Unit 1 - The Chemistry of Life
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch. 1-5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
4 properties of water
cohesion/adhesion, expansion upon freezing, universal solvent, moderation of temperature
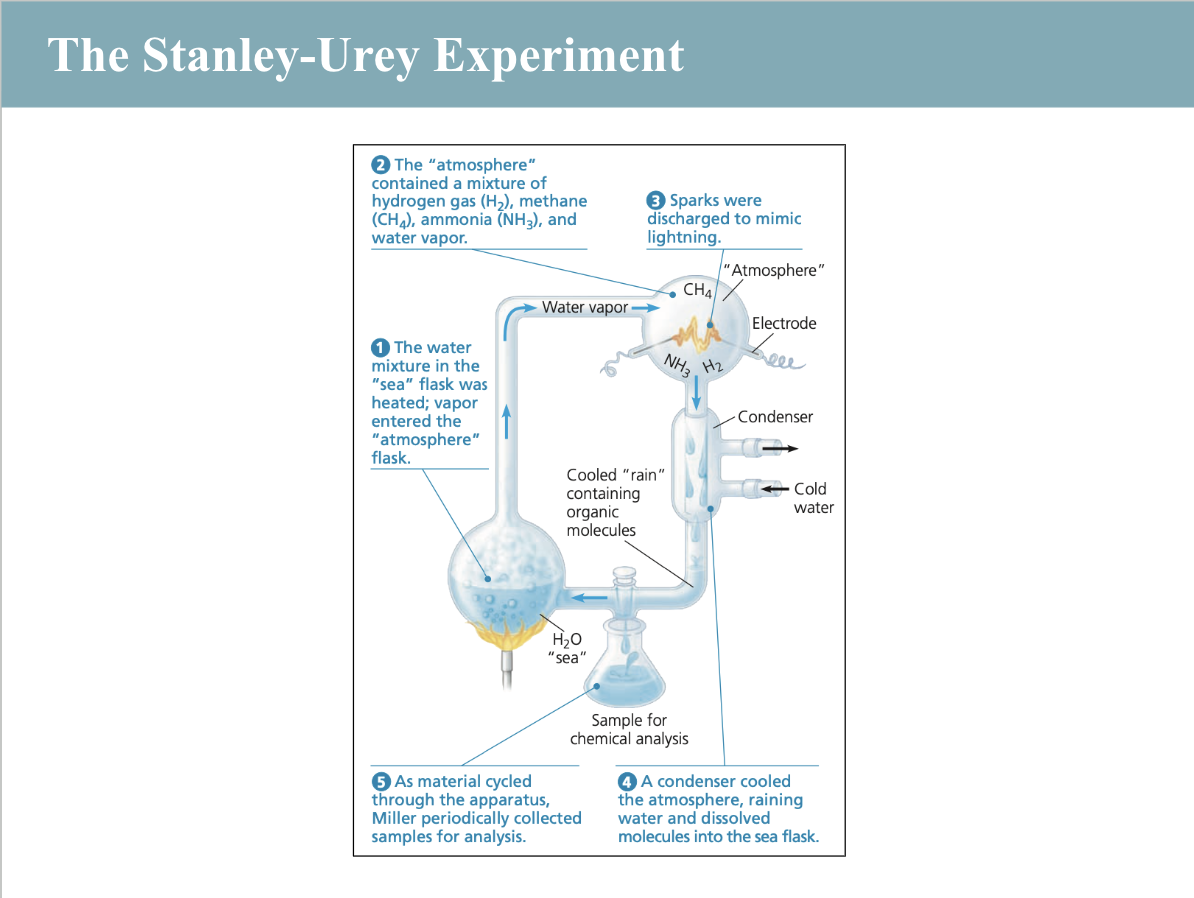
miller-urey experiment
experiment that simulated early Earth conditions to test the origin of life by creating amino acids from simple molecules
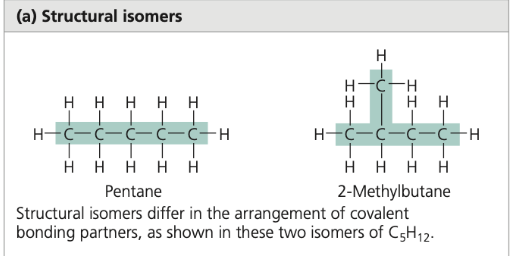
isomers
compounds with the same atoms but different properties and structural arrangements
structural isomers
isomers that differ in the arrangement of atoms in space but have the same molecular formula
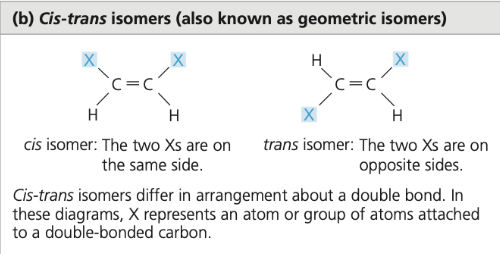
cis-trans isomers
isomers that differ in the arrangement of atoms across a double bond, affecting their properties
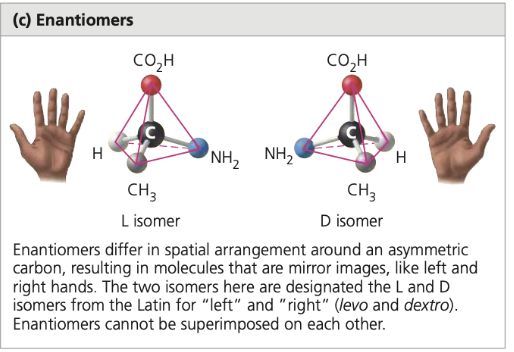
enantiomers
isomers that are mirror images of each other, often affecting biological activity
thalidomide (comes in R and S enantiomers)
R-thalidomide was a drug that was used as a sedative to alleviate morning sickness for pregnant women; S-thalidomide is a teratogen that causes severe birth defects; lots of birth defects in the 1960s
common functional groups
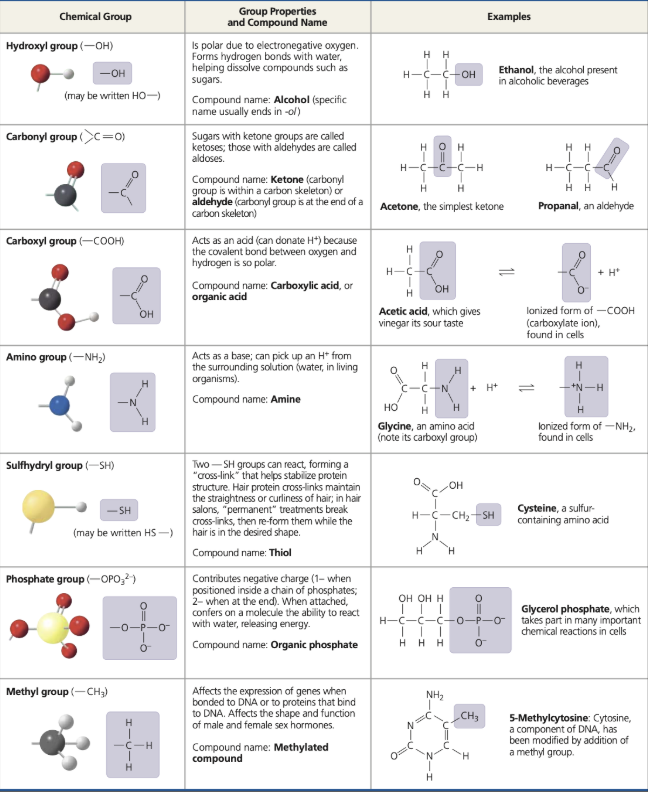
basic definition of ATP
adenosine triphosphate, primary energy-transferring molecule
buffers
substances that minimize changes in pH and pOH in a solution (e.g. blood acidity)
carbohydrates (monomer, polymer, bond)
monosaccharides, polysaccharides, glycosidic linkages
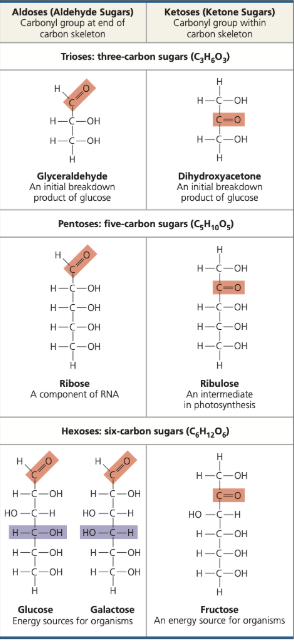
lipids (monomer, polymer, bond)
fatty acids, triacylglycerols, ester linkages
proteins (monomer, polymer, bond)
amino acids, polypeptides, peptide bonds
nucleic acids (monomer, polymer, bond)
nucleotides, polynucleotides, phosphodiester linkages
maltose & sucrose
maltose = glucose + glucose (1-4)
sucrose = glucose + fructose (1-2)
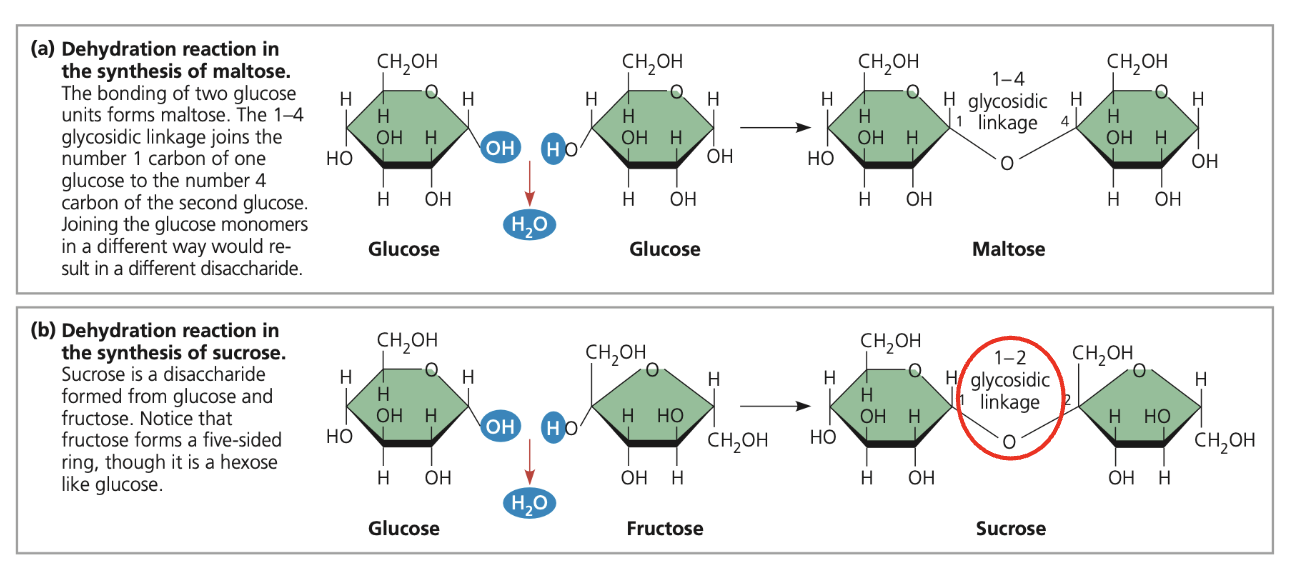
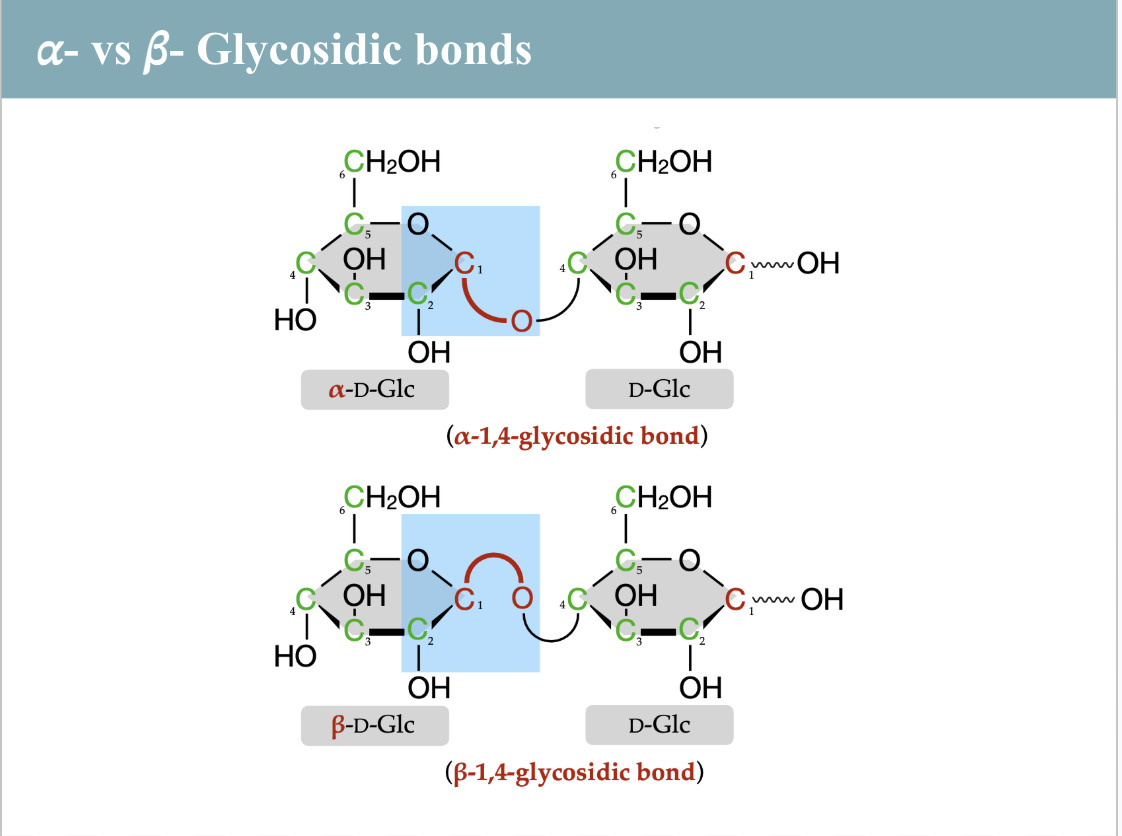
alpha vs beta glycosidic linkages
glucose polysaccharides
starch (amylose - unbranched, amylopectin - somewhat branched), glycogen (extensively branched), cellulose (unbranched)
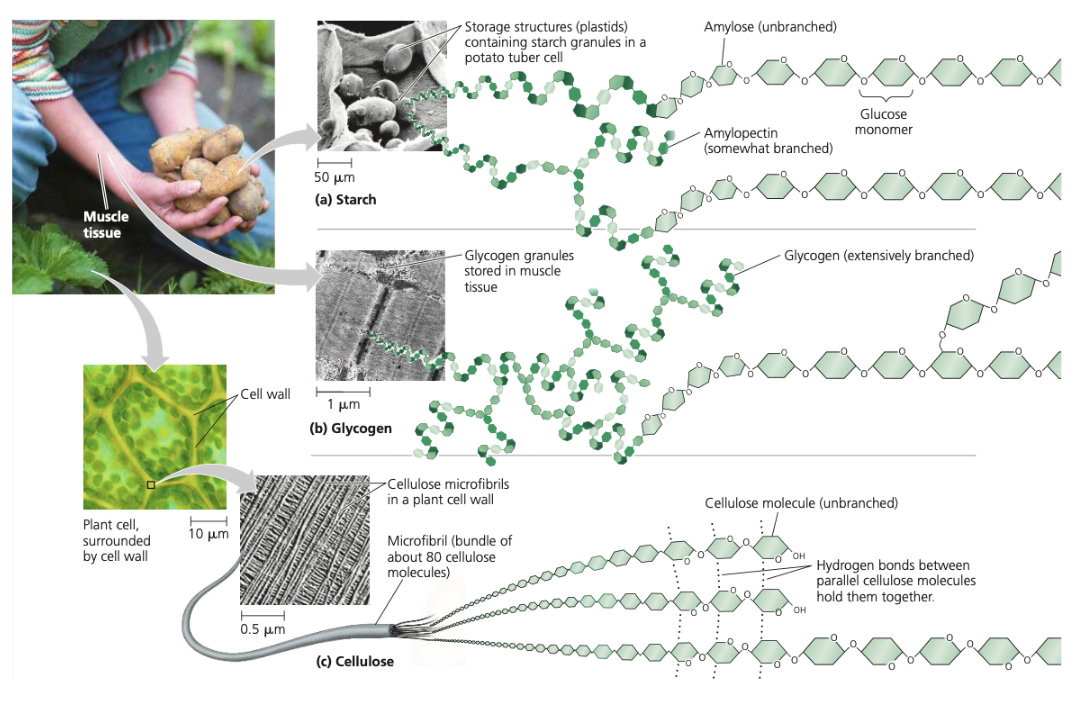
cellulose
1-4 beta glycosidic linkages, human enzymes can’t digest, insoluble fiber
chitin
found in arthropod exoskeletons and fungi cell walls, also a strong polysaccharide
lipids (quality & types)
hydrophobic, 3 most important types: fats, phospholipids, steroids
fats (structure, types, function)
triacylglycerol: 3 fatty acids joined to a glycerol by an ester linkage
saturated: no double bonds in fatty acid chain
unsaturated: one or more double bonds
trans: created through hydrogenation, converting unsaturated fats to saturated fats by adding hydrogen - creates saturated fats with trans double bonds
function: energy storage
Humans and other mammals store fats in adipose cells, which cushion vital organs and insulate the body
phospholipids (structure, function)
two fatty acids and a phosphate group are attached to a glycerol
AMPHIPATHIC
when phospholipids are added to water, they form a lipid bilayer - cell membrane
steroids (structure, example)
carbon skeleton with 4 fused rings
e.g. cholesterol is a component in animal cell membranes (maintains stability by reducing fluidity at moderate temperatures and reducing packing at low temperatures)
high levels of cholesterol may contribute to cardiovascular disease
amino acid structure
alpha carbon connected to H, amino group on left, carboxyl group on right, R group
all the amino acids (20)
nonpolar hydrophobic:
glycine; gly; g - alpha helix breaker
alanine; ala; a
valine; val; v
leucine; leu; l
isoleucine; ile; i
methionine; met; m - sulfur
phenylalanine; phe; f - rings, UV light-absorbing
tryptophan; trp; w - rings, UV light-absorbing, precursor of serotonin biosynthesis
proline; pro; p - alpha helix breaker
polar hydrophilic:
serine; ser; s
theronine; thr; t
cysteine; cys; c - sulfur, disulfide bridges
tyrosine; tyr; t - rings, UV light-absorbing, CHEESE
asparagine; asn; n
glutamine; gln; q
charged hydrophilic:
acidic:
aspartic acid; asp; d
glutamic acid; glu; e
basic:
lysine; lys; k
arginine; arg; r
histidine; his; h
4 levels of protein structure
primary: polypeptide, peptide bonds
secondary: alpha helices and beta pleated sheets, hydrogen bonding between backbone
tertiary: polypeptide folding via side chain interactions and hydrophobic interactions
quaternary: interactions between polypeptide chains
sickle-cell disease
Glutamine → Valine (change in primary structure) leads to sickle cell beta subunit, sickle cell hemoglobin, oxygen carrying capacity is greatly decreased
chaperonins
protein molecules that assist the proper folding of other proteins, parts: cap and hollow cylinder
protein denaturation
alterations in pH, salinity, temperature, or other environmental factors can cause proteins to denature → biologically inactive
x-ray crystallography
commonly used to determine 3D structure of proteins
nucleic acids
construct genes which code for proteins, DNA and RNA
nucleotides
monomers of nucleic acids, pentose sugar + phosphate + nitrogenous base, link via phosphodiester bonds (between 3’ OH- group and 5’ phosphate) forming sugar-phosphate backbone
nitrogenous bases
adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil
A and G are purines - double ring
C, U, T are pyrimidines - single ring
Chargaff’s rule
A with T or U, 2 hydrogen bonds
C with G, 3 hydrogen bonds