CH6 Skeletal System Anatomy & Phyisology
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
describe osteoporosis
- bone resorption exceeds deposit
- bone mass declines
- matrix remains normal
- common in POSTMENOPAUSAL WOMEN
- porous & thin
what are the risk factors of osteoporosis?
- petite body form
- insufficient exercise
- diet poor in CALCIUM and PROTEIN
- smoking
- immobility
- hormone-related conditions
what are the known preventions of osteoporosis?
- calcium
- vitamin d supplements
- weight bearing exercises
describe paget's disease
- excessive and haphazard bone deposit and resorption cause bone to be made fast and poorly
- high ratio of spongy to compact bone
- reduced mineralization
describe osteomalacia
- bones are POORLY MINERALIZED
- results in soft & weak bones
- pain upon bearing weight
place the four major stages of healing a fracture
- (1) Hematoma formation
- (2) Fibrocartilaginous callus formation
- (3) Bony callus formation
- (4) Bone remodeling
what is hematoma formation?
blood clotting
what is fibrocartilaginous callus formation?
- repair tissue
- fibroblasts cartilage, & osteogenic cells begin reconstruction of bone
what is bony callus formation?
new trabeculae
describe the classification of fractures
- position of bone ends after fracture: Nondisplaced & displaced
- Completeness of break: Complete & Incomplete
- Whether skin is penetrated: Compound & Closed
what are the position of bone ends after fracture?
- nondisplaced: ends that retain normal position
- displaced: ends are out of normal alignment
what are the completeness of break fractures?
- complete: broken all the way through
- incomplete: not broken all the way through
what is "whether skin is penetrated" fractures?
- compound (open): skin is penetrated
- simple (closed): skin is not penetrated
what is the epihyseal plate?
- growth plate in children
- growth occurs in diaphysis (long bone)
- not fused
thin layer of cartilage that lies between the epiphysis and metaphysis
what is the epiphyseal line?
- diaphysis & epiphysis fuse
- no growth
- ossified (stopped growing / OLD)
FUSION
examples of long bone? be able to identify it
- longer than they are wide
- limb bones
- have expanded ends
humerus, femur
examples of short bone? be able to identify
- cube-shaped bones
- vary in size and number
carpals, tarsals
examples of flat bone? be able to identify it
- thin
- flat
- slightly curved
sternum, scapula, ribs, skull bones
examples of irregular bone? be able to identify it
- complicated shapes
vertebrae, hip bones
examples of sesamoid bone? be able to identify it
- within tendons
patella
identify the parts of a long bone
- epiphysis: ends of long bone
- diaphysis: shaft of long bone
- articular cartilage (covers joint surfaces)
- compact & spongy bone
- epiphyseal line
- periosteum
- endosteum
- medullary cavity
what is hyaline cartilage?
- provides support
- flexibility
- resilience
- most abundant
- contains collagen fibers
what is elastic cartilage?
- similar to hyaline cartilage
- contains elastic fibers
where can you find elastic cartilage?
- external ear
- epiglottis
what is fibrocartilage?
- thick collagen fibers
- has great tensile strength
where can you find fibrocartilage?
- menisci of knee
- vertebral discs
what is red marrow?
- found within trabecular cavities (spongy bone) & diploe of flat bones
what is yellow marrow?
- MADE MOSTLY OF FAT
- can be converted to red if person is anemic
what is osteoblasts?
- BUILDING
- bone forming cells that secrete osteoids
what is osteoids?
- unmineralized bone matrix
- made up of collagen and calcium-binding proteins
what is osteogenic cells?
- AKA osteoprogenitor cells
- mitotically active (stem cells in periosteum & endosteum)
- DIFFERENTIATE INTO OSTEOBLAST
what is osteocytes?
- mature bone cells in lacunae that no longer divide
- maintain bone matrix
- acts as stress or strain sensors
what is bone lining cells?
- help maintain bone matrix
- flat cells on bone surfaces
place the steps involved with endochondral ossification
- (1) bone collar forms around the diaphysis of the hyaline cartilage
- (2) central cartilage of diaphysis calcifies and develops cavities
- (3) periosteal bud invades internal cavities, leads to formation of spongy bone
- (4) diaphysis elongates, medullary cavity forms
- (5) epiphyses ossify
what is primary ossification centers lead to?
- DIAPHYSIS
- first area of bone to start ossifying
- blood vessels infiltrate perichondrium, converting to periosteum
- mesenchymal cells specialize into osteoblasts
what is secondary ossification centers lead to?
- EPIPHYSIS
- develops in the epiphyseal region after birth
what is closed reduction?
physician manipulates bone to correct position
what is open reduction?
- surgical pins or wires secure ends
think of opening patient
where is hyaline cartilage found?
- articular (joints)
- costal (ribs)
- respiratory (larynx)
- nasal cartilage (nose tip)
what is osteoclasts?
- CRUSH (think clasts = crush)
- responsible for bone resorption
- break down
what does endochondral ossification form replaces what?
hyaline cartilage
what does intramembranous ossification replaces what?
fibrous membrane
what bone form from endochondral ossification?
all bones INFERIOR to the skull except clavicle bones
(below skull)
what bone form from intramembranous ossification?
- skull bones & clavicle
- frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, clavicle
steps of the endochondral ossification?steps of the endochondral ossification?
(1) Bone collar forms around diaphysis of cartilage
(2) Central cartilage in diaphysis calcifies and develops cavities
(3) Periosteal bud invades cavities, leading to formation of spongy bone
(4) Diaphysis elongates, and medullary cavity forms
(5) Epiphyses ossify
steps of the intramembranous ossification?
(1) Ossification centers are formed when mesenchymal cells cluster and become osteoblasts
(2) Osteoid is secreted, then calcified
(3) Woven bone is formed when osteoid is laid down around blood vessels, resulting in trabeculae
(4) Lamellar bone replaces woven bone, and red marrow appears
what is growth hormone?
stimulates epiphyseal plate activity (infancy & childhood)
what is thyroid hormone?
modulates activity of growth hormone
(ensures proper proportions)
what is testosterone and estrogen hormone?
puberty - promotes growth spurts
what is diploe?
thin plates of SPONGY bone
in FLAT, SHORT, or IRREGULAR BONES
what are the functions of the bones?
- support
- protection
- movement
- mineral & growth factor storage
- triglycerides (fat) storage
- blood cells formation/production
- hormone production (insulin)
what is an osteon?
- structural unit of compact bone
- tiny weight bearing pillars
what are sherpey's fibers?
- dense irregular CT
- consists of bundles of strong collagenous fibers
- secures the bone matrix
what is sharpey's fibers connection to the periosteum?
CONNECT PERIOSTEUM TO BONE MATRIX
what is periosteum?
- white
- double-layered membrane
- covers external surfaces except joints
What are Volkmann's canals?
connect blood vessels and nerves of periosteum, medullary cavity, and central canal
- CANALS WITH VEINS AND ARTERIES
LEARN EVERYTHING ON THE DIAGRAM!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
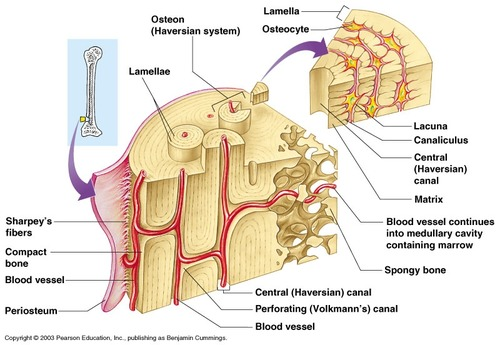
What is in the Haversian canal?
- runs through core of OSTEON
- contains BLOOD VESSELS and NERVE FIBERS
- LAMALLAE (contains collagen fibers)
what is responsible for its high tensile strength and flexibility of the bone?
collagen fibers
What is responsible for its resilience of the bone?
Sacrificial Bonds
What is responsible for the hardness and allows bone to resistance to compression?
Hydroxyapatites
What is appositional growth?
makes cartilage growth increase in width
What is interstitial growth?
makes cartilage growth increase in density and length
what is the effect on calcitonin in humans?
lower calcium levels in your blood
What makes up a spongy bone?- made up of trabeculae
- made up of trabeculae
- open spaces BETWEEN trabeculae are filled with red/yellow marrow
what is trabeculae?
a honeycomb of small, needle like or flat pieces of bone
what is osteogenesis?
- process of bone tissue formation
- AKA ossification
what is wolf's law?
- bones grow or remodel in response to demands placed on them
what is comminuted fracture?
- bone fragments into 3 or more pieces
- common in older age whose bones are more brittle
think COMMUNITY OF BONES FRAGMENT
what is spiral fracture?
- excessive TWISTING FORCES are applied to bone
- cracks in oblique way
what is greenstick fracture?
- bone breaks incompletely (not all the way)
- one side of shaft breaks while other bends
- common in children (bcuz of more organic matrix)
what is compound fracture?
- skin is penetrated
- bone breaks through skin
what is simple fracture?
- skin is NOT penetrated
- bone breaks but still within the insides of skin
what is nondisplaced fracture?
- bone remains aligned
- still in regular position
- ends retain normal position
what is displaced fracture?
- bones are not anatomically aligned
- not in position
- ends are out of normal alignment

what is depressed fracture?
broken bone portion is pressed inwards
think HAMMERED
what is compression fracture?
- bone is CRUSHED
- common in porous bones
COLLAPSING

where is the lacunae?
cells encased in small cavities (collagen fiber)
where is the osteocytes?
found in mature bones
where is the canaliculi?
hair light canals that connect lacunae to each other & central canal
where is the volkman's canal?
canal's lined with endosteum that occur at right angles to central canal
where is the periosteum?
covers outside of compact bone
where is the circumferential lamellae?
- outer layer of the bone matrix
- layers of lamellae extend around entire surface of diaphysis
- superficial to endosteum
where is the haversian canal?
runs through core of osteon
where is the osteon?
haversian system
where is the compact bone?
dense outer layer on every bone
where is the spongy bone?
made up of a honeycomb-like (trabeculae)
what is osteocalcin?
- secreted by bones
- helps to regulate insulin secretion, glucose levels, & metabolism