Lecture 10 and 11 - Signaling in the Immune System
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What are the two forms that kinases can have in signal transduction?
Intrinsic receptor tyrosine kinases (ex: FLT3, c-Kit)
Noncovalently associated kinases (ex: TCR, BCR, JAKs)
What ligand class does the protein domain SH2 bind?
phophotyrosine
What ligand class does the protein domain SH3 bind?
proline
What ligand class does the protein domain PH bind?
phosphoinositides
What is the role of adaptor proteins?
they promote the interaction of multiple signaling molecules
ex: LAT in TCR signaling
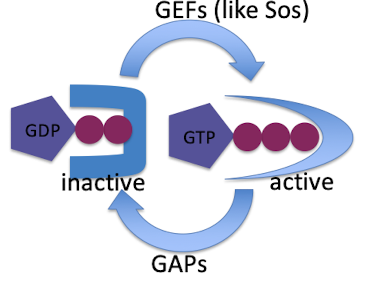
What is the role of G proteins/GTPases in signaling?
they serve as molecular switches
Ras family proteins
GDP bound form is inactive, GTP bound form is active
GEFs catalyze binding of GTP (ex: Sos)
GAPs accelerate GTP to GDP hydrolysis
How are signals transduced from outside of the cell to inside the cell?
signaling molecules are recruited to membrane
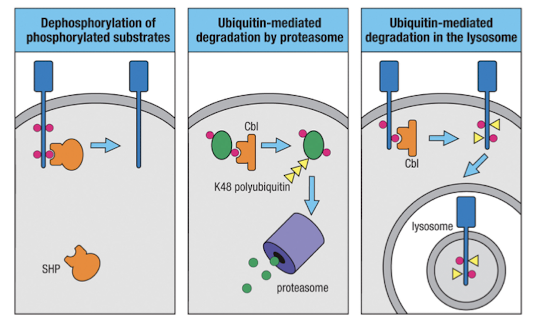
What allow for cells to be repeatedly responsive?
the signaling must be turned on and off
phosphatases vs kinases (ex: SHP - phosphatase)
polyubiquitination → proteasomal degredation (ex: Cbl - ubiquitin ligase)
single/di-ubiquitinated proteins are targeted for degredation in lysosome
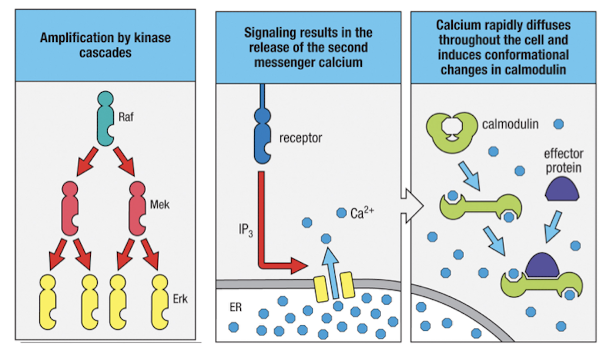
Amplification cascades
cause large cellular response after signal is initiated
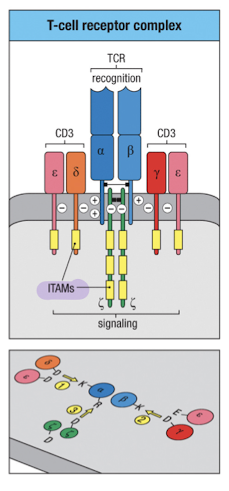
Why does the TCR associate with ITAM containing proteins?
TCR doesn’t have intracellular signaling domains
TCR cannot reach cell surface without CD3 chains
CD3 chains + ζ chains = 10 ITAM motifs
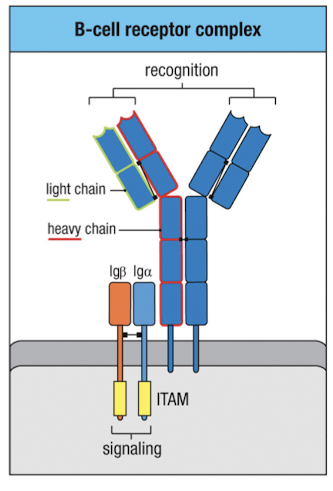
BCR complex with ITAM proteins
Igα and Igβ each have one Ig like domain and one ITAM domain
signaling is initiated by Src-family kinase-mediated phosphorylation
What is the role of Lck in TCR signaling?
Lck is a src-family tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates ITAMs on CD3 chains
What happens after CD3 ITAMs are phsophorylated by Lck?
The ITAMs recruit ZAP-70, which is also phosphorylated by Lck
How is Lck activity regulated?
2 regulatory tyrosines: Y505 and Y394
Y505 is inhibitory when phosphorylated, CD45 phosphatase dephosphorylates it to prime Lck
Csk kinase can re-phosphorylate Y505
Y394 is auto-phosphorylated by Lck to become active
What is kinetic proofreading in TCR signaling?
the TCR must be engaged with the MHC for a sufficient “dwell time” in order to initiate signaling
How does Zap70 become activated?
it is initially autoinhibited, but phosphorylated ITAMs recruit it and it uses SH2 domains to interact with the ITAM before being activated by Lck
What types of receptors do ITAM domains activate?
NK cells, macrophages, neutrophils, mast cells, basophils, etc
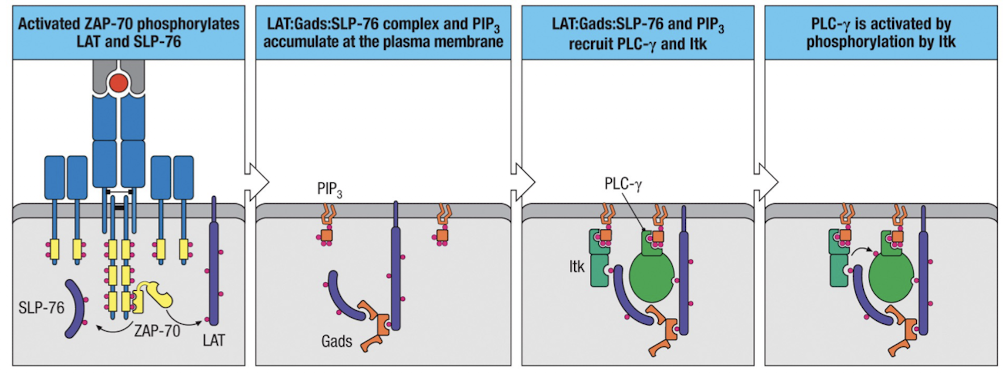
What does ZAP-70 do after it is activated?
It phosphorylates scaffold proteins LAT and SLP-76
How does ZAP-70 lead to PLC-γ activation?
LAT and SLP76 are joined by Gads
inactive PLC-γ is recruited to the complex by PIP3 (which comes from PI3K)
Itk is recruited by PIP3 and SLP76
Itk phosphorylates and activates PLC-γ
How does PLC-γ initiate a large Ca2+ influx into the cell?
PLC-γ cleaves PIP2 to generate IP3 and DAG
IP3 binds recptors in the ER membrane that cause the release of calcium
depletion of ER stores causes aggregation of STIM1
What is the significance of STIM1 in TCR signaling?
it binds to ORAI1 in the plasma membrane to form the CRAC channel, which enables lots of Ca2+ to enter the cell.
What is the significance of IP3?
IP3 binds receptors in the ER membrane to trigger calcium release into the cell
IP3 comes from PIP2 cleaved by PLC-γ
What is the significance of DAG?
DAG activates PKCθ and RasGRP (a Ras GEF) which leads to the activation of transcription factors
DAG activates Ras which initiates a downstream MAPK cascade involving Raf, Mek, and Erk
Erk then enters the nucleus and activates genes via phosphorylation
it also causes activation of NFkB
How does transcription factor NFAT become activated?
serine-threonine phosphorylation retains NFAT in cytoplasm
when Ca2+ binds calmodulin, it then activated calcineurin (serine/threonine phosphatase)
calcineurin dephosphorylates NFAT
What does Ras signaling result in?
activation of transcription factor AP-1
Erk phosphorylates Elk-1, a TF that induces FOS
JNK is activated by PKC-θ, it then enters the nucleus and phosphorylates c-Jun
JUN/FOS dimers = AP-1
What 3 transcription factors are critical for turning on genes involved in T cell activation?
NFAT, AP-1, and NFκB
What are the 4 things that TCR activation induces?
Transcription factor activation
metabolic changes and increased T cell survival
tight integrin adhesion
cytoskeletal reorganization
What is the significance of AKT?
AKT leads to enhanced T cell survival
it phosphorylates Bad, which releases pro survival Bcl2
AKT alters cellular metabolism
cause release of GAP from Rheb, active Rheb drives mTOR activation
induces expression of nutrient transporters and activity of glycolytic enzymes supporting cell growth
metabolic change allows lymphocytes to proliferate once every 4-8 hrs when active
How is AKT activated?
activation of PI3K generates, PIP3
PIP3 recruits PDK1 which activates AKT
What 4 things result from mTOR activation?
increased lipid production
increased ribosome biosynthesis
increased mRNA synthesis
increased protein translation
How does TCR signaling promote tight integrin adhesion?
Rap1 activation
LAT:Gads:SLP-76 recruits ADAP
ADAP activates Rap1
Rap1 causes accumulation of the integrin LFA1 and conversion to a high affinity conformation (allows tight adhesion of T cell to APC)
What is the significance of Vav in TCR activation?
Vav causes changed in actin via Cdc42
Vav (a GEF) is recruited to PIP3 and LAT:Gads:SLP-76 complex
WASp is recruited to the complex
Vav activates g protein Cdc42, which activates WASp
WASp recruits proteins that induce actin polymerization
what does a WASp deficiency cause?
Wiskott-Adich syndrome
absence of WASp causes low platelet counts, Ig deficiency, snd viral susceptibility
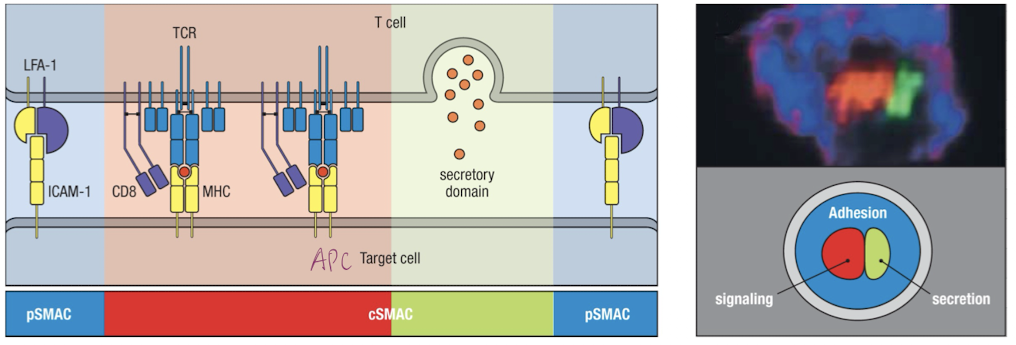
What is the cause and effect of the immunological synapse?
Cause = TCR stimulation
Effect = directional secretion
both actin cytoskeleton and microtubules must reorganize in order to point at target cells
What is the cSMAC and pSMAC
cSMAC = central supermolecular activation complex
pSMAC = peripheral supermolecular activation complex
How is the BCR complex similar to TCR?
the signaling process is homologous
BCR associates with ITAM containing Igs (alpha and beta)
syk = ZAP-70 homolog
ITAMs phosphorylated by Blk, Fyn, or Lyn
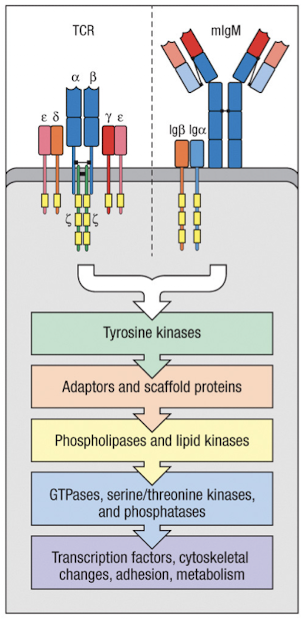
Summary of Antigen receptor signaling
TCR/BCR → Tyrosine kinases → adaptors and scaffold proteins → phospholipases and lipid kinases → GTPases, serine/threonine kinases, phosphatases → transcription factors, cytoskeletal changes, adhesion, metabolism
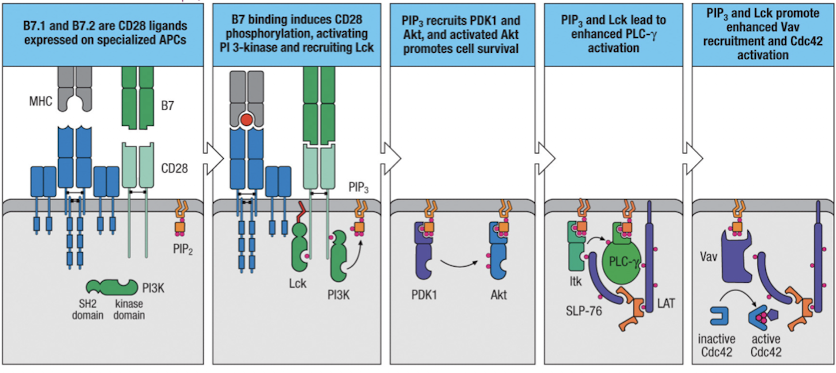
What is required for PI3K activation?
T cell co-stimulation through CD28 is required for PI3K activation
What is the significance of CD28?
CD28 binds B7.1 and B7.2 on APC and is phosphorylated by Ick
CD28 recruits and activates PI3K, which phosphorylates PIP2 to generate PIP3
What are the roles of PIP3?
recruits AKT and PDK1 leading to AKT activation → survival and metabolic changes
binds Itk, which activates PLC-γ → TF activation
binds Vav, enabling Cdc42 activation and Wasp activation → cytoskeletal changes
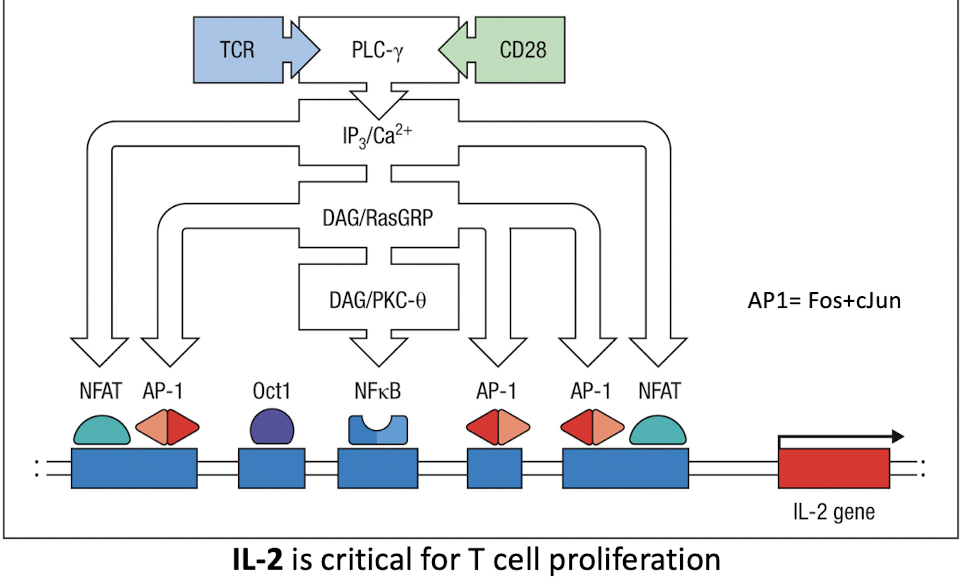
What happens when TCR and CD28 work together?
They transduce all signals needed for IL-2 transcription
IL-2 is critical for T cell proliferation
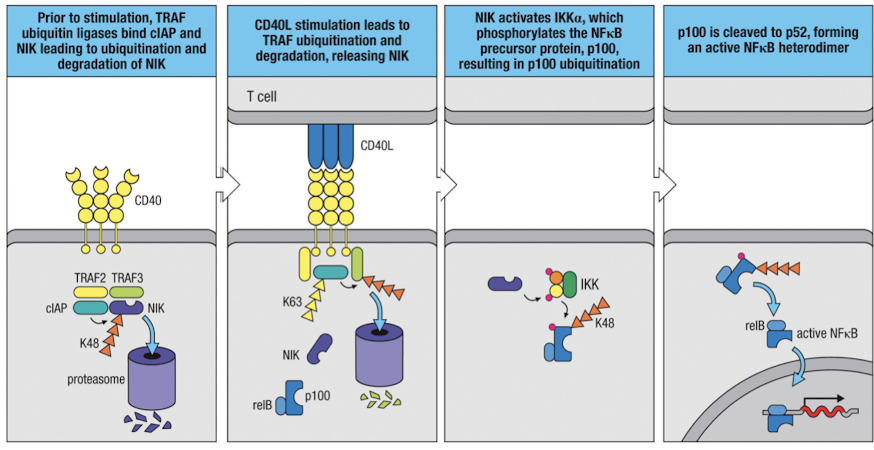
How does the TNFR superfamily augment B cell activation?
CD40L on T cells activates CD40 on B cells
in absence of CD40, NIK is K48 ubiquitinated and degraded (CD40 ligation causes NIK stabilization)
NIK activates IKKα, which phosphorylates p100 (NFkb precursor)
P100 is cleaved to form p52, which makes a dimer with relB
CD40 activation is essential for activation of naive B cells
What is the significance of CTLA-4?
CTLA-4 is an inhibitory receptor that inhibits T cell activation
it isn’t recruited to the plasma membrane until TCR is activated
has a higher affinity for B7.1 and B7.2 than CD28
outcompetes CD28 binding for B7 to inhibit T cells
critical to prevent uncontrolled T cell proliferation
What receptors are related to CD28, except they are inhibitory?
CTLA-4, PD-1, and BTLA
What does it mean when a receptor has ITIM or ITSM motifs?
ITIM containing receptors inhibit activation of multiple immune cells
recruit SHP and SHIP (phosphatases)
long isoforms of KIR inhibit NK cells by binding self MHC-I molecules
PD-1 recruits SHP2, which dephosphorylates CD28
What molecule is inhibitory for BCR signaling?
FcγRIIB - keeps antigens present as immune complexes from activating naive B cells
What are CAR T cells?
Chimeric antigen receptor T cells
understanding lymphocyte signaling has led to their design
they are used for treatment of immune system diseases