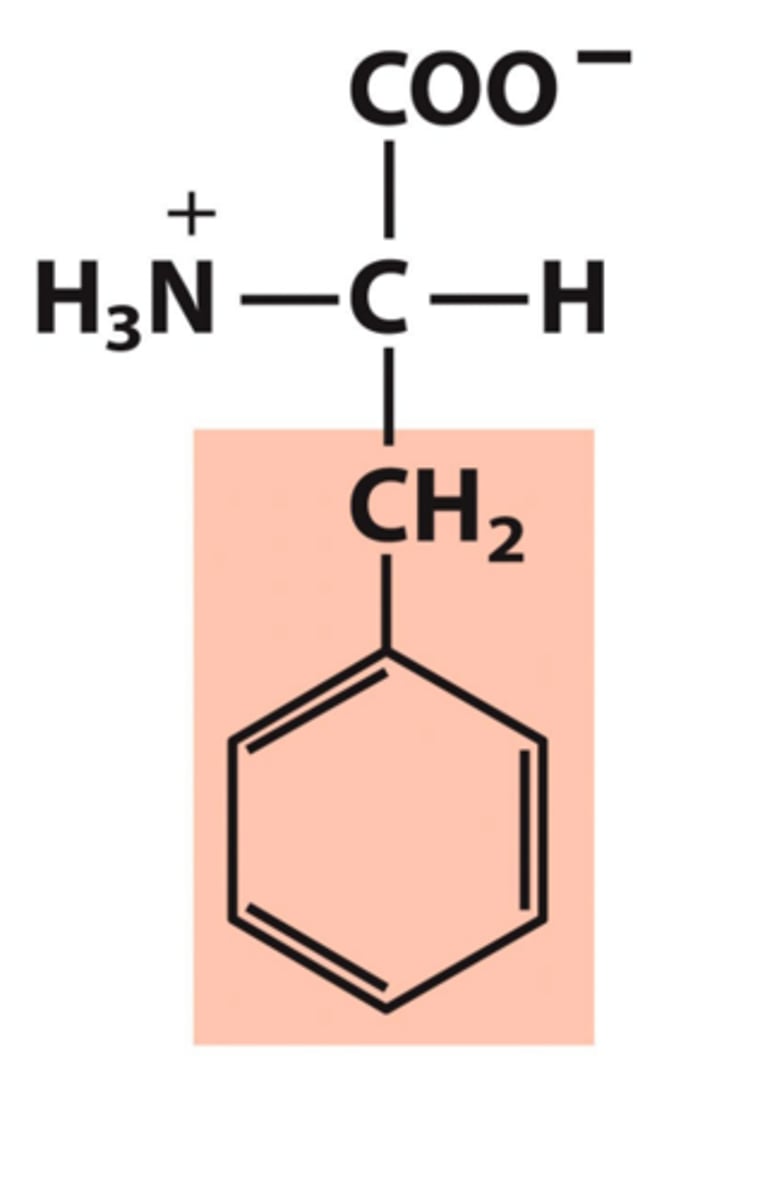
Proline, Pro, P
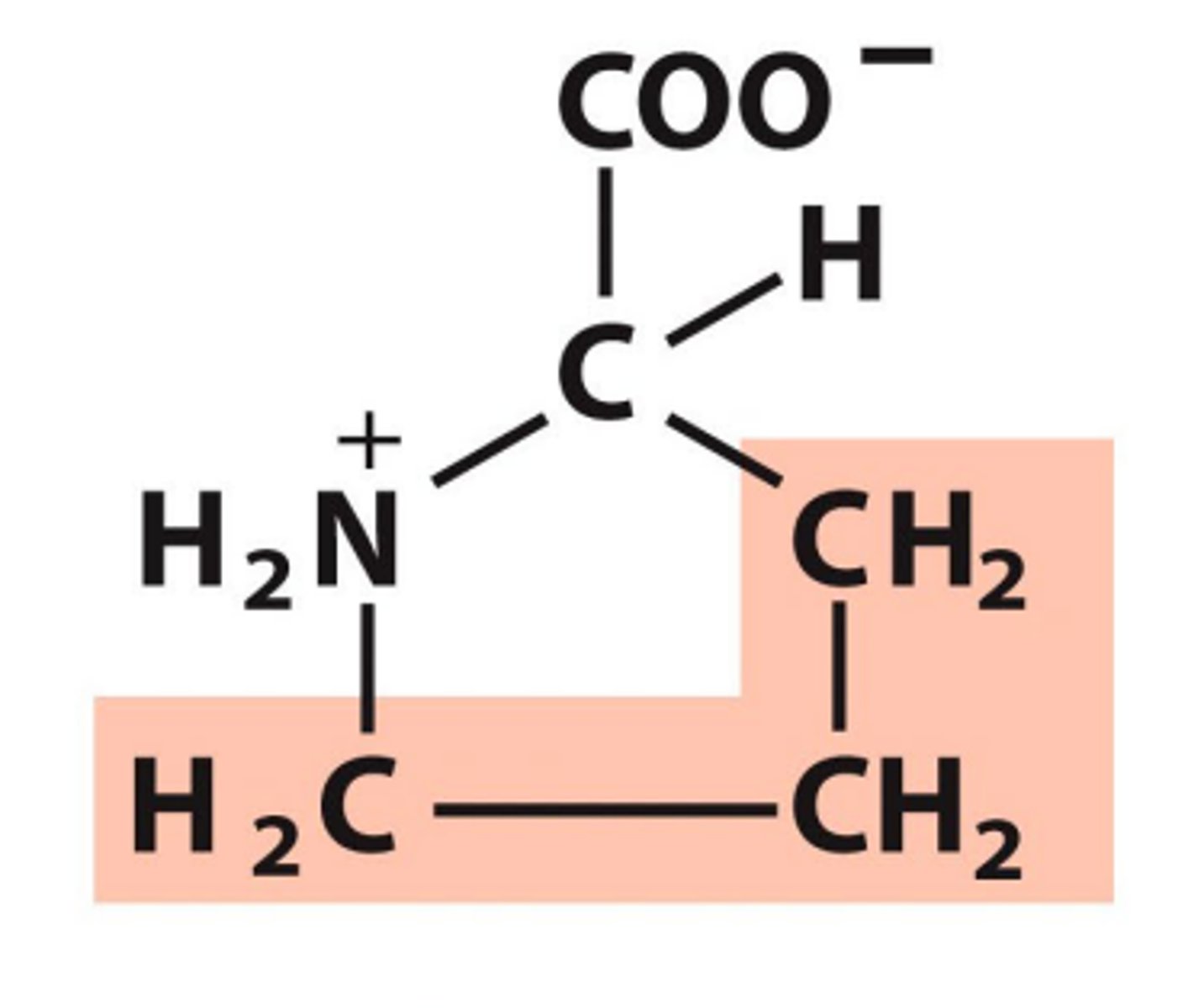
Serine, Ser, S
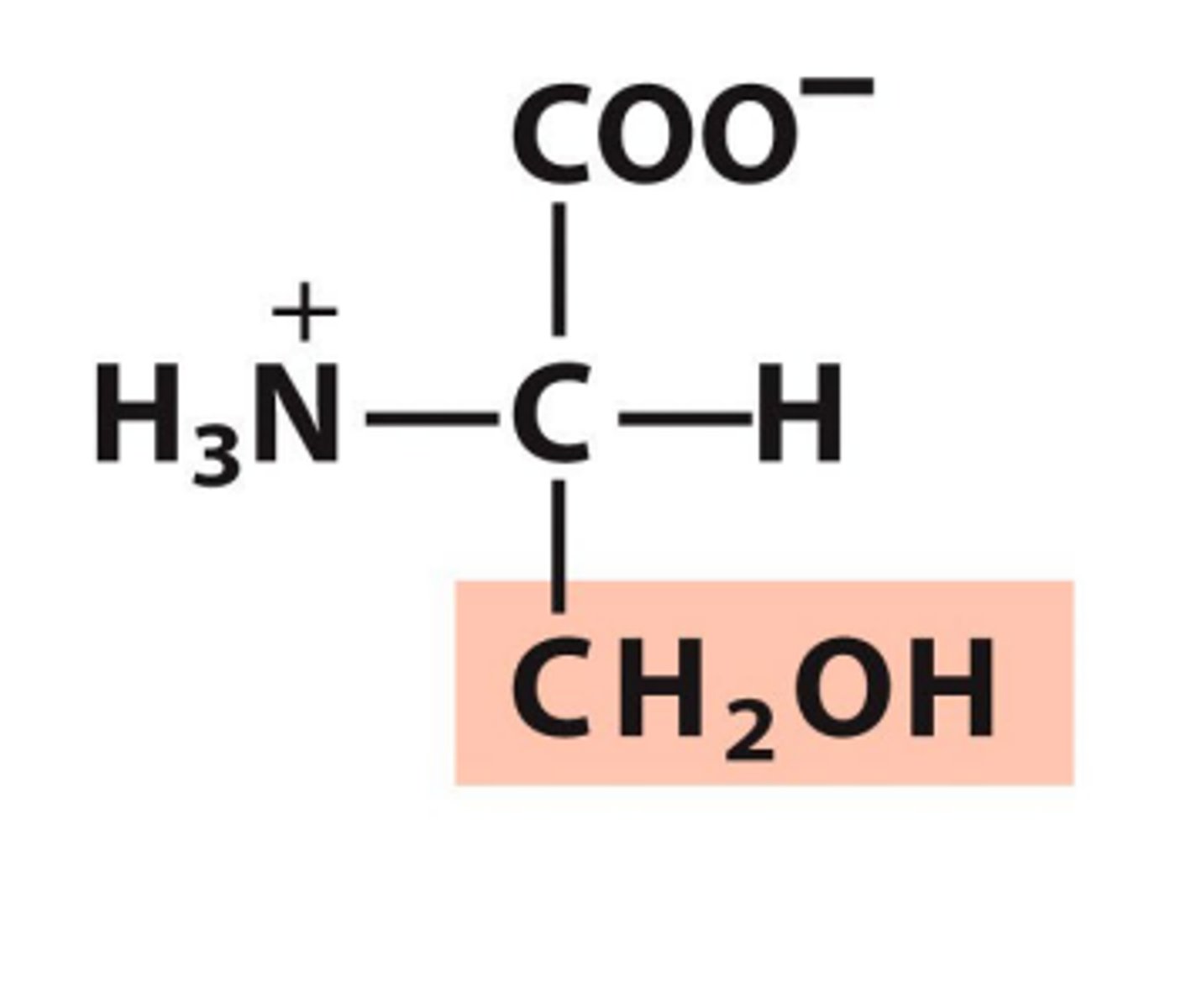
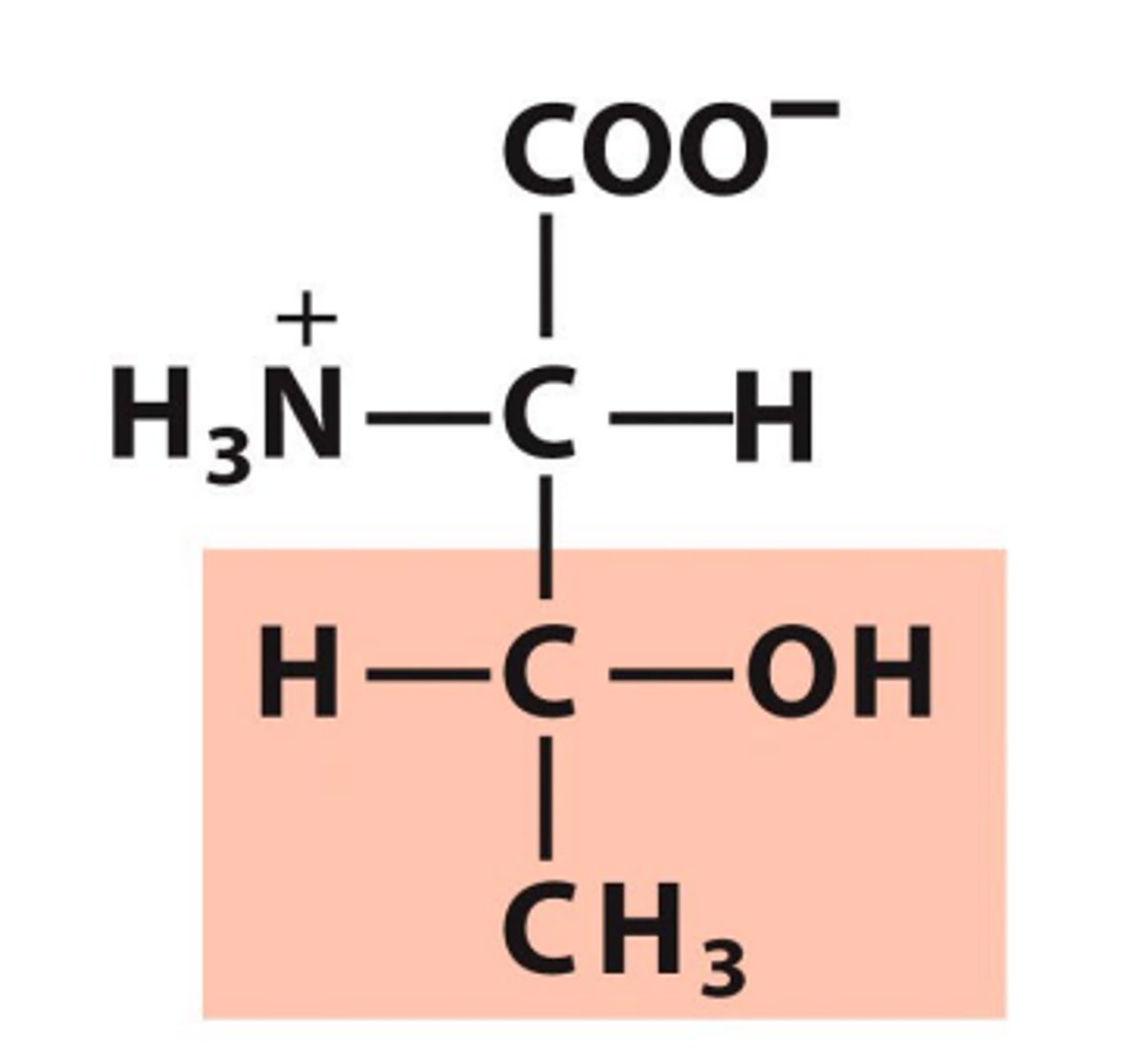
Threonine, Thr, T
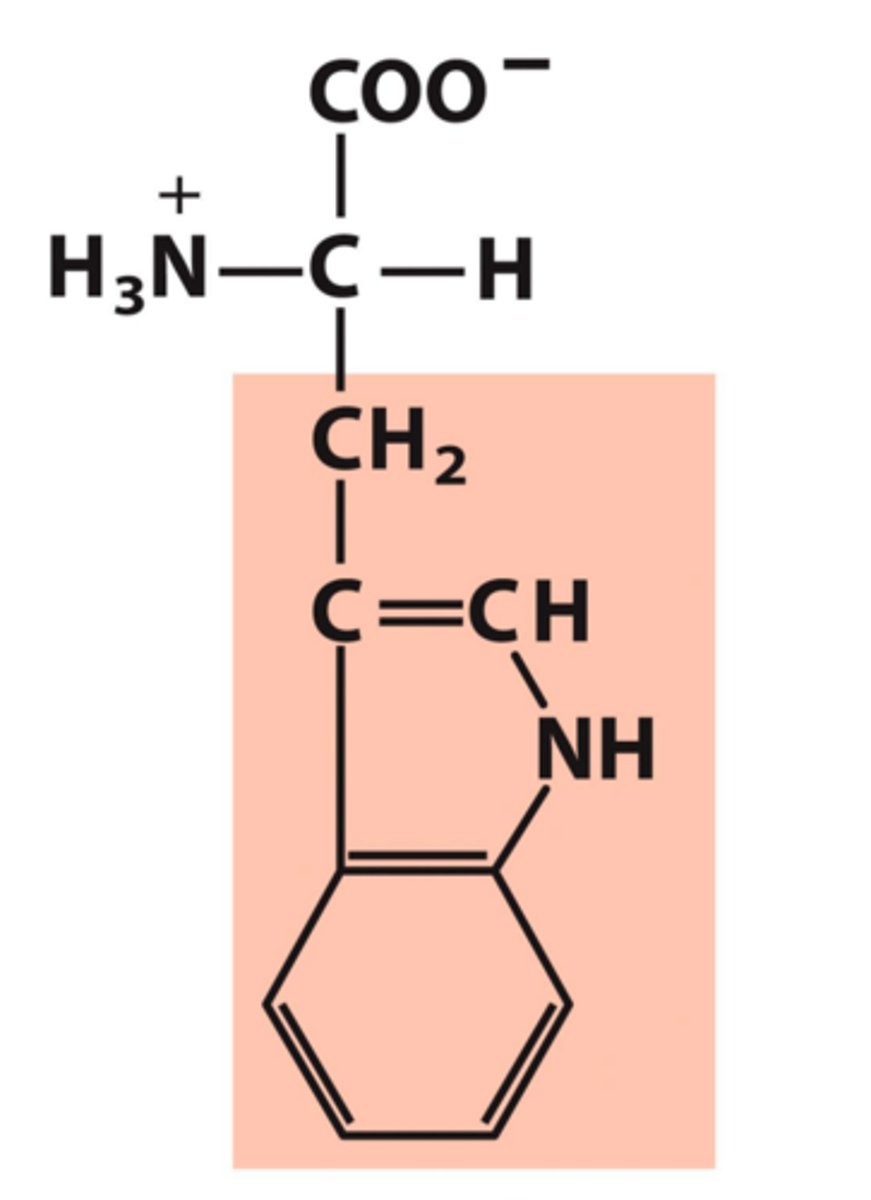
Tryptophan, Trp, W
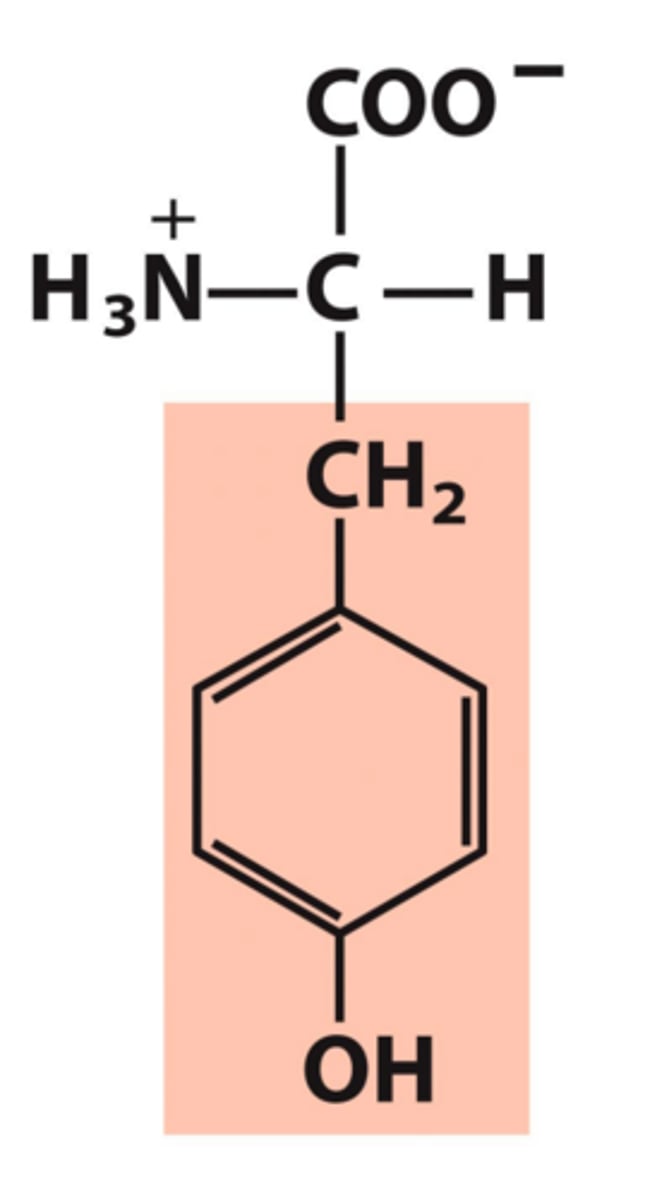
Tyrosine, Tyr, Y
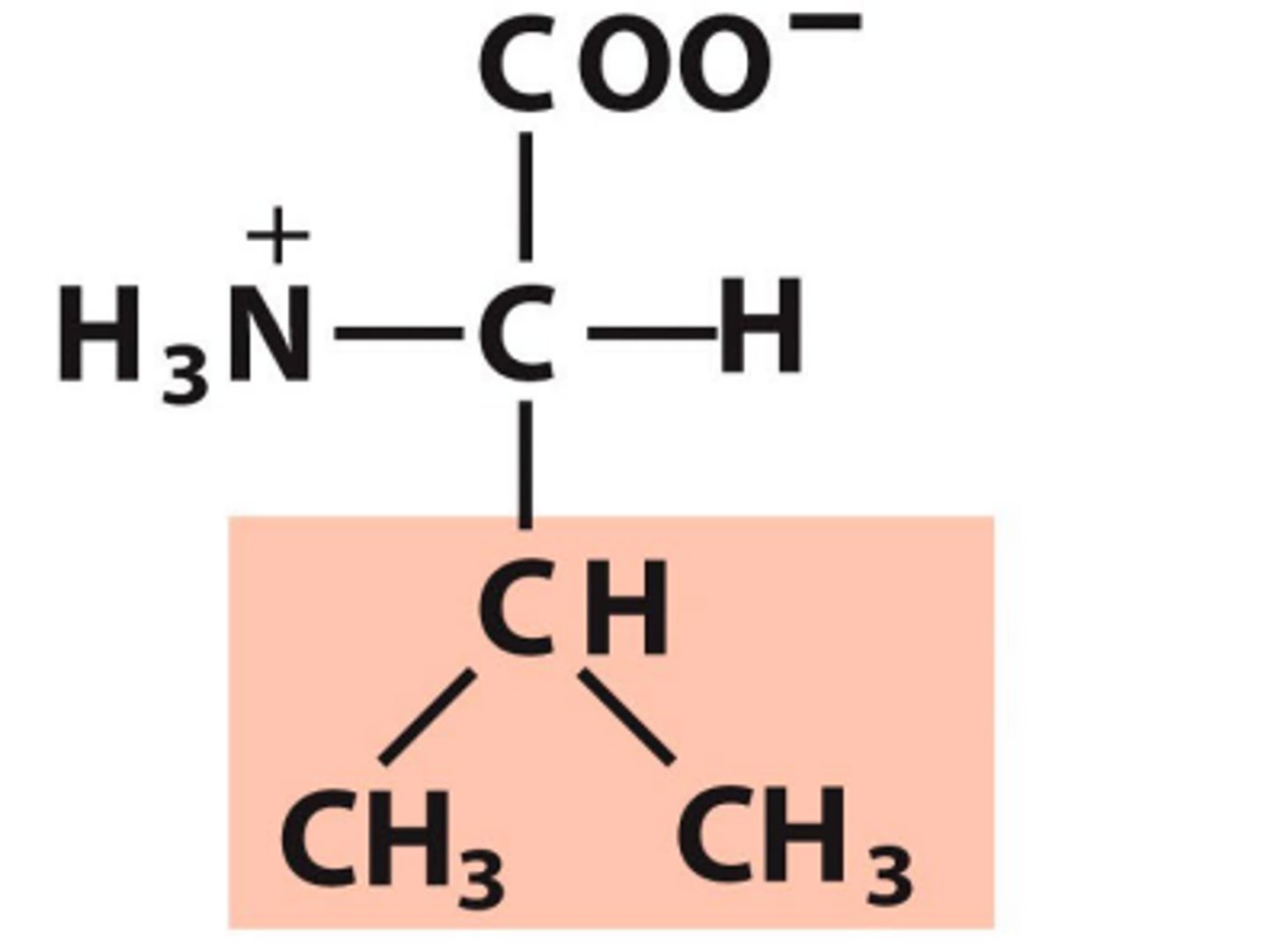
Valine, Val, V
glucose
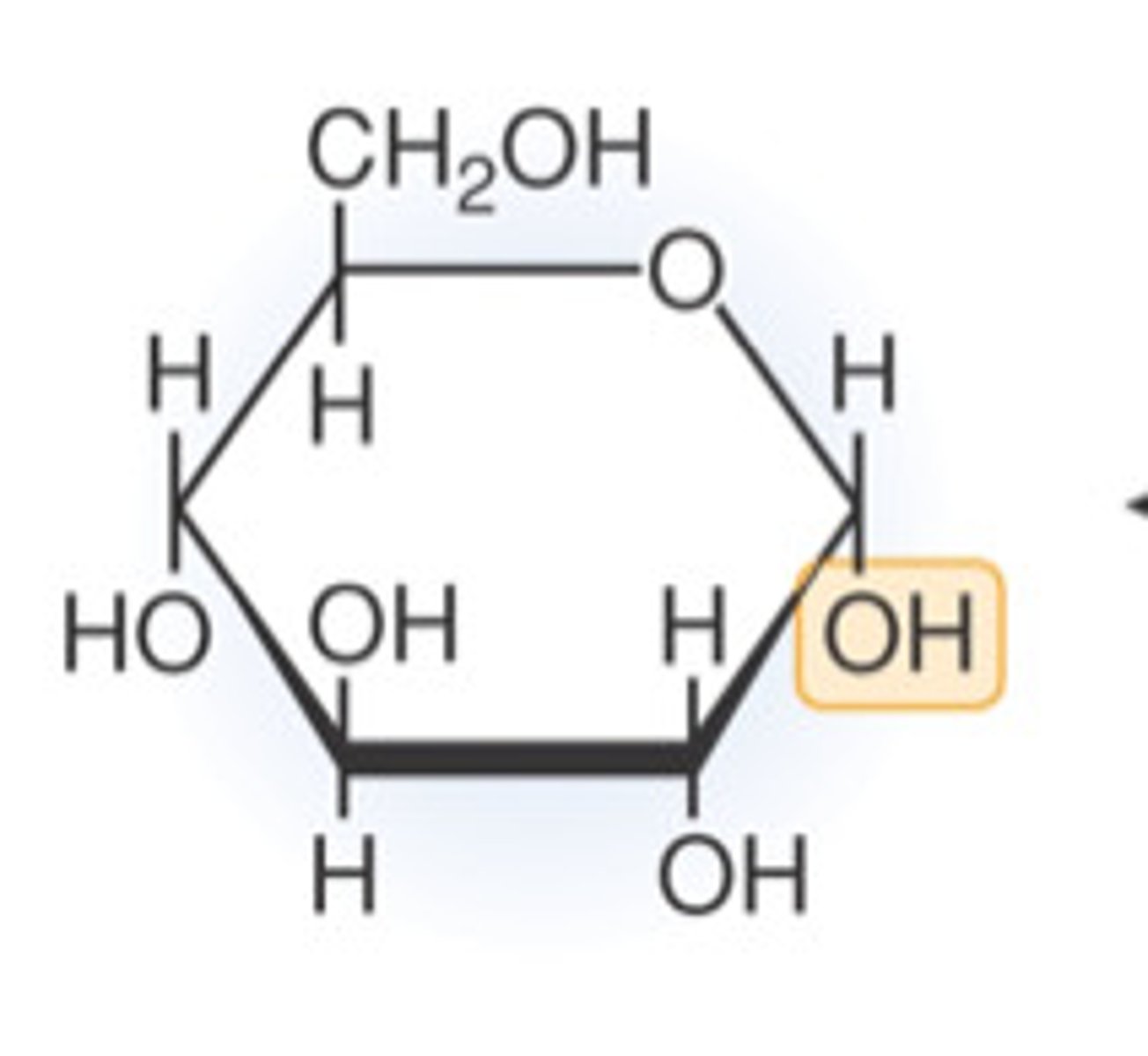
glucose-6-phosphate
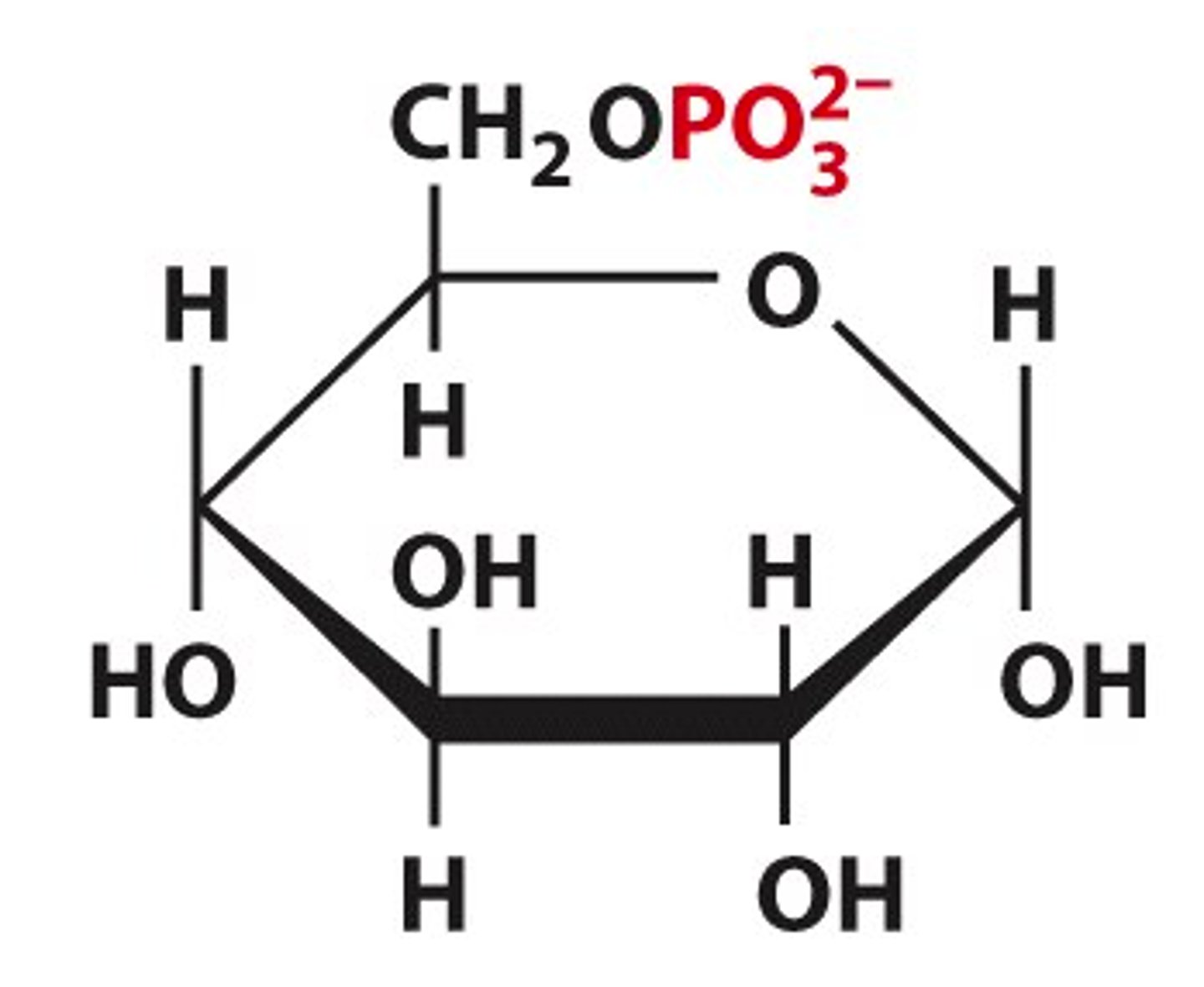
fructose-6-phosphate
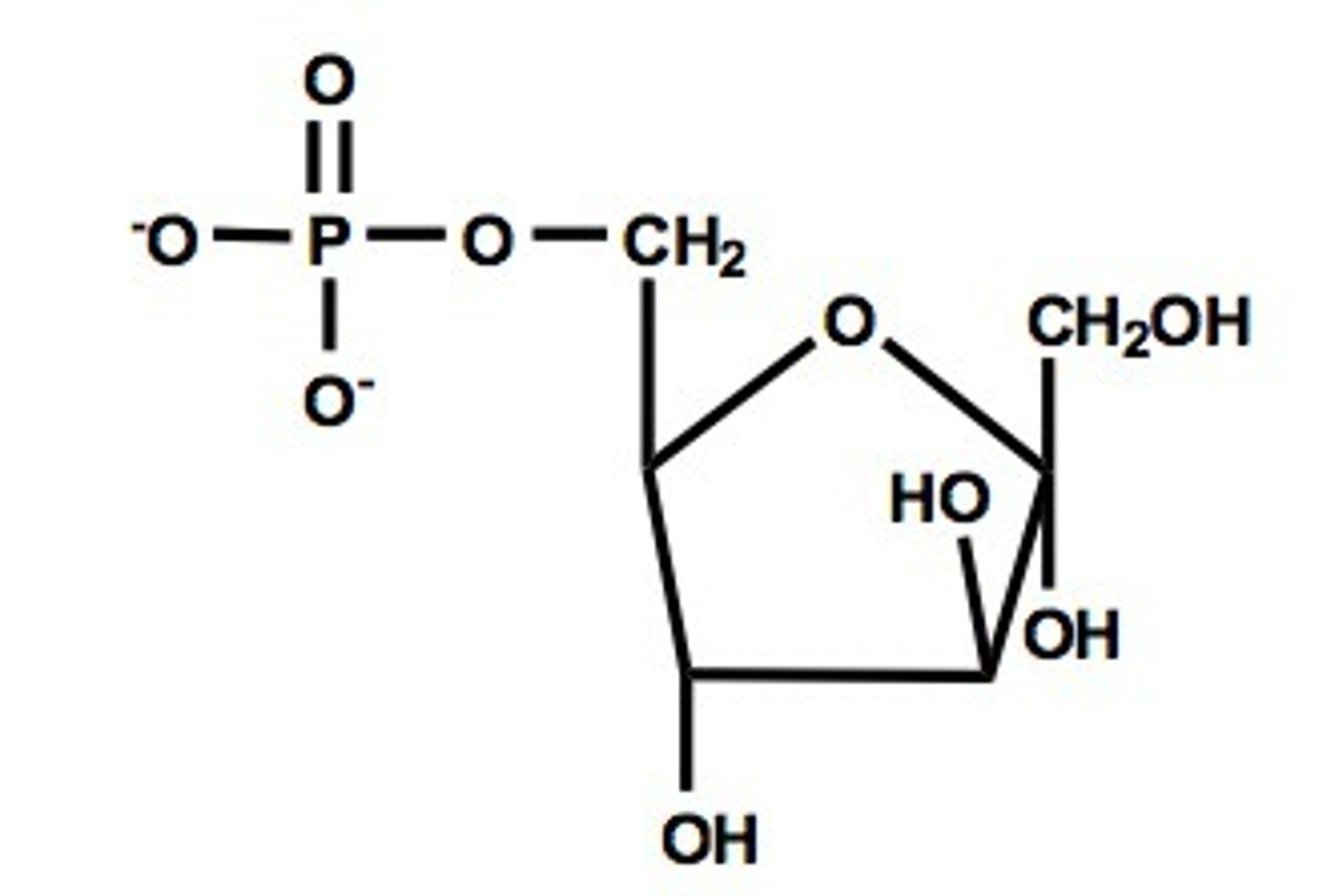
fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
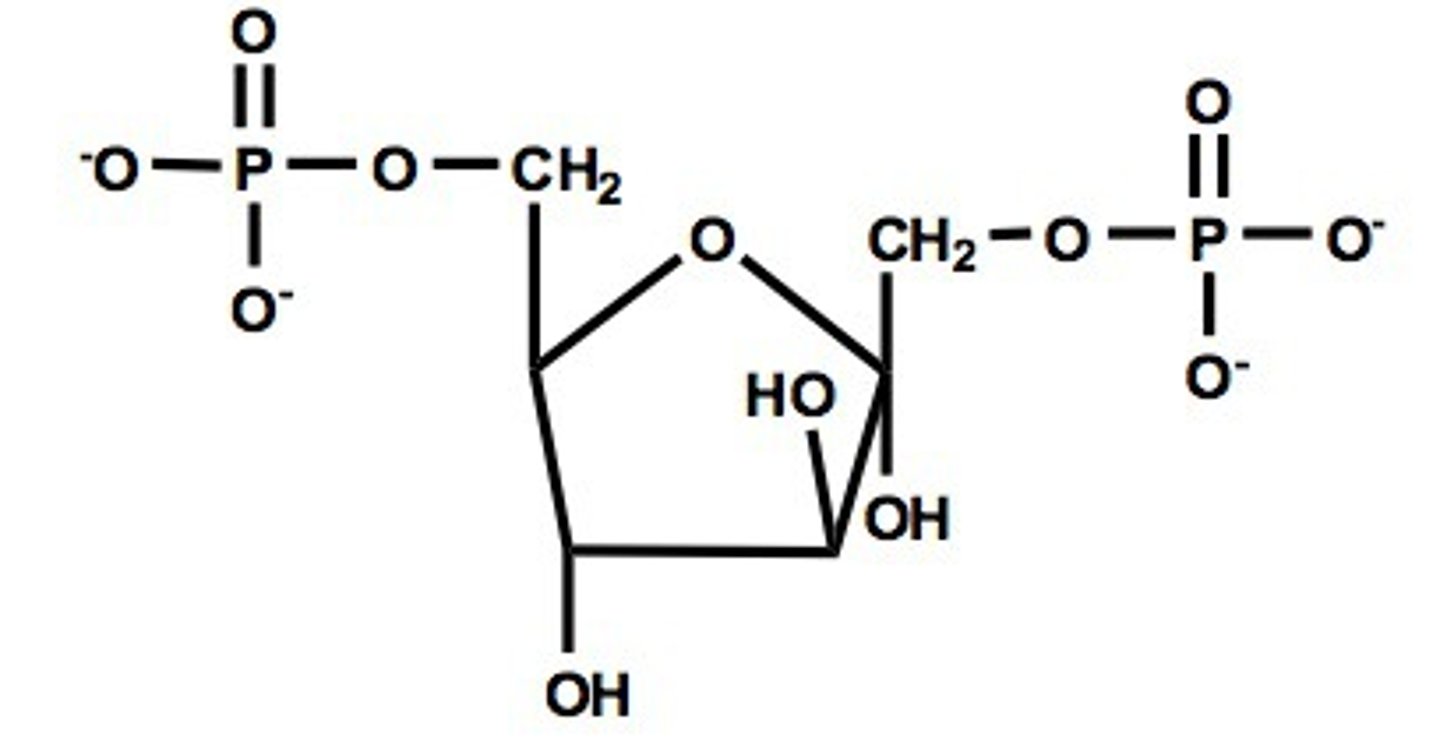
DHAP
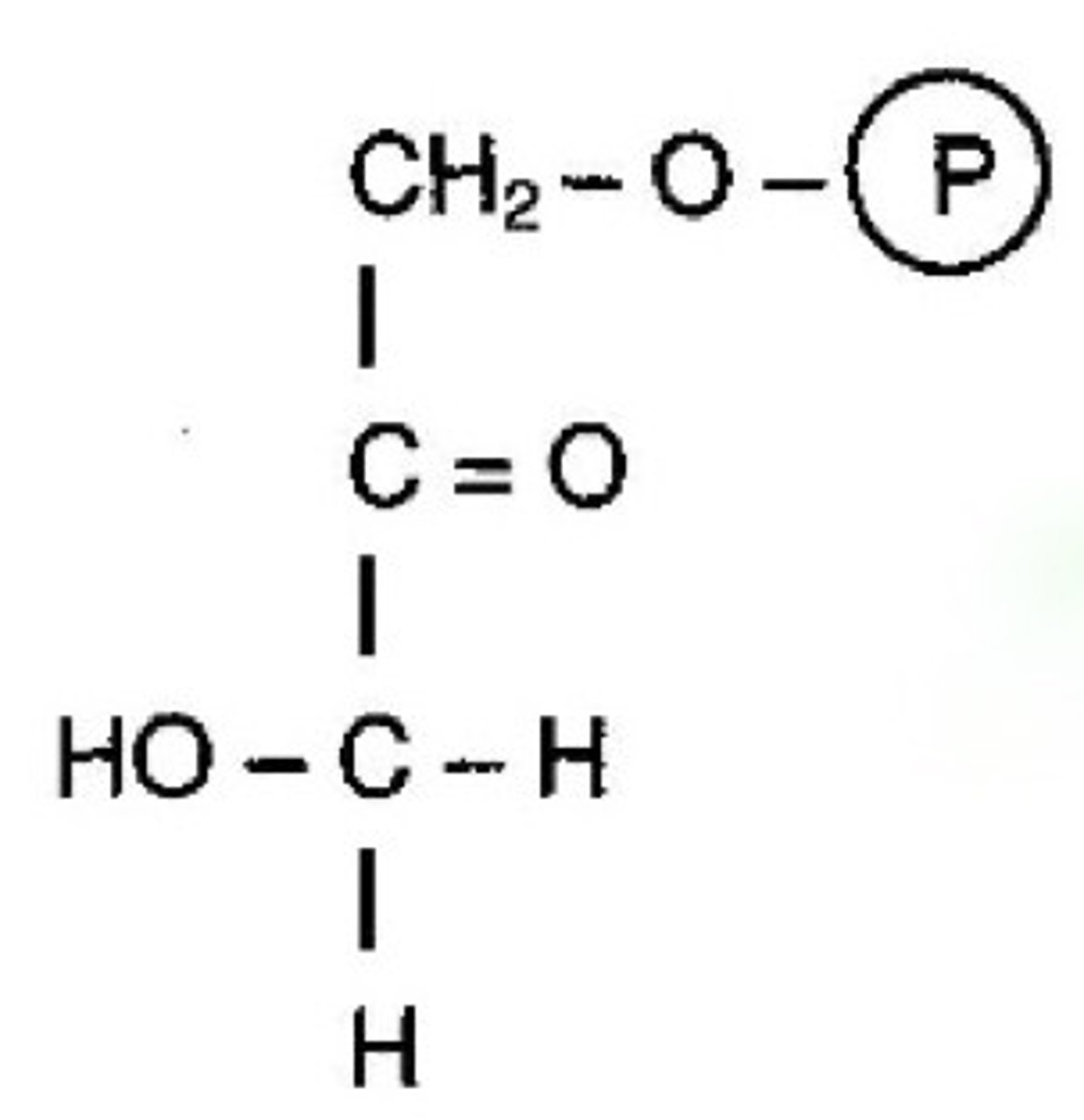
G-3-P
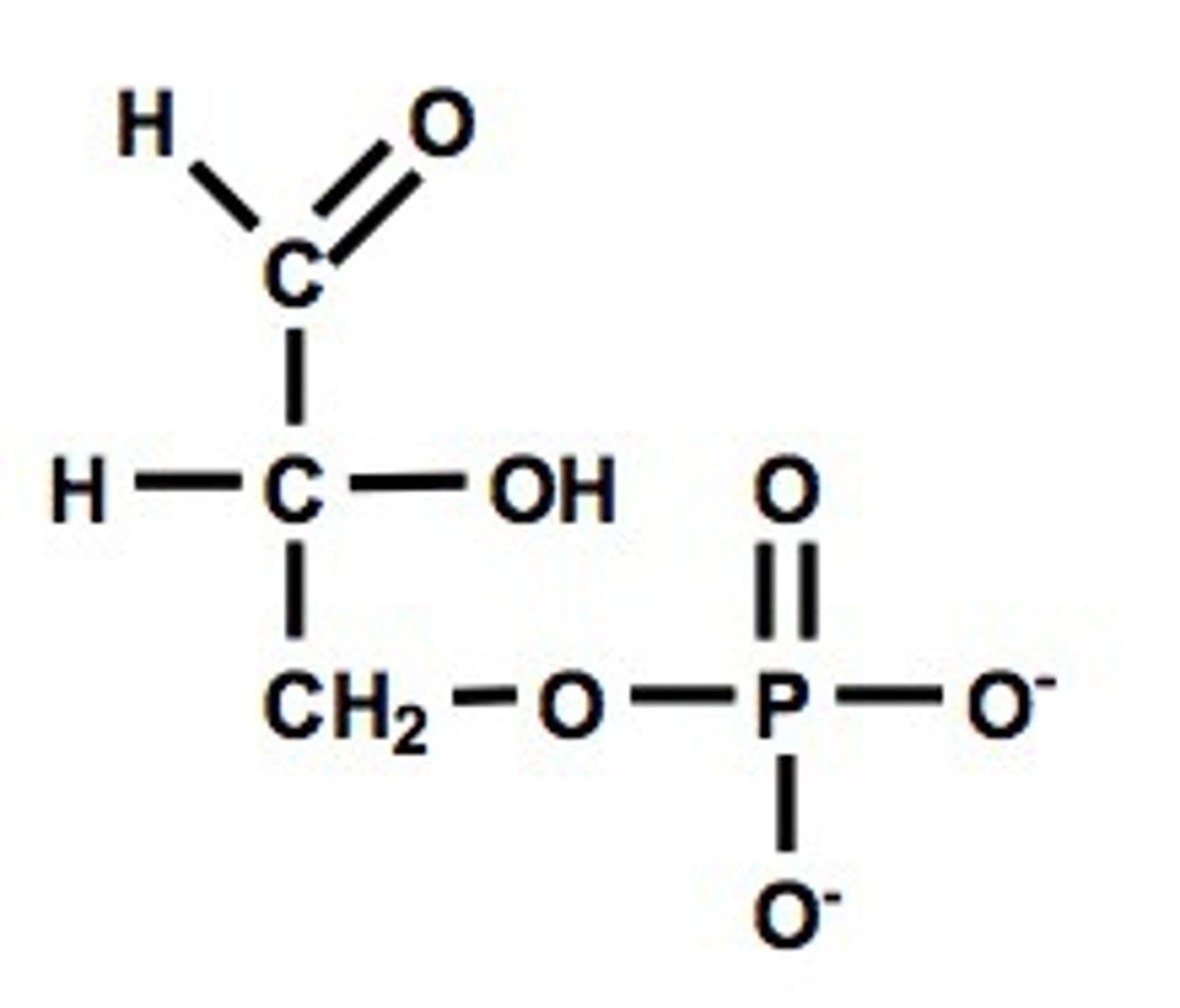
1,3-BPG
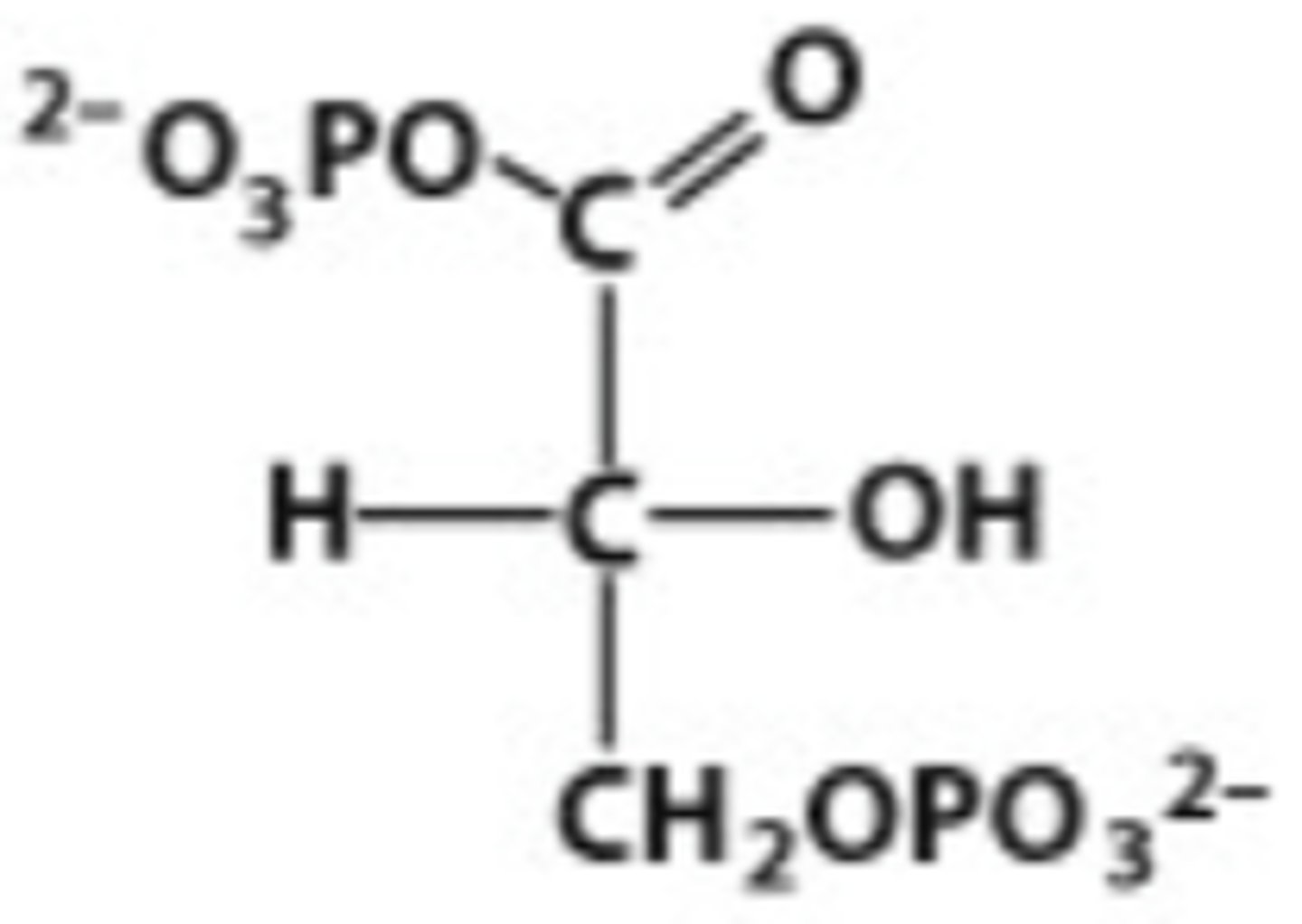
3-PG
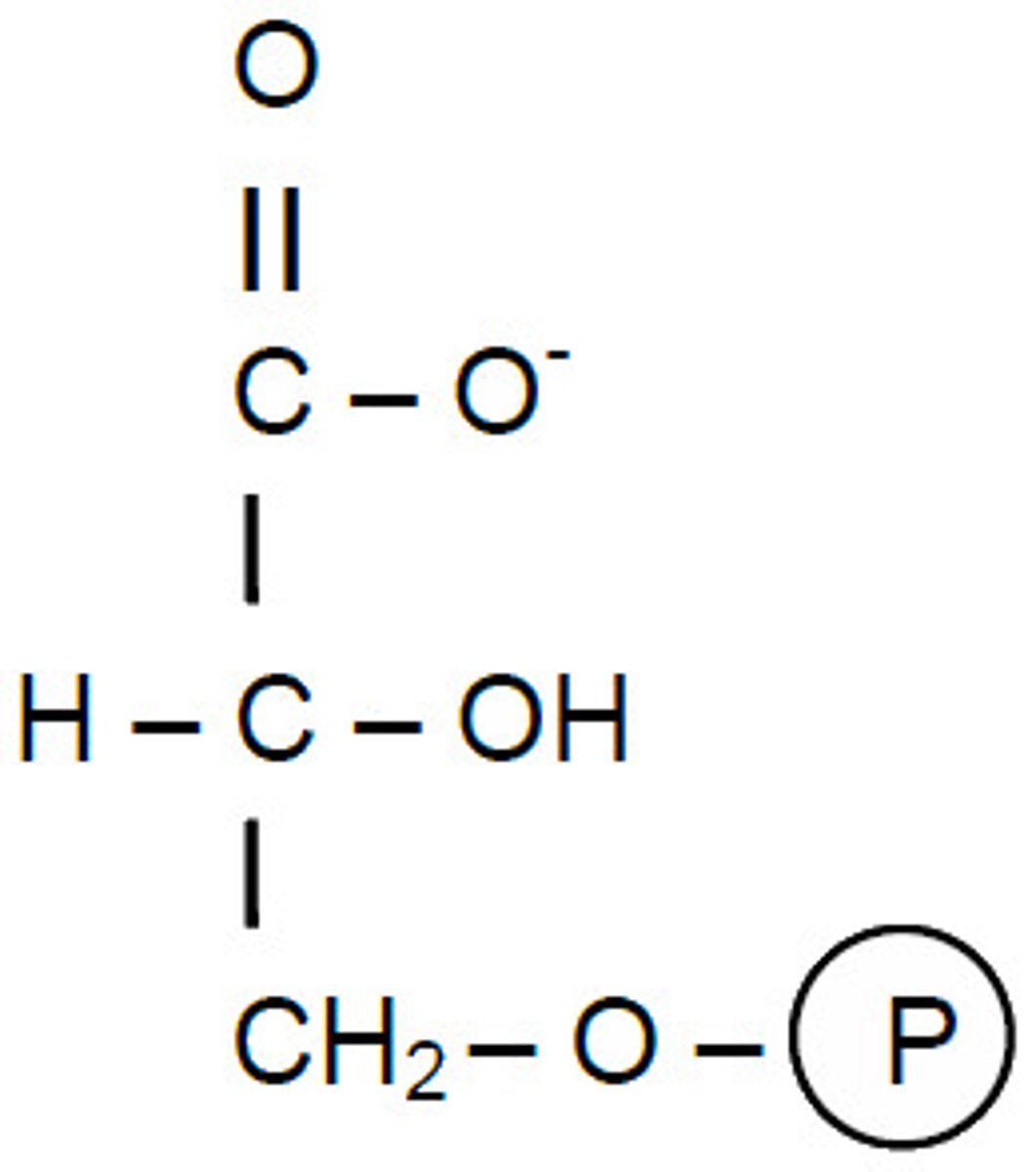
2-PG
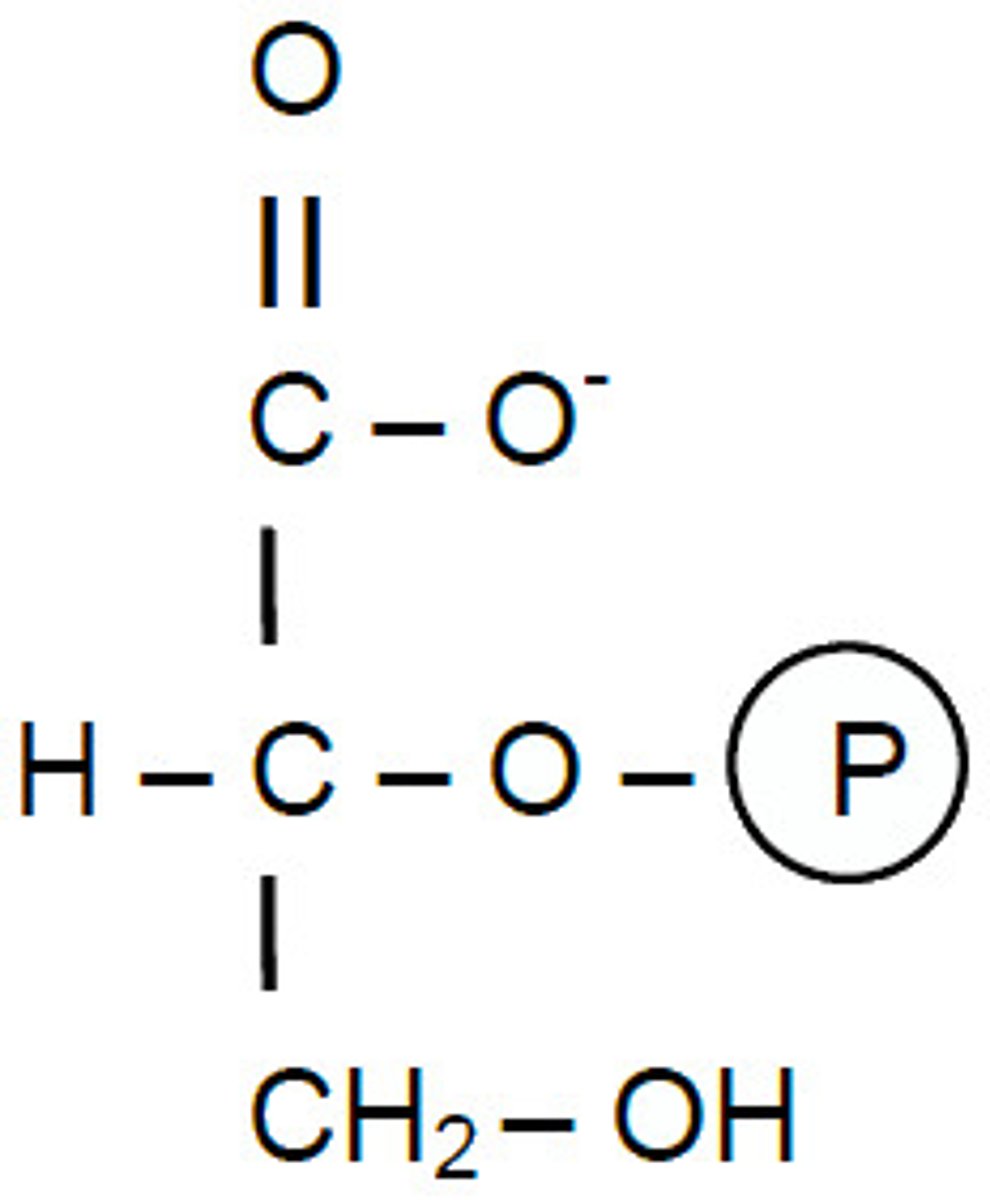
PEP
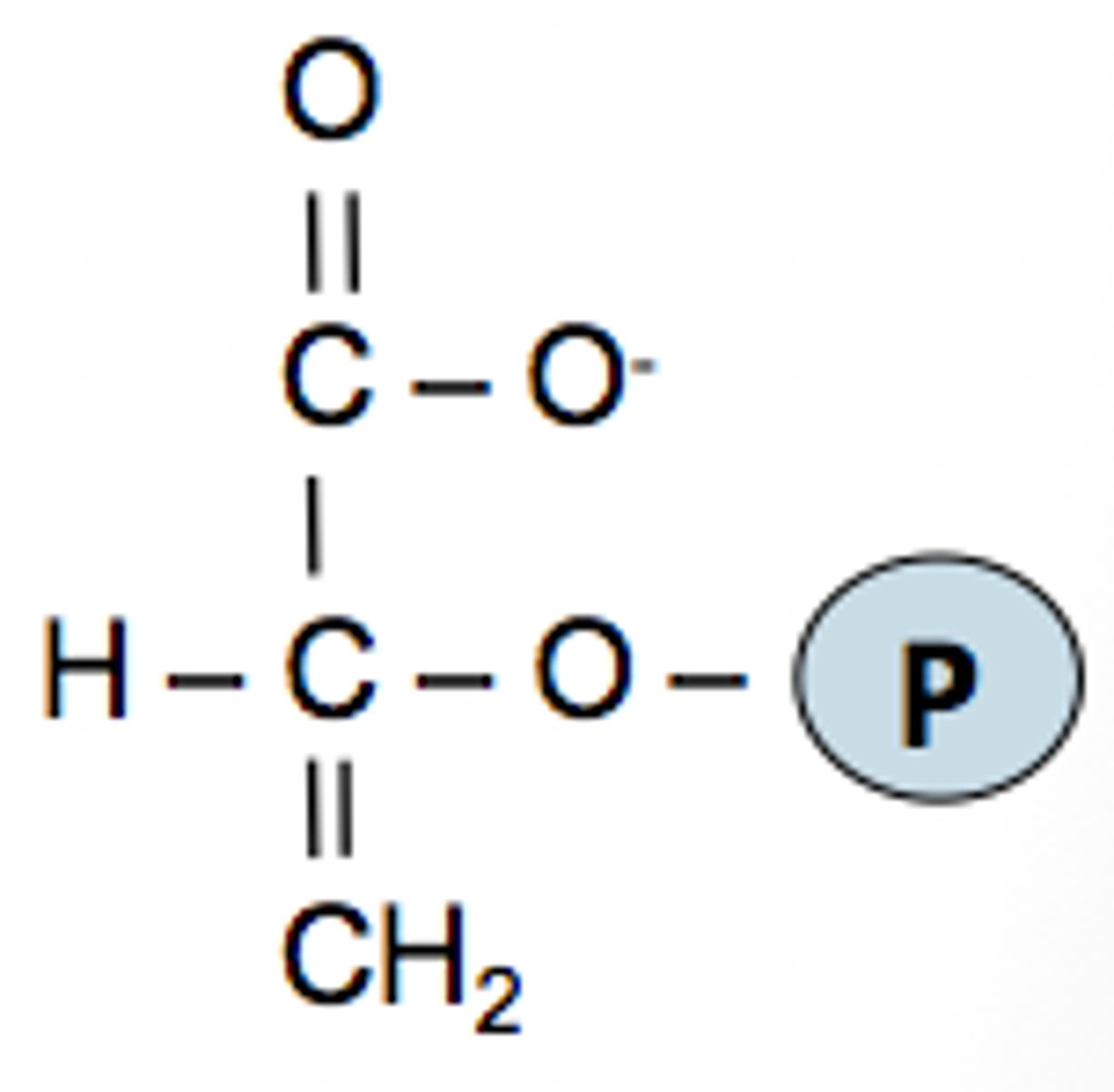
pyruvate
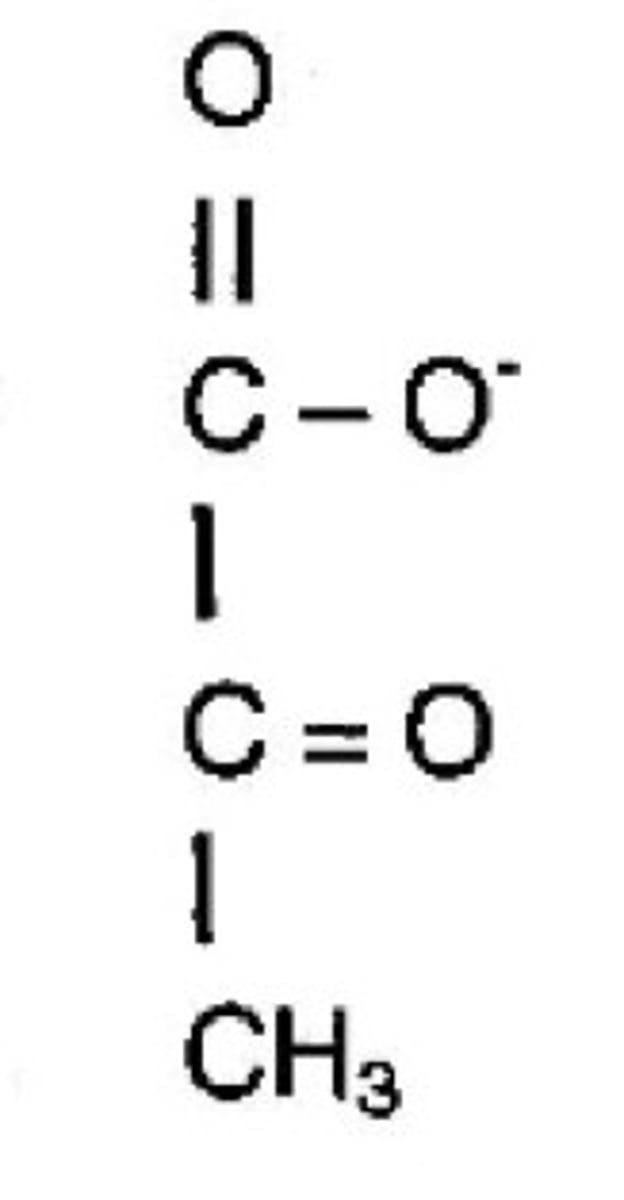
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
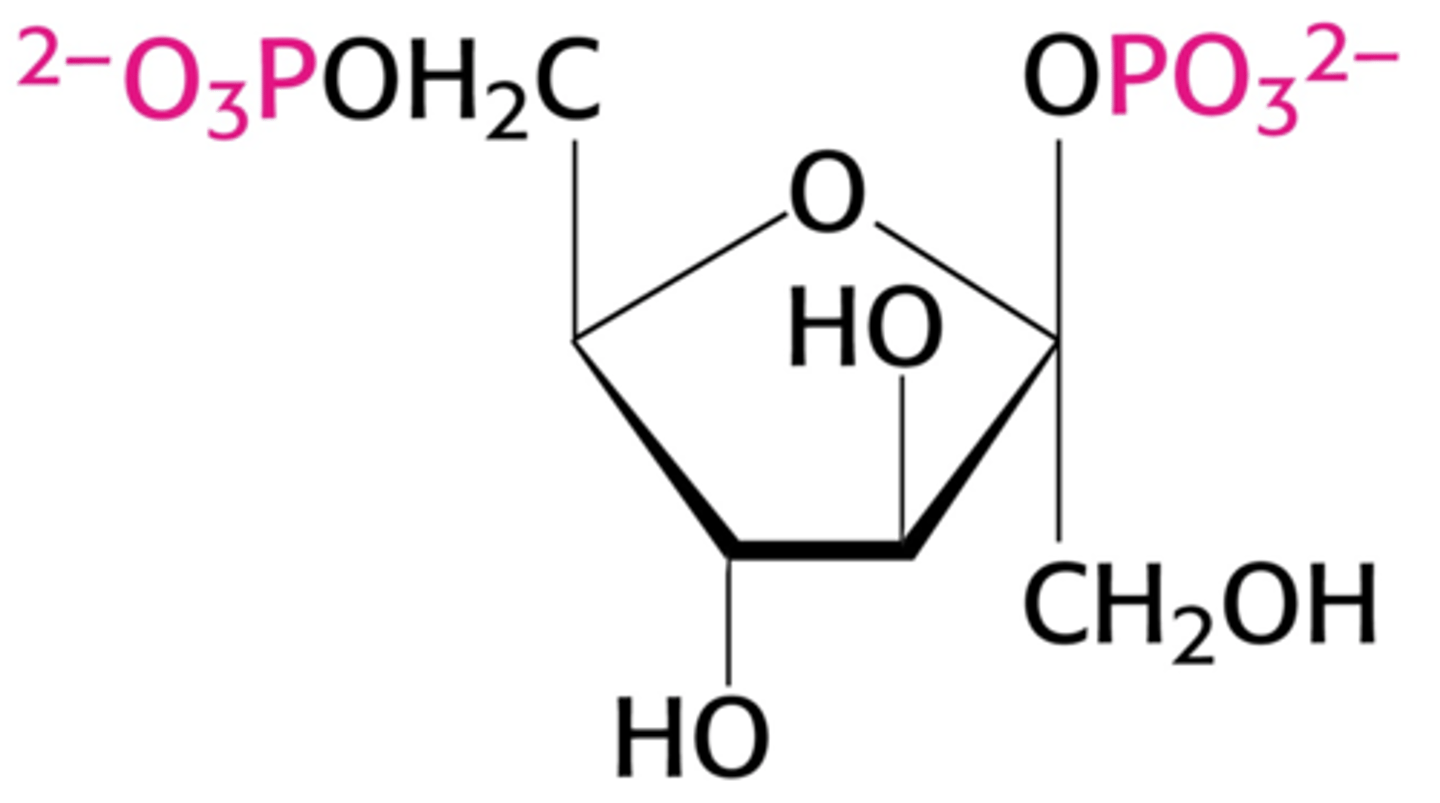
acetyl-CoA
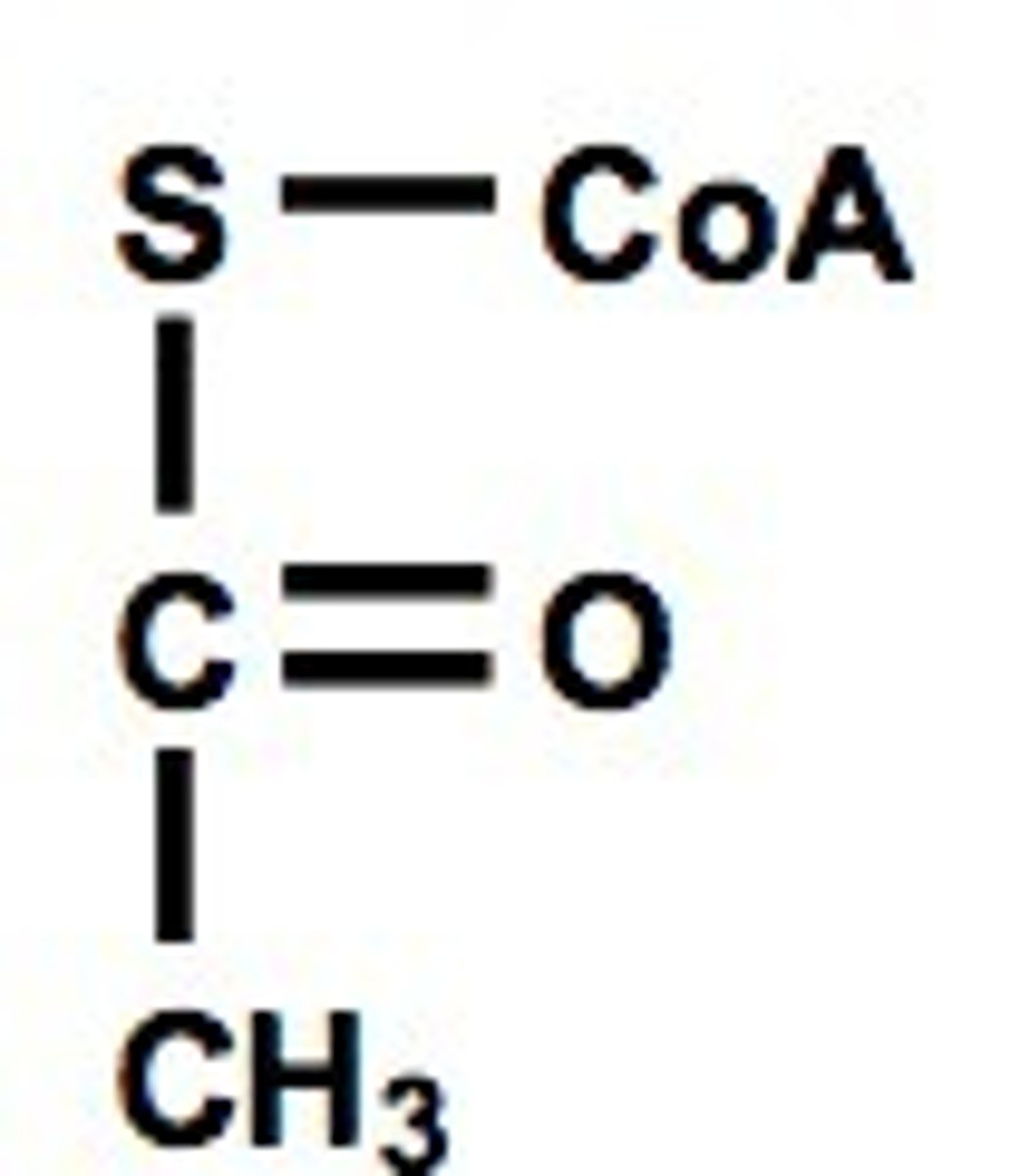
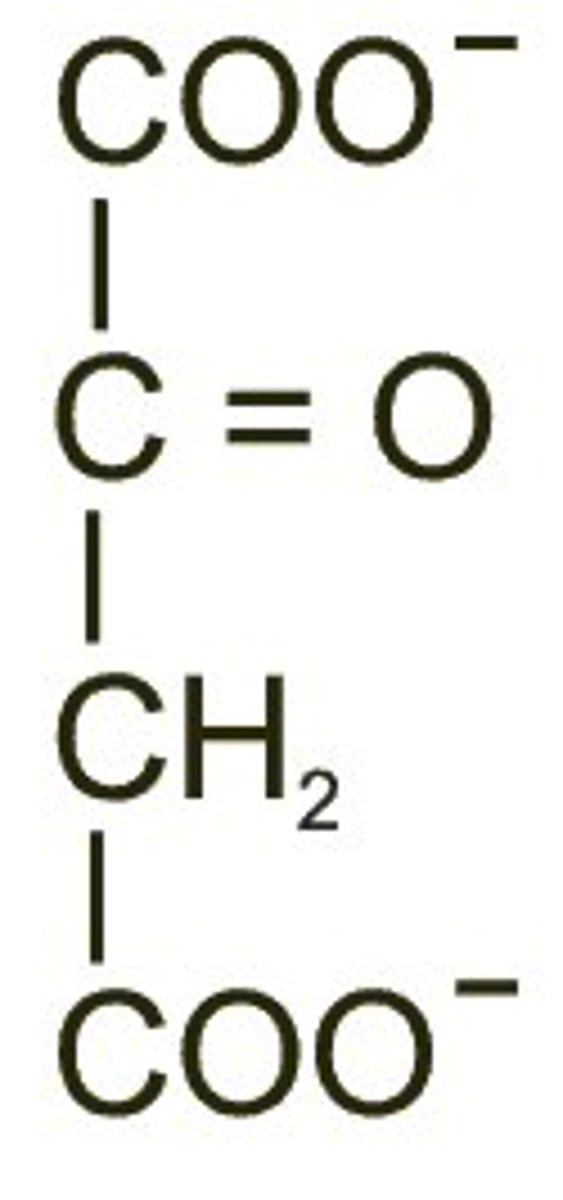
oxaloacetate
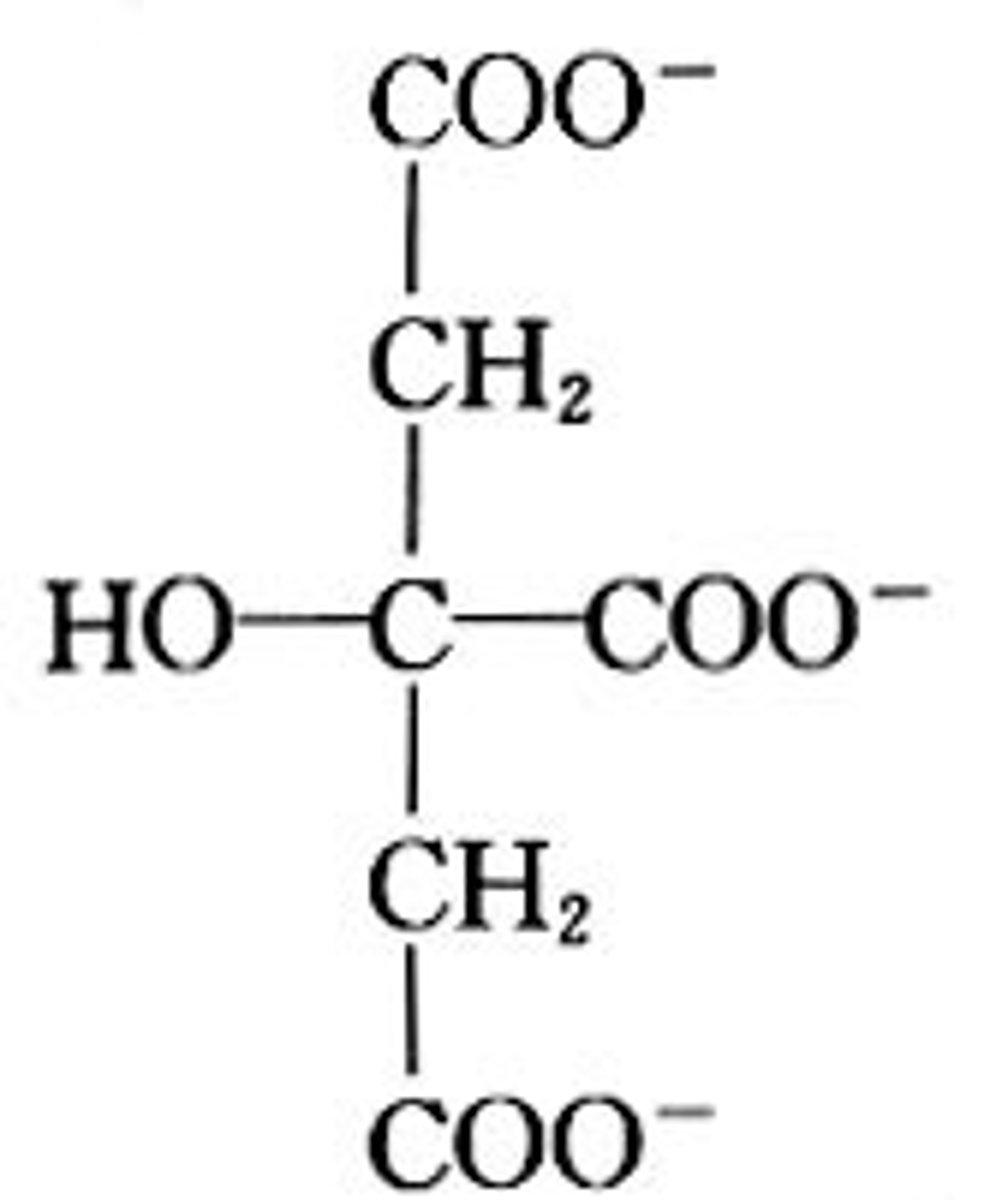
citrate
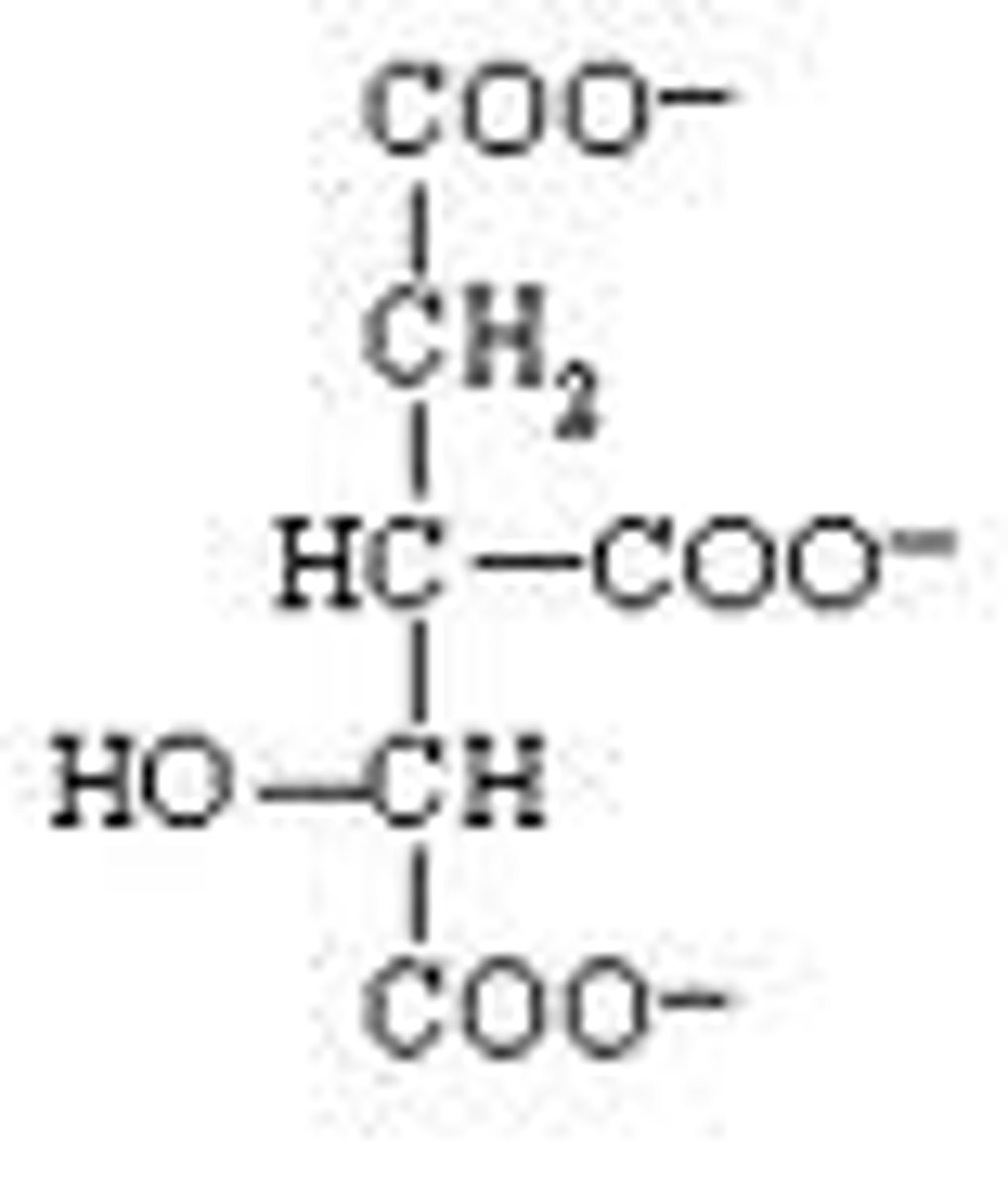
isocitrate
alpha-ketoglutarate
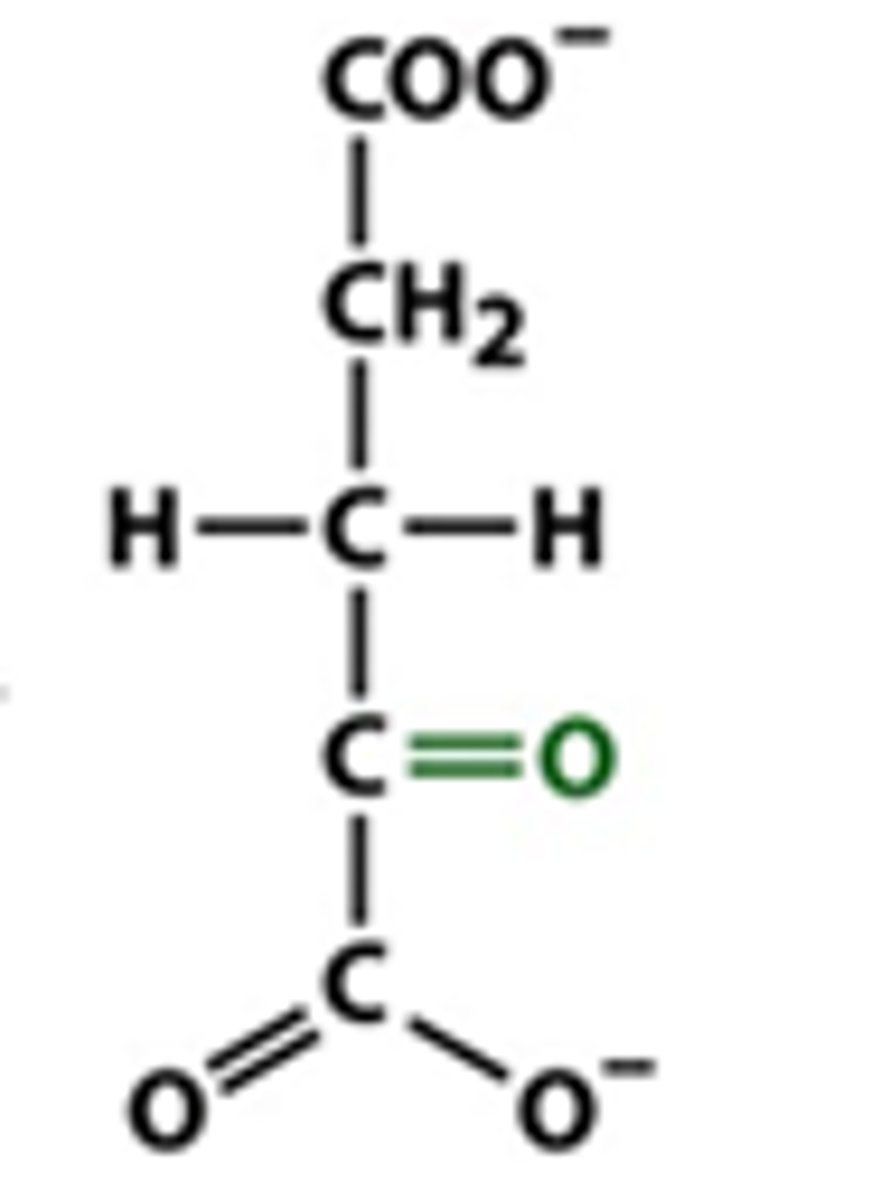
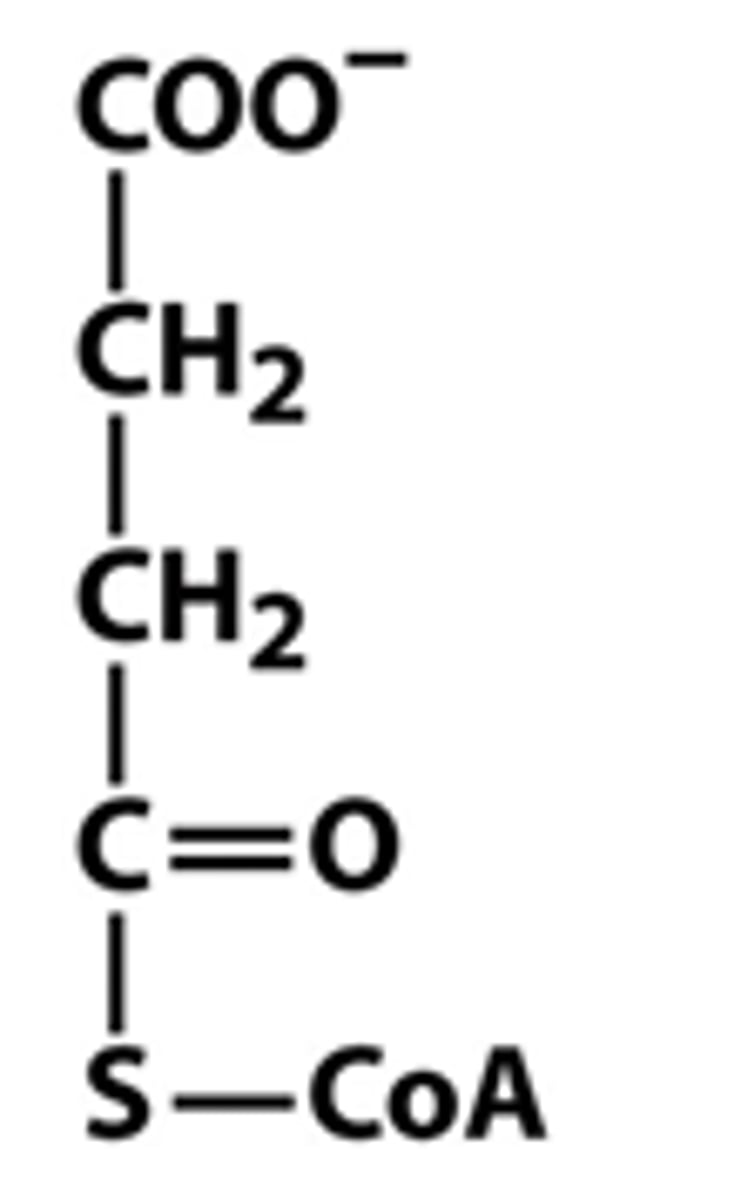
succinyl-CoA
succinate
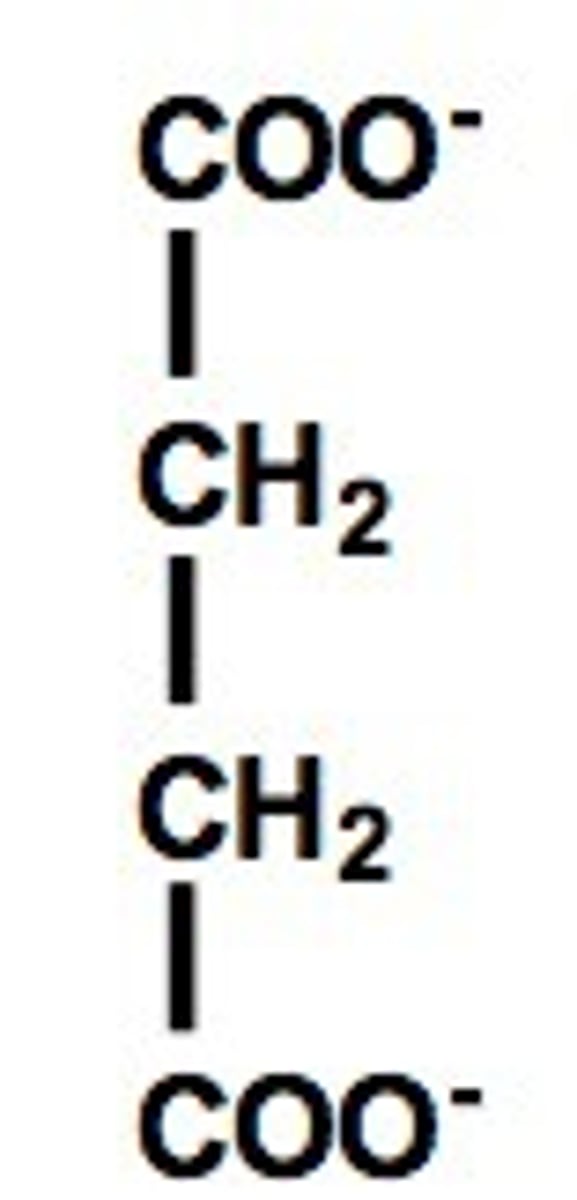
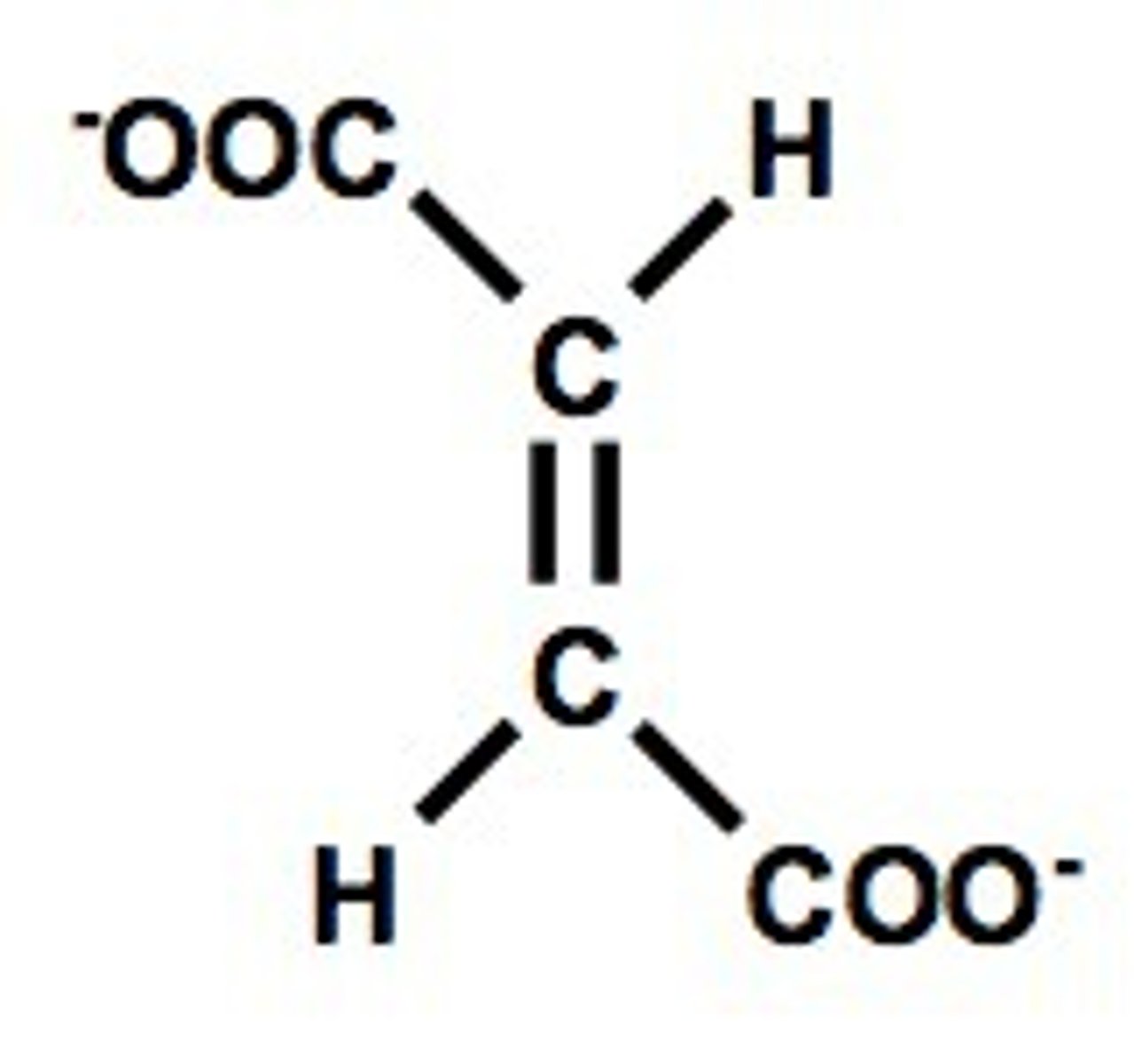
fumarate
malate
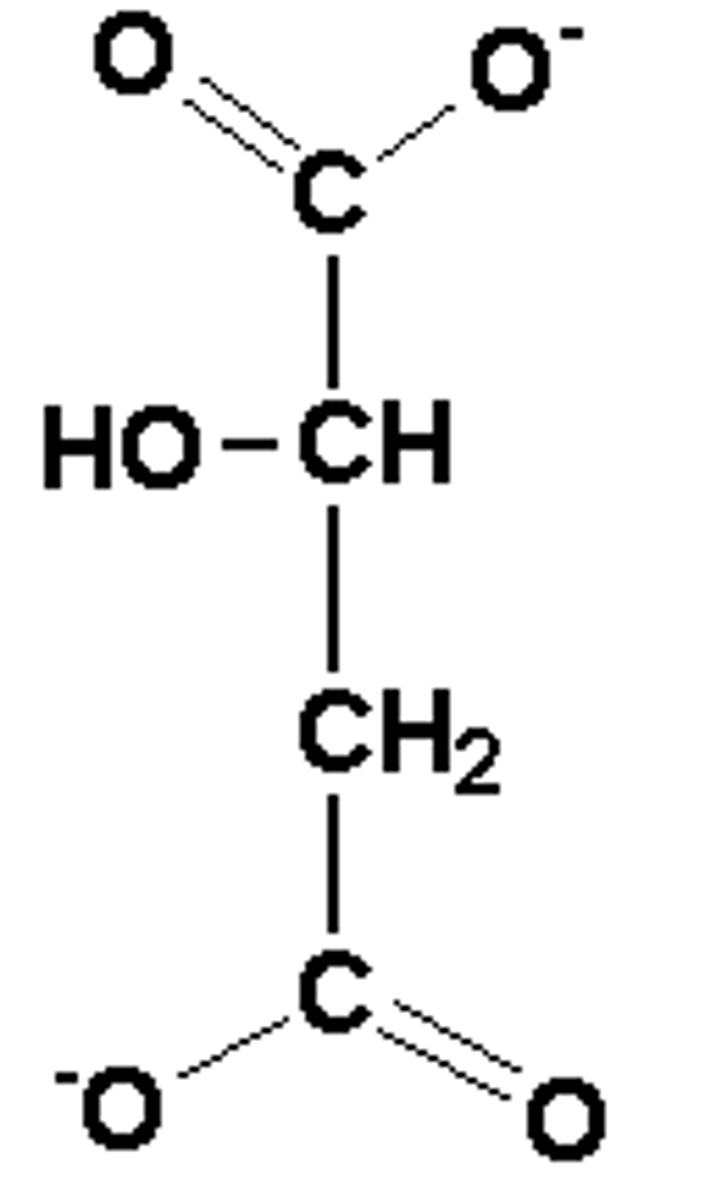
What is the order of structures in the TCA?
Acetyl-CoA → Oxaloacetate→ Citrate → Isocitrate → α-ketoglutarate → Succinyl-CoA → Succinate → Fumarate → Malate
What happens during prophase I of meiosis?
Crossing over occurs between homologous chromosomes.
What separates in anaphase I vs anaphase II of meiosis?
Anaphase I: homologous chromosomes. Anaphase II: sister chromatids.
In oogenesis, during which stages of meiosis are polar bodies formed?
One polar body forms during meiosis I and a second forms during meiosis II, due to unequal cytokinesis.
What type of inhibitor binds to both E and ES complex with unequal affinity?
Mixed inhibitor.
What does a noncompetitive inhibitor do to Vmax and Km?
It decreases Vmax but does not change Km.
How does an allosteric site differ from the active site on an enzyme?
Allosteric sites bind regulators (activators or inhibitors) that change enzyme activity without interacting with the substrate directly.
What happens to fluid pressure as height or velocity increases in a vertical pipe?
With height, pressure decreases to maintain total energy (Bernoulli’s principle).
As velocity increases, pressure decreases (Bernoulli’s principle).
What happens to fluid velocity when cross-sectional area decreases?
Velocity increases due to the continuity equation (A1v1 = A2v2).
What causes a rightward shift in the hemoglobin oxygen dissociation curve, and what does it promote?
A drop in pH or rise in CO₂ (Bohr effect) promotes oxygen release.
Why are steroid hormones able to cross the cell membrane?
They are nonpolar and lipid-soluble, so they diffuse through membranes.
What is the function of helper T cells?
They activate B cells and cytotoxic T cells by releasing cytokines.
What terminates GPCR signaling after activation?
The α subunit hydrolyzes GTP → GDP, inactivating itself and reassociating with the βγ subunit.
What does Torricelli's Law state about fluid speed from a hole in a container?
v = √(2gh), where h is the depth of the hole below the fluid surface.
What is the change in entropy when a protein folds?
Entropy decreases because folding leads to a more ordered state.
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics?
The total entropy of the universe always increases over time.
How do ΔH and ΔS determine spontaneity?
ΔH < 0, ΔS > 0 → always spontaneous
ΔH > 0, ΔS < 0 → never spontaneous
ΔH < 0, ΔS < 0 → spontaneous at low T
ΔH > 0, ΔS > 0 → spontaneous at high T
What is the direction and function of afferent vs efferent neurons?
Afferent: carry sensory input from tissue → CNS
Efferent: carry motor output from CNS → muscles/glands
What are the key steps in the GPCR → cAMP → PKA pathway?
Ligand binds GPCR → activates Gs protein
Gs activates adenylate cyclase → converts ATP to cAMP
cAMP activates Protein Kinase A (PKA)
PKA phosphorylates target proteins
Phosphodiesterase breaks down cAMP → ends signal
What activates protein kinase A, and what does it do?
Activated by rising cAMP; it phosphorylates proteins to trigger cellular responses (e.g., gene transcription, glycogen breakdown).
Do steroid hormones bind intracellular or extracellular receptors?
Intracellular. Because they are lipid-soluble and pass through the cell membrane.
What is the function of tight junctions in epithelial cells?
They prevent leakage between cells via the paracellular pathway.
What is the primary stimulus that regulates breathing rate?
Changes in blood pH, specifically CO₂-induced H⁺ concentration.
Where do naïve B cells become activated and undergo clonal expansion?
In lymph nodes, after encountering a specific antigen.
Which immune cells release perforin to lyse virally infected or cancerous cells?
Cytotoxic T cells and natural killer (NK) cells.
What is the function of somatic hypermutation?
To increase the diversity and affinity of antibody variable regions.
Which MHC class presents antigens to CD8⁺ cytotoxic T cells?
MHC Class I — found on all nucleated cells; presents endogenous antigens.
What is a naïve T helper cell?
A T helper cell that has not yet encountered its specific antigen.
What is the basic structure of waxes?
Long-chain fatty acids linked to alcohols forming esters.
What hormone is released by the adrenal medulla in stress response?
Epinephrine.
What hormone is released by the adrenal cortex in stress and metabolic regulation?
Cortisol.
In GPCR signaling, what enzyme is activated after Gs protein activation to increase cAMP levels?
Adenylate cyclase.
How does aldosterone affect ion exchange in the kidney?
It increases Na+ reabsorption and K+ secretion in the distal tubule.
What does renin do to affect blood pressure?
It initiates the RAAS cascade by converting angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, leading to vasoconstriction and aldosterone release to raise BP.
What type of glycosidic bonds form the linear and branched structure of glycogen?
α-1,4 (linear) and α-1,6 (branch points).
What enzyme breaks α-1,4 glycosidic bonds in glycogenolysis?
Glycogen phosphorylase.
Where does beta-oxidation occur?
In the mitochondrial matrix.
What are the products of beta-oxidation of even-chain fatty acids?
Multiple acetyl-CoA molecules are produced (2-carbon units). Unsaturated fatty acids require isomerization due to double bonds but still yield 1 acetyl-CoA per 2-carbon unit.
Which process produces NADPH?
Pentose phosphate pathway (oxidative phase).
What type of inhibition decreases both Km and Vmax?
Uncompetitive inhibition.
Which enzyme catalyzes the rate-limiting step of glycolysis? What are the key regulatory molecules for PFK-1?
Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1). Inhibited by ATP and citrate; activated by AMP and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate.
Which cofactor is required by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP).
How many ATP equivalents are generated by one NADH?
2.5 ATP.
How many ATP equivalents are generated by one FADH₂?
1.5 ATP.
Which complex of the ETC does not pump protons?
Complex II.
What is the function of Complex IV in the ETC?
Reduces oxygen to water.
What does the inner mitochondrial membrane contain for ATP production?
ATP synthase.
What stimulates gluconeogenesis during fasting?
Glucagon and cortisol.
What is the precursor for prostaglandin synthesis?
Arachidonic acid.
What is the structure of hemoglobin?
2 alpha and 2 beta polypeptide chains.
What hormone is released when blood volume increases?
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP). Promotes natriuresis (excretion of Na⁺ in urine) Increases water excretion, Inhibits RAAS (renin, angiotensin II, aldosterone), Dilates blood vessels → lowers blood pressure
What is the primary function of the small intestine villi?
Increase surface area for absorption.
What two substances are secreted by parietal cells?
HCl and intrinsic factor.
What is the name of the enzyme that breaks down starch into maltose?
Salivary amylase.
Where does bile enter the digestive system and what is its primary function?
Into the duodenum through the bile duct. Emulsify fats to aid in digestion by increasing surface area for lipase activity.
What are the three parts of the small intestine?
Duodenum, jejunum, ileum.
What is the function of the gallbladder?
Stores and concentrates bile.
What enzyme breaks down proteins in the stomach?
Pepsin.
Where does most nutrient absorption occur?
In the small intestine, primarily the jejunum.