Water experiments
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
To determine Total Suspended Solids (in p.p.m.) in a Water Sample via Filtration. To determine Total Dissolved Solids (in p.p.m.) in a Water Sample via Evaporation. To Measure the Amount of Free Chlorine in Swimming Pool Water Using a Comparator / Colorimeter
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Describe how the concentration of suspended solids in Sample A of swimming pool water could have been measured
Known volume of water sample //
through filter paper //
of known mass //
dry in an oven //
find new mass of filter paper and residue
Calculation - 2015 Q3 part b)
[ remember 1p.p.m. = 1mg / L ]
What solution was titrated against a known volume of Sample C (swimming pool water) to determine its total hardness?
EDTA / ethylenediamenetetraacetic acid
When some of Sample C was boiled, filtered, and re-analysed for hardness, the result was 175 p.p.pm.
Suggest a reason why the second result was significantly lower than the first, 220 p.p.m.?
Temporary hardness removed / only permanent hardness remaining
Identify a reagent used to detect free chlorine in a water sample
DPD (diethylphenylenediamine) /
KI (potassium iodide) and H+
Describe how a comparator or a colorimeter could have been used to estimate the concentration of free chlorine in Sample D of swimming pool water
Comparator
Add reagent (DPD) /
stir (dissolve, mix) /
compare colour with chart /
read concentration (ppm)
Colorimeter
Prepare standard solutions of reagent /
note colorimeter readings /
plot graph of concentration versus reading (absorbance) /
read concentration (p.p.m.)
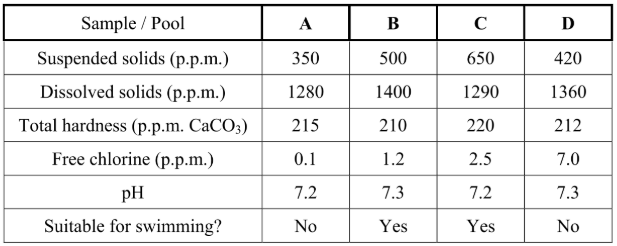
Which of the test results led to pools A and D being considered unsuitable for swimming?
Free chlorine
What problem might arise for swimmers in
i) pool A.
ii) pool D?
i) Infection / microorganisms
ii) taste / smell / nausea / eye (skin) irritation / skin burning / breathing problems
What is the general principle of all colorimetric experiments?
Intensity of colour / absorbance / transmittance //
proportional to concentration
Identify a suitable reagent to test for free chlorine in swimming pool water and state the colour which develops when this reagent reacts with free chlorine
KI (potassium iodide) → brown / red /
DPD tablet → pink
Give the name or formula of a free chlorine species in swimming pool water.
Chlorine (Cl2, dichlorine)
Give a reason why the concentration of free chlorine in treated drinking water is usually between 0.2-0.5 p.p.m. whereas in swimming pool water it should be between 1-5 p.p.m.
Greater concentration needed to kill pathogens added by swimmers /
drinking water has much fewer pathogens /
drinking water is less contaminated
swimming pool water more contaminated
would be dangerous to drink / bad taste
Calculation 2006 Q3 part e)