Biogeochemical Cycles
3.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/42
Earn XP
Last updated 11:32 PM on 5/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
1
New cards
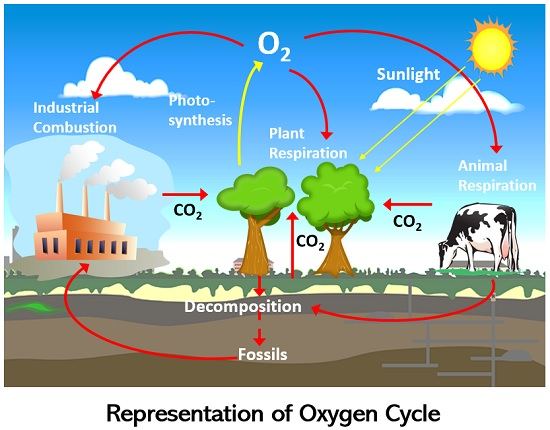
Carbon-Oxygen Cycle
The continuous exchange of carbon and oxygen from non-living environment and to the living.
2
New cards
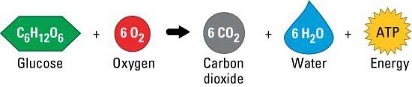
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Organisms break down glucose for energy. Oxygen is the input, carbon dioxide output.
3
New cards
Anaerobic Respiration
When oxygen is absent glucose breaks down with a catalyst releasing energy.
4
New cards
Ocean Acidification
When atmospheric carbon reacts with water, forming carbonic acid in the ocean.
5
New cards
How does carbonic acid affect the environment?
It can erode away skeletons and rocks in ecosystems.
6
New cards
Carbon Sinks
Store carbon for a period of time.
7
New cards
Examples of Carbon Sinks
Plants, animals, oceans.
8
New cards
Cellular Respiration
\
Organisms combine food molecules and oxygen, gives off carbon dioxide. Basically plant breathing.
Organisms combine food molecules and oxygen, gives off carbon dioxide. Basically plant breathing.
9
New cards
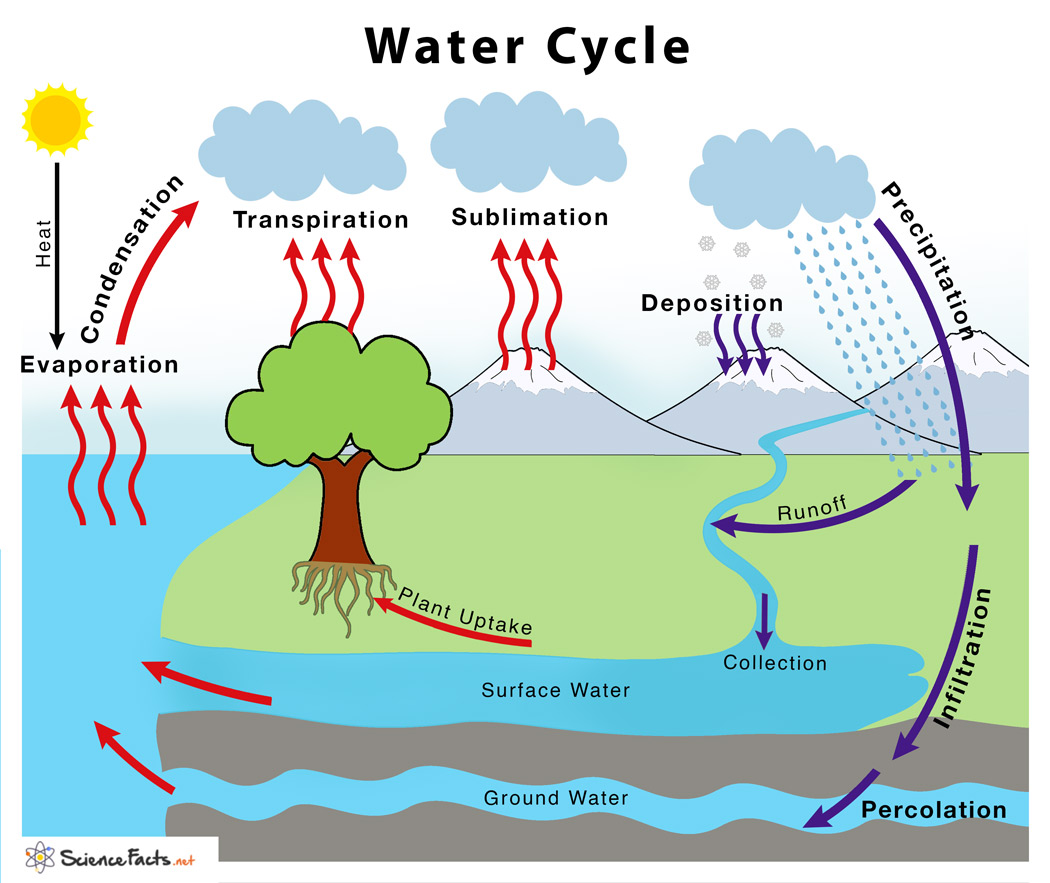
Water Cycle
The continuous movement of water on and above the Earth’s surface powered by the sun.
10
New cards
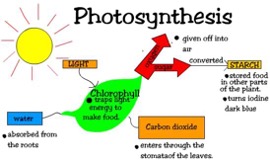
Photosynthesis
Plants use the sun’s energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and sugars.
11
New cards
Stages of the Water Cycle
Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, infiltration, transpiration, surface run-off.
12
New cards
Evaporation
Liquid to gas, molecules rise into the air in the form of water vapour.
13
New cards
Condensation
Gas to liquid, water cools and forms clouds.
14
New cards
Precipitation
When cloud is fully condensed, water falls in the form of rain, sleet, snow etc.
15
New cards
Infiltration
Water soaks into the ground collecting in layers of rock.
16
New cards
Transpiration
Groundwater is absorbed by plant roots when water evaporates from plants, photosynthesis.
17
New cards
Surface Run-off
Water that cannot soak into the ground, flows across land.
18
New cards
Human Impacts on the Water Cycle
* Deforestation: evaporation is disrupted, decreased precipitation, decreased respiration.
* Enhanced Greenhouse Effects: Earth’s temperature rises and therefore so does the evaporation rate.
* Enhanced Greenhouse Effects: Earth’s temperature rises and therefore so does the evaporation rate.
19
New cards
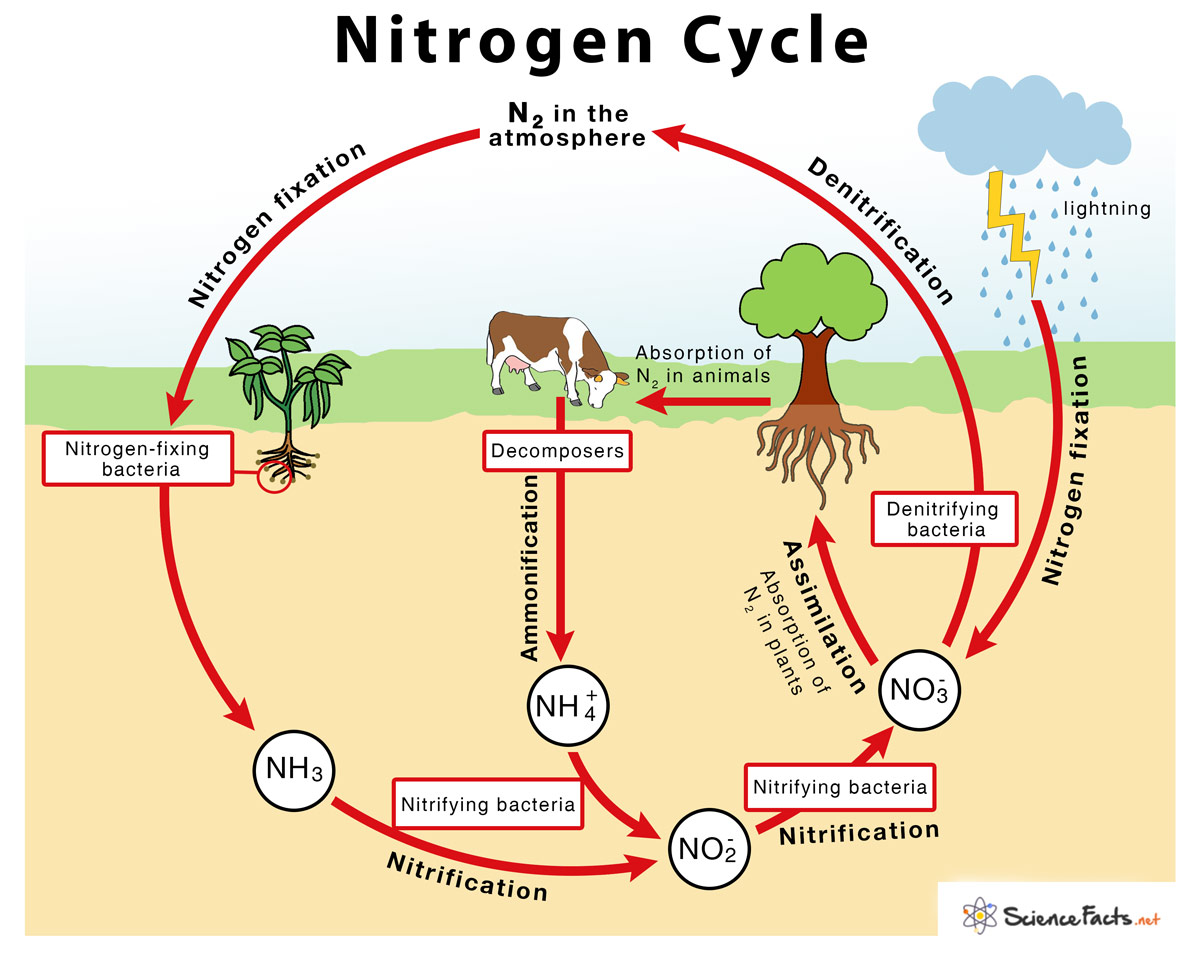
Nitrogen Cycle
The process of how nitrogen changes forms as it is recycled through the biosphere.
20
New cards
Importance of Nitrogen in the Biosphere
It is crucial for forming proteins.
21
New cards
Forms of Oxygen and where they’re found.
Inorganic: Nitrogen gas in the atmosphere. Organic: Wastes & living and dead organisms.
22
New cards
Types of Proteins in the Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen fixing
Nitrifying
Denitrifying
Nitrifying
Denitrifying
23
New cards
Nitrogen Cycle: Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixing bacteria take up atmospheric nitrogen, converting it to ammonia.
24
New cards
Processes that Fix Nitrogen:
Nitrogen FixationLightning
25
New cards
Nitrogen Cycle: Nitrification
Nitrifying bacteria converts ammonia to nitrite and nitrate ions.
26
New cards
Nitrogen Cycle: Assimilation
Plants absorb ammonium, nitrate, and nitrites.
27
New cards
Nitrogen Cycle: Ammonification
Decomposers return nitrogen to soil by converting compounds in dead organisms to ammonia.
28
New cards
Nitrogen Cycle: Denitrification
Denitrifying bacteria converts nitrates and nitrites to nitrogen gas, releasing it into the atmosphere.
29
New cards
How do animals receive nitrogen?
By feeding on plants that have nitrogen in their roots, they get their nitrogen. Then the food chain continues this process.
30
New cards
Haber-Bosch Process
Synthetic fertilisers where atmospheric nitrogen reacts with hydrogen, turning it to ammonia.
31
New cards
Effects of Nitrogen Fertiliser
Excessive nutrients in water, leading to excessive bacterial growth.
32
New cards
Human Impacts on the Nitrogen Cycle
Burning fossil fuels, nitrogen fertilisers, agriculture.
33
New cards
Eutrophication
Water become excessively enriched with minerals and nutrients.
34
New cards
Algae Blooms
Algae colonies that grow out of control, producing toxic or harmful effects on living organisms.
35
New cards
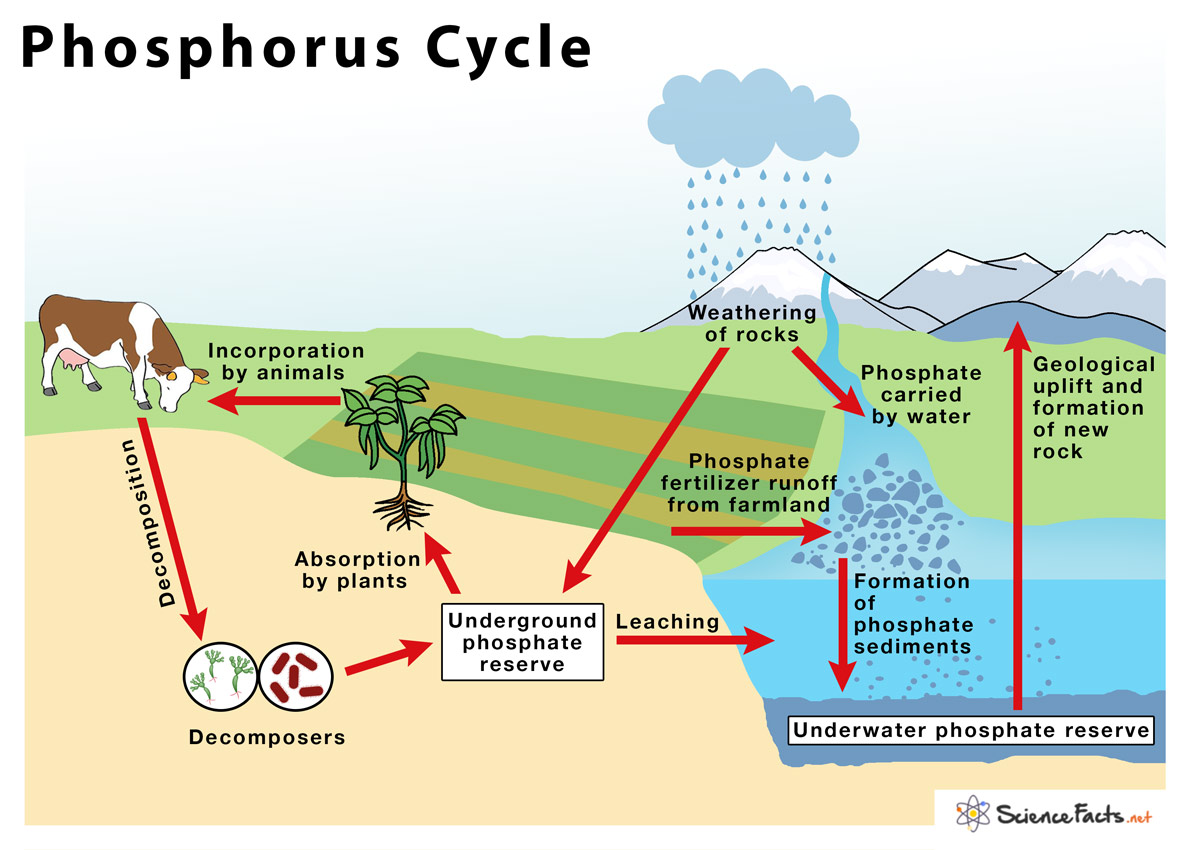
Phosphorus Cycle
The process of transformation and locations of phosphorus through the hydrosphere, lithosphere and biosphere.
36
New cards
Importance of the Phosphorus in the Biosphere
Required for ATP energy, nucleic acids, cell membranes, and bones.
37
New cards
What is Biogeochemical Cycle does not enter the Atmosphere?
Phosphorus cycle.
38
New cards
Phosphorus Cycle: Weathering
Rocks release phosphate ions and minerals.
39
New cards
Phosphorus Cycle: Assimilation
Plants take inorganic phosphate from soil for use.
40
New cards
Phosphorus Cycle: Decomposition
Dead organisms wastes decompose and organic phosphate is returned to the soil.
41
New cards
Phosphorus Cycle: Mineralisation
Organic forms of phosphate are given to plants via bacteria. This bacteria breaks down organic matter into inorganic phosphate.
42
New cards
Phosphorus Cycle: Sedimentation
Phosphorus can form rocks and end up in sediments.
43
New cards
Human Impact on the Phosphorus Cycle
Mining for phosphorus, relocating it. Altering the distribution of phosphorus.