Unit 2: Lipids
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
lipids
have low solubility in water
high solubility in np solvents
mostly hydrocarbons
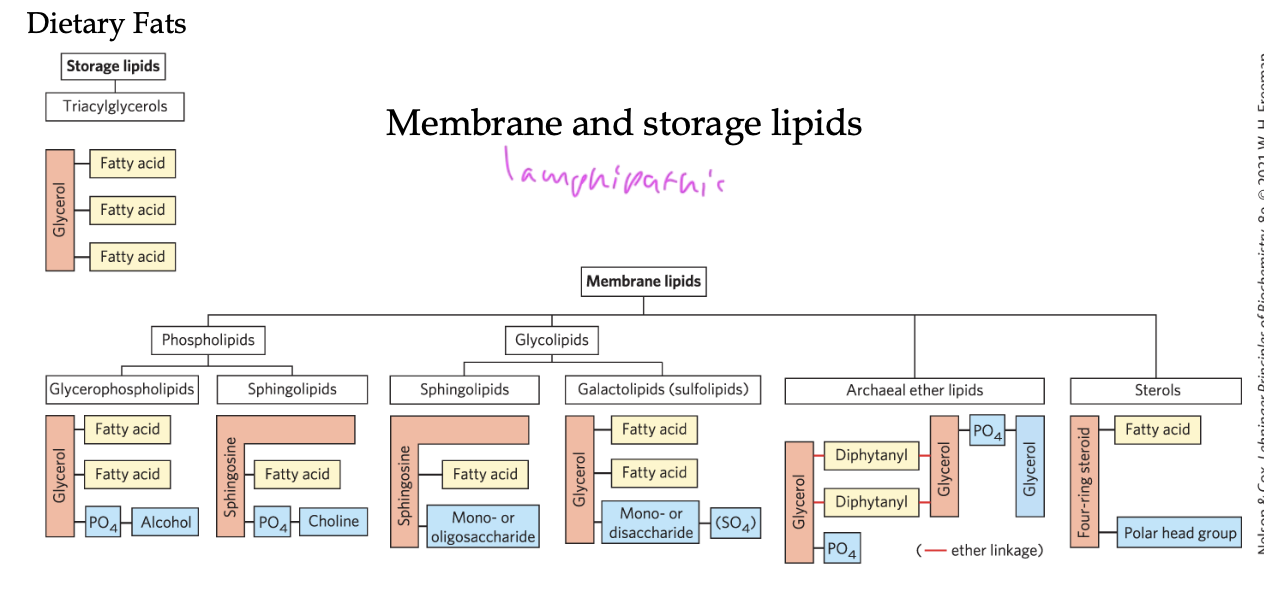
membrane lipids are
amphipathic
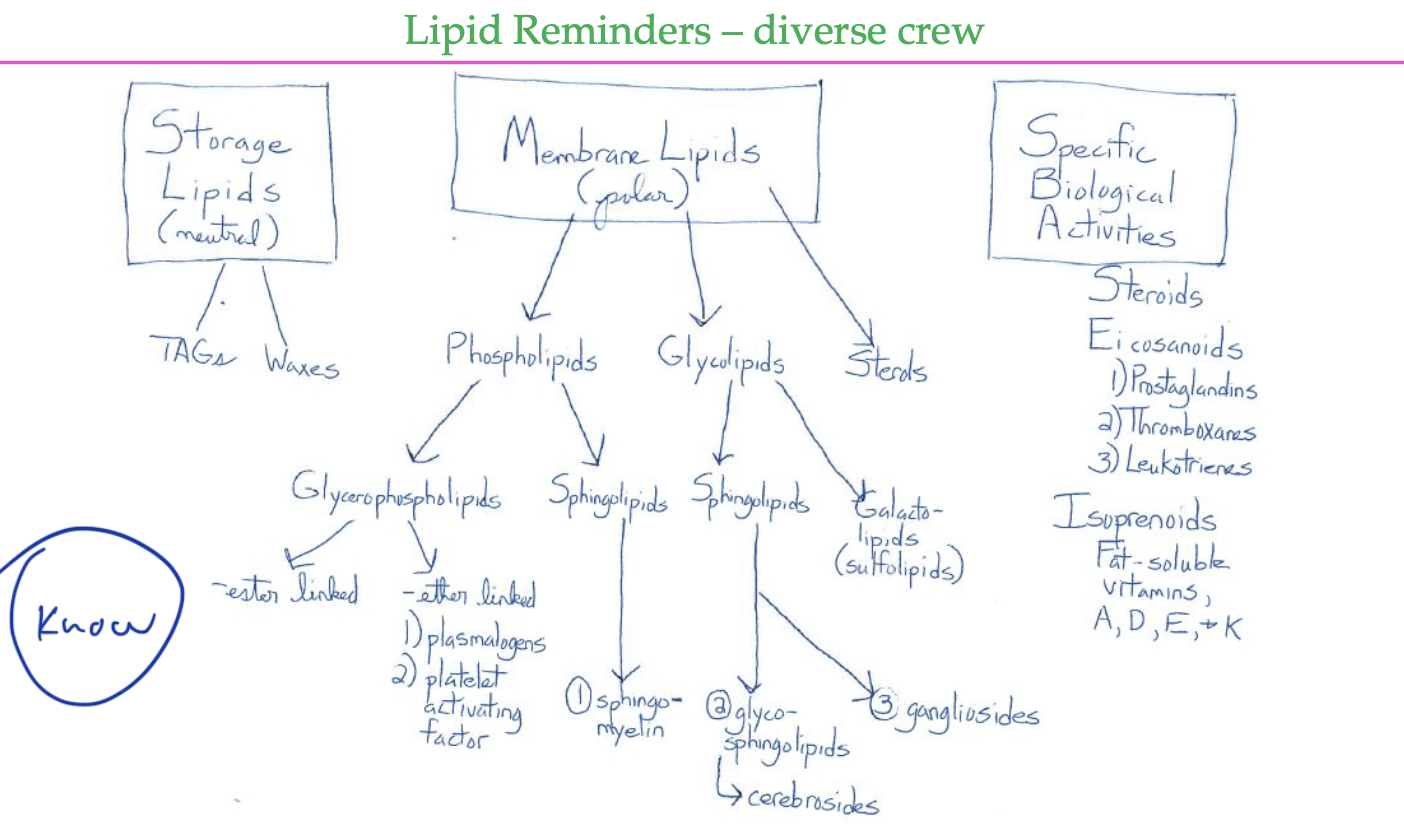
types of lipids
what percent of calories should come from fat
20-35%
healthy aspects of fat in diet
promote satiety
carry fat-soluble vitamins (like coenzymes)
major source of fatty acids (omega 3 and omega 6)
important precursors to eicosanoids (signaling molecules)
lipids are very
diverse molcules
cells use __% of their genes to synthesize lipids
5%
ubiquinone
lipid important for shuttling in the ETC
sterols
hormones used in cell signaling
lipids are classified by
function
storage
membrane
signaling
coenzymes
pigments
antioxidants
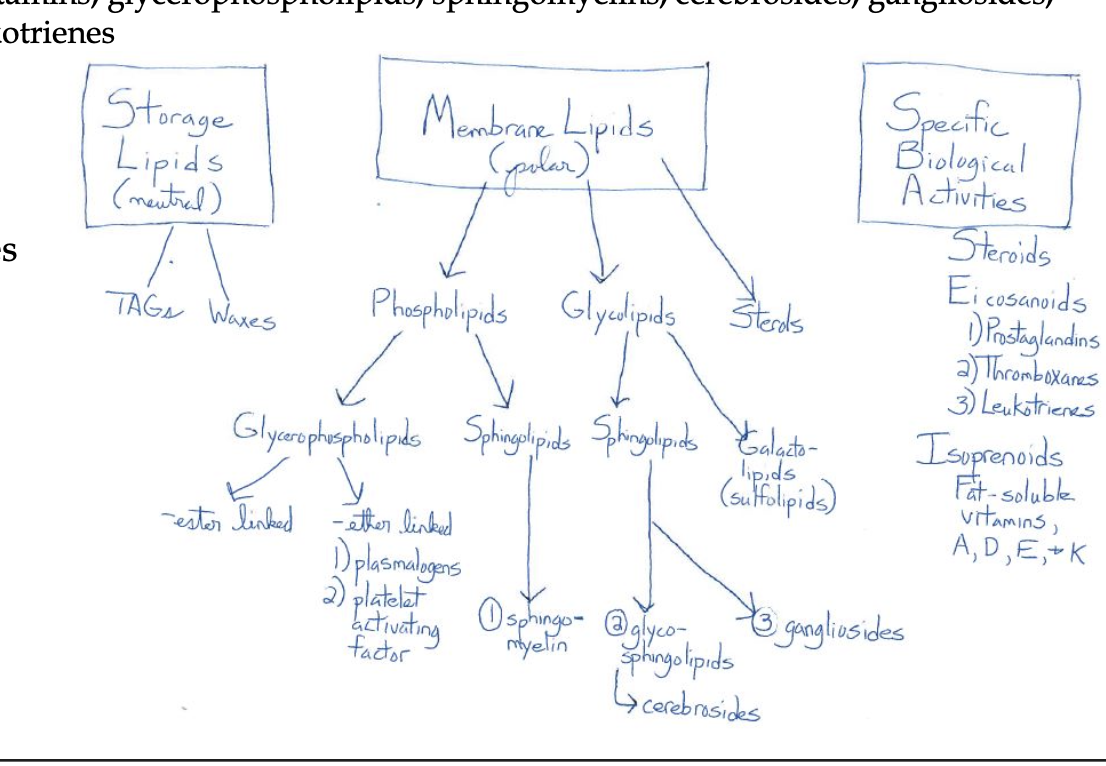
every lipid type
triacylglycerols
waxes
phospholipids
sphingolipids
glycolipids
eicosanoids
steroids
lipoproteins
fat-souble vitamins
glycerophsopholipids
sphinegomyelins
cerebrosides
gangliosides
prostaglandins
thromboxanes
leokotrienes
which lipid is the simplest?
fatty acids
fatty acids
are often constituents of more complex lipids
made up of a long hydrocarbon tail and a carboxyl head group
usually have an even number of carbons (12-24)
most are unbranched
C1 is the carbon by the carboxylic head
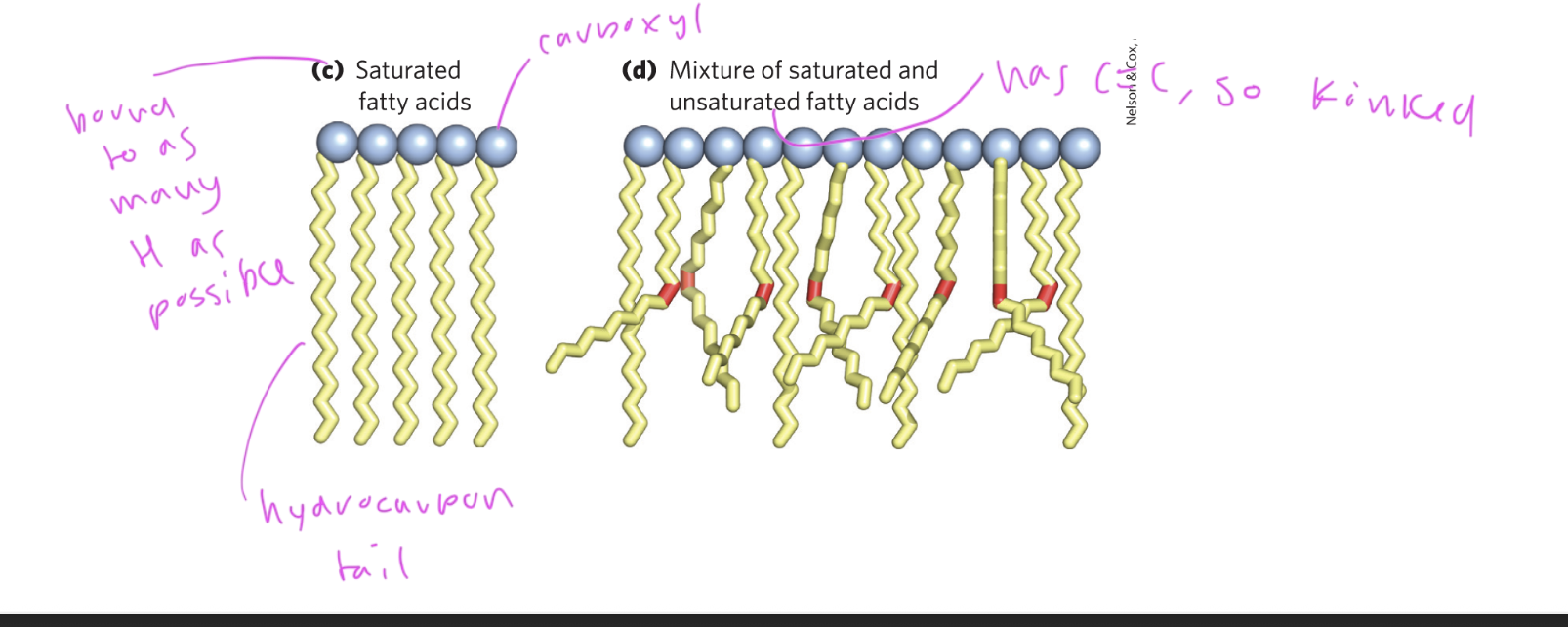
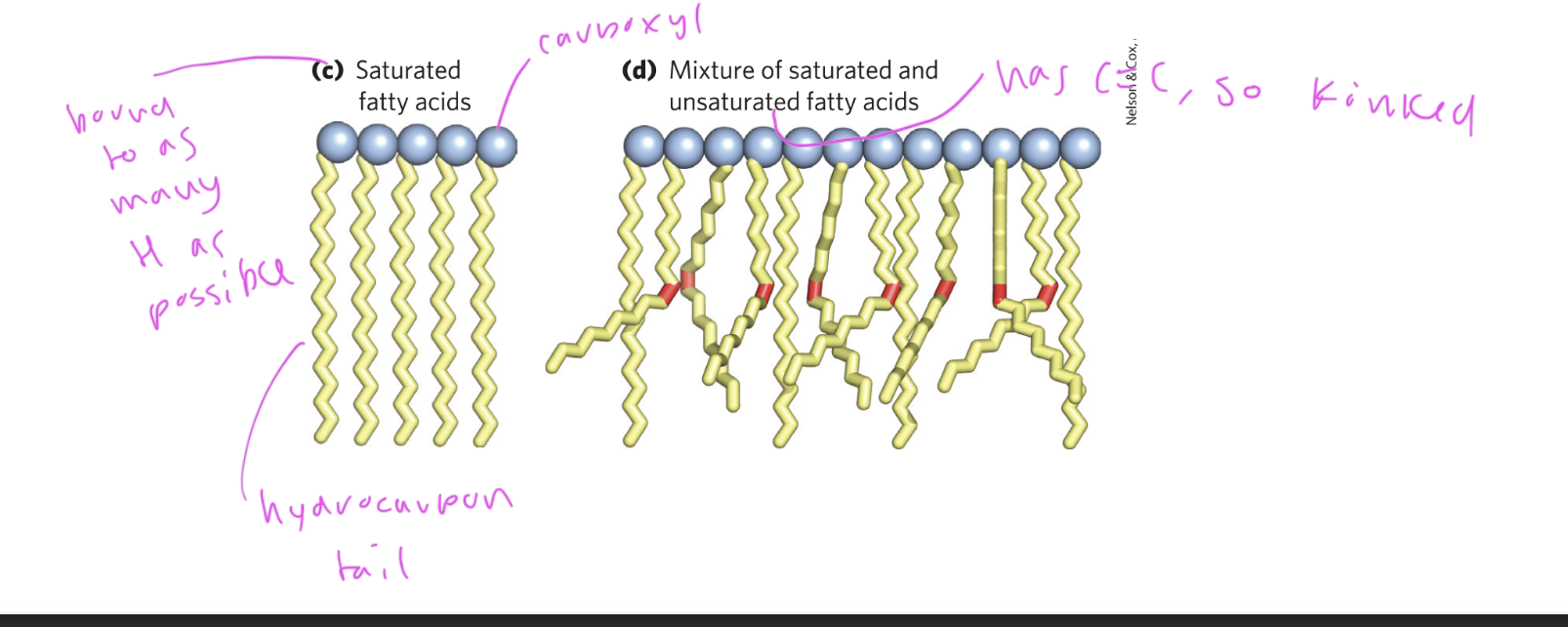
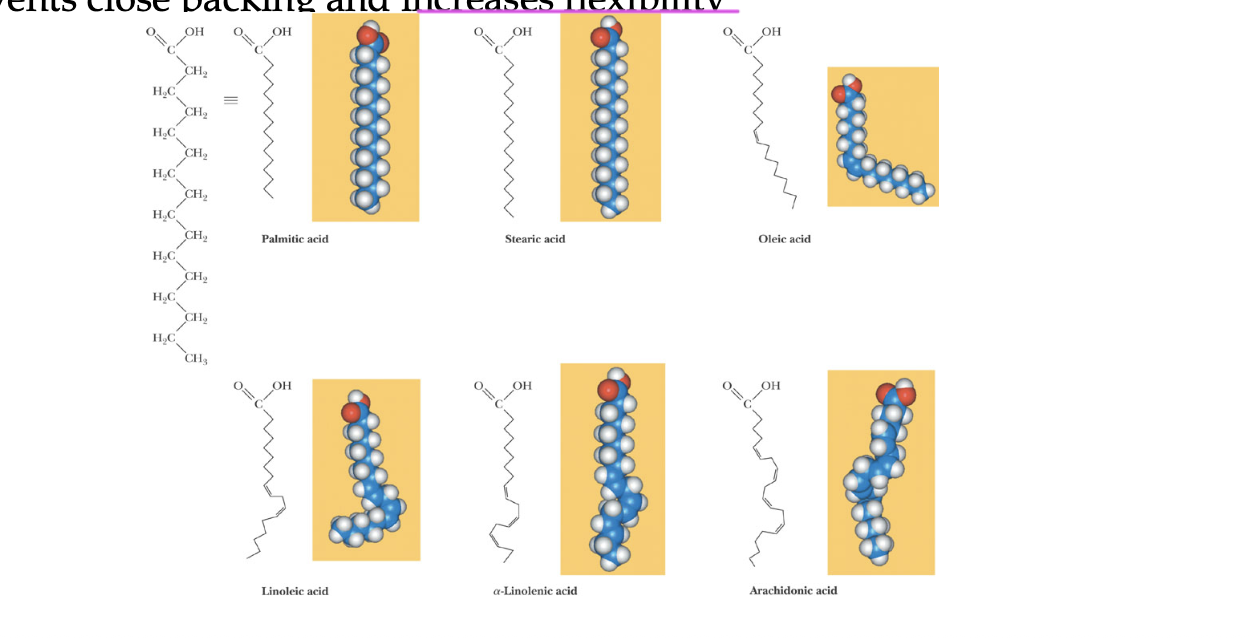
saturated fatty acids
straight, not kinked
have as many hydrogens bound to the tail as possible, since no C=C bonds
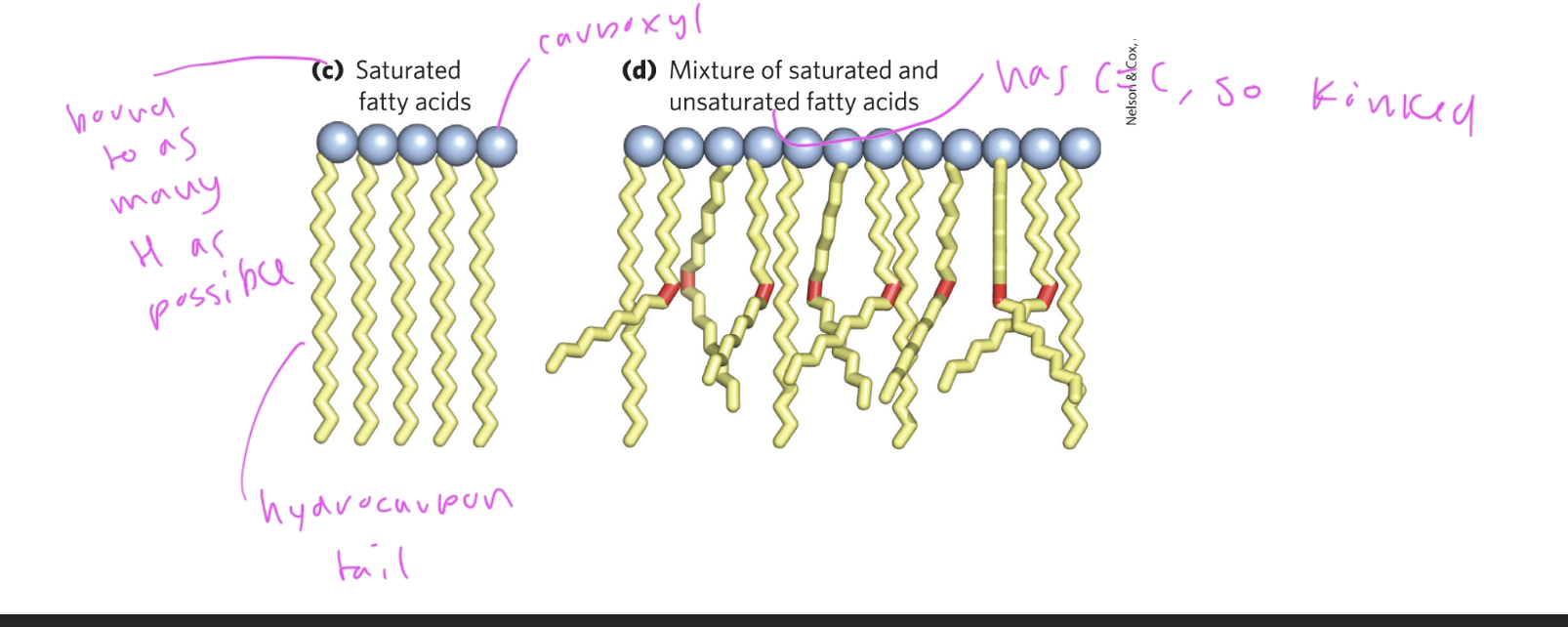
unsaturated fatty acids
kinked due to C=C bonds, which also causes it to have fewer hydrogens, so “unsaturated”
monosaturated has one C=C bond in the chain, polyunsaturated has more than one double bond
double bonds are usually at positions C9,12,15
carboxylic acids have highly reduced _____
hydrocarbon chains (4-36 carbons)
fatty acid naming
#carbons: #double bonds (Δ^#carbon where double bond starts)

saturated fatty acid chains can adopt
extended conformations
______ fatty acids are more abundant in nature than _____
unsaturated are more abundant than saturated
double bonds in natural unsaturated fatty acids are typically in _____ conformation
cis
this causes the chain to kink and incr flexibility since it prevents close packing
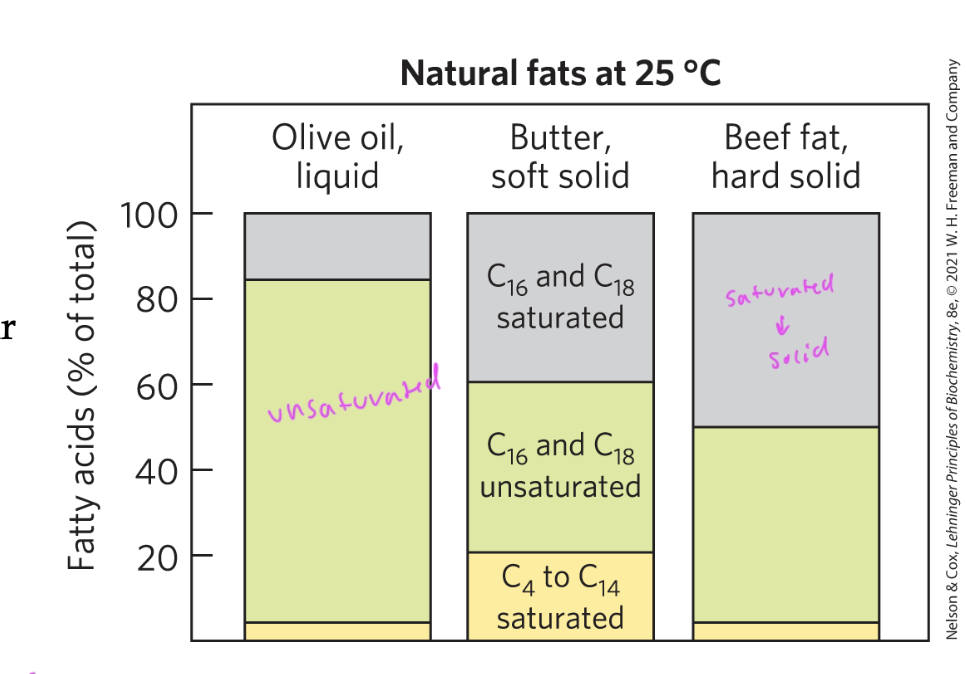
more solid fats have a greater proportion of saturated fats due to ____
VDWs forces being higher in more solid fats
fatty acids rarely occur in a _____ state
free, uncomplexed
how do free fatty acids circulate the body of vertebrates?
they bind to a protein carrier called serum albumin
fatty acids are typically present as _______ derivatives
carboxylic acid
often esterified to glycerol (to form triglycerides) or other backbone structures
fatty acids like to bind to something
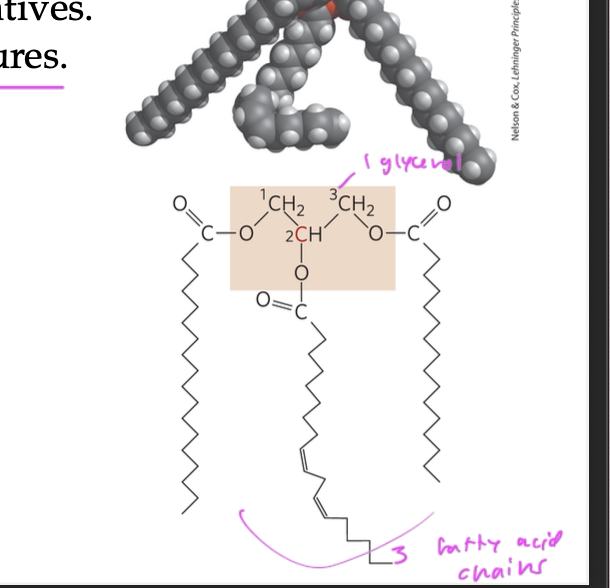
triglycerides are aka
fats, and TAGs
fatty acid esters of glycerol
have 3 fatty acids each ester linked to a single glycerol molecule
serves as a major energy source for organisms
humans store energy as there fats for up to weeks
TAGs are the most reduced form of carbon in nature, so it has super high PE due to so many np bonds, and good for energy storage
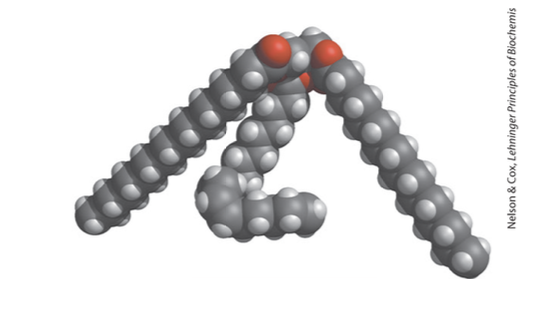
adipose tissue
forms because fats are hydrophobic and want to aggregate in the aqueous body
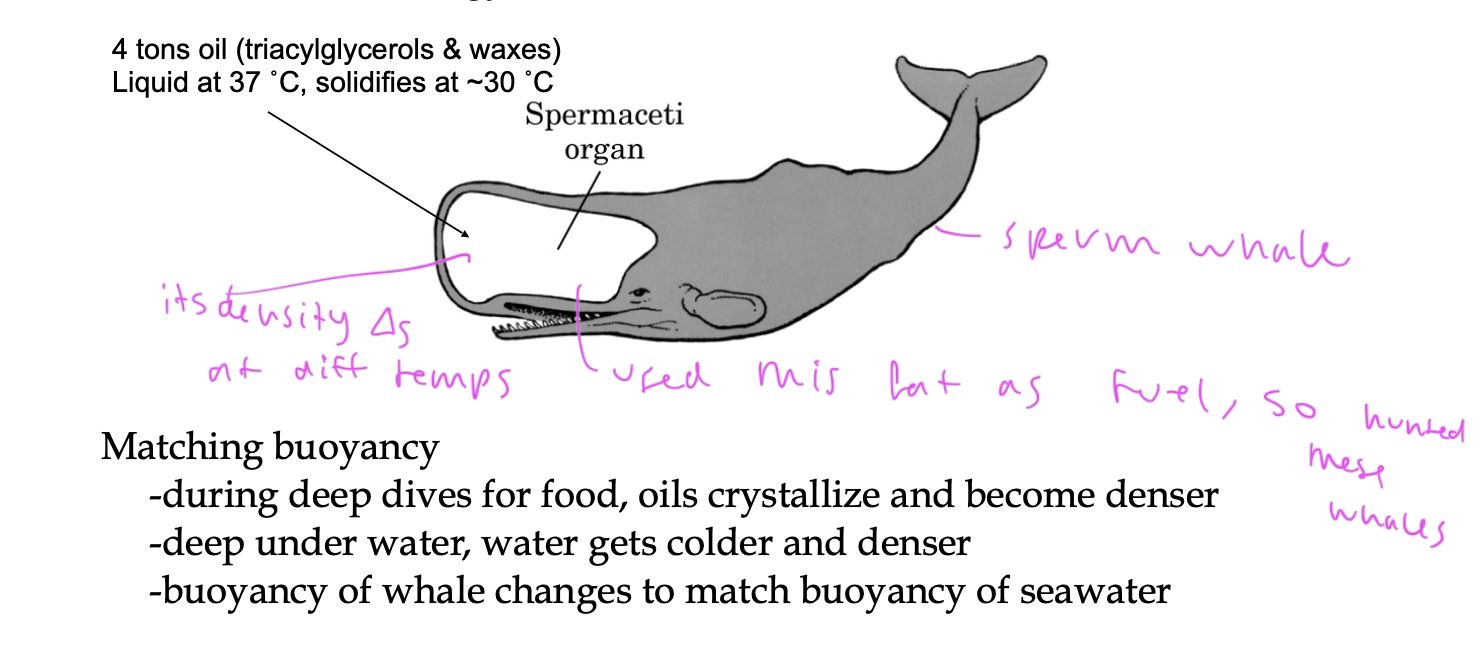
TAGs are used for ____ in many animals
insulation and energy source
sperm whales use it in their head to be able to dive deep down
people used to hunt their heads for fuel since it has so much oil /fat in there
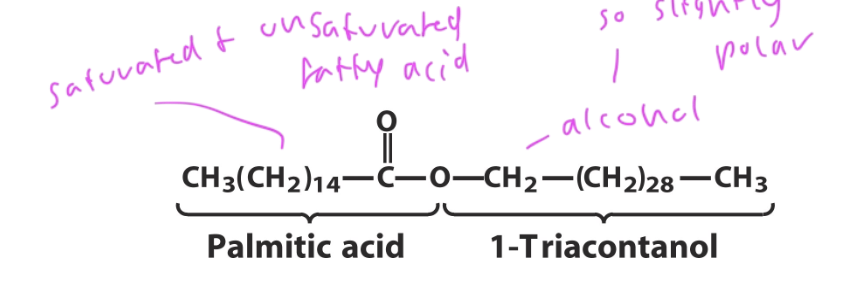
wax
used for storage and as a water repellent
formed form esters of long chain saturated (C14-36) and unsaturated with long-chain alcohols (C16-30)
used to protect hair, skin, makes up beeswax to be water repellent, birds cover their wings in it to repel water, etc
polar lipids in membranes
have a polar head group and np tail (uaully attached to fatty acids)
differ in their backbones, fatty acids, and head groups
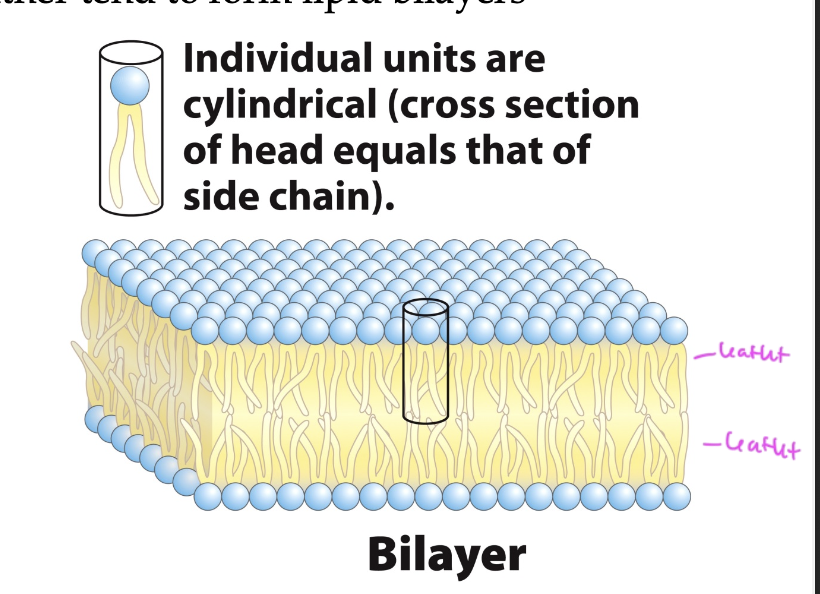
each side of a lipid bilayer is called a
leaflet
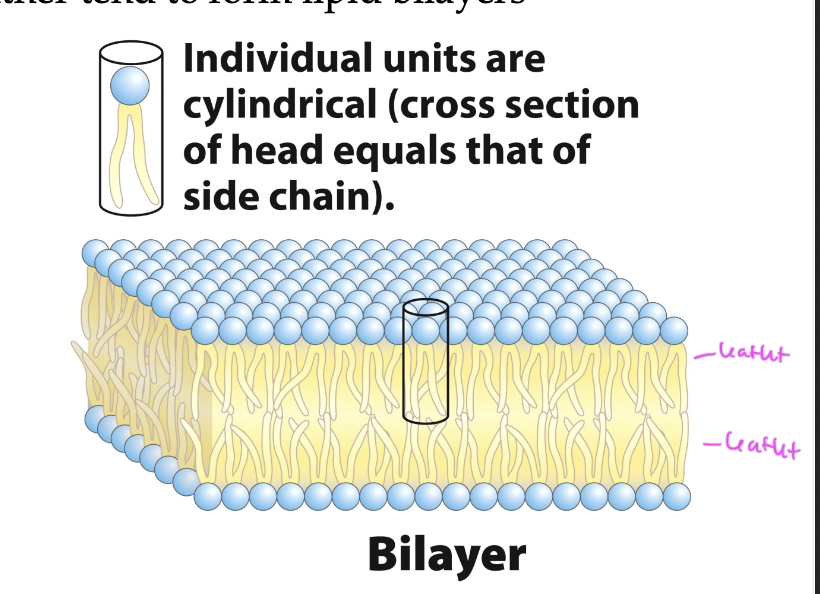
membrane lipids
are amphipathic
form bilayers
one layer faces cytoplasm and the other faces ECM
for membranes of organelles, one side faces cytosol and the other faces organelle lumen
bilayers are 4-5nm think
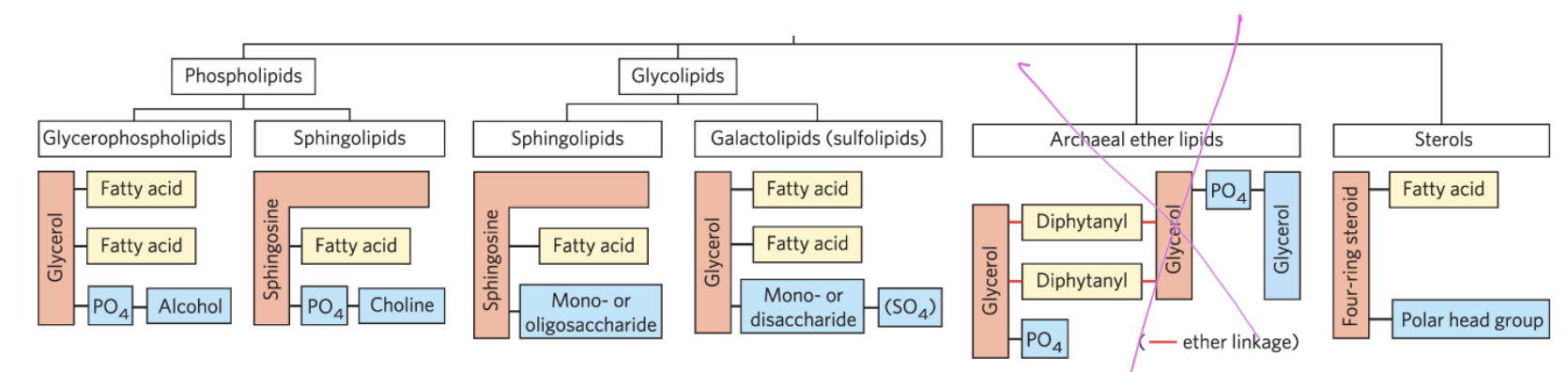
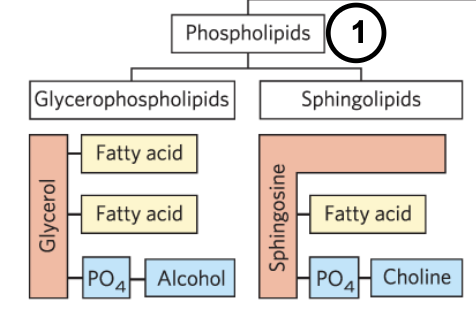
phospholipids
have a hydrophobic region attached to a phosphate, attached to a polar head group
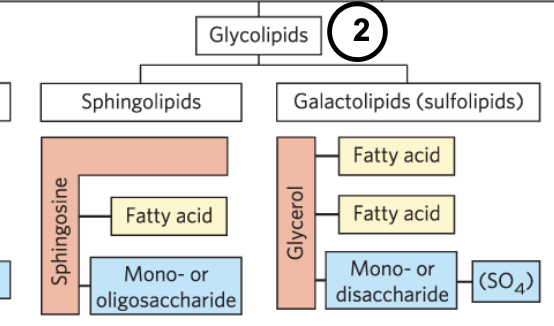
glycolipids
have a hydrophobic region attached to a polar head group that is a sugar
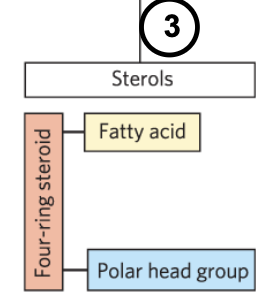
sterols
four fused hydrocarbon rings
rigid
if a phospholipid has a ____ backbone, it is a ____
if glycerol backbone, glycerophospholipid
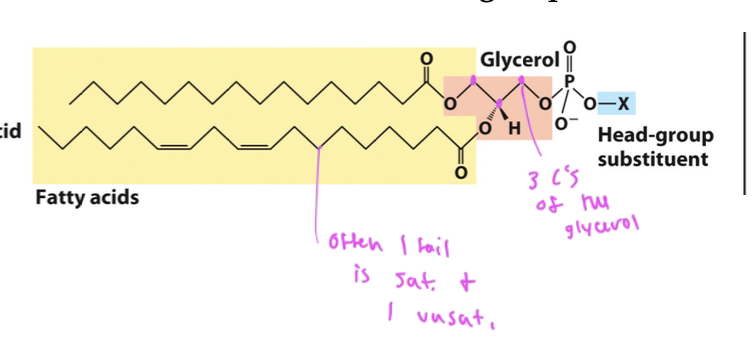
has 2 fatty acids at C1 and C2 (usually one is saturated and one is not) each is connected to an OH on the glycerol to form ester linkages
C3 has the polar or charged head group that is attached to the backbone by a phosphate
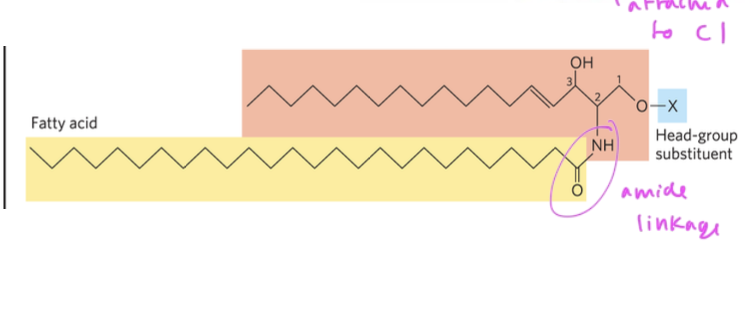
if sphingosine backbone, phosphosphingolipid
has only one fatty acid at C2 (since sphingosine already has/is a hydrocarbon chain on it)
the fatty acids connects to the backbone via an amide linkage
has its polar head group at C1
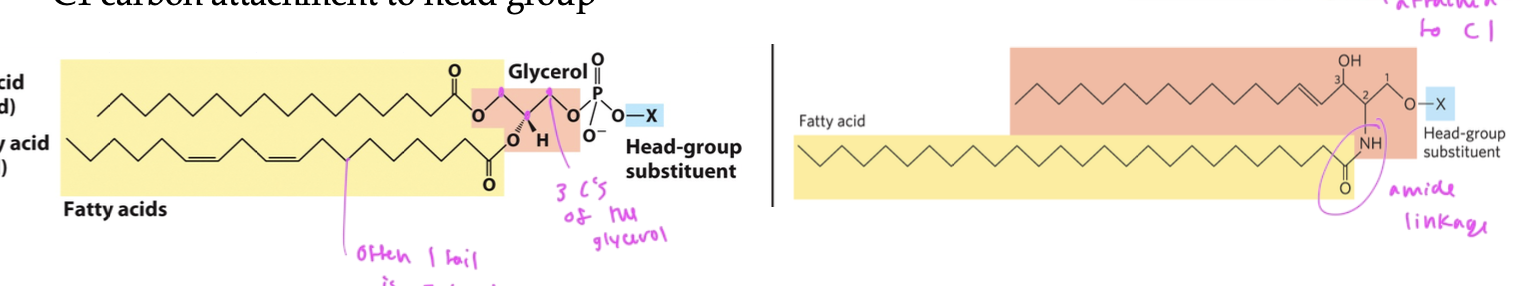
glycerophospholipid
has 2 fatty acids at C1 and C2 (usually one is saturated and one is not) each is connected to an OH on the glycerol to form ester linkages
C3 has the polar or charged head group that is attached to the backbone by a phosphate
phosphosphingolipid
has only one fatty acid at C2 (since sphingosine already has/is a hydrocarbon chain on it)
the fatty acids connects to the backbone via an amide linkage
has its polar head group at C1
glycerophospholipid polar head groups
polar groups are esterified to the backbone
phosphatidic acid: lacks a head group (is parent coumpound)
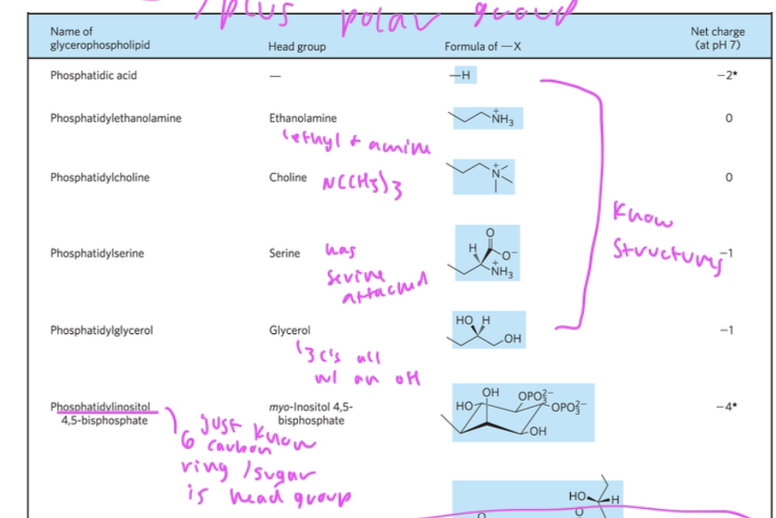
phosphatidylethanolamine: has ethanolamine has head group (ethyl connected to an amine)
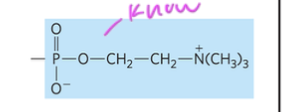
phosphatidylcholine: has choline (N(CH3)3 head group
phosphatidylserine: has serine head group
posphatidyglycerol: has glycerol as head group
phosphatidylionsitol: has 6 carbon sugar ring as head group
parent compound of glycerophospholipids
phosphatidic acid (lacks the polar head group)
phosphatidylethanolamine head group
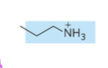
phosphatidylcholine head group
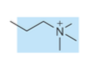
phosphatidylserine head group
phosphatidyglycerol head group
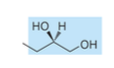
phosphatidylionsitol head group
6 carbon sugar ring structure
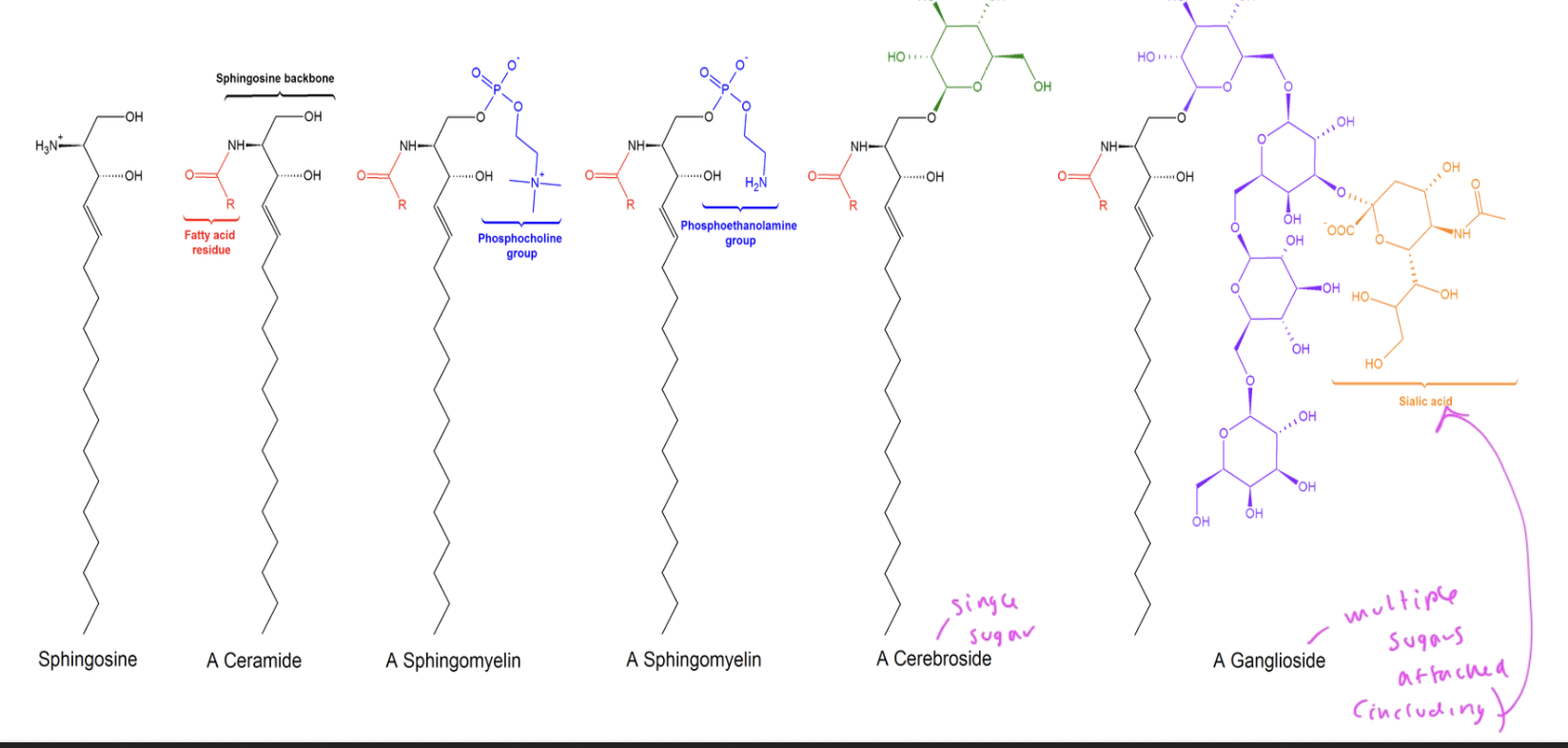
parent compound of sphingolipids
ceramide (which is sphingosine with a fatty acid)
diff types of sphingilipids
ceramide is parent compound
sphingomyelin
glucosylceramide
lactosylceramide
ganglioside
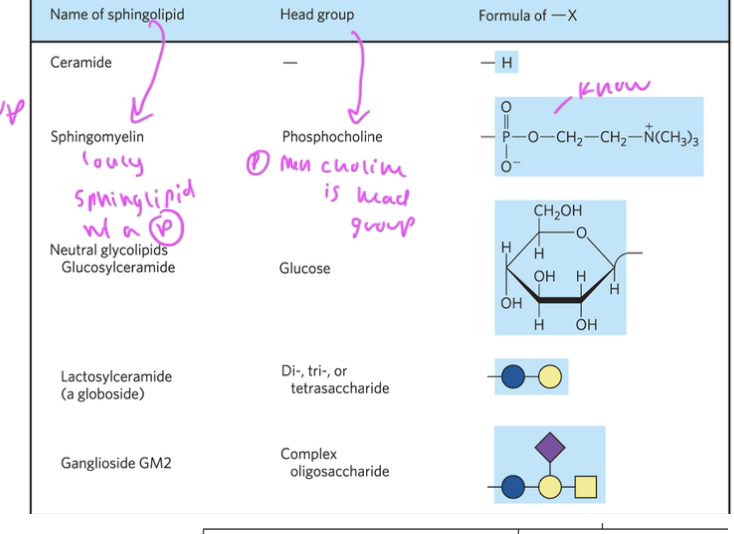
sphingomyelin
sphingolipid with a phosphocholine head group
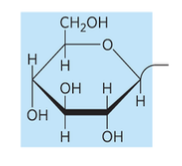
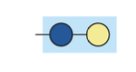
glucosylceramide
sphingolipid with glucose head group
lactosylceramide
sphingolipid with di, tri, or tetrasaccharide head group
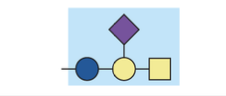
ganglioside
sphingolipid with complex oligosaccharide head group
sphingolipids are under the glycolipid subcategory if they have
sugars but no phosphate attached
3 subclasses of sphingolipids
sphingomyelins
have phosphate attached to a choline as head group
cerebrosides
have one sugar as head group and are glycolipids since no phosphate
gangliosides
have multiple sugars attached but no phosphates, so is a glycolipid
cerebrosides and gangliosides are both classified as glycosphingolipids and are in the brain/nervous system
ex: sphingomyelines form the myelin sheath to insulate neurons
there are many types of sphingolipids
can have one or more sugars attached
each has their polar head group attached to the C3 1-hydroxyl of their sphingosine
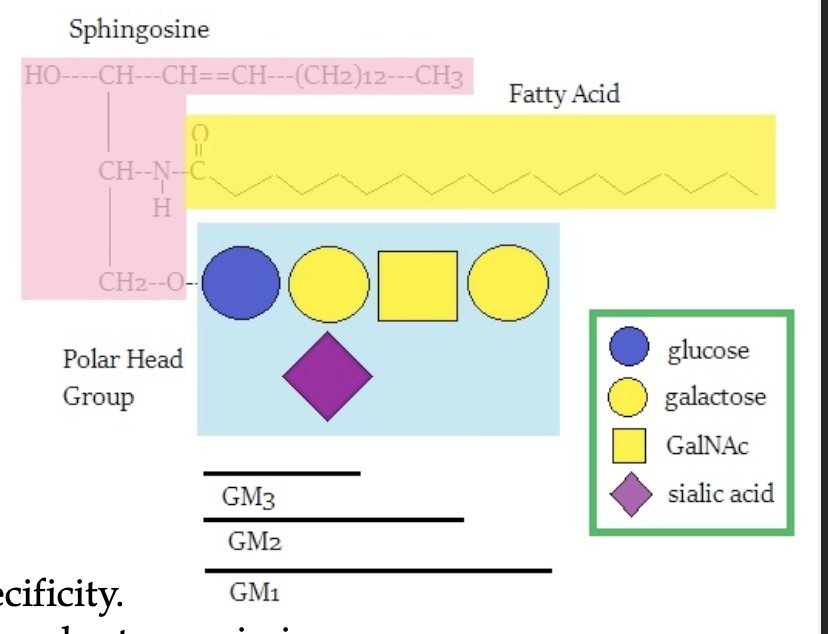
gangliosides
a complex glycosphingolipid
have a ceramide backbone with two or more esterified sugars attached, one of which must be sialic acid
functions in cell-to-cell recognition, tissue immunity, nerve impulse transmission, GM2 builds up in people with Tay-Sachs disease
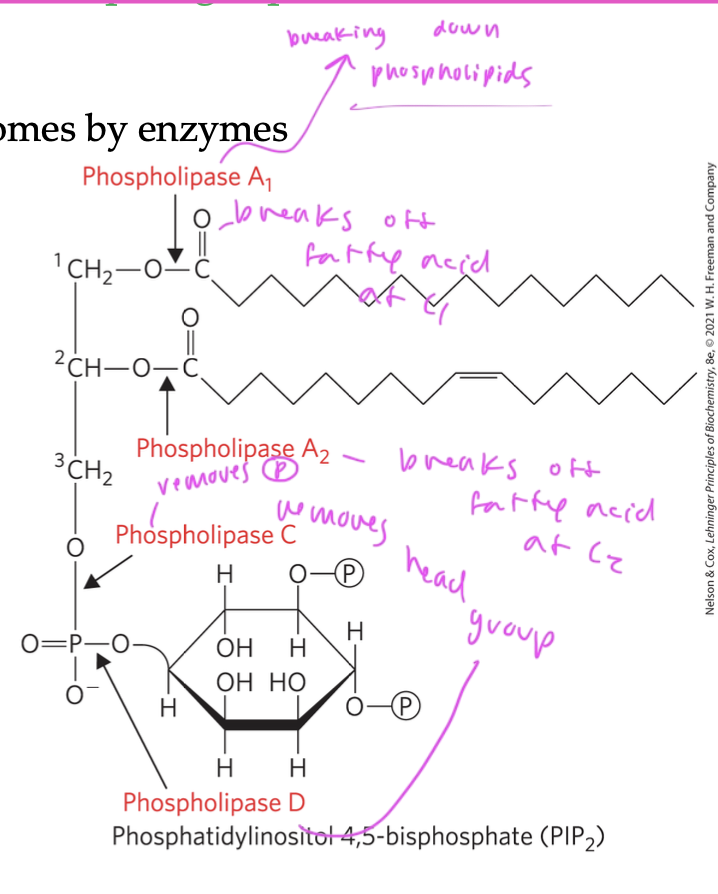
phospholipids and sphingolipids can be degraded by
lipases
enzymes in lysosomes
each hydrolyzable bond in the lipid has its own enzyme that can degrade it, see example on slide how one enzyme removes the head group, one the fatty acid number one, etc
enzymes remove each sugar in a stepwise fashion
defects in lipid homeostasis can lead to
several disease
lysosomal storage diseases
lysosomal storage diseases
a genetic affect that causes accumulation of lipids in cells when gangliosides are not being degraded by lysosomal enzymes properly
this prevents the lysosome from doing its normal function and can be deadly
you need an enzyme to break down each type of sugar in the lipid
isoprene
5 carbon unit
isoprenoids are steroids made up of isoprenes
isoprenoids
steroids made up of isoprenes
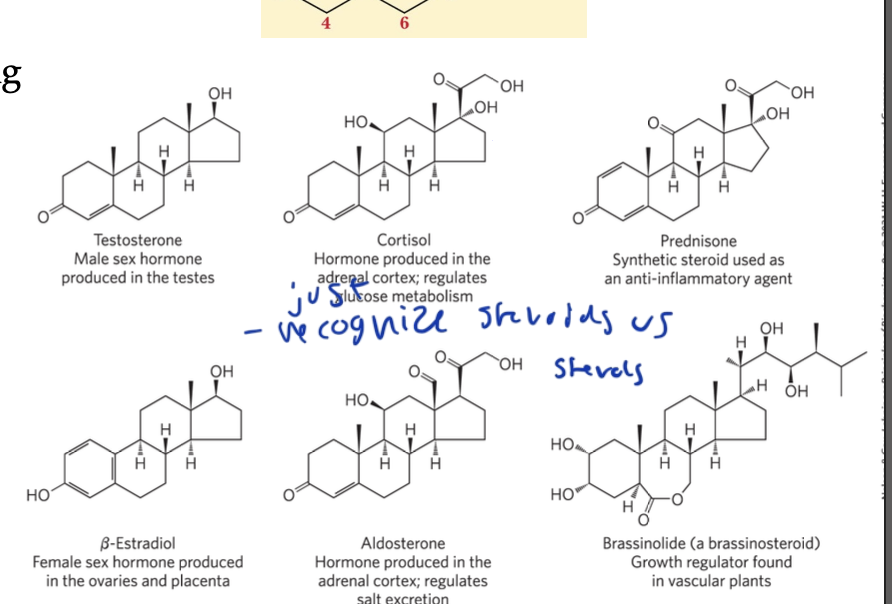
ex of steroid hormones
testosterone
estradiol
cortisol
5 lipid vitamins
A, D, E, K, Q
sterols
subcategory of steroids
terpenes
a diverse group of molecules often recognized by their characteristic flavors, colors, odors
3 types of Eicosanoids
prostaglandins
thromboxanes
leokotrienes
most bacteria cannot synthesize
sterols
but most eukaryotes can
sterol structure
four fused carbon rings that is almost planar forms the main section
has a hydroxyl polar head group off of one ring
has various side chains
see image of cholesterol
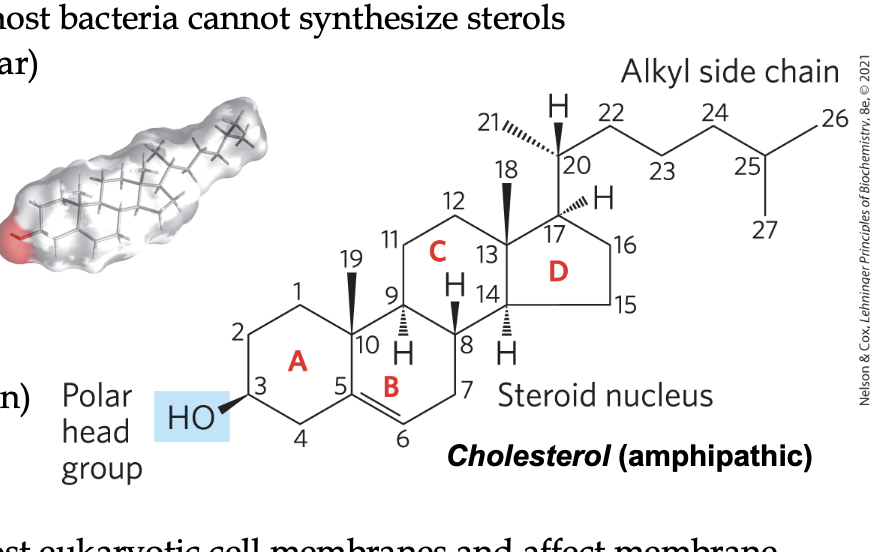
all steroid hormones are derived from
cholesterol
sterols (like cholesterol) affect
membrane fluidity
if there are more sterols between unsaturated fatty acid chains in a membrane, fluidity of the membrane
decr, since the sterols incr the VDWs forces of the unsaturated fatty acids
if there are more sterols between saturated fatty acid chains in a membrane, fluidity of the membrane
incr, since sterols disrupt the VDWs between saturated fatty acid chains
_____ are isoprene/terpene based lipids
steroid hormones
steroid hormones
oxidized derivatives of sterols
have sterol structure but with shorter/no side chains and more oxygens bound
steroid hormones are signalers that travel through the blood on protein carriers. They bind to nuclear receptors of trigger gene expression changes
terpenes
have multiple isoprene structures, each of 5 carbon units, but have conjugated double bonds, which absorb visible light
so multiple isoprenes with conjugated pi bonds together in a single molecule
recognized for their odor/bright color/flavor (pigments)
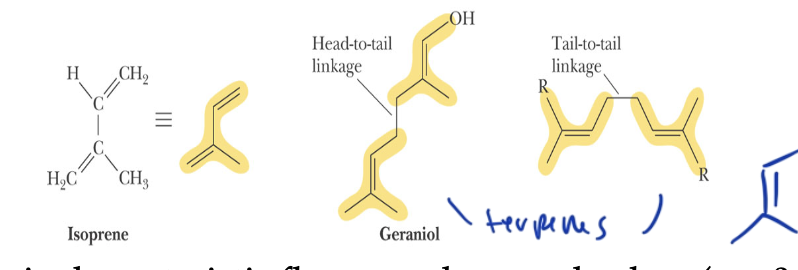
more isoprenes in a molecule means the ____ is longer
terpene
vitamin A
aka retinol
is a terpene
20 carbon hormone
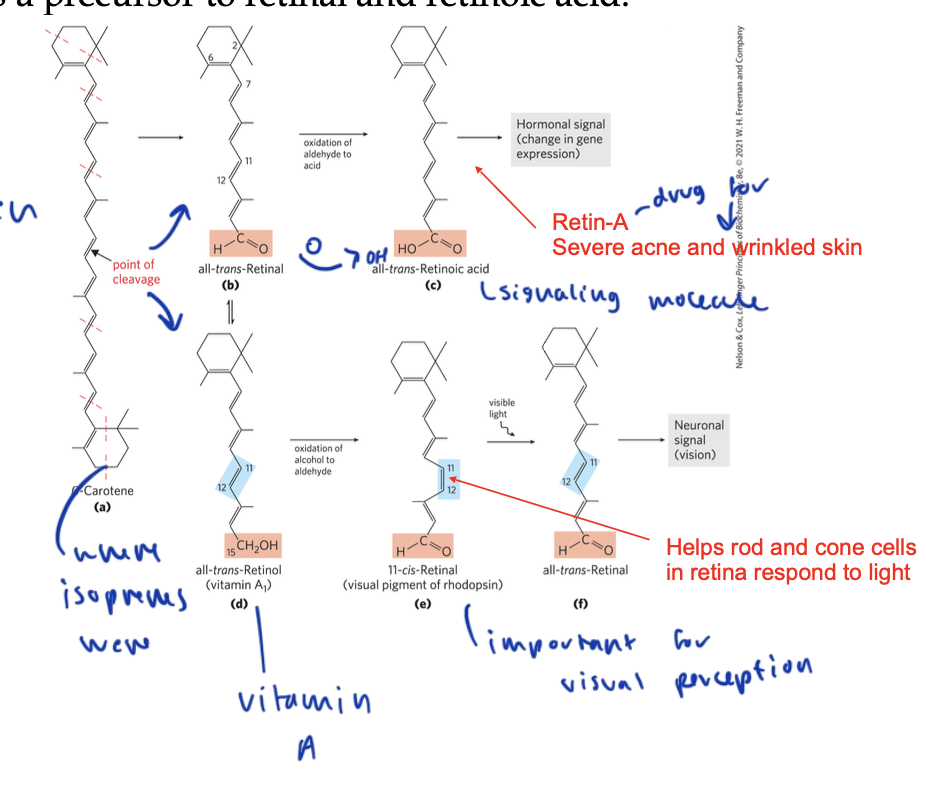
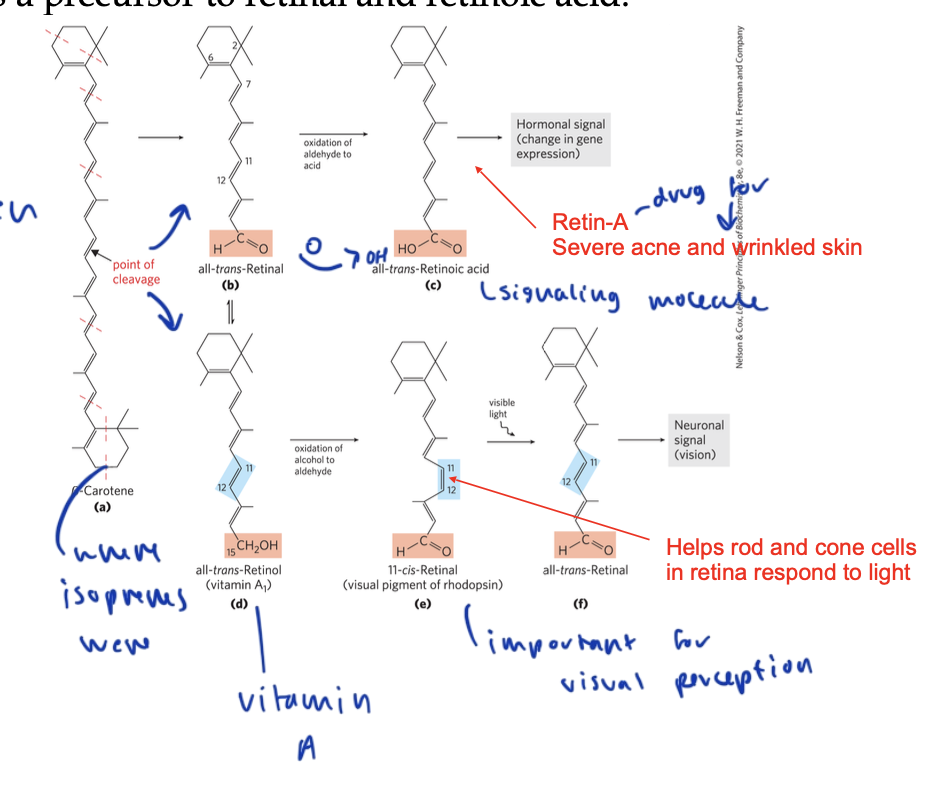
its predecessor is beta-carotene, which splits to form two retinols, (which are vitamin A) which can form retinoic acid (which regulates gene expression in skin development) or 11-cis retinal, which is used for vision
its derivative 11-cis retinol is used for visual perception and helps rod and cone cells in the retina respond to light
the derivative Retin-A is used to treat severe acne and wrinkled skin
all vitamins structure
one ring with a long hydrocarbon chain OR
two rings with a long hydrocarbon chain in between them
lipid vitamins
A, D, D3, E, K, Q
cannot be made in the body, so require a proper diet to be obtained
ADEK are all fat soluble
vitamin A is found in
fish oils, liver, eggs, whole milk, butter
people developed rice that expresses beta-carotene so that people do not become vitamin A deficient (since beta-carotene cleaves to form vitamin A)
deficiency causes dry skin and eyes, delayed development, and night blindness
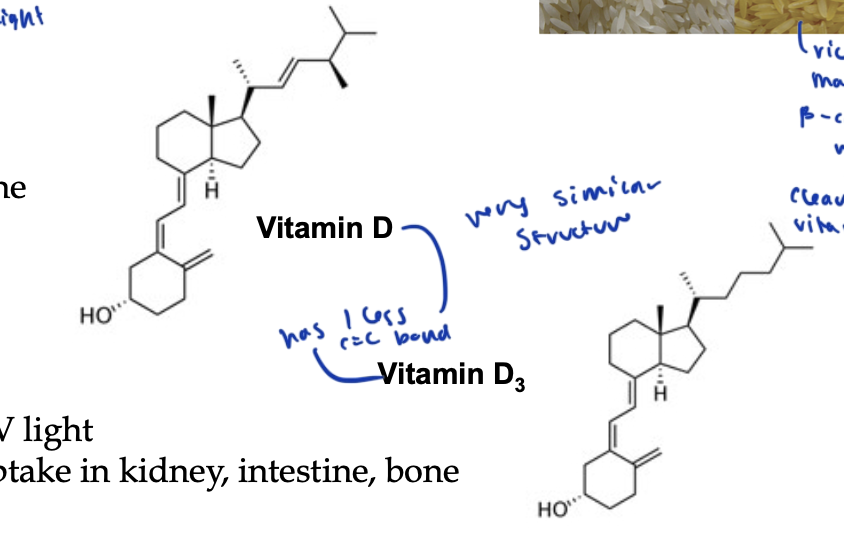
vitamin D is found in
milk, butter
deficiency causes defective bone formation or rickets
vitamin D3 is found in
when we get UV light from the sun
regulates metabolism of calcium uptake in the kidneys, intestine, and bone
what is the only difference between Vitamin D and D3 structure?
D3 has one less double bond
vitamin E
destroys oxygen radicals (which are harmful)
found in eggs, oil, wheat germ
is an antioxident
deficiency causes scaly skin and muscle weakness
vitamin K
helps blood clot
deficiency slows blood clotting
K1 cofactor is found in green plant leaves
Vitamin Q / ubiquinone
used as e- carrier in the ETC of ATP synthesis in mitochondria and chloroplasts
aka coenzyme Q
eicosanoids
lipids that act as paracrine hormones/ signaling molecules
parent compound is arachidonic acid, which is just one chain of a phospholipid, which gets cleaved to form each subcategory of eicosanoids
includes prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leokotrienes
different enzymes modify arachidonic acid to form the three subcategories
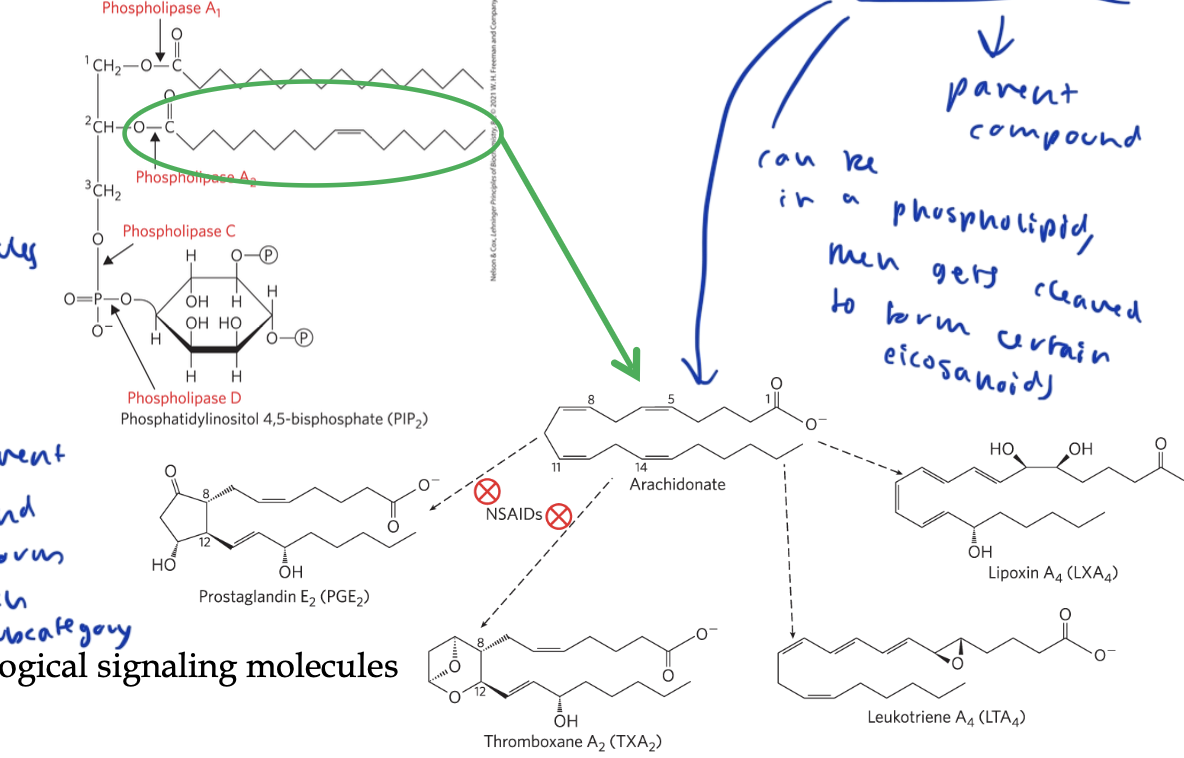
arachidonic acid
a chain in a phsopholipid that gets cleaved to form the eicosanoids
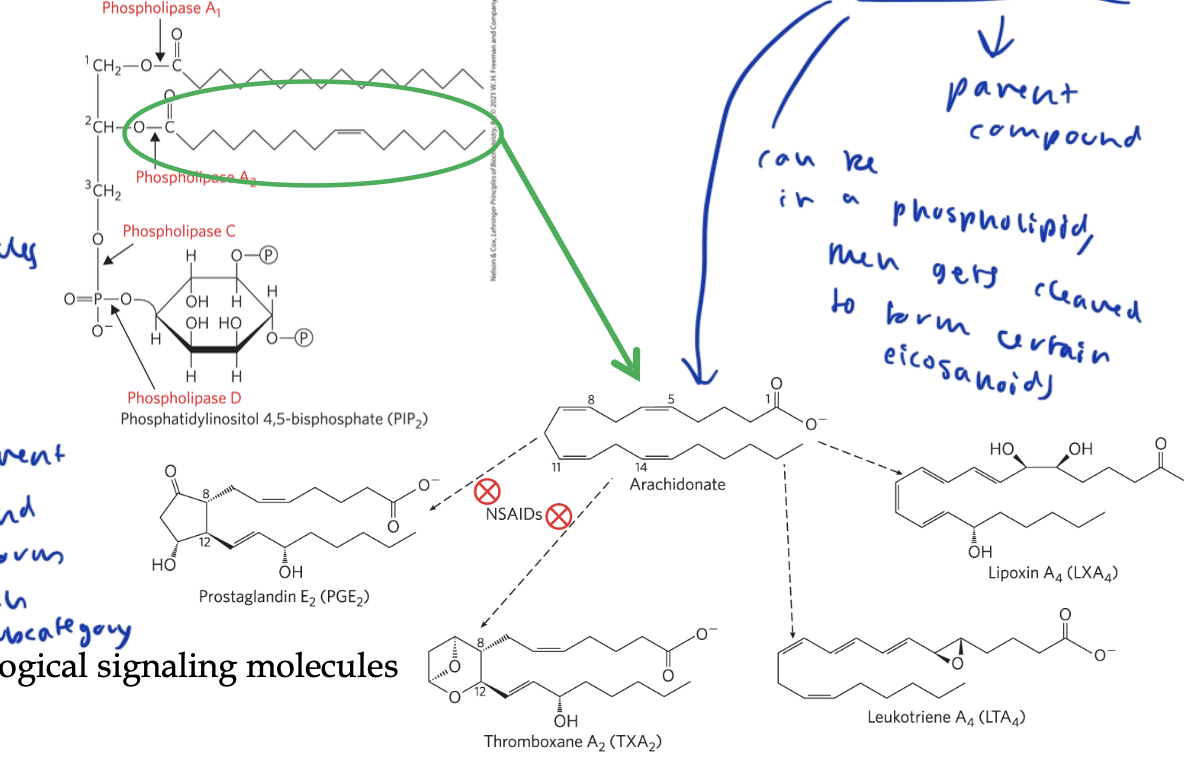
prostaglandins
an eicosanoid that contains a 5 carbon ring
stimulate smooth muscle, elevates blood, uterine contractions, part of inflammatory response, pain reception
thromboxanes
an eicosanoid that contains a 6 carbon ring with an ether
produced by platelets for blood clotting
NSAIDS
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
treat the inflammatory response by inhibiting COX enzymes, which are what break apart arachidonic acid to form prostaglandins and thromboxanes
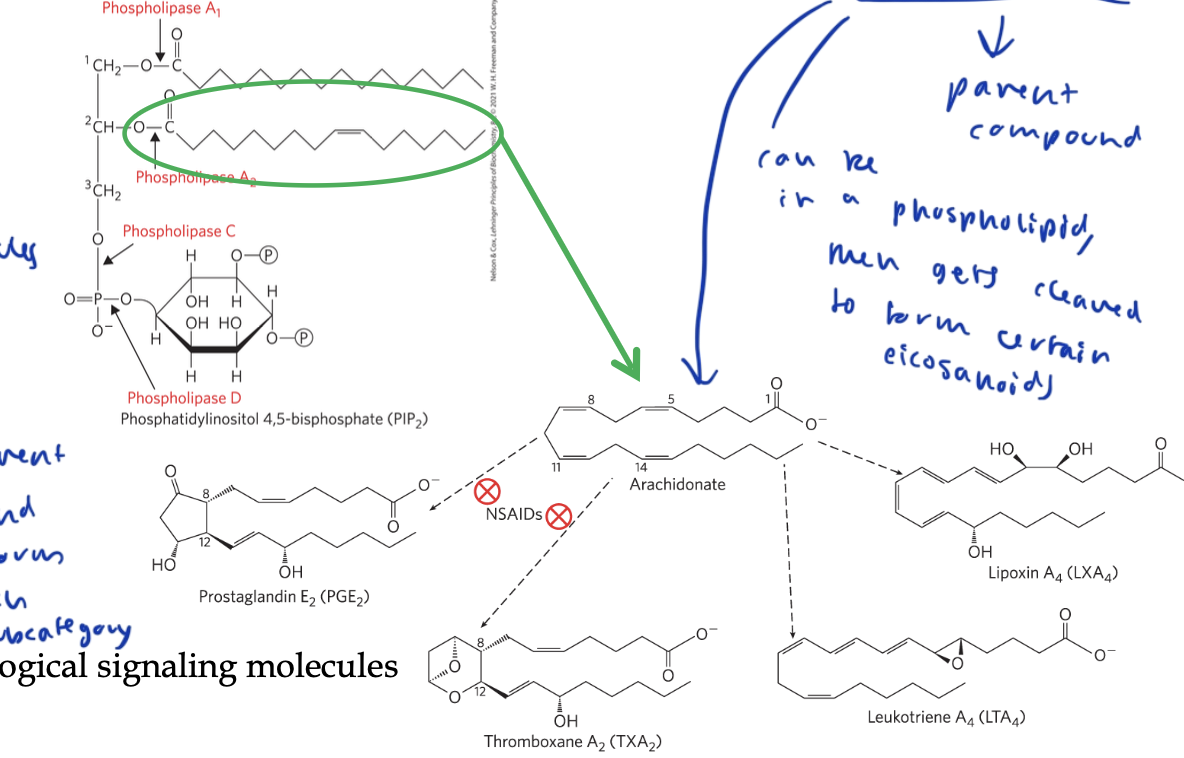
leukotrienes
eicosanoids formed of 3 conjugated double bonds
trigger smooth muscle contraction in the airway, which can trigger anaphylaxis
predisone targets the enzyme that breaks down arachidonic acid into leokotriene to reduce the effects of possible anaphylaxis/ airway contraction
know this chart
main role of sphingolipids
cell recognition
since their sugars are easily detected on the cell surface
cholesterol is the precursor for
steroid hormones
cholesterol is also a membrane lipid