General Principles of Drug Action: Receptor Pharmacology – Agonists
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is a receptor
A receptor is a molecule to which a drug binds to bring about change in function of the biological system
What are ligands
A ligand is a chemical which specifically binds to a receptor. An agonist is a ligand
Outline some characteristics of a receptor
Receptor possess structural and steric specificity
Receptors are saturable and finite
Receptors are expressed in select tissues
What does the dose-response curve show
dose response curve refers to the relationship between the effect of a drug and the amount of drug given
What does the size of the response depend on
The size of response varies with the proportion of receptors occupied by the agonist which varies with the concentration of the agonist
What parameters can you obtain from Dose response curves
Emax and EC50
What is Emax and EC50
Emax is the maximum effect an agonist can produce regardless of dose
EC50 is an effective concentration of drug required to produce 50% of maximal effect
In dose binding curve what can be found
Bmax and Kd
What is Bmax and Kd
Bmax: Maximum number of receptors bound
Kd: Concentration at which 50% of receptors are bound
What is the Langmuir equation
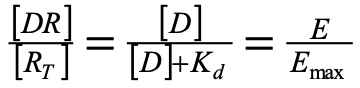
What does the Langmuir equation show
The Langmuir equation shows that the amount of frug bound to the receptor is dependent on the drug concentration and Kd
When are spare receptors present
When EC50 is less than Kd
What is an agonist , partial agonist and antagonist
An agonist is a drug that activates its receptor upon binding eliciting
a full response (effect)
A partial agonist binds to its receptor but produces a smaller
effect (Emax) at full dosage then a full agonist
An antagonist is a substance that binds to a receptor but does
not activate and can block the activity of other agonists