biology: chemistry of life, elements of life
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
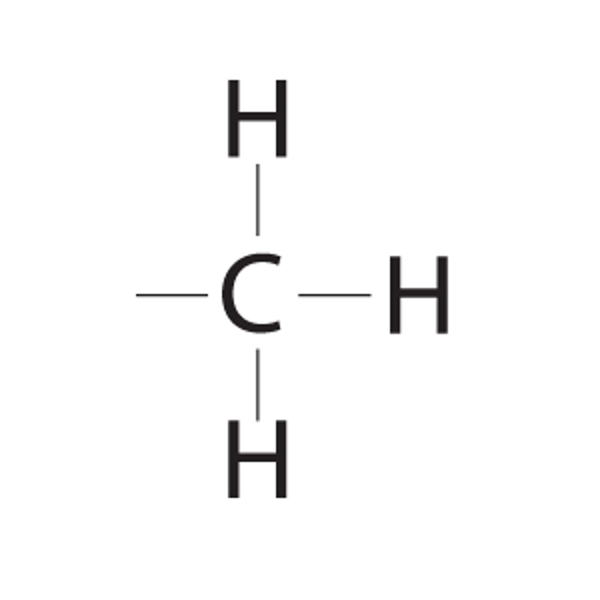
methyl group
-CH3
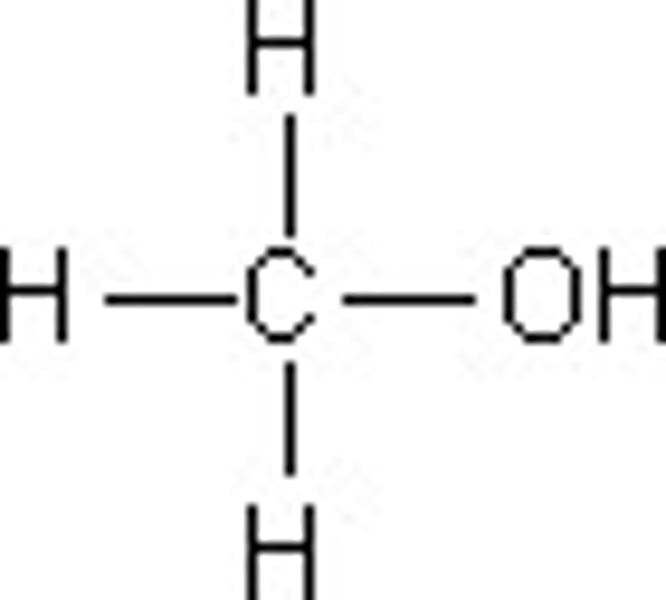
hydroxl group
-OH
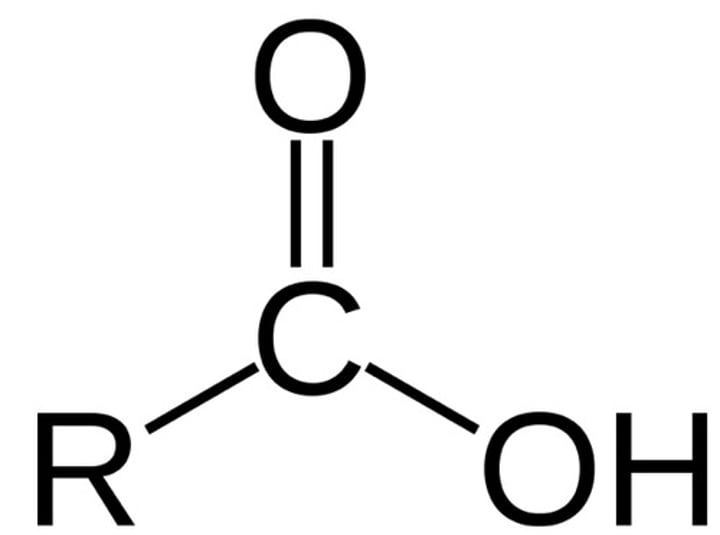
carboxyl group
-COOH
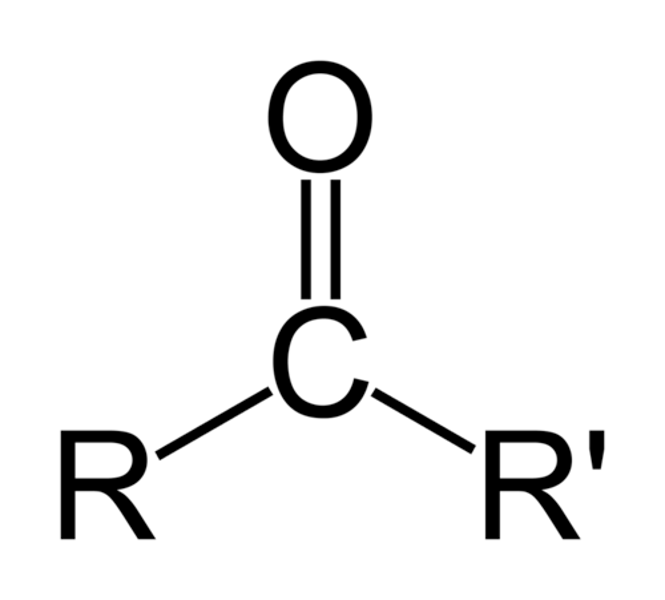
carbonyl group
-C=O
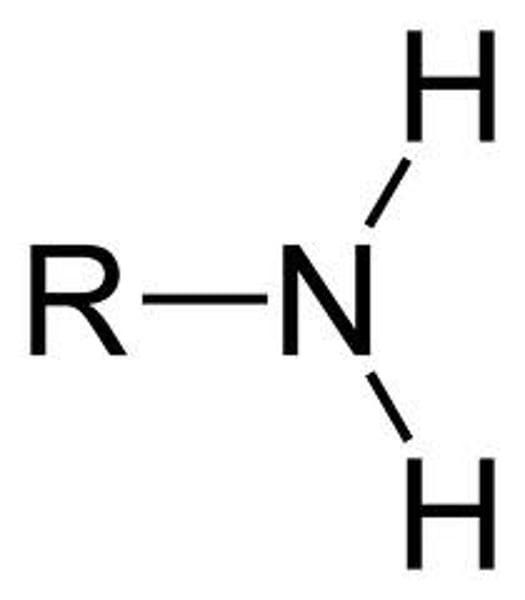
amino group
-NH2
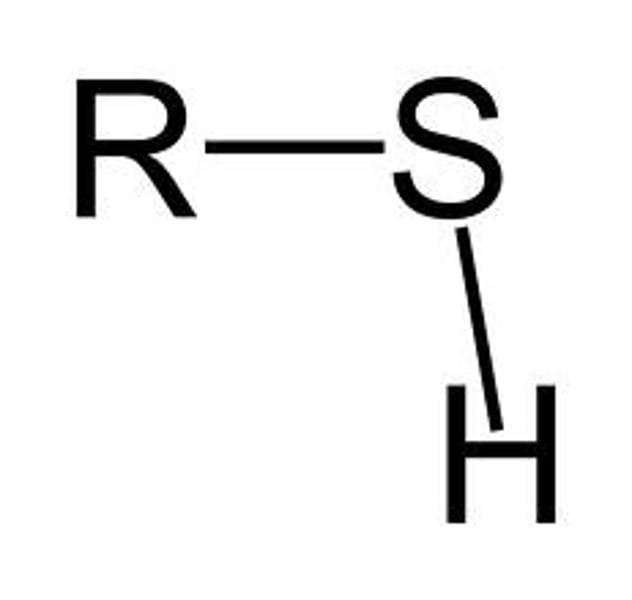
sulfhydryl group
-SH
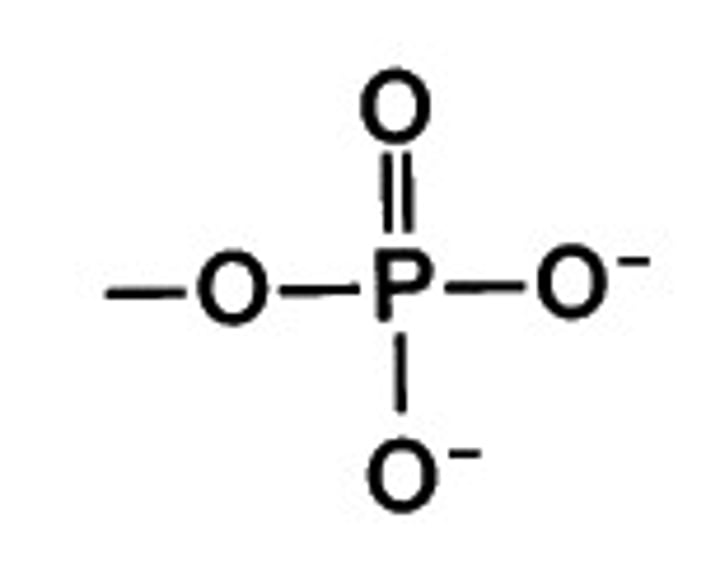
phosphate group
-OPO3 2-
organic compounds
containing carbon and hydrogen
hydrocarbons
contain only carbon and hydrogen
macromolecule
large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules
macromolecule classes
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
monomers
building blocks of polymers
polymers
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
dehydration synthesis/reaction
chemical reaction where two monomers are linked together with the loss of H20
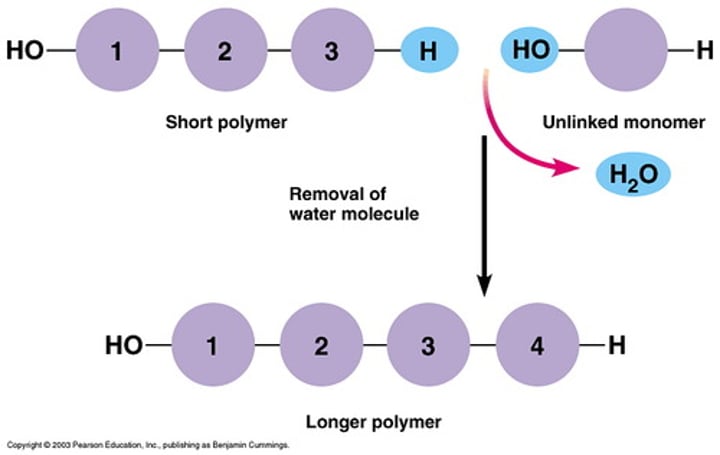
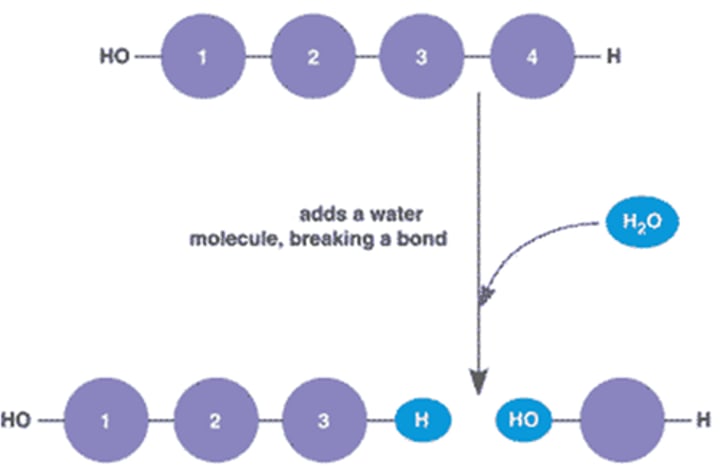
hydrolsis
chemical breakdown of compound due to adding H20
polarity
the property of having poles or being polar due to unequal sharing of electrons
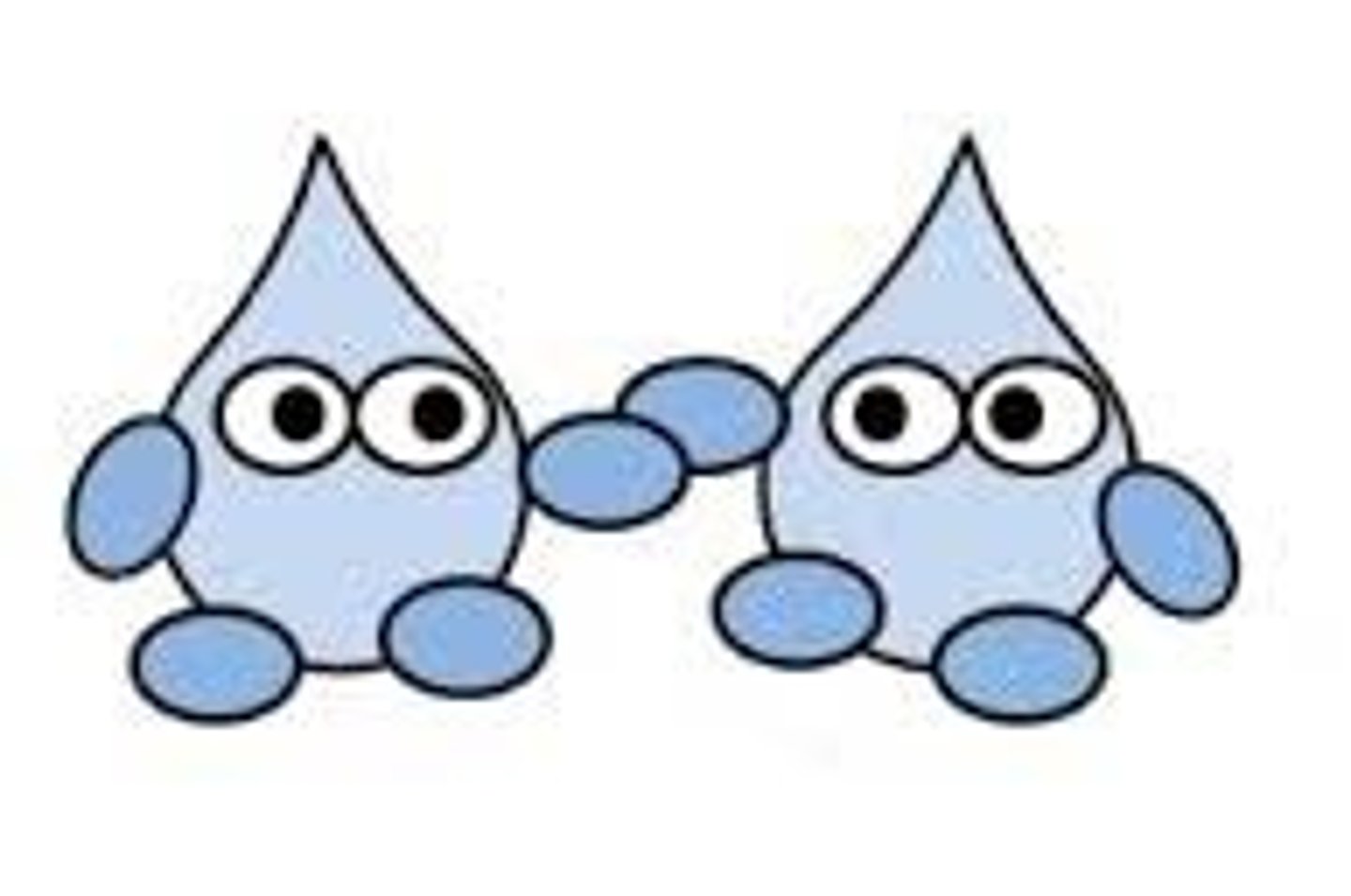
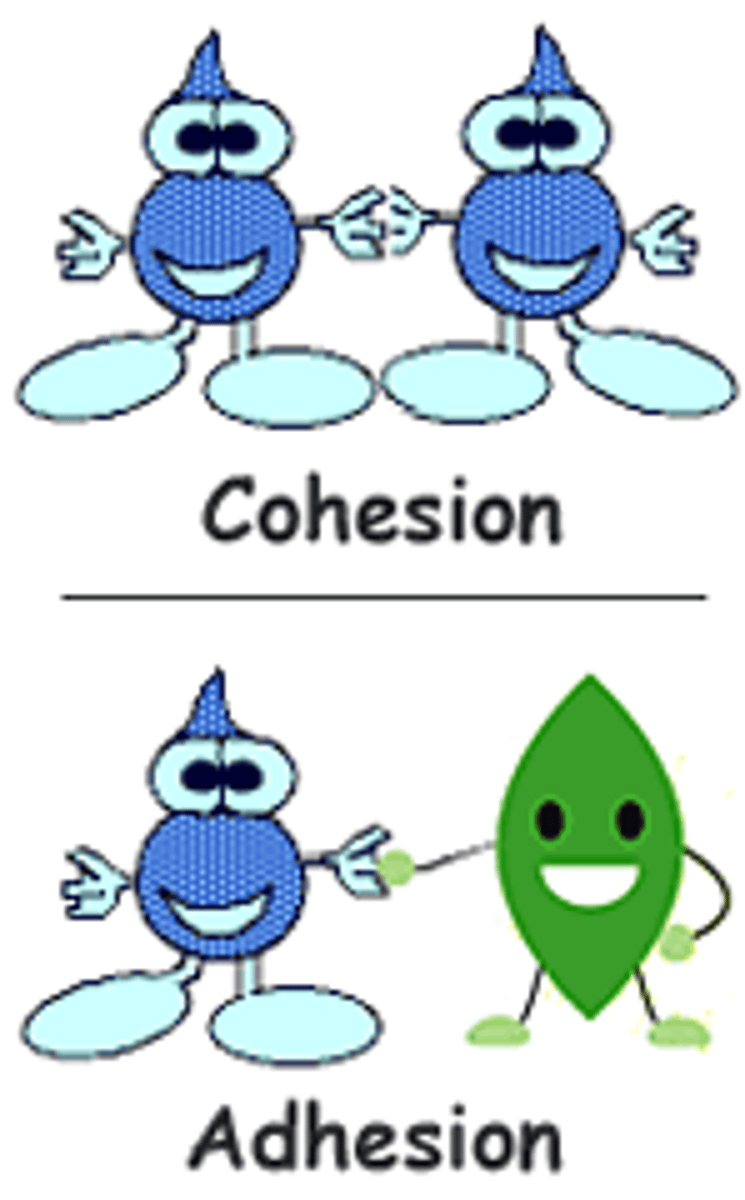
cohesion
attraction (covalent) between molecules of the same kind due to polarity
adhesion
attraction between molecules of different kinds due to polarity of H2O
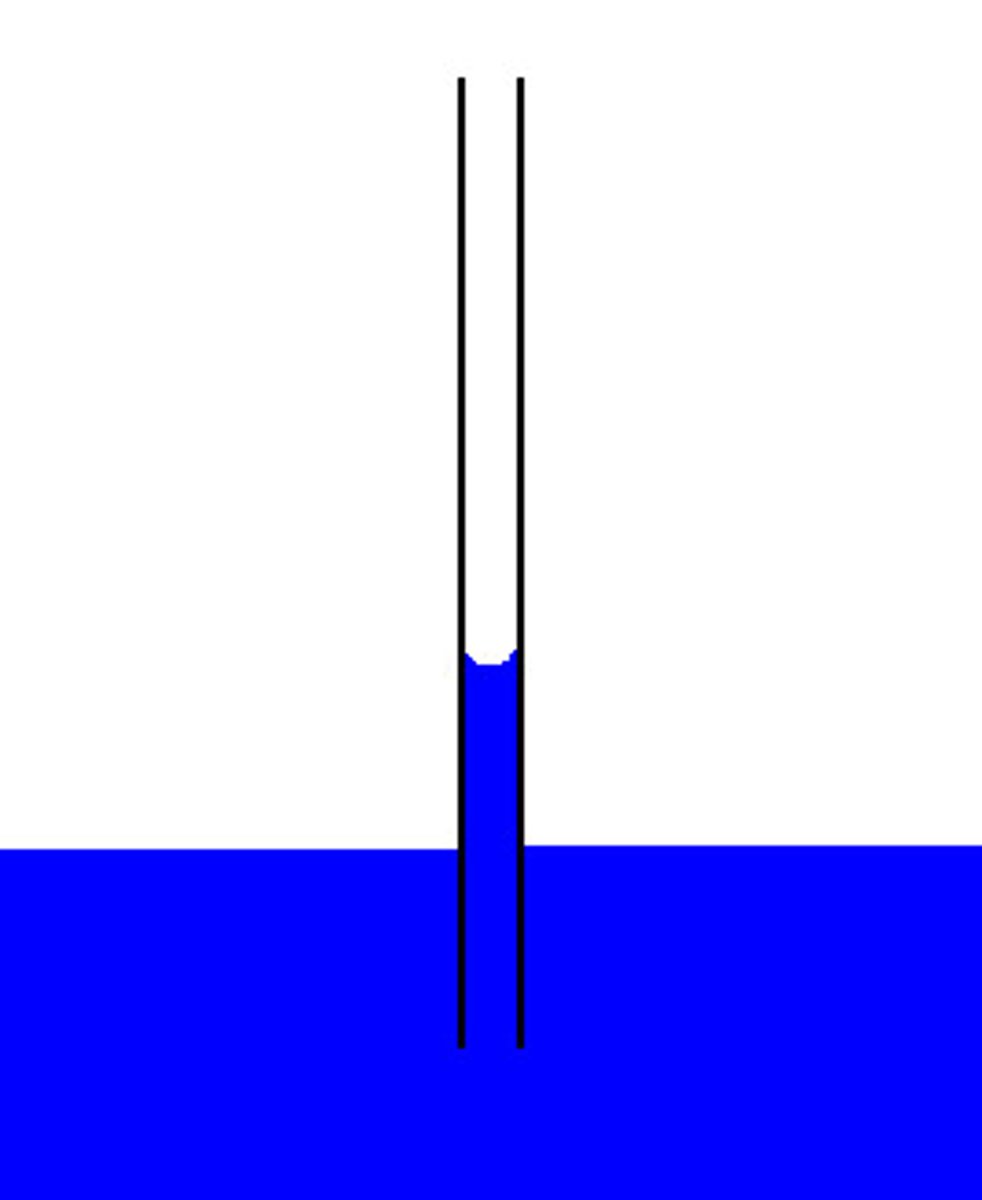
capillary action
tendency of water to rise in a thin tube, due to high adhesion and cohesion combined
temperature control
H2O having the ability to resist change in temperature due to hydrogen bonds
density
H2O molecules expand and become less dense (water), and looses ability to move
solvent
dissolving agent in solution
solution
mix of substances
solute
substance which is dissolved
universal solvent
H2O, due to polarity and ability to dissolve many different solutes
surface tension
the force of hydrogen bonds acting as a net for the surface of water