Recombinant DNA Techniques and Protein Biotechnology Methods
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
185 Terms
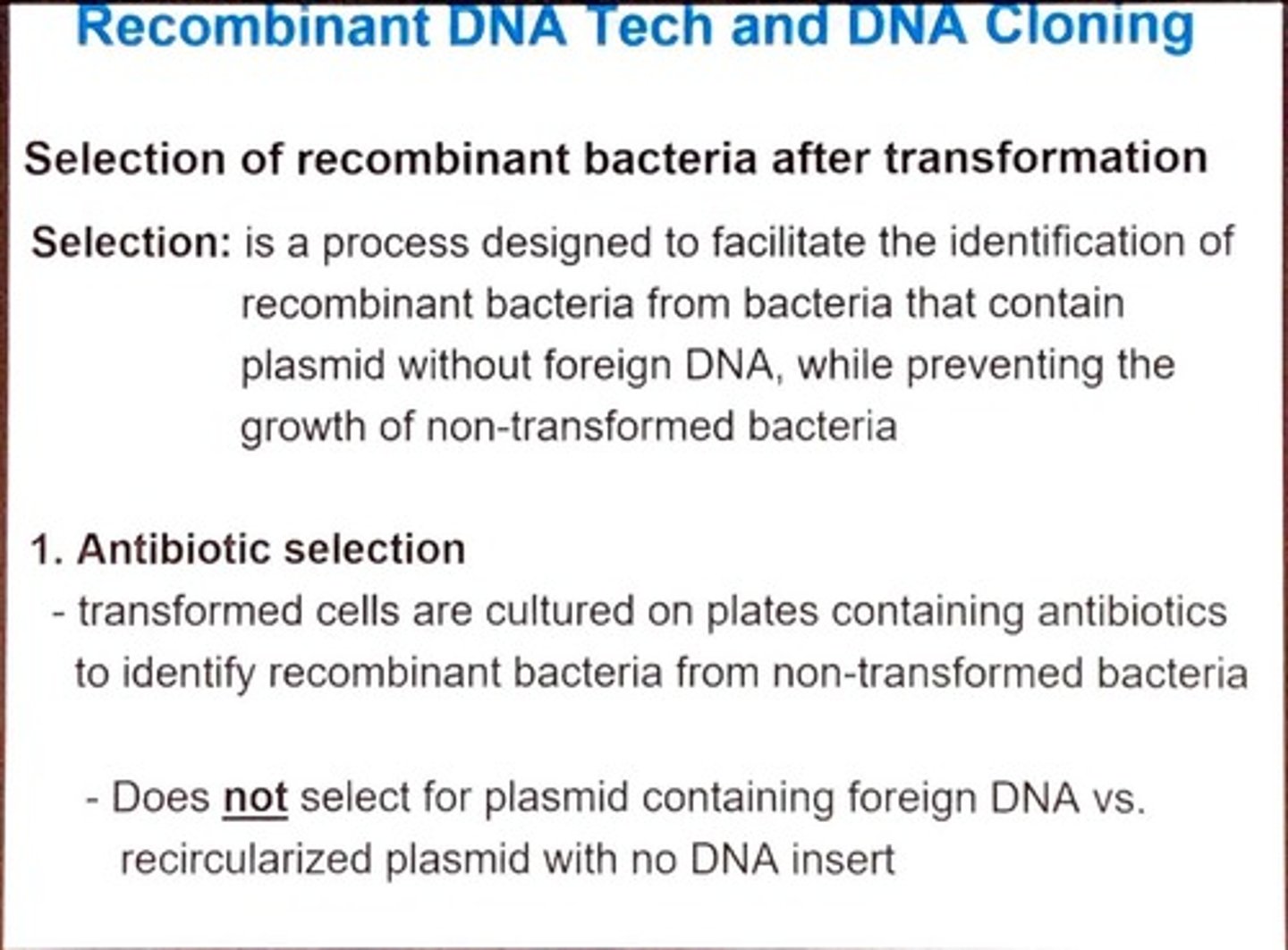
What is the purpose of selection in recombinant DNA technology?
To identify recombinant bacteria that contain plasmids with foreign DNA while preventing the growth of non-transformed bacteria.
How does antibiotic selection work in identifying recombinant bacteria?
Transformed cells are cultured on plates with antibiotics; only those with the plasmid survive.
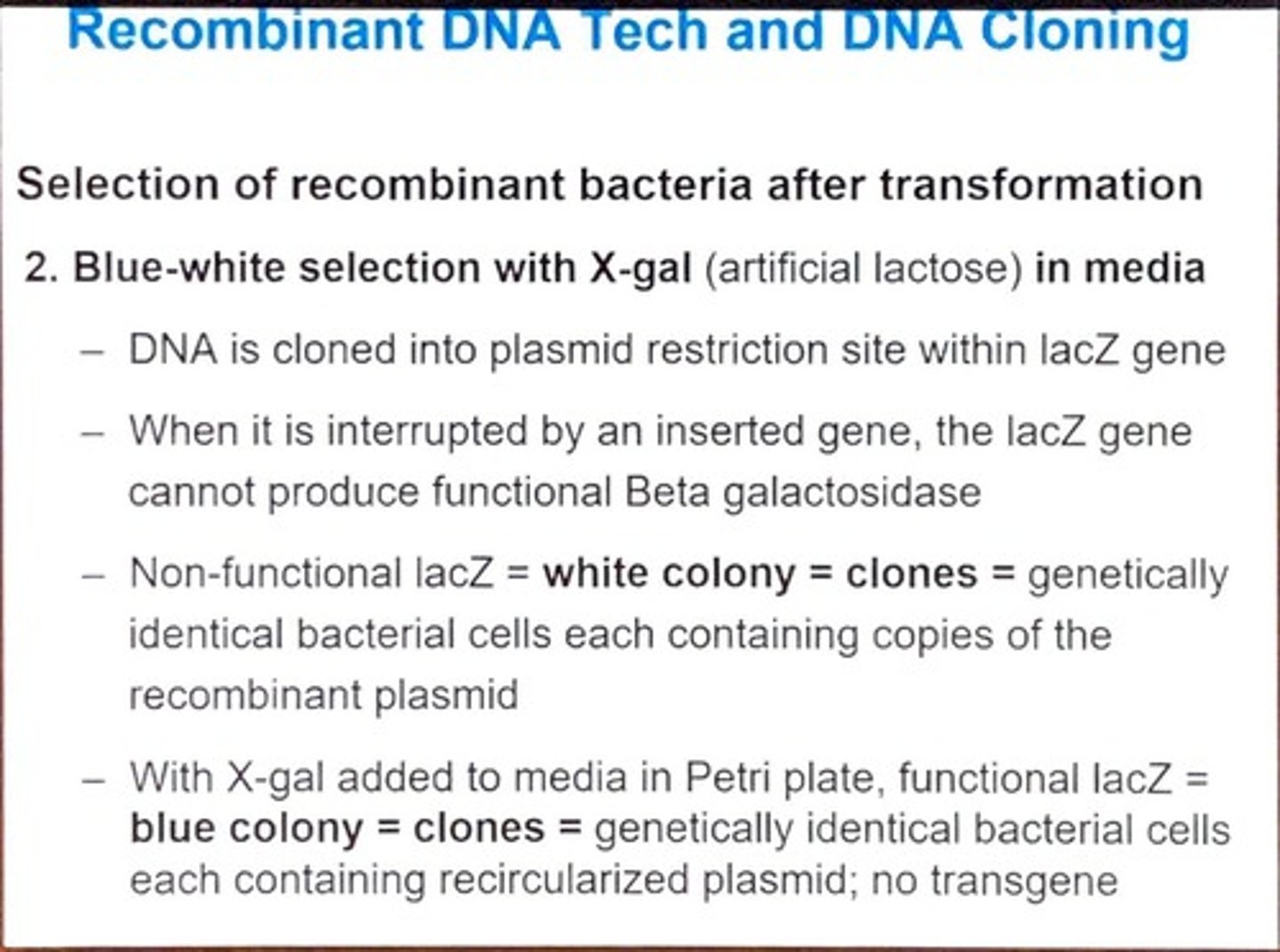
What is blue-white selection and how does it work?
It uses X-gal in media to differentiate between colonies; white colonies indicate successful insertion of a gene into the lacZ gene, while blue colonies indicate no insertion.
What is the first recombinant human protein marketed?
Insulin, introduced in 1982.
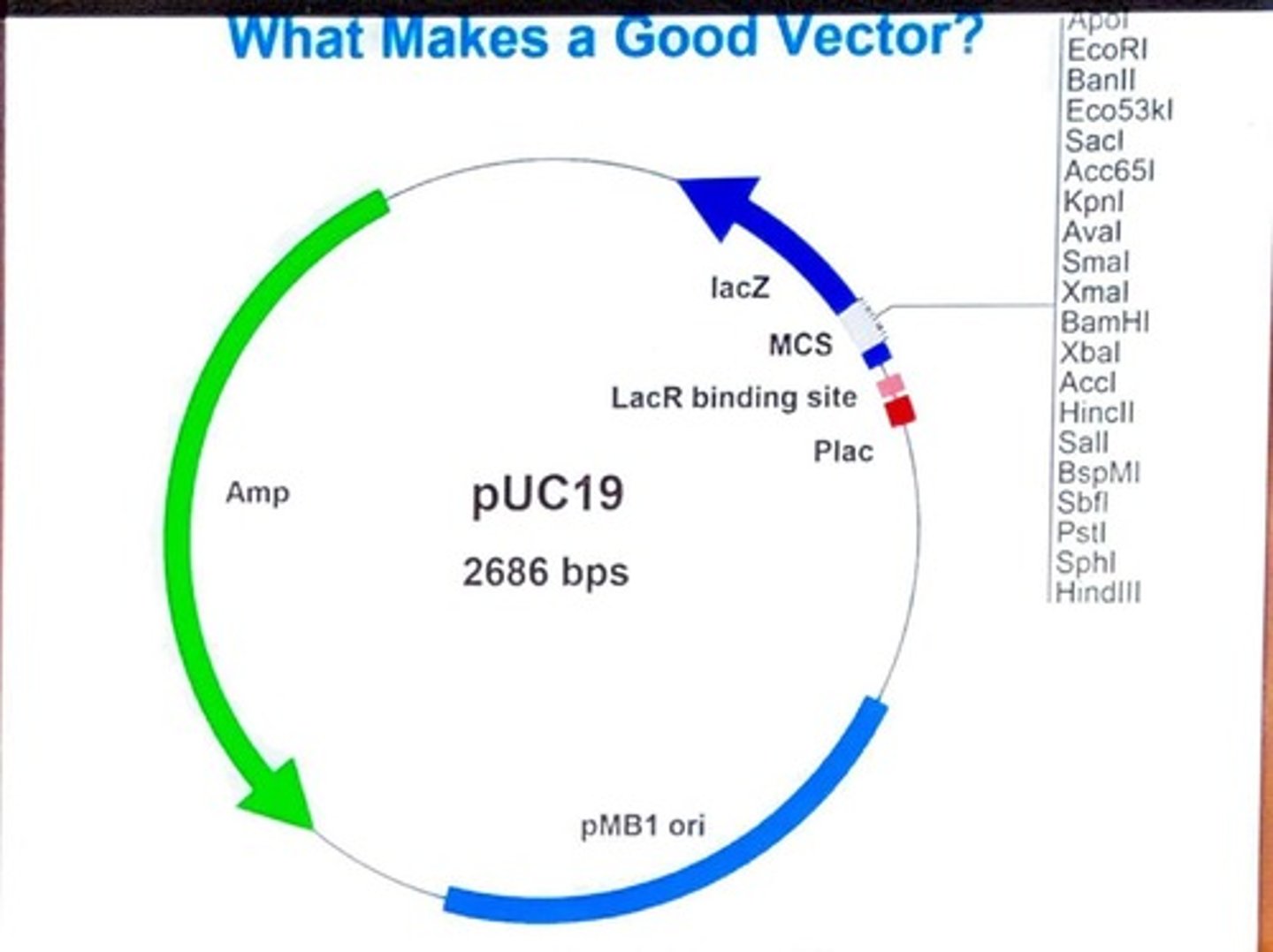
What are the practical features of a good plasmid vector?
Size, origin of replication, multiple cloning site (MCS), selectable marker genes, RNA polymerase promoter sequences, and DNA sequencing primers.
What is the role of the origin of replication (ori) in plasmids?
It allows plasmids to replicate independently from the host chromosome.
What are genomic DNA libraries?
Collections of cloned DNA fragments from an organism's chromosomal DNA, allowing for the isolation of genes of interest.
What is a disadvantage of genomic libraries?
They include introns along with exons, making it difficult to isolate coding sequences.

What is a cDNA library?
A collection of cloned DNA fragments synthesized from mRNA, representing actively expressed genes.

What is an advantage of cDNA libraries over genomic libraries?
cDNA libraries do not contain introns and represent only actively expressed genes.
What is the process of creating a cDNA library?
mRNA is extracted, reverse transcribed to cDNA, and then cloned into plasmids for transformation into bacteria.
What prevents restriction enzymes from digesting a bacterium's own genome?
Methylated DNA protects the bacterial genome from being cut by its own restriction enzymes.
What is the significance of the lacZ gene in blue-white selection?
When interrupted by an inserted gene, it cannot produce functional beta-galactosidase, leading to white colonies.
What is the role of DNA ligase in recombinant DNA technology?
It covalently bonds DNA fragments together, such as inserting a gene of interest into a plasmid.
What is the purpose of selectable marker genes in plasmid vectors?
They allow for the identification of transformed colonies that have successfully taken up the plasmid.
What is the function of the multiple cloning site (MCS) in a plasmid?
It contains recognition sites for several restriction enzymes where DNA inserts can be cloned.
What is the significance of the first recombinant human growth hormone?
It was marketed in 1985 and was a significant advancement in recombinant DNA technology.
Why is it challenging to create a cDNA library from certain tissues?
If the tissue does not have a high abundance of mRNA for the gene of interest, it can be difficult to isolate enough material.
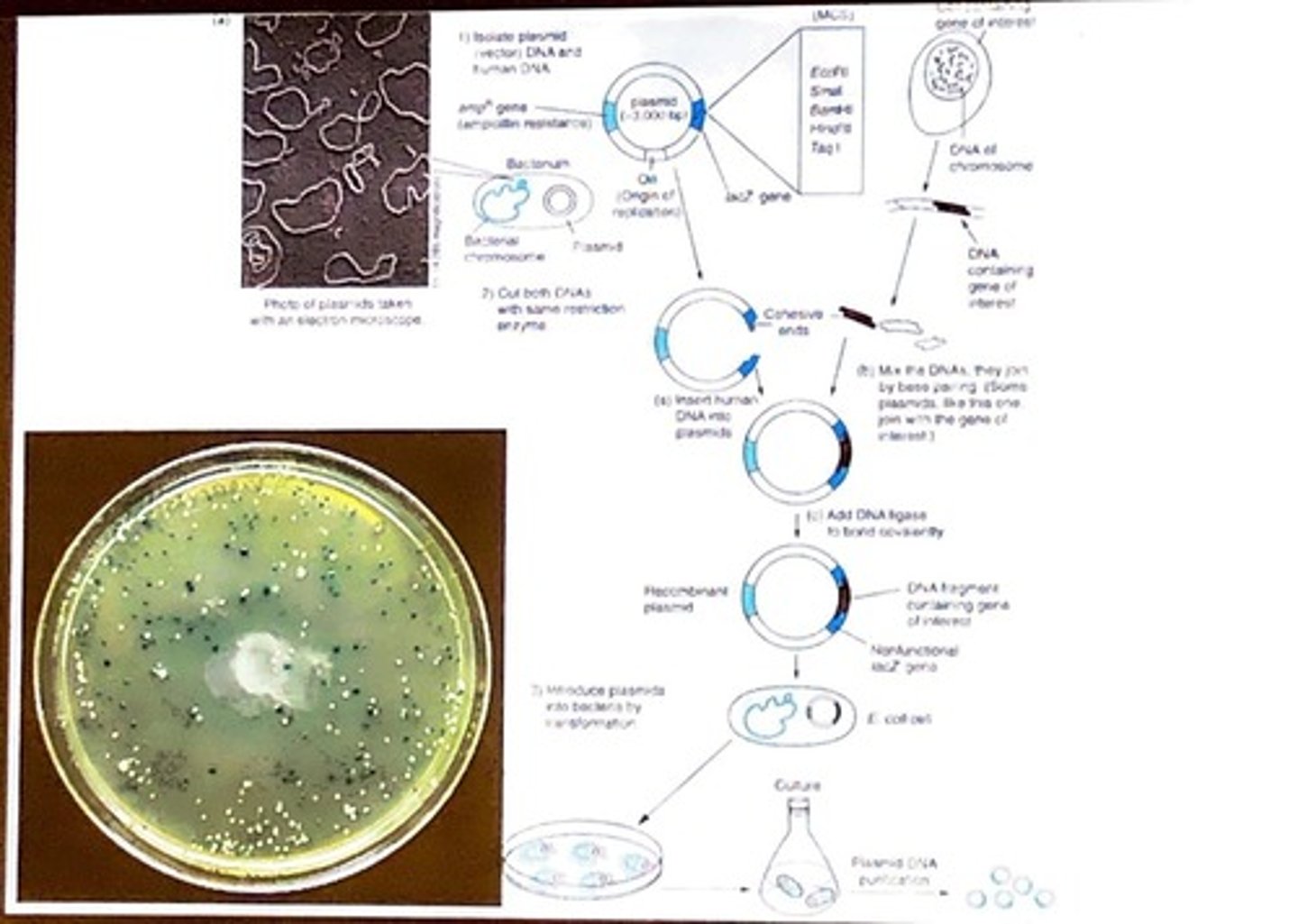
What is the purpose of using restriction enzymes in cloning?
They cut DNA at specific sequences, allowing for the insertion of foreign DNA into plasmids.
What are the two types of DNA libraries?
Genomic DNA libraries and complementary DNA (cDNA) libraries.

What does the term 'transformation' refer to in recombinant DNA technology?
The process of introducing plasmids into bacterial cells.
What is a common method for screening DNA libraries?
Using probes to identify specific genes of interest among the cloned fragments.
What is the role of cohesive ends in DNA cloning?
They allow for the joining of DNA fragments through base pairing after being cut by the same restriction enzyme.
What is the significance of using short linker DNA sequences in cDNA library creation?
They provide restriction enzyme recognition sites for cloning into plasmids.
What is the function of RNA polymerase promoter sequences in plasmid vectors?
They facilitate transcription of the inserted gene in vitro and in vivo.
What is the purpose of screening a DNA library?
To isolate and identify specific genes of interest from a collection of cloned DNA fragments.
What are plasmids used for in gene cloning?
Plasmids are introduced into bacteria to carry recombinant DNA.
What is the purpose of colony hybridization?
To identify the gene of interest by screening bacteria with recombinant DNA.

What is the role of the nylon or nitrocellulose filter in colony hybridization?
It captures denatured DNA from lysed bacterial cells for further analysis.
How is the DNA denatured during colony hybridization?
By treating the filter with an alkaline solution or UV exposure.
What is hybridization in the context of colony hybridization?
The binding of a probe to complementary sequences on the filter.
What is the purpose of washing the filter after hybridization?
To remove excess unbound probe before detection.
What is the significance of using a probe tagged with a radioactive nucleotide or fluorescent dye?
It allows for the detection of the hybridized DNA on the filter.
What is the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
A technique for amplifying specific DNA sequences rapidly.
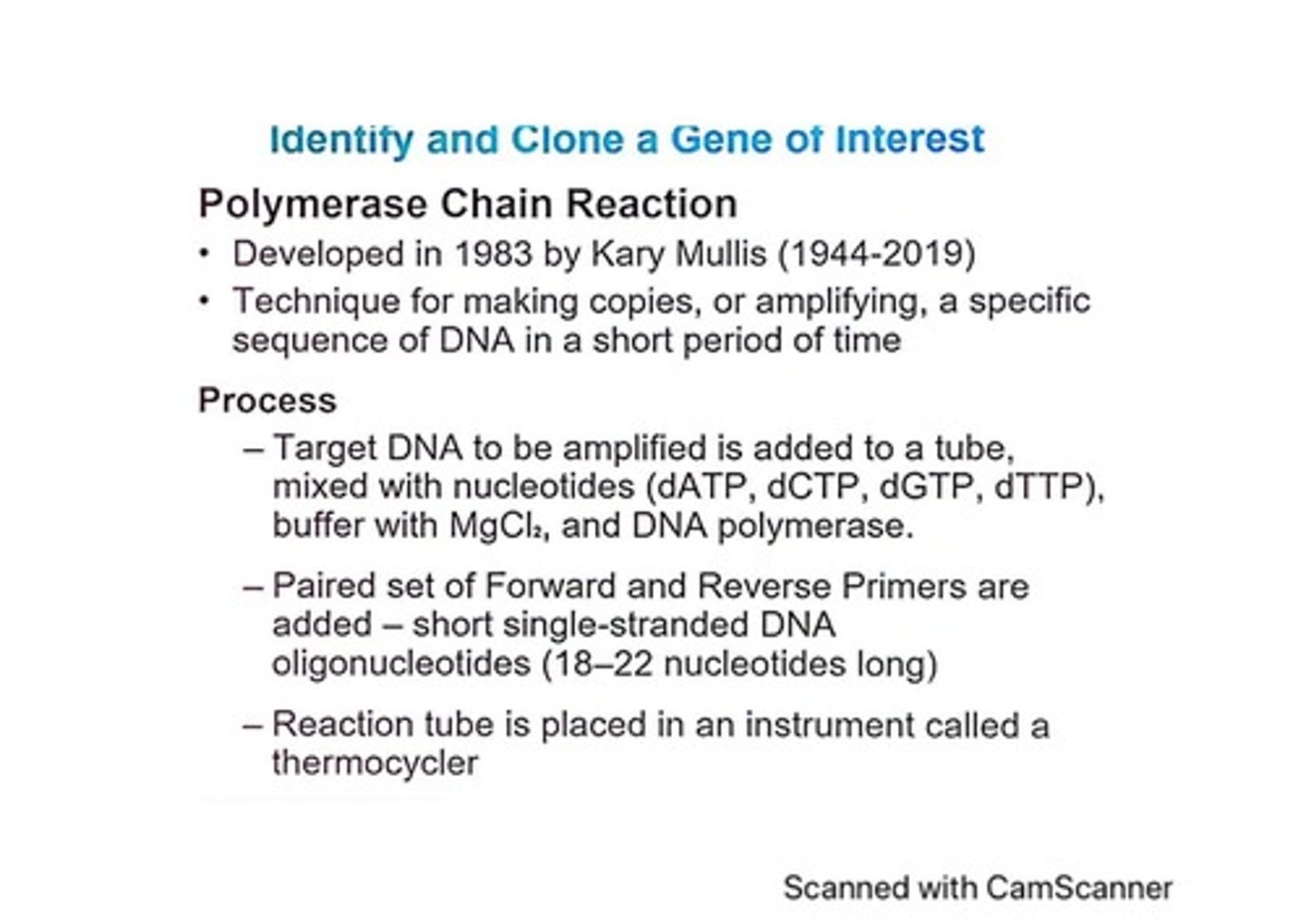
Who developed the PCR technique and when?
Kary Mullis in 1983.
What are the main components added to the PCR reaction tube?
Target DNA, nucleotides, buffer with MgCl2, and DNA polymerase.
What are primers in PCR?
Short single-stranded DNA oligonucleotides that initiate DNA synthesis.
What are the three stages of a PCR cycle?
Denaturation, annealing, and extension.
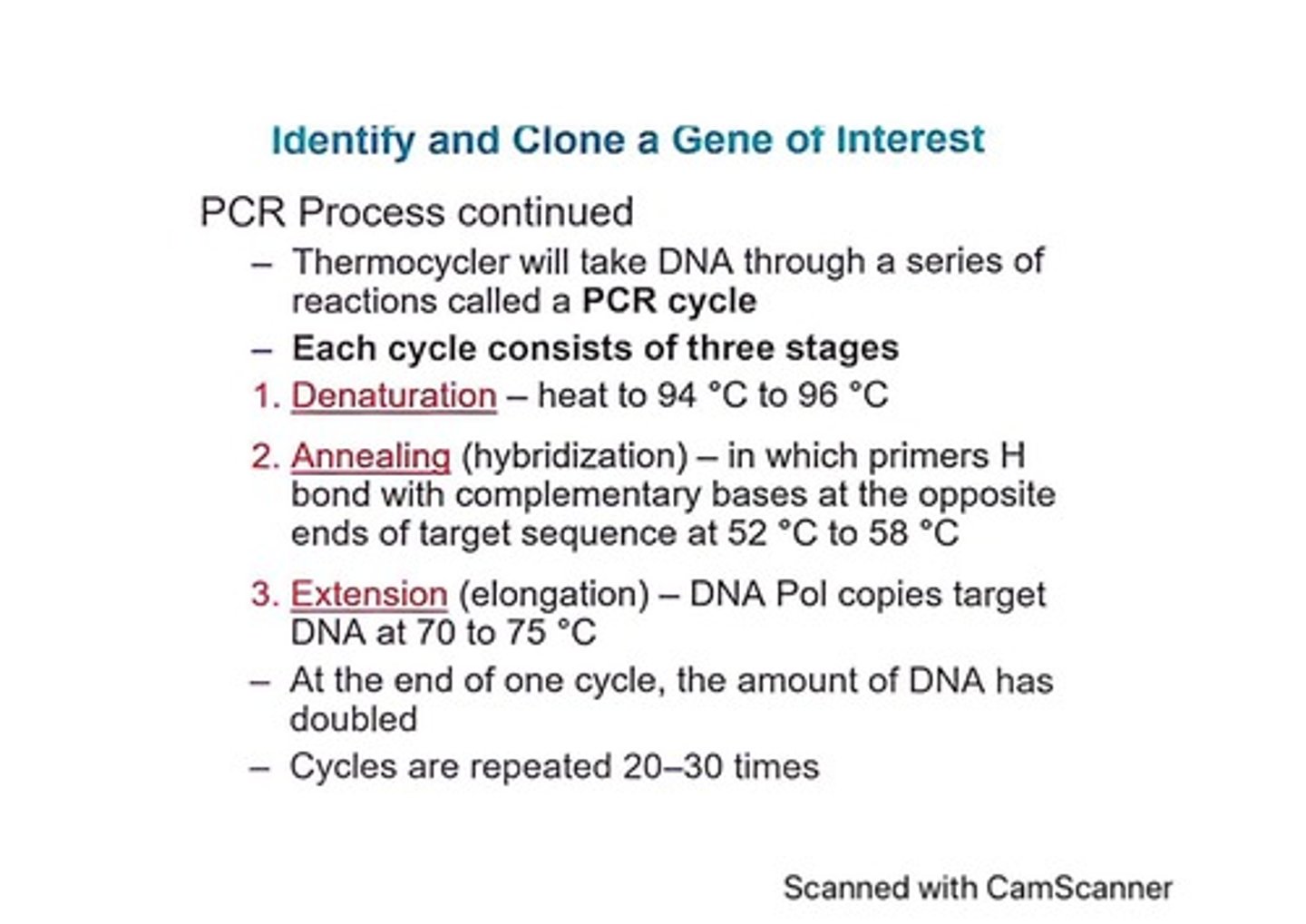
At what temperature does denaturation occur in PCR?
94 °C to 96 °C.
What happens during the annealing stage of PCR?
Primers bind to complementary bases on the target DNA.
What is the extension stage in PCR?
DNA polymerase copies the target DNA at 70 to 75 °C.
How many copies of DNA are produced after 22 PCR cycles starting from one molecule?
4,194,304 copies.
What is Taq DNA polymerase and why is it used in PCR?
It is a heat-stable enzyme from Thermus aquaticus, suitable for high-temperature PCR cycles.
What is a disadvantage of PCR?
It requires prior knowledge of the DNA sequence to design primers.
What is the Sanger method of DNA sequencing?
A chain termination method that uses dideoxynucleotides to terminate DNA strand elongation.
What components are required for the Sanger sequencing reaction?
Single primer, all four dNTPs, DNA polymerase, and one ddNTP.
How are the fragments generated in Sanger sequencing analyzed?
They are separated on a polyacrylamide gel and visualized using autoradiography.
What is the significance of reading the gel from bottom to top in Sanger sequencing?
It allows for determining the sequence of nucleotides in the cloned gene.
What is the typical length of DNA sequences generated per Sanger sequencing reaction?
200-400 nucleotides.
What is the role of ddNTPs in Sanger sequencing?
They terminate DNA synthesis, creating fragments of varying lengths for analysis.
What is the advantage of using PCR in gene cloning?
It allows for rapid amplification of DNA from small starting amounts.
What is a T vector in cloning?
A vector with single-stranded thymine nucleotides that can base pair with adenine ends of PCR products.
What method does high throughput computer automated sequencing use?
The Sanger method using capillary electrophoresis.
How many nucleotides can be sequenced per reaction using the Sanger method?
Greater than 600 nucleotides.
What was the significance of the Sanger method in genetics?
It was very helpful for completing the Human Genome Project.
What is the advantage of using only 1 reaction tube in Sanger sequencing?
It simplifies the procedure compared to using 4 reaction tubes.
What are ddNTPs and how are they used in sequencing?
Dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs) are labeled with different fluorescent dyes to terminate DNA strand elongation during sequencing.
How are DNA samples separated in capillary electrophoresis?
Samples are separated on a single-lane capillary gel scanned with a laser beam.
What does the laser do in the Sanger sequencing process?
It stimulates the fluorescent dye on each DNA fragment, which emits light at different wavelengths for each ddNTP.
What is an electropherogram?
A graphical representation of the emitted light patterns that reveals the nucleotide sequence.
What is the role of the computer in the Sanger sequencing process?
The computer analyzes the light patterns and converts them into the nucleotide sequence.
What is the purpose of cycle sequencing with Big Dye Terminator?
To incorporate fluorescently labeled ddNTPs into the DNA sequence during PCR amplification.
What is the function of polymerase in DNA sequencing?
Polymerase integrates nucleotides into a growing DNA strand during replication.
What technology does the Ion Torrent PGM utilize?
It utilizes the release of H+ ions on a semiconductor chip for sequencing.
What is the significance of the Oxford Nanopore Technologies in sequencing?
It allows for single molecule reads of over 10 kb with an approximate error rate of 5%.
What is Southern blotting used for?
To determine gene copy number, gene mapping, gene mutation detection, and PCR product confirmation.
Who developed the Southern blotting technique?
Ed Southern in 1975.
What is the first step in the Southern blotting process?
Digesting chromosomal DNA into small fragments with restriction enzymes.
How are DNA fragments prepared for Southern blotting?
Fragments are separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and then transferred onto a nylon or nitrocellulose membrane.
What is the purpose of treating the gel with an alkaline solution in Southern blotting?
To denature the DNA fragments for transfer to the membrane.
What is the purpose of a filter (blot) in molecular biology?
To permanently attach DNA by baking or exposing it to UV light.
How is the number of gene copies represented in blotting techniques?
The number of bands on film represents the gene copy number.
What is the first step in Southern blotting?
Restriction fragment preparation using enzymes like BamHI and EcoRI.
What does Northern blotting analyze?
mRNA produced by a tissue, similar to Southern blotting but for RNA.
What is the main difference between Southern and Northern blotting?
Southern blotting analyzes DNA, while Northern blotting analyzes RNA.
What is the purpose of reverse transcription PCR?
To study mRNA levels when detection levels are below that of Northern blotting.
What is the process of reverse transcription PCR?
Isolate mRNA, use reverse transcriptase to create cDNA, and amplify it using PCR.
What does real-time or quantitative PCR (qPCR) measure?
It quantifies PCR amplification reactions in real time using fluorescent dyes.
What are Taqman probes used for in qPCR?
They are complementary to specific regions of target cDNA and emit fluorescent light when cleaved.
What is the role of SYBR Green in qPCR?
It binds to double-stranded DNA and emits fluorescent light as more DNA is copied.
What is fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) used for?
To identify the chromosome location of a gene and its copy number.
How does the FISH technique work?
Chromosomes are isolated, hybridized with a fluorescent probe, and illuminated to indicate binding.
What does fluorescence on more than one chromosome indicate in FISH?
It may indicate the presence of genetic disorders or multiple gene expressions.
What is a challenge in biotechnology related to proteins?
Understanding and controlling protein folding during the manufacturing process.
What can incorrectly folded proteins lead to?
Diseases such as Alzheimer's, cystic fibrosis, and certain cancers.
What are the two regular second structures of proteins described by Pauling and Corey?
Alpha helices and beta sheets.
What happens if a protein is folded incorrectly?
The desired function of the protein is lost, potentially leading to detrimental effects.
What is the significance of the number of bands in a Southern blot?
It indicates the presence and quantity of specific DNA sequences.
What is the role of agarose gel in blotting techniques?
To separate DNA or RNA fragments based on size during electrophoresis.
What is the purpose of hybridization in blotting techniques?
To allow labeled probes to bind to complementary DNA or RNA sequences.
What imaging techniques can be used to detect probe binding?
Autoradiography, chemiluminescence, or other imaging methods.
What is the significance of the threshold cycle in qPCR?
It indicates the cycle number at which the fluorescence exceeds the background level, correlating with gene expression.
What is the function of a DNA marker in gel electrophoresis?
To provide a reference for the sizes of the DNA fragments being analyzed.
What is the purpose of using a labeled probe in blotting?
To visualize the presence of specific DNA or RNA sequences after hybridization.
What is the role of NaOH in the Southern blotting process?
To denature DNA in the gel before blotting.
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The sequence in which amino acids are linked together.
What characterizes the secondary structure of proteins?
It occurs when chains of amino acids fold or twist at specific points, forming shapes due to hydrogen bonds.
What are the two most common shapes in secondary protein structure?
Alpha helix and beta sheet.
Describe the alpha helix structure.
A right-handed spiral formed by hydrogen bonds linking an amino acid's nitrogen atom to the oxygen atom of another amino acid.
What is a beta sheet?
A structure formed by hydrogen bonds linking nitrogen and oxygen atoms, resulting in parallel or anti-parallel chains.