Organizational Behavior Test 1
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lei Huang- Auburn University
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
WHAT IS ORGANIZATION?
A consciously coordinated social unit, composed of two or more people, that functions on a relatively continuous basis to achieve a common goal or set of goals
WHAT MAKES ORGANIZATIONS
SUCCESSFUL?
Products that can potentially revolutionize the way people live
Almost perfect strategic planning
Keep innovating
Embracing changes
Reward and retain the best talent
WHAT IS THE FIRST WAY AN ORGANIZATION IS SUCCESSFUL?
Products that can potentially revolutionize the way people live
WHAT IS THE SECOND WAY AN ORGANIZATION IS SUCCESSFUL?
Almost perfect strategic planning
WHAT IS THE THIRD WAY AN ORGANIZATION IS SUCCESSFUL?
Keep innovating
WHAT IS THE FOURTH WAY AN ORGANIZATION IS SUCCESSFUL?
Embracing changes
WHAT IS THE FIFTH WAY AN ORGANIZATION IS SUCCESSFUL?
Reward and retain the best talent
WHAT PUTS ORGANIZATIONS
IN TROUBLE?
Unclear vision
Bad leadership
Stop innovating
Maladaptive to market changes
Losing talents
WHAT IS THE FIRST REASON THAT AN ORGANIZATION CAN GET INTO TROUBLE?
Unclear vision
WHAT IS THE SECOND REASON THAT AN ORGANIZATION CAN GET INTO TROUBLE?
Bad leadership
WHAT IS THE THIRD REASON THAT AN ORGANIZATION CAN GET INTO TROUBLE?
Stop innovating
WHAT IS THE FOURTH REASON THAT AN ORGANIZATION CAN GET INTO TROUBLE?
Maladaptive to market changes
WHAT IS THE FIFTH REASON THAT AN ORGANIZATION CAN GET INTO TROUBLE?
Losing talents
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE SEVEN KEY
ELEMENTS:
Work specialization
Departmentalization
Chain of command
Span of control
Centralization/decentralization
Formalization
Boundary spanning
Work Specialization
Refers to the degree to which tasks in the
organization are subdivided into separate jobs
Division of Labor Within Work Specialization:
• Repetition of work
• Makes efficient use of employee skills
• Increases employee skills through repetition
• Less between-job downtime increases productivity
• Specialized training is more efficient
• Allows use of specialized equipment
MAJOR PROBLEMS OF WORK SPECIALIZATION:
• Boredom
• Fatigue
• Stress
• Low productivity
• Poor quality
• Absenteeism
• High turnover
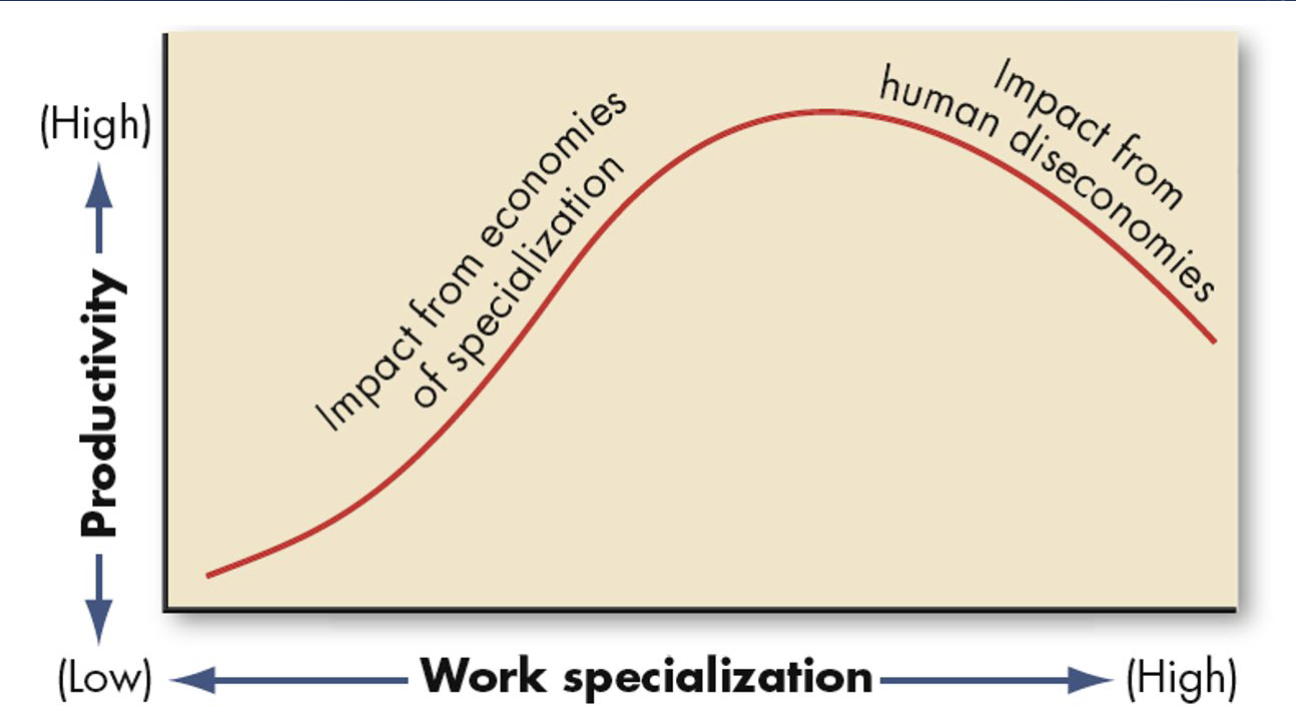
(DIS)ECONOMIES OF WORK SPECIALIZATION
Inverted U-shaped relationship between work specialization and productivity – specialization is good until a breaking point; after that, extreme work specialization leads to lower productivity
SOLUTIONS TO FIX JOB BOREDOM
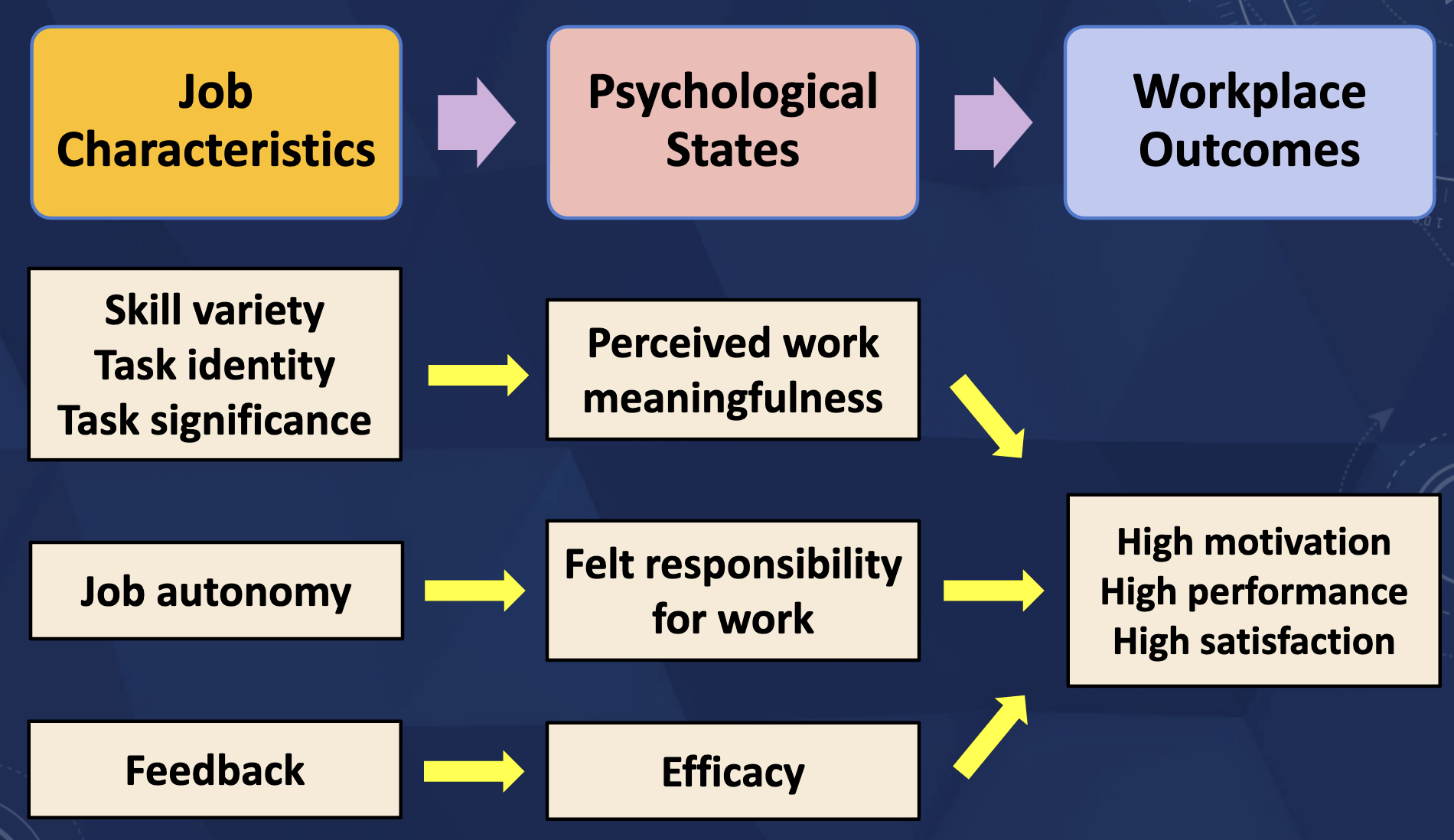
Job Enlargement
Increase the width of the job, increasing the number of tasks for a given job
Job Enrichment
Increase the depth of the job, increasing the degree of responsibility an employee has over a job
What is Job Enlargement used for?
Intended to reduce boredom and fatigue by increasing the variety of tasks performed
Job Enlargement also means..
“HORIZONTAL job expansion”
Job Enrichment means..
“VERTICAL job expansion”
What is Job Enrichment used for?
Intended to increase work autonomy by
allowing greater decision-making power
What does Job Enrichment require?
Requires a flexible organizational structure to allow employees to act flexibly and creatively
Four Basic Ways of Job Crafting
Acquiring structural support (e.g., requesting
coordination or collaboration from another work
unit on a project)
Increasing social resources (e.g., expanding
social networks)
Increasing challenging job demands (e.g.,
setting up more aggressive work goals to fuel up
your energy/passion at work)
Reducing hindering job demands (e.g., ignoring
requests for unnecessary cross-departmental
meetings)
Departmentalization
Refers to the grouping of jobs so common
tasks can be coordinated
Departmentalization Grouping by:
FUNCTIONS PERFORMED
TYPE OF PRODUCT OR SERVICE OFFERED
GEOGRAPHY OR TERRITORY
PROCESS DIFFERENCES
TYPE OF CUSTOMER
Chain of command
Refers to an unbroken line of authority that extends from the top of the organization to the lowest echelon
Authority
Rights inherent to management to give orders and
expect the orders to be obeyed
Unity of command
Specify how many direct supervisors a
person has (typically only one)
What does chain of command clarify?
Clearly clarify who reports to whom, still necessary in many organizations to ensure effectiveness
Span of control
Refers to the number of subordinates a manager
supervises
Typical size of span of control:
5-14 (most commonly seen 8-9)
Narrow span of control may lead to:
expense of additional layer of management
increased complexity of vertical communication
overly tight supervision and less autonomy
What does a wider span of control increase?
Organizational efficiency
What does the size of span of control depend on?
Leadership hierarchy and/or leadership capability
Centralization
Refers to the degree to which decision-making is concentrated at a single point/person in the organization
Advantages of a decentralized organization (most popular today)
Can act more quickly to solve problems
More people providing input into key decisions made at the top
Employees less likely feel alienated from those who make decisions that can potentially affect their work
Advantages of a centralized organization (most seen in traditional business & military)
• Can be very efficient if top management demonstrates great leadership
• Direct collective effort towards resolving a critical issue
• Clear direction if leadership has vision and strong execution
Do small businesses favor centralization or
decentralization?
Centralization
Do family businesses favor centralization or
decentralization?
Centralization
CENTRALIZATION VS. DECENTRALIZATION

Formalization
Refers to the degree to which jobs (or ways of doing things) within the organization are standardized
High formalization means what
Minimum amount of discretion
High formalization can increase what
Operational efficiency if standards are great
Low formalization means what
That job behaviors are relatively non-programmed so employees have a great deal of freedom to exercise discretion at work
Low formalization is not necessarily good because why
Everyone has their own agenda while the achievement of team goals/objectives relies on interdependent effort
Boundary spanning
Occurs when individuals form relationships with
people outside their formally assigned groups
Boundary spanning encourages what
Extensive internal communication
Boundary spanning assigns what
Formal liaison roles or develop committees of individuals from different areas of the organization
Employees with experience in multiple functions are more likely to engage in what?
Boundary spanning
To what degree are activities subdivided into
separate jobs?
Work specialization
On what basis will jobs be grouped together?
Departmentalization
To whom do individuals report?
Chain of command
How many individuals can a manager
supervise directly?
Span of control
To what degree will there be rules and
regulations to direct employees?
Formalization
Do individuals from different areas/functions
regularly interact?
Boundary spanning
SIMPLE STRUCTURE
A structure characterized by a low degree of departmentalization, wide spans of control, authority centralized in a single person, and
little formalization
KEY features of Simple Structure
• Clearly defined line of authority/power and responsibilities
• Minimum level of duplicate personnel
• Most commonly seen structure in small businesses
Strengths of Simple Structure
• Simple, fast, and flexible
• Inexpensive to maintain
• Accountability is clear
Weaknesses of Simple Structure
• Difficult to maintain in anything other than
small organizations
• Risky - everything depends on one person
BUREAUCRACY/FUNCTIONAL STRUCTURE
A structure characterized primarily by standardization and hierarchy.
It can be seen as an extension to simple structure but with many more layers/hierarchies
KEY features of BUREAUCRACY/FUNCTIONAL Structure
Centralized authority
Decisions flow via chain of command
Narrow span of control
Highly routine operating tasks
Very formalized rules and regulations
Little flexibility for change
Strengths of BUREAUCRACY/FUNCTIONAL Structure
• Centralized decision-making
• Functional economies of scale
• Minimum duplication of personnel and
equipment
Weaknesses of BUREAUCRACY/FUNCTIONAL Structure
• Obsessive concern with rules and regulations
• Lack of employee discretion to deal with
problems
• Subunit conflicts with organizational goals
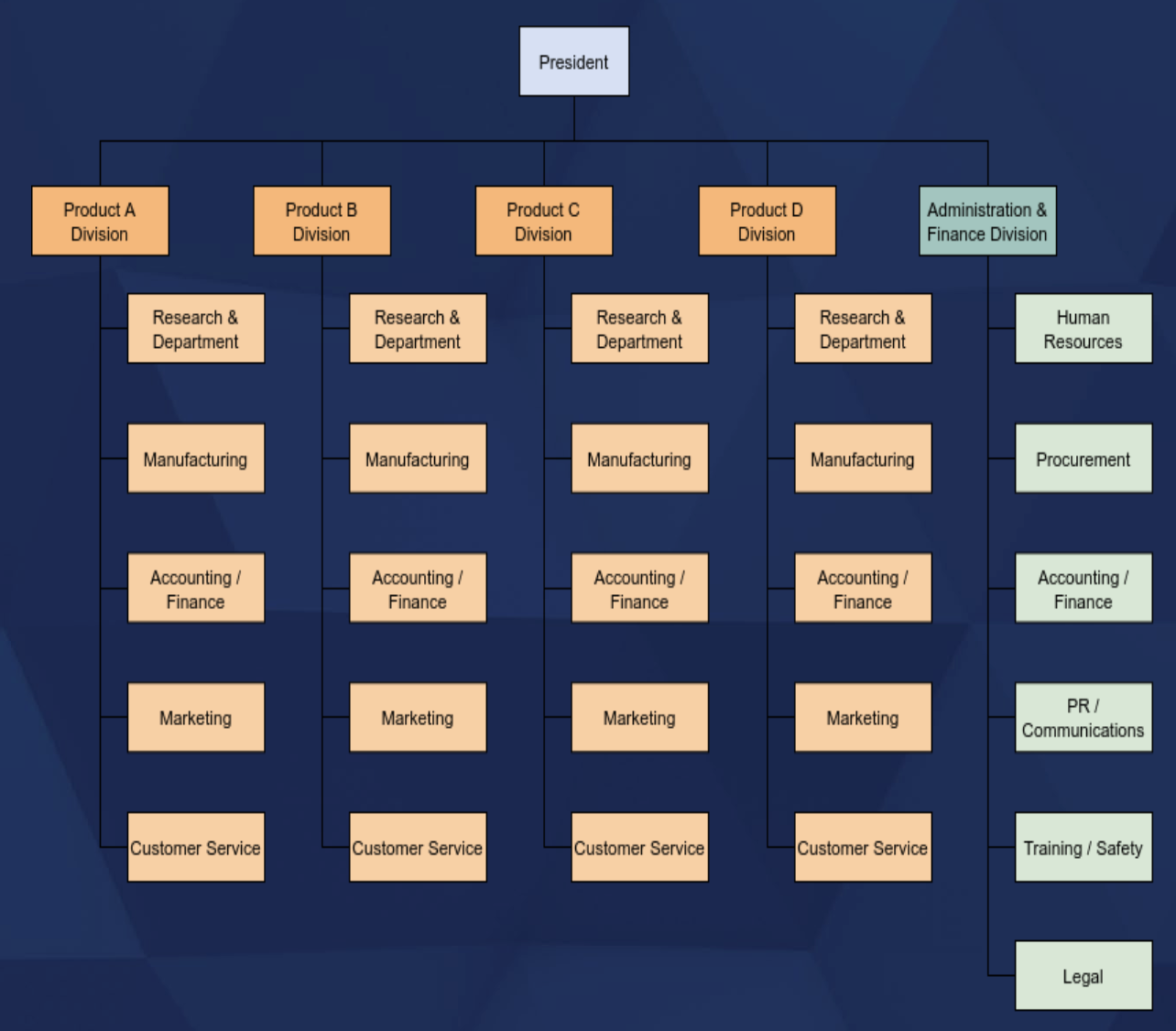
DIVISIONAL STRUCTURE
A collection of functions working together to make products and offer services.
KEY features of DIVISIONAL STRUCTURE
• Divisions create smaller, manageable parts of a firm
• Divisions are created based on the nature and the needs of the firm
• Functional managers (e.g., HR, accounting, marketing) report to divisional managers who then report to corporate management
PRODUCT STRUCTURE
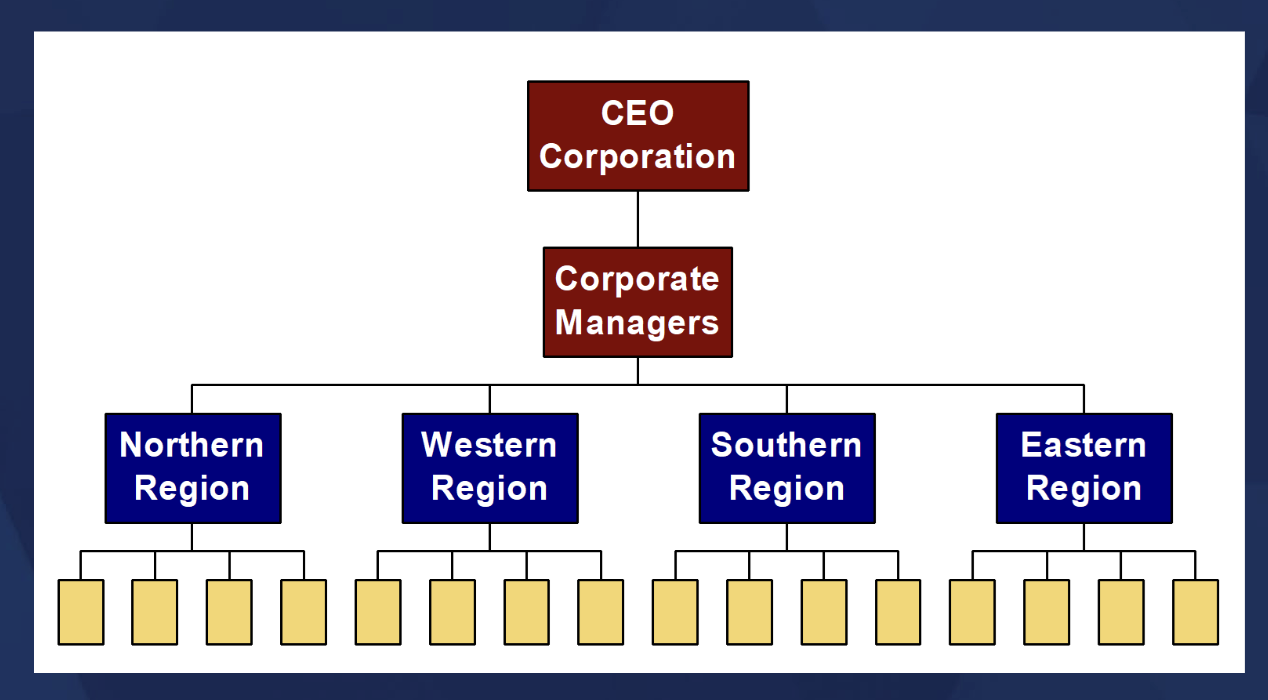
GEOGRAPHIC STRUCTURE
MARKET STRUCTURE
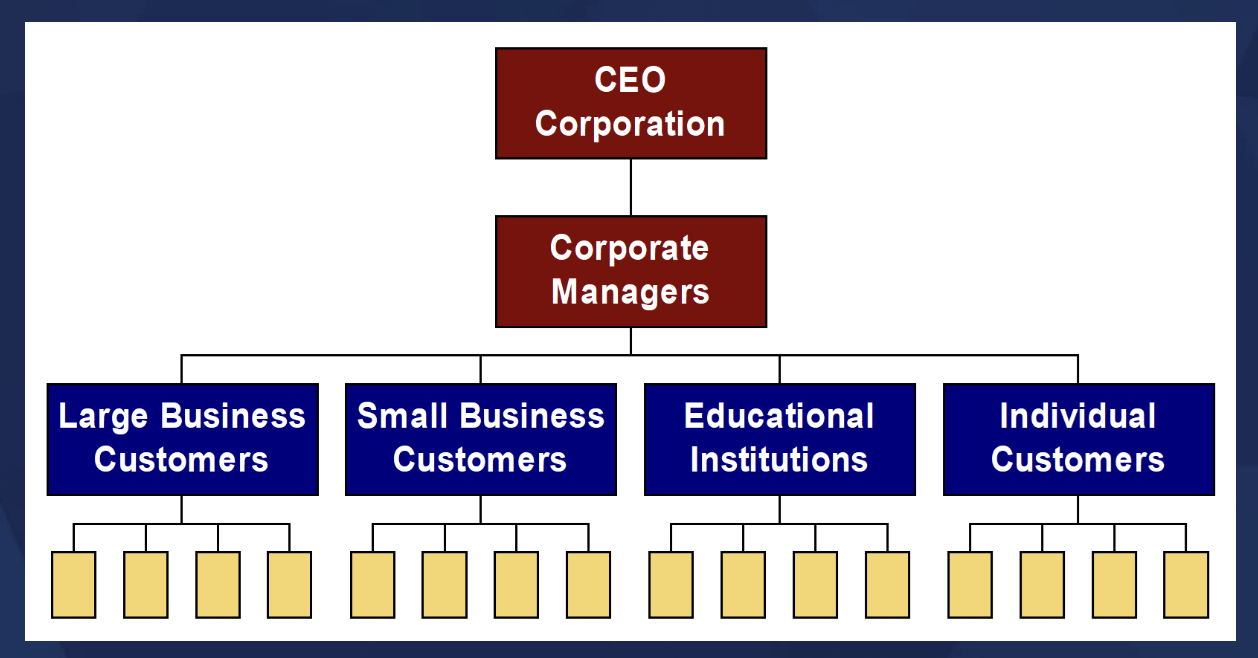
HYBRID STRUCTURE
Combines elements from different traditional organizational structures, most typically mixing aspects of both functional and divisional structures and therefore allowing for more flexibilities in adapting to the specific needs of each business or
market or consumer group
KEY features of HYBRID STRUCTURE
• Decentralized decision-making due to
high level of scalability
• Cross-divisional/functional collaboration
• High adaptability to market changes
• High flexibility with changeable
structures if needed
Hybrid Structure
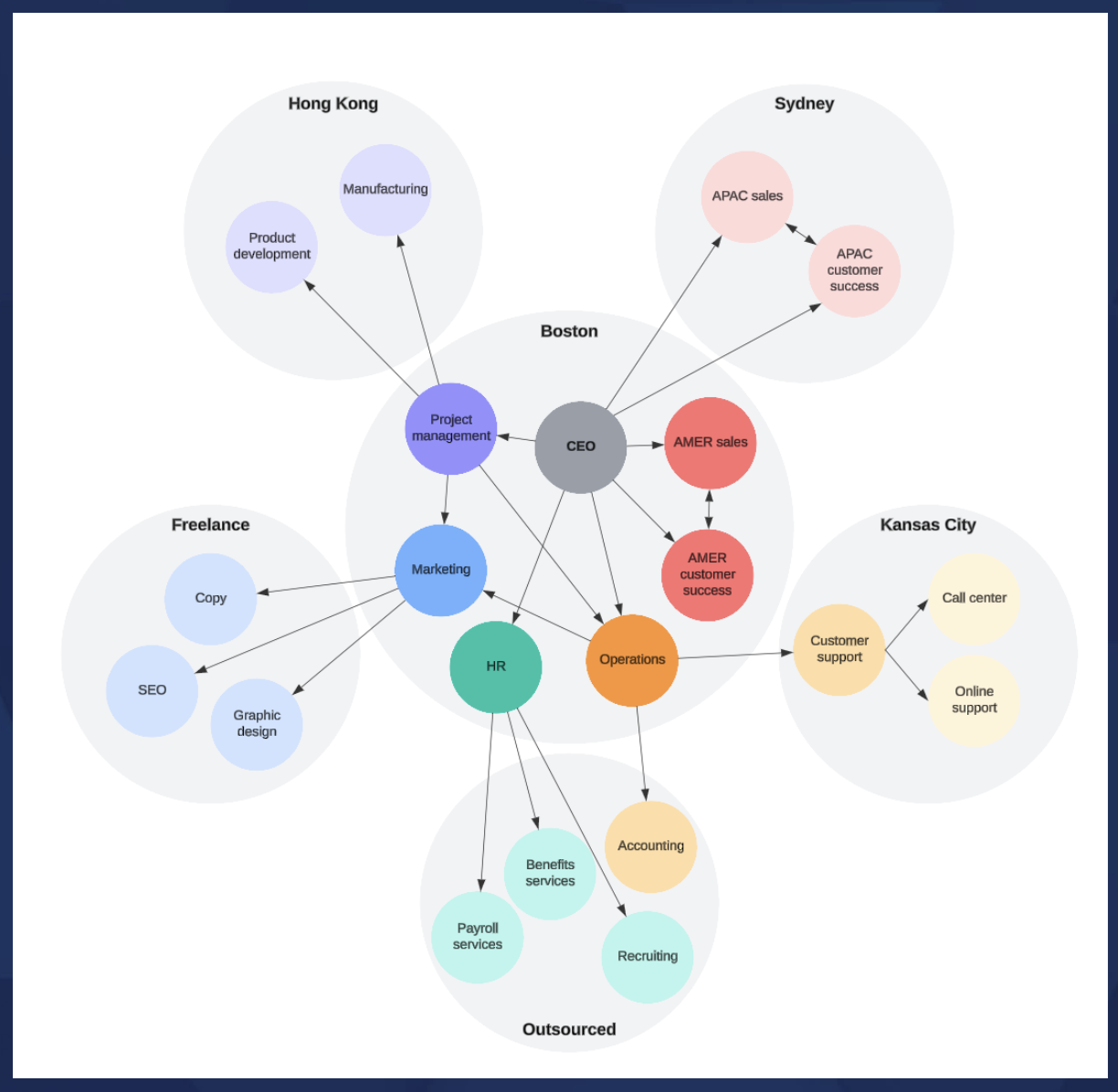
MATRIX STRUCTURE
A structure that creates dual lines of authority and combines functional and product departmentalization
KEY features of MATRIX STRUCTURE
• Gains the advantages of functional and product departmentalization while avoiding their weaknesses
• Facilitates coordination of complex and interdependent activities
• Breaks down the unity-of-command concept
Matrix Structure
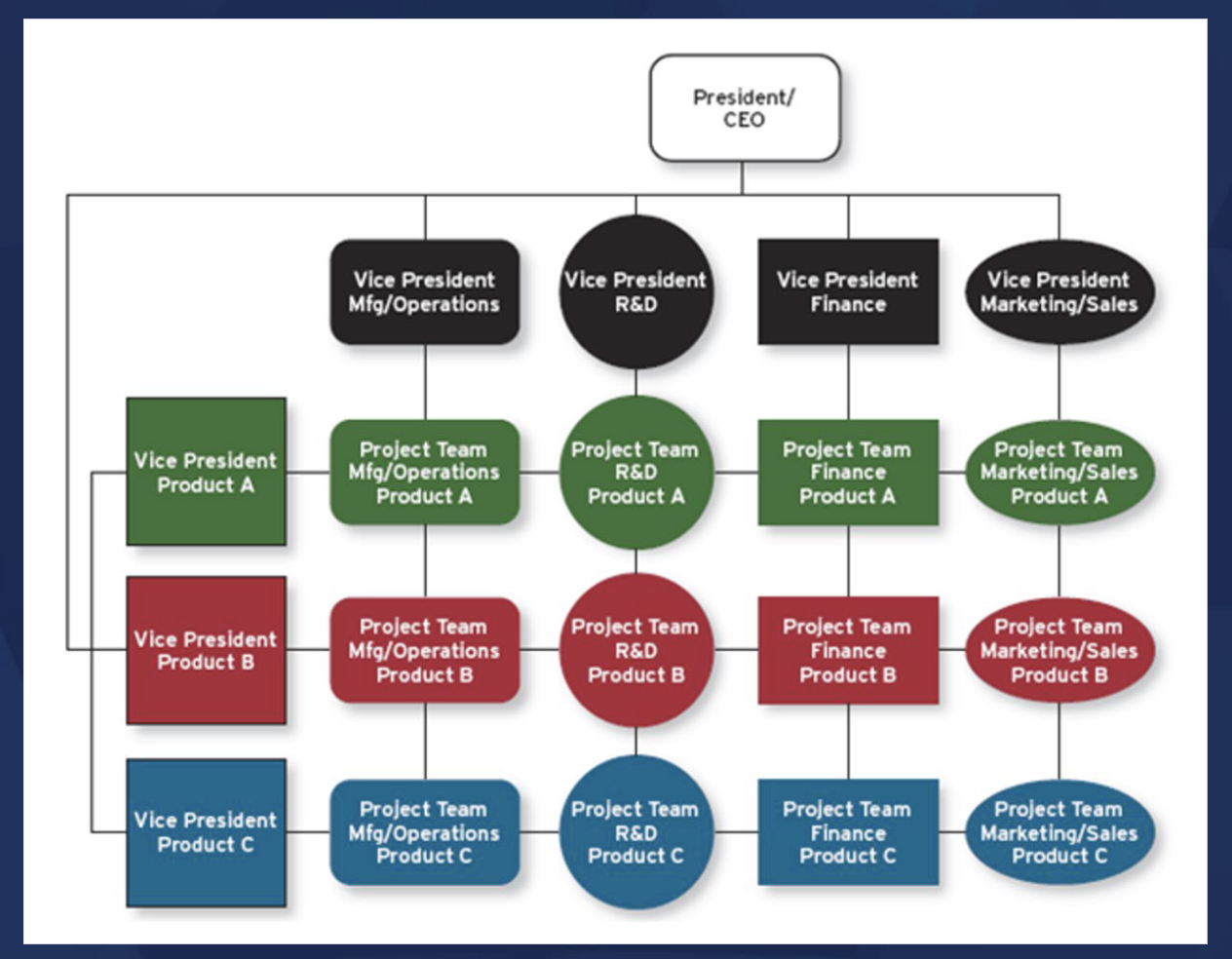
Strengths of Matrix Structure
• Facilitate significant level of task
interdependence
• Facilitate much greater level of boundary
spanning that leads to employee creativity
• Knowledge is not institutionalized within a
specific domain, so employees can learn more
as they engage different areas of work
Weaknesses of Matrix Structure
• Create employees’ confusion about how to
prioritize different things
• Foster power struggles or even conflicts among
managers over their own agenda
• Place greater level of stress on employees
• Create unbalanced expectations across areas
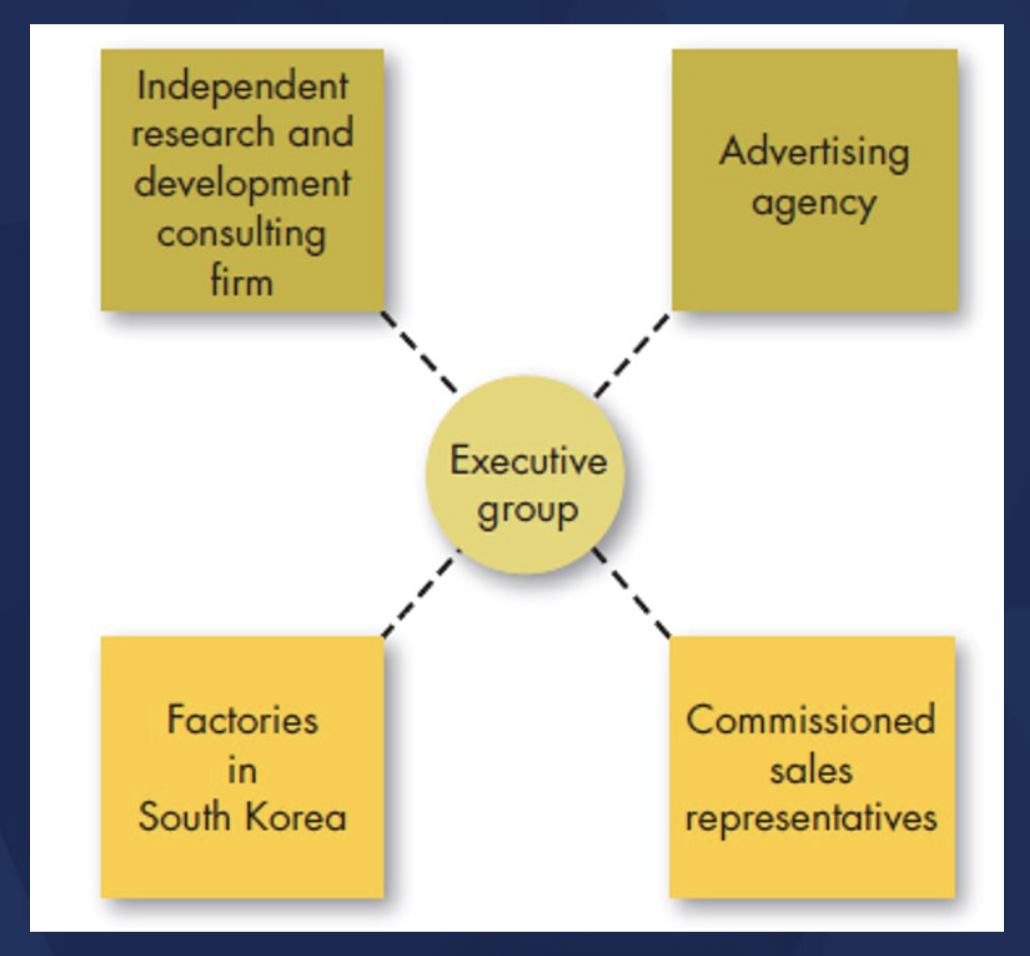
VIRTUAL STRUCTURE
Typically a small, core organization that outsources major business functions
Virtual Structure does what?
• Builds on a small network of “collaborators”, not necessarily employees
• Highly centralized with little or no departmentalization
• Extremely flexible – can quickly adapt to task environment with re-assembly of
a new network of “collaborators” depending on what needs to be done
• Major weakness: Reduces management’s control over key parts of its business
• Typical example: social-media based small business
Virtual Structure
CIRCULAR STRUCTURE
A structure with less formal reporting structures where employees are able to regularly interact with core executives/managers and work together on different projects
Things to know about Circular Structure
• Leader-follower communication channel is very open and flexible
• Characterized with very high level of mutual trust, respect, and confidence in each other’s professional capabilities
• Very popular structure among technology-based start-ups
• Other examples: small law firms or consulting companies
Circular Structure
WHAT IS ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE?
• A common perception held by
members of the organization
• A system of shared meaning – a
set of key characteristics that the
organization values
• The shared beliefs, values and
assumptions that exist in an
organization
CHARACTERISTICS OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE
• Stable over time – not changing
with people moving in/out
• Shaped by the founder or people at
the VERY TOP of the hierarchy
• Implicit (not explicitly observable)
• Reflects who we are, NOT who we
aspire to be
Important things to note about Organizational Culture
Significant structural change may
reshape culture and lead to employee
perceptions of misfit with new culture
• Takes time for newcomers to
understand and adapt to
• Serves as means of institutionalization
– people act and think in similar ways,
but this may hinder creativity
TYPICAL MISCONCEPTIONS ABOUT
ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE
• Only large organizations/companies need to worry about culture
• Culture = Workplace harmony
• Once a strong culture is in place, it WILL take care of itself and live through all the turbulence
• Consultants can come in fixing the culture problem
FUNCTIONS OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE
• Conveys a sense of identity for its members
• Defines the boundary between one organization and others (i.e., differences in products, services, structures, people)
• Enhances the stability of the social system – when
confronted with change or uncertainty, culture unites & guides people
• Facilitates the generation of commitment to something larger than self-interests
• Serves as a sense-making and “control” mechanism to direct employees’ work behaviors
Dominant Culture
Expresses the core values shared by the
majority of an organization’s members
Subcultures
• Mini-cultures within an organization, typically
defined by department designations and
geographical separation
• Those who have strong informal influence
shape subcultures
• Subcultures may change – NOT as stable as
dominant culture