Micro Chapter 20: Antimicrobial Drugs
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Alexander Fleming
Antimicrobial Drugs
In 1928, this man saw that a fungal colony of Penicillium contaminated his agar plate and resulted in the inhibition of bacterial growth.
1940
Antimicrobial Drugs
The year the first clinical trails of penicillin begins.
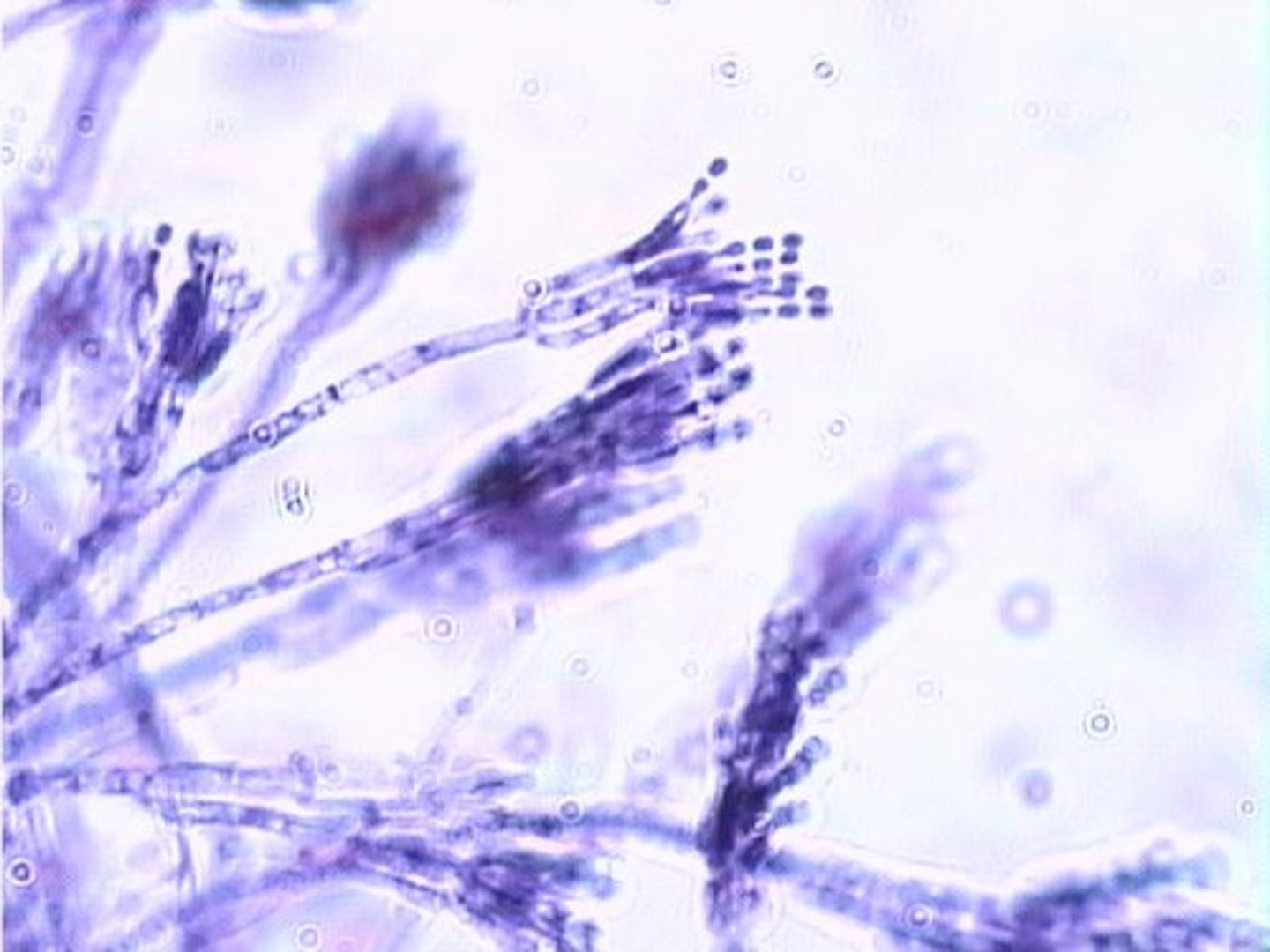
Penicillium chrysogenum
Representative Sources of Antibiotics
The fungi that produce penicillin
selective toxicity
Features of Antimicrobial Drugs
Means we want to kill the microbe without harming the host, which is difficult to achieve.
bacteriostatic
Features of Antimicrobial Drugs
Antimicrobial action in which the microbe will be inhibited from growing.
bactericidal
Features of Antimicrobial Drugs
Antimicrobial action in which the microbe will be killed.
broad spectrum
Features of Antimicrobial Drugs
Antimicrobial action in which drugs can affect many different organisms, such as affecting Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
narrow spectrum
Features of Antimicrobial Drugs
Antimicrobial action in which drugs only affect a few types of microorganisms.
half-life
Features of Antimicrobial Drugs
Tissue distribution and metabolism of antimicrobial drugs is measured as this.
intrinsic
Microbial Resistance
Means the drug has no effect on the body.
intrinsic
Microbial Resistance
Penicillin has no effect on viruses. This is an example of which microbial resistance?
acquired
Microbial Resistance
Resistance due to mutations or new genetic elements.
acquired
Microbial Resistance
Microorganisms gaining an R (resistance)-factor plasmid via transformation, conjugation, or transduction is an example of which microbial resistance?
blocking, inactivation, alteration, efflux
Microbial resistance
Fill in the blank:
Mechanisms of microbial resistance:
1. __________ entry
2. _______________ by enzymes
3. _______________ of target molecule
4. __________ of antibiotic
porins
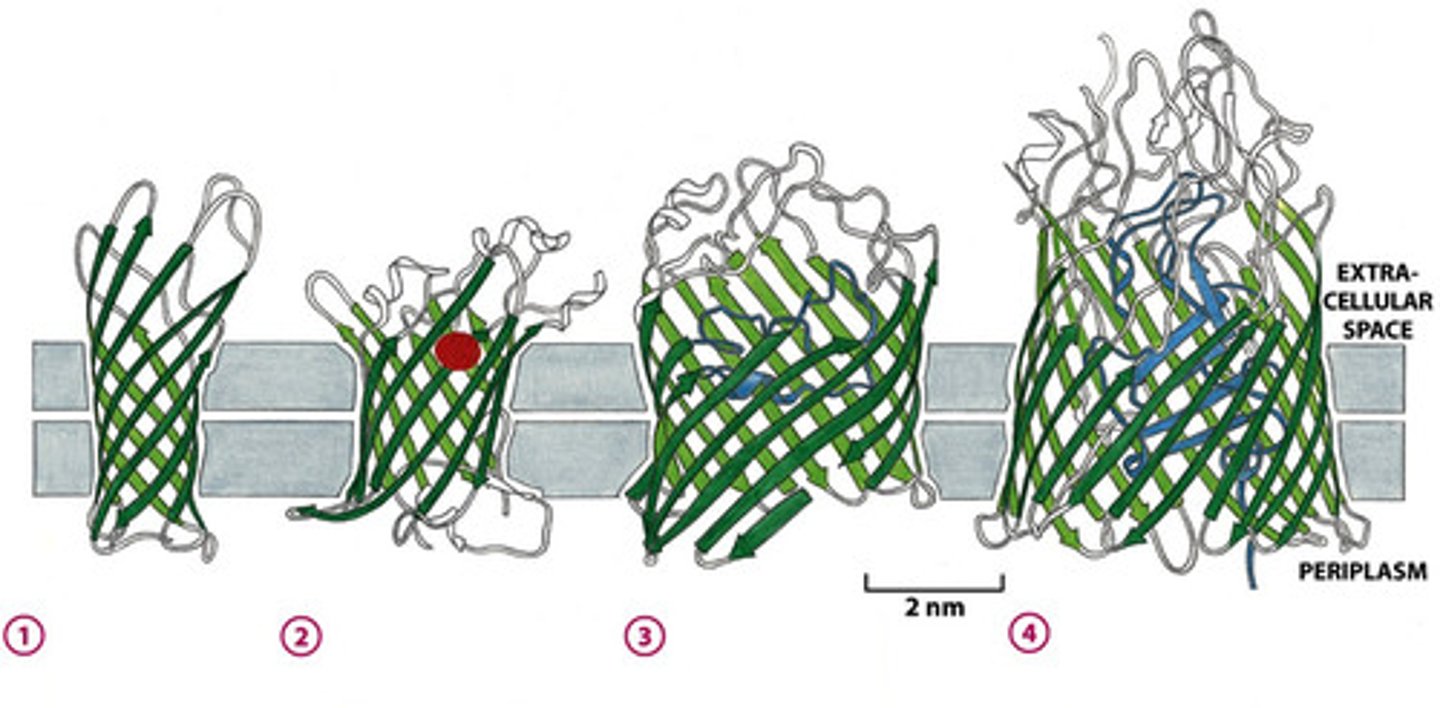
How Can Microbes Become Resistant?
Some bacteria can contain these proteins in their cell walls to block entry.
beta-lactamase
How Can Microbes Become Resistant?
Some bacteria can inactivate the central rings of penicillins with which enzyme?
protease
How Can Microbes Become Resistant?
HIV can alter the shape of this enzyme when targeted by an antimicrobial drug, thus altering the target molecule.
tetracycline
How can microbes become resistant?
Some bacteria such as Pseudomonas have a resistance (R) mechanism of pumping this antibiotic out of their cells, thus can undergo efflux of antibiotics.
Pseudomonas
How can microbes become resistant?
Name a bacteria genus that contains efflux (R) pumps.
prescribing, education
Approaches for prevention and control of antibiotic resistance
Fill in the blank:
Physicians and other health care workers must exercise proper ___________ practices and provide patient __________.
select for resistance
Approaches for prevention and control of antibiotic resistance
When patients fail to follow instructions for antibiotic dosing, they often need to take it again, which helps the pathogen do what?
limitations
Approaches for prevention and control of antibiotic resistance
Fill in the blank:
The public needs to understand the ___________ of antibiotics. For example, they cannot be taken when you have the cold or flu.
antibiotics
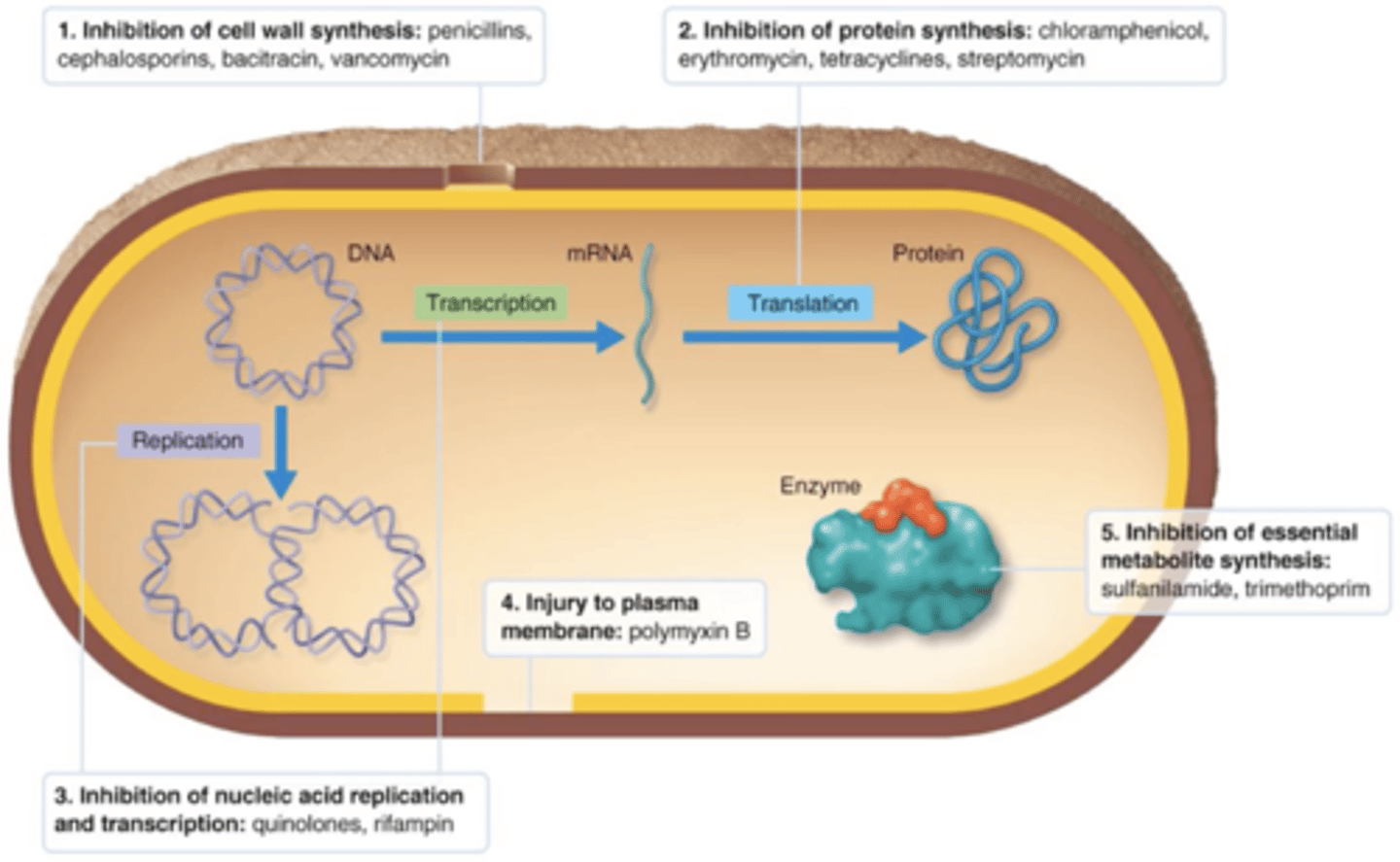
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs
Antimicrobial drugs that can do 1 or more of the following:
1. Inhibit cell wall synthesis
2. Inhibit protein synthesis
3. Injure the plasma membrane
4. Inhibit synthesis of essential metabolites (metabolic pathways) such as in transcription or translation
penicillins
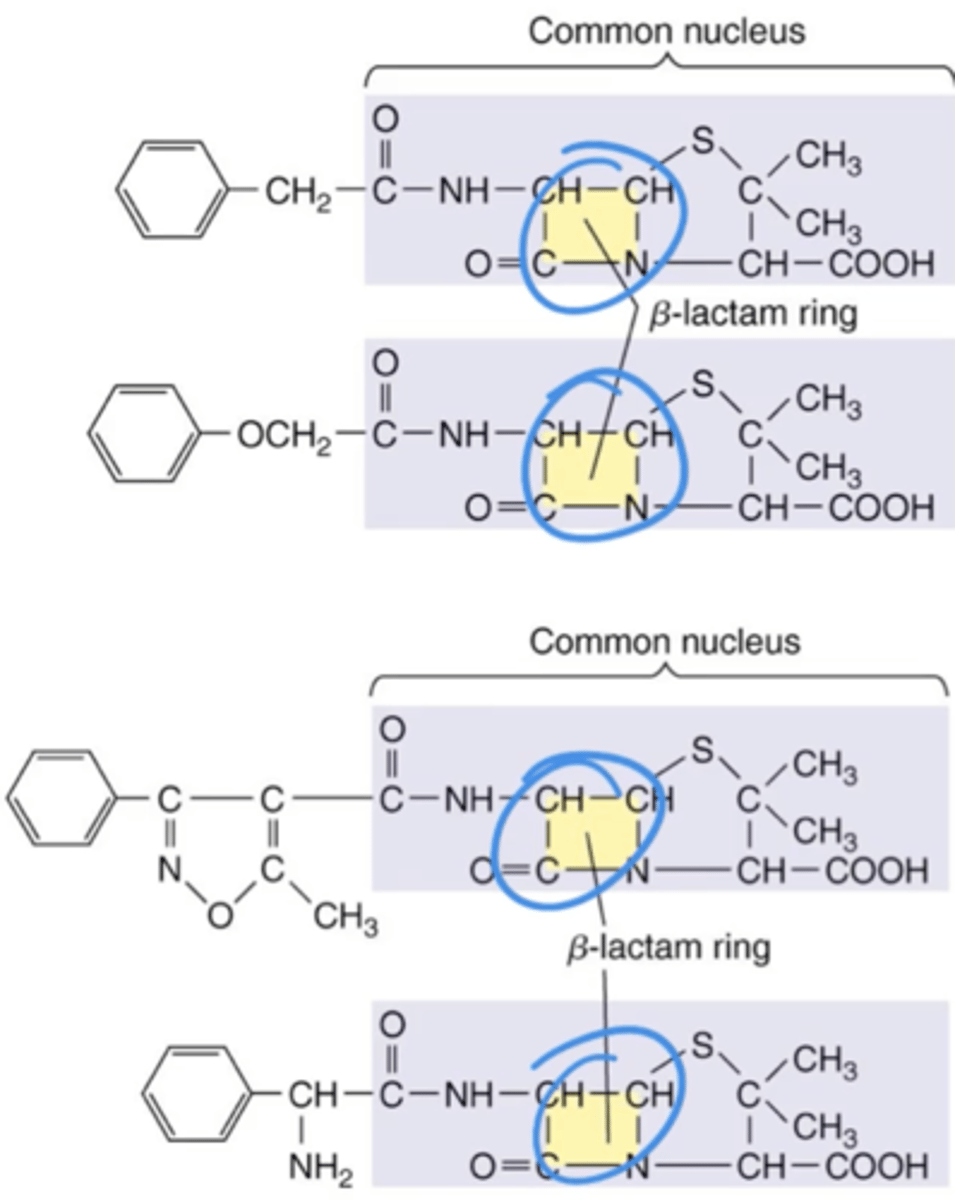
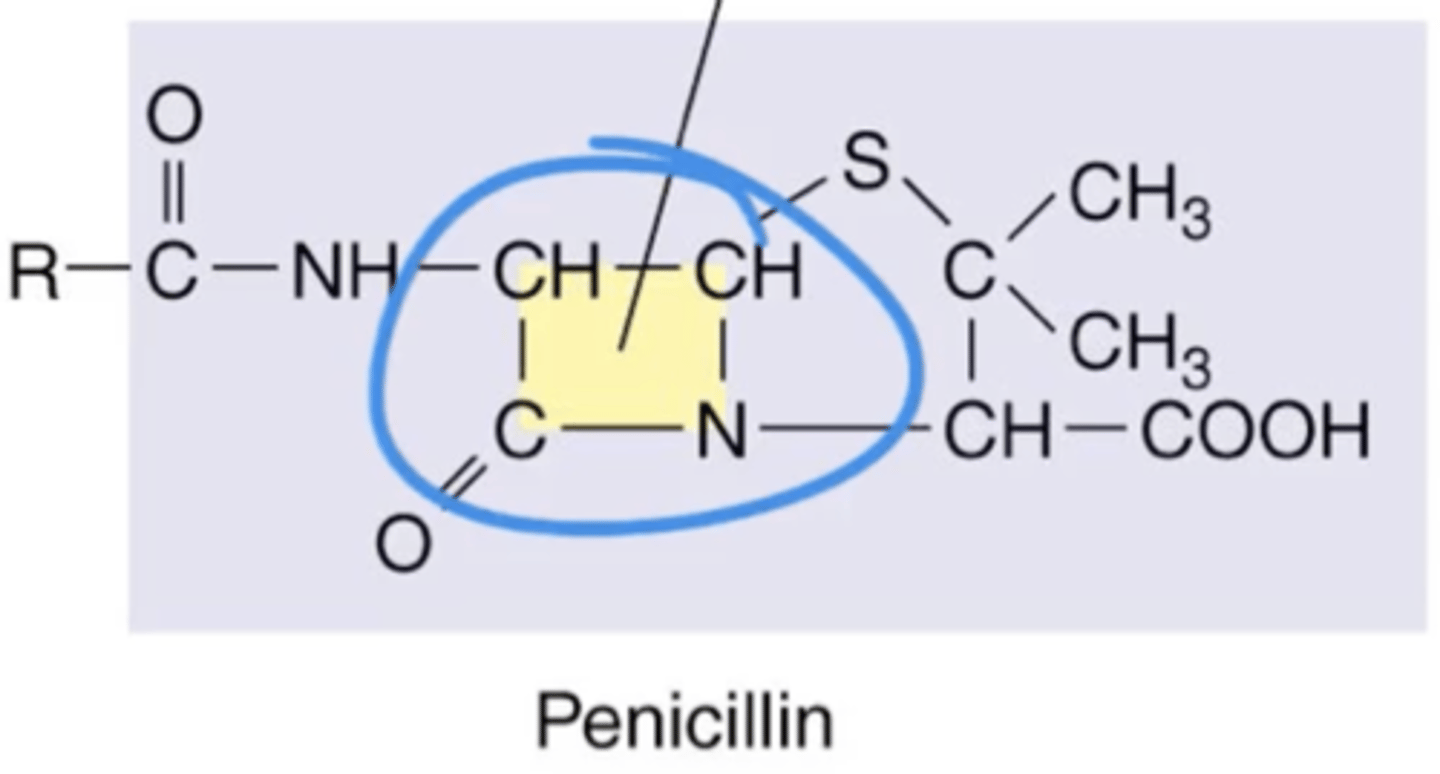
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs
Antibiotics that inhibit peptidoglycan synthesis. Contain central structures called beta-lactam rings. 2 types:
1. Natural
2. Semisynthetic
penicillins
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs
Antibiotics that inhibit cell wall synthesis. 2 types:
1. Natural
2. Semisynthetic
beta-lactams (beta-lactam drugs)
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
Penicillins are also called?
Gram-positive
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
Which bacteria are more susceptible to penicillins?
narrow
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
If penicillins target Gram-positive bacteria, are the drugs narrow or broad-spectrum?
natural
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
Penicillins produced by Penicillium. Include:
- Penicillin G
- Penicillin V
beta-lactamase (penicillinase)
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
Some bacteria are resistant to penicillin because they can produce which enzyme?
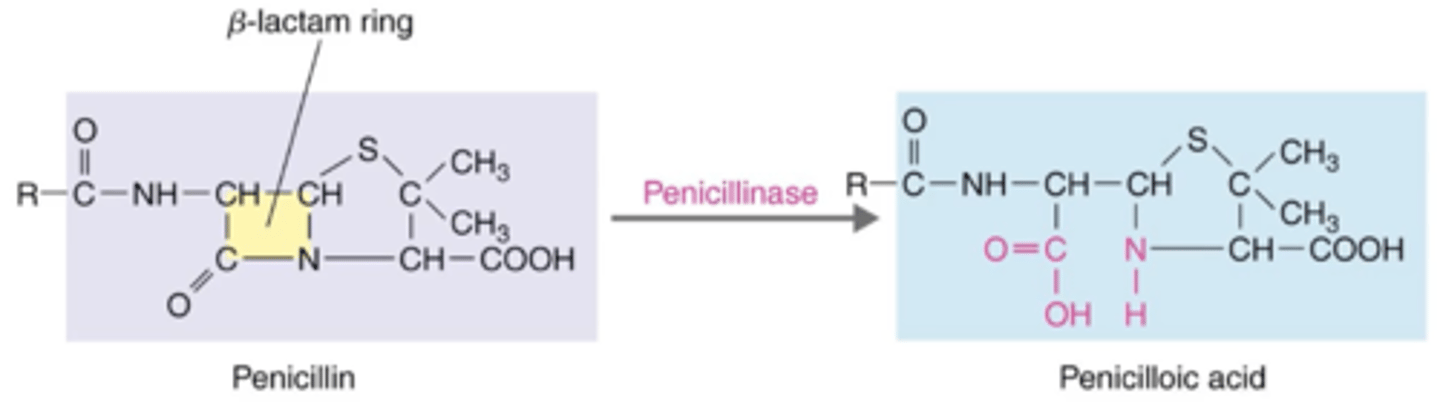
penicillinase
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
Beta-lactamase is also called?
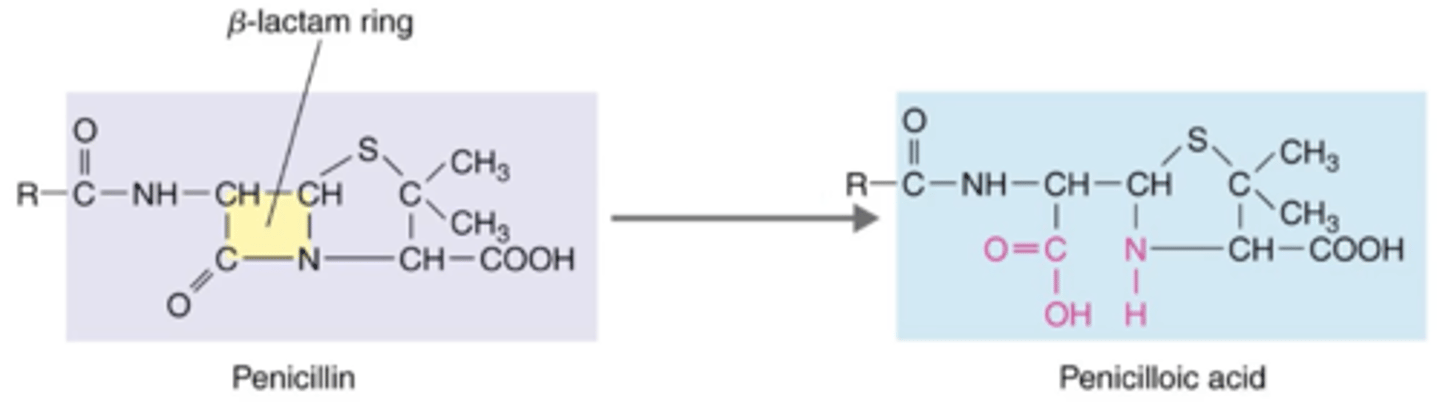
breaks beta-lactam rings (of penicillin)
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
What is the mode of action of beta-lactamase?
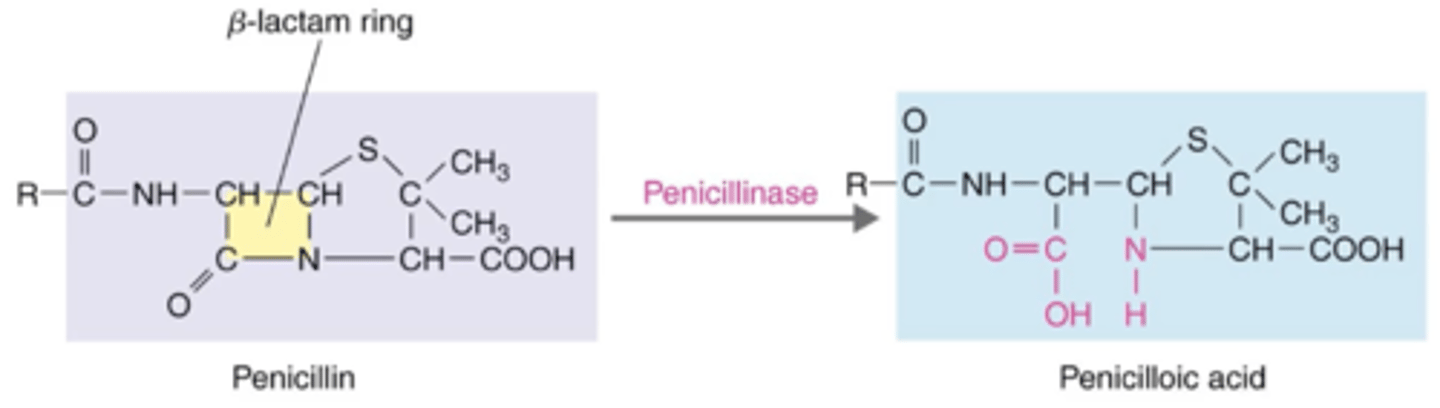
exoenzyme
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
What kind of enzyme is beta-lactamase (penicillinase)?
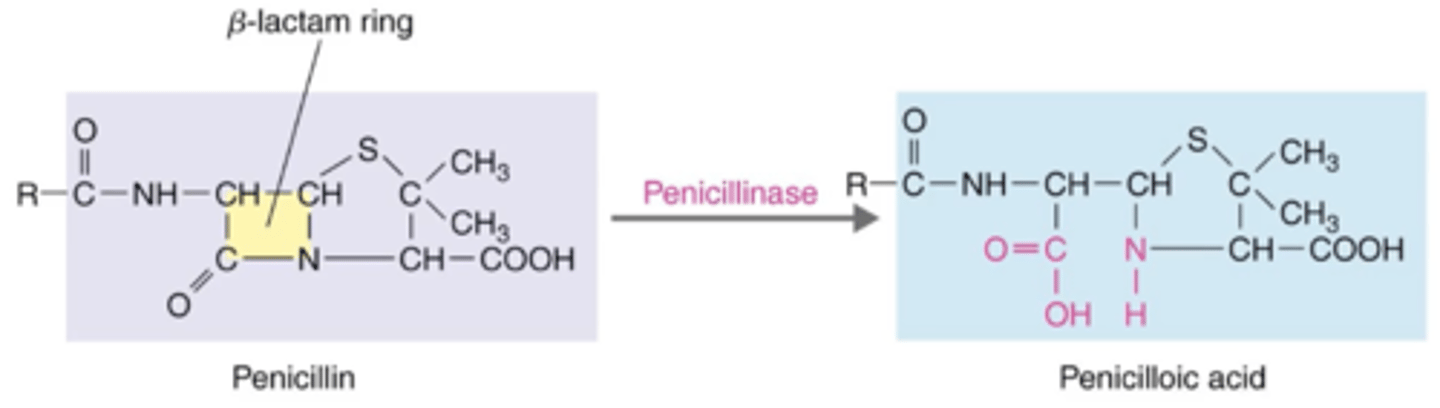
semisynthetic
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
Penicillins that were modified and produced in a lab to provide resistance to beta-lactamase or provide extended spectrum. Include:
- Methicillin (resists beta-lactamase)
- Ampicillin (extended)
- Amoxicillin (extended)
methicillin
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
Name 1 semisynthetic penicillin that is resistant to beta-lactamase
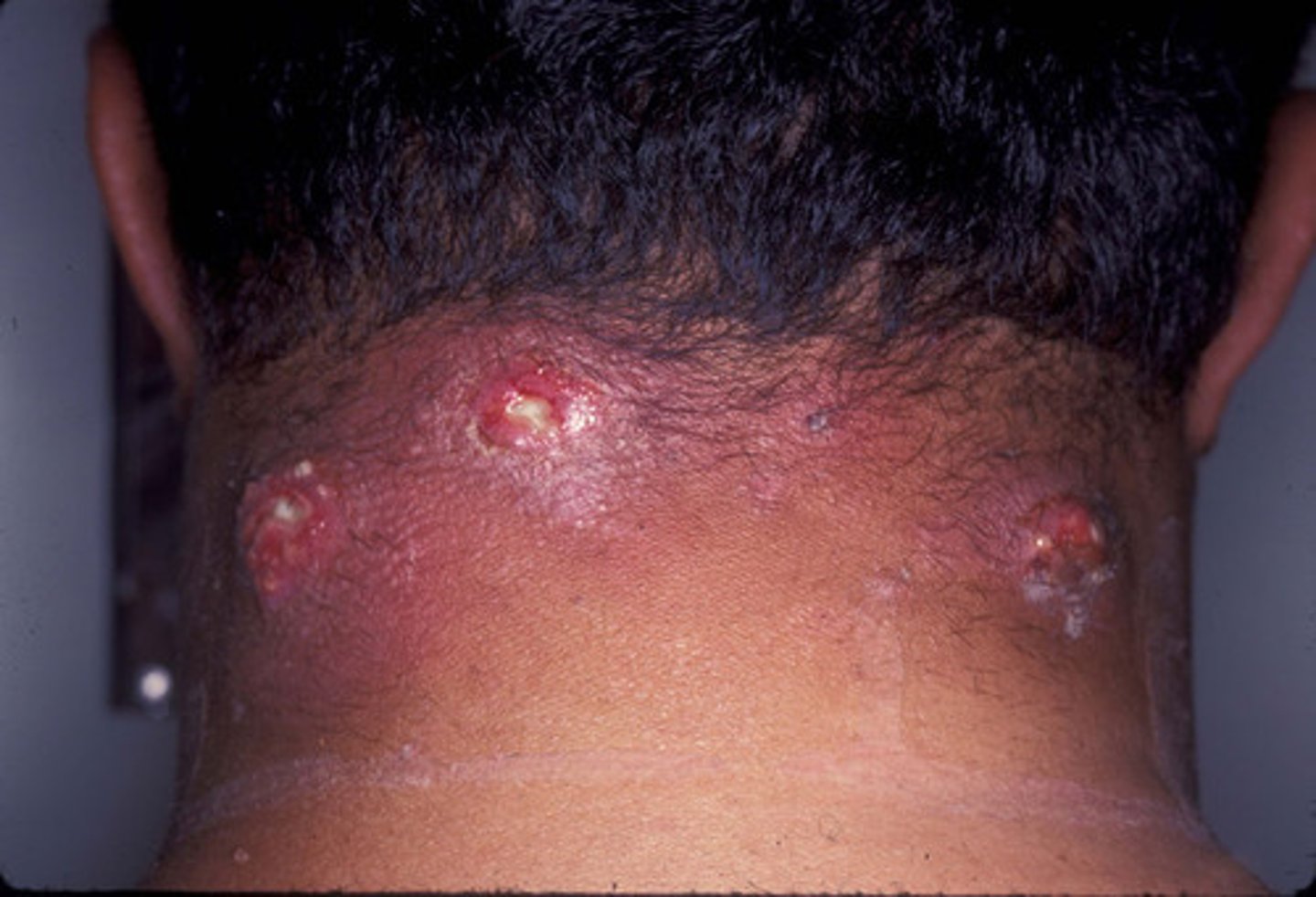
Staphylococcus aureus
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
Which bacteria can develop resistance to semisynthetic penicillin methicillin?
MRSA
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is commonly called?
ampicillin, amoxicillin
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
Name 2 extended-spectrum semisynthetic penicillins that also target Gram-negative bacteria.
broad
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
If ampicillin and amoxicillin target Gram-positive and negative bacteria, are the drugs narrow or broad-spectrum?
beta-lactamase inhibitors
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
Penicillins are often prescribed along with these drugs to provide drug synergism. E.g., clavulanic acid.
beta-lactamase inhibitor (non-competitive)
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
Clavulanic acid is an example of what kind of drug?
non-competitive
Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis (Penicillins)
What kind of enzyme inhibitor is clavulanic acid?
beta-lactam ring
Other Antibiotics that Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis
Some beta-lactam antibiotics like cephalosporins act similarly to penicillins, but have a different type of what?
vancomycin
Other Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis
A polypeptide antibiotic that is used to treat methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
antimycobacterials
Other Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis
These drugs specifically target mycolic acid. Include:
- Isoniazid (INH), which inhibits mycolic acid synthesis
- Ethambutol, which inhibits integration of mycolic acid in the cell wall
isoniazid (INH), ethambutol
Other Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis
Name 2 antimycobacterials; antibiotics effective against Mycobacterium.
inhibits mycolic acid synthesis
Other Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis
How does isoniazid (INH) work against mycolic acid?
inhibits integration of mycolic acid in the cell wall
Other Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis
How does ethambutol work against mycolic acid?
70S
Antibiotics That Inhibit Protein Synthesis
What kind of ribosomes do bacteria have?
80S
Antibiotics That Inhibit Protein Synthesis
What kind of ribosomes do eukaryotes have?
chloramphenicol
Antibiotics That Inhibit Protein Synthesis
- Binds to 50S ribosomes, thus inhibits peptide bond formation
- Broad-spectrum
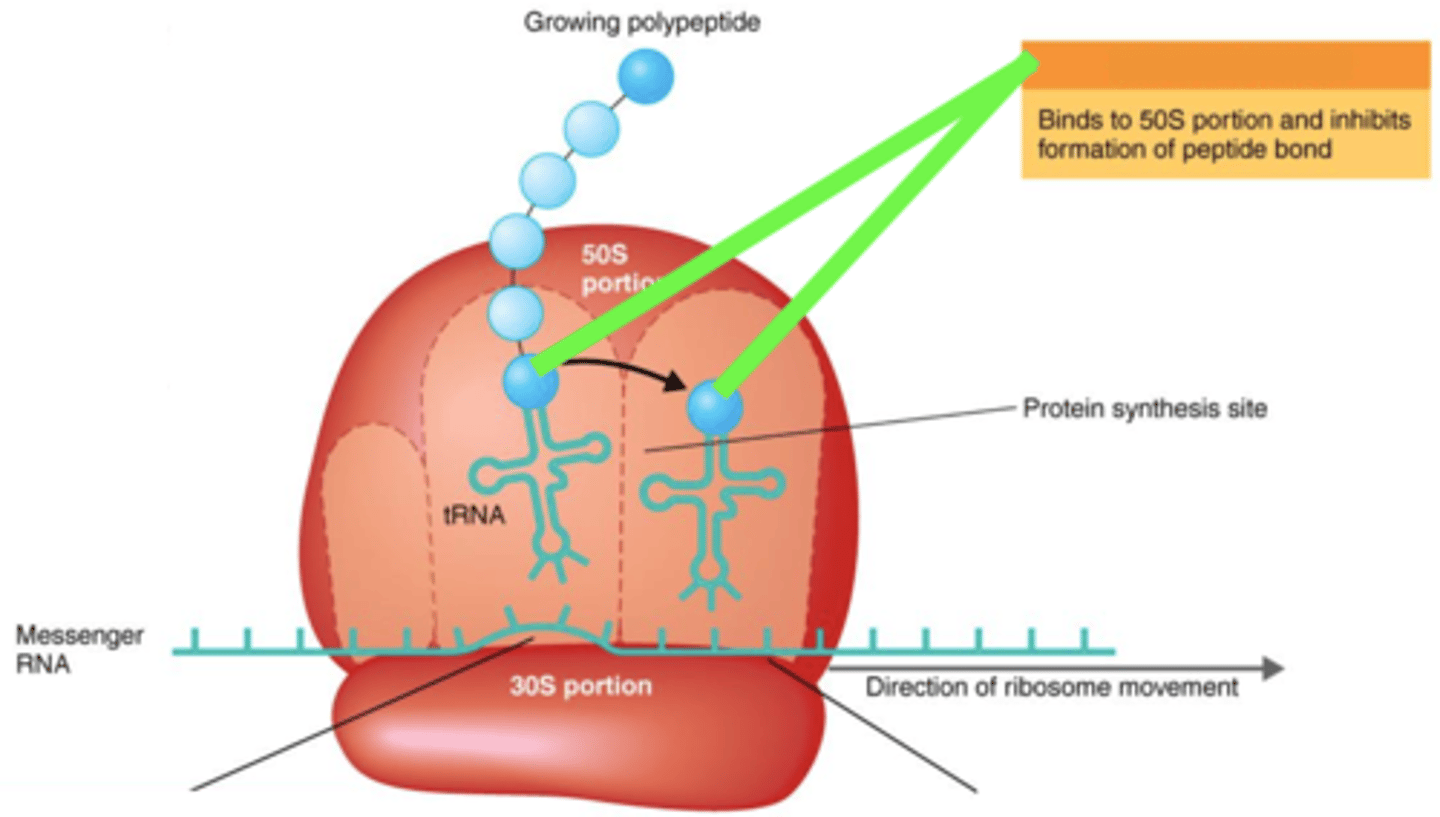
protein synthesis
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs
Actions of chloramphenicol, streptomycin, tetracycline, and erythromycin damage what?
streptomycin
Antibiotics That Inhibit Protein Synthesis
- Binds to 30S ribosomes, thus causing mRNA to be read incorrectly; an aminoglycoside
- Broad-spectrum
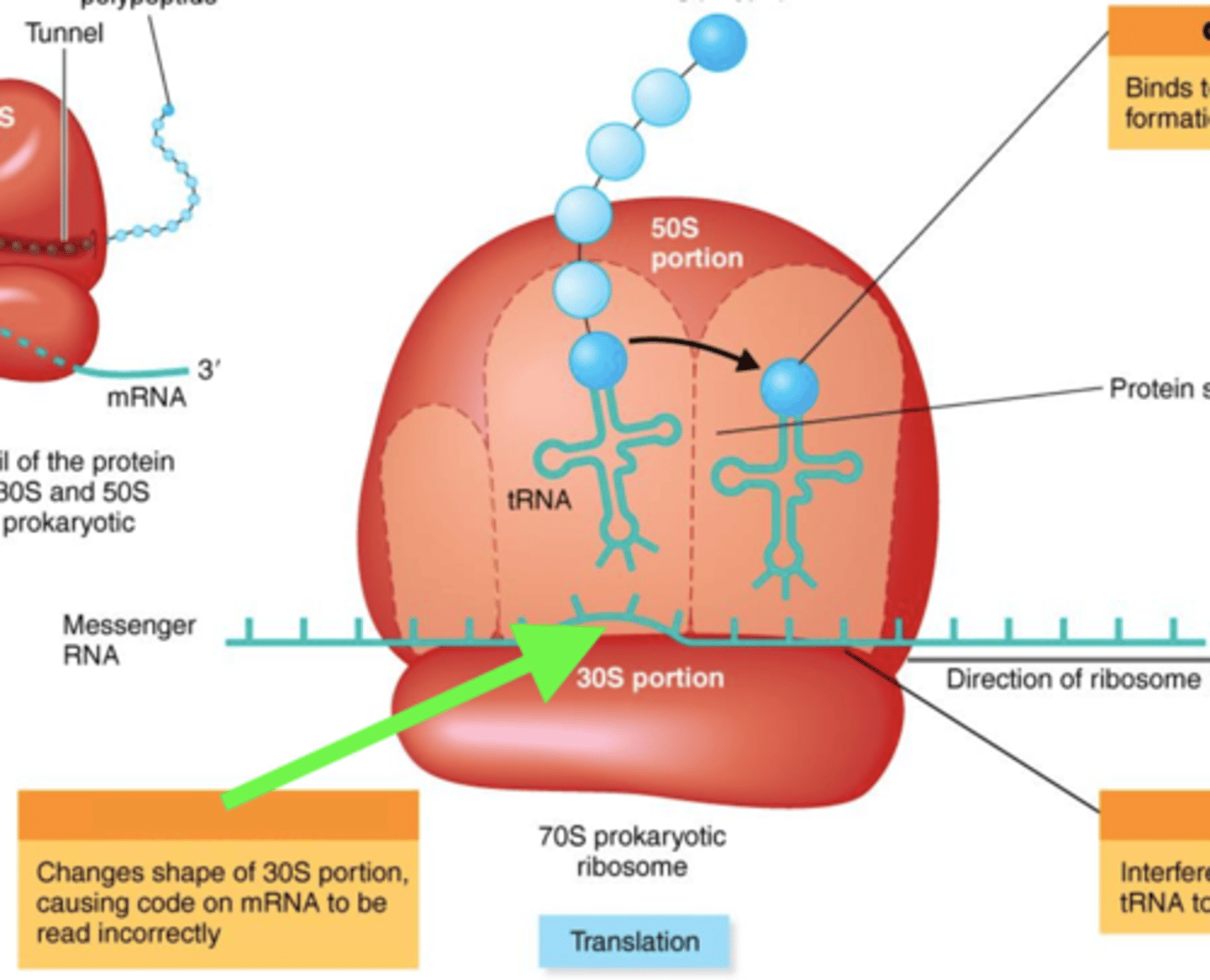
tetracycline
Antibiotics That Inhibit Protein Synthesis
- Binds to 30S ribosomes, thus blocking incoming tRNA from binding to mRNA
- Broad-spectrum
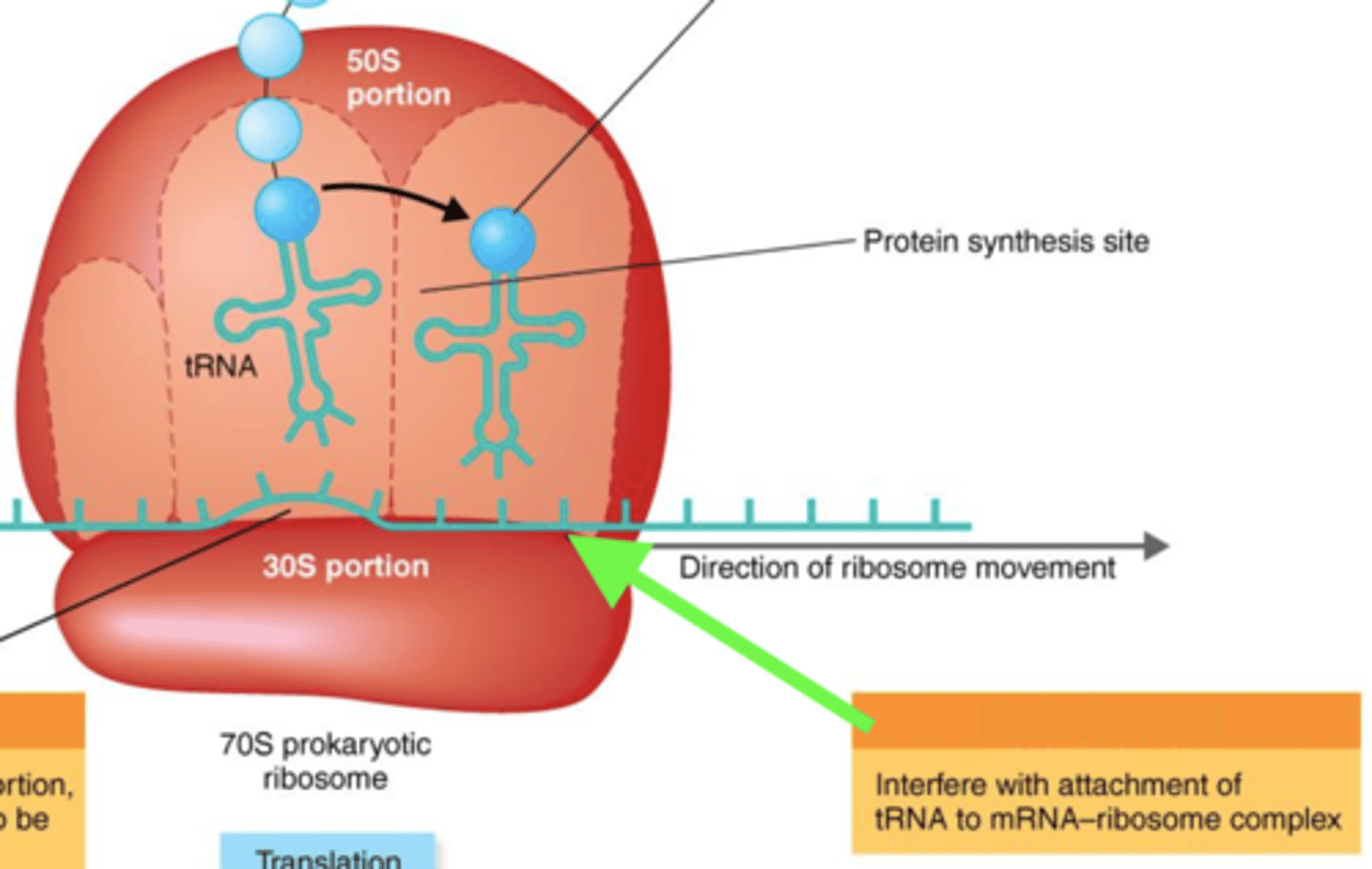
erythromycin
Antibiotics That Inhibit Protein Synthesis
- Binds 50S ribosomes, thus blocking continuation of protein synthesis; a macrolide
- Broad-spectrum
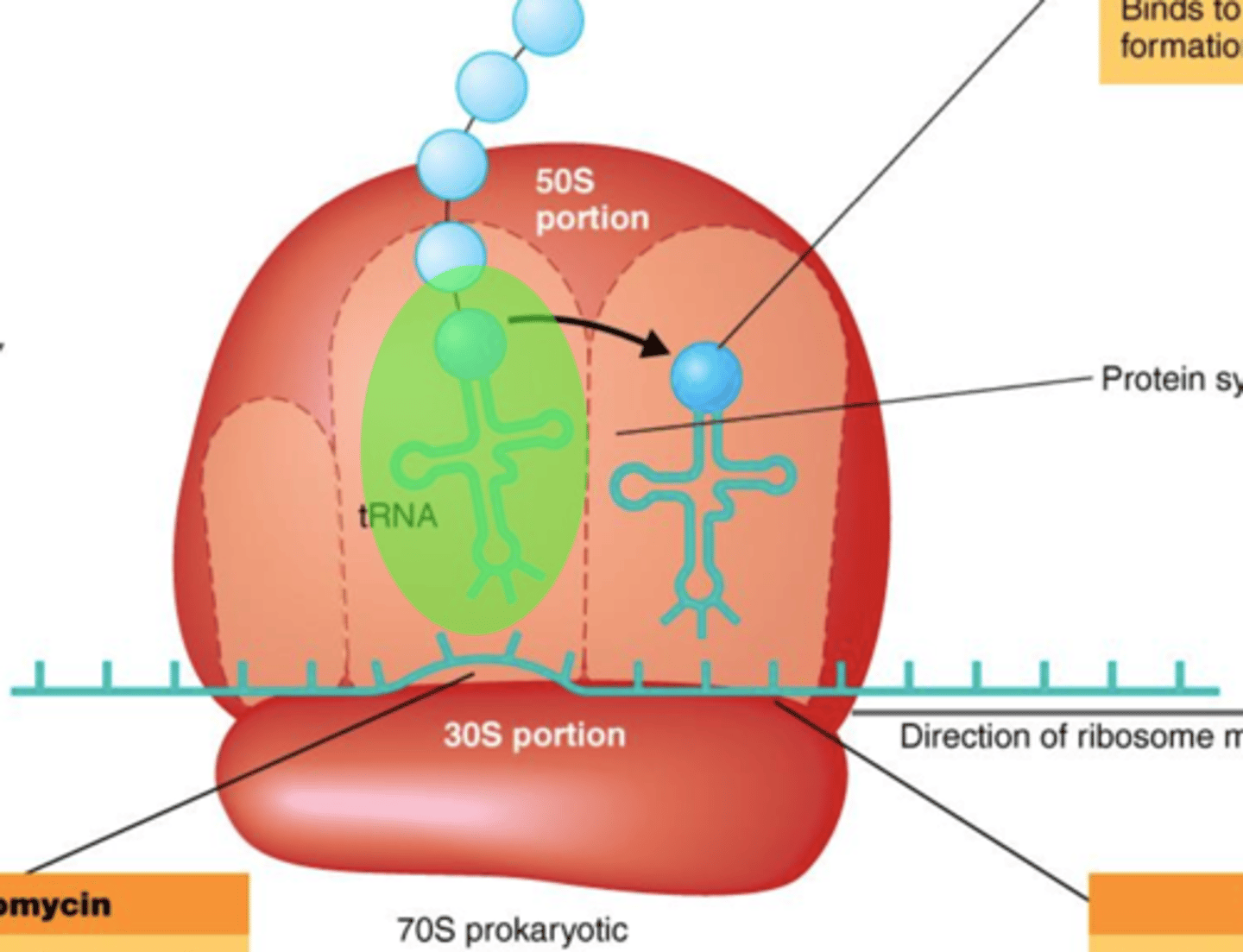
membranes
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs
Actions of lipopeptides cause injury to what?
lipopeptides
Injury to Membranes
Drugs that affect synthesis of bacterial plasma membranes. Include:
- Daptomycin (attacks bacterial cell membranes)
- Polymyxin B (effective against gram-negatives)
nucleic acid synthesis
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs
Actions of rifamycin, quinolones, and fluoroquinolones such as ciprofloxacin (cipro) inhibit what?
ciprofloxacin (cipro)
Antibiotics that Inhibit Nucleic Acid Synthesis
An important fluoroquinolone. Therefore, it inhibits DNA gyrase from uncoiling DNA, which is required for DNA replication.
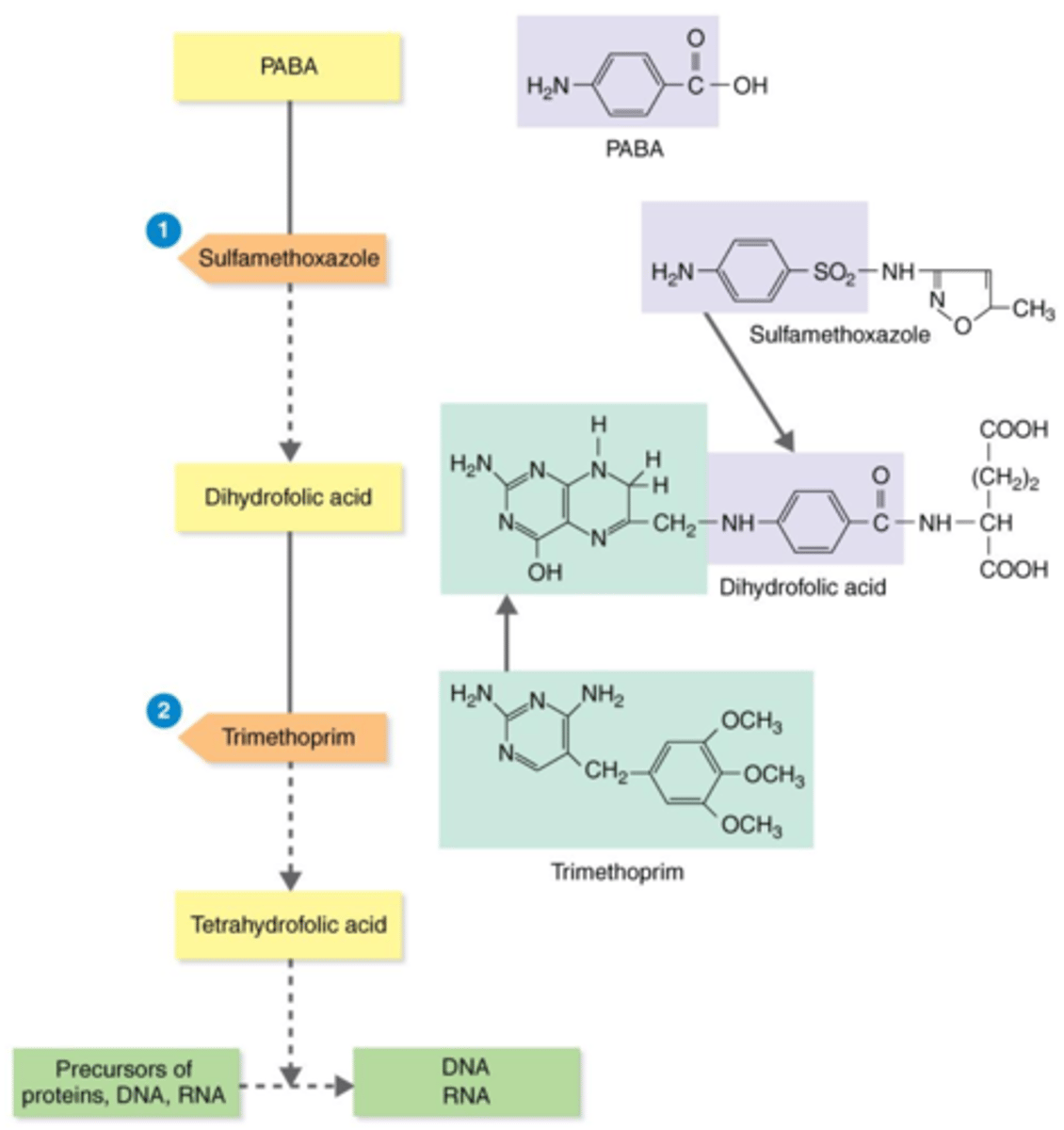
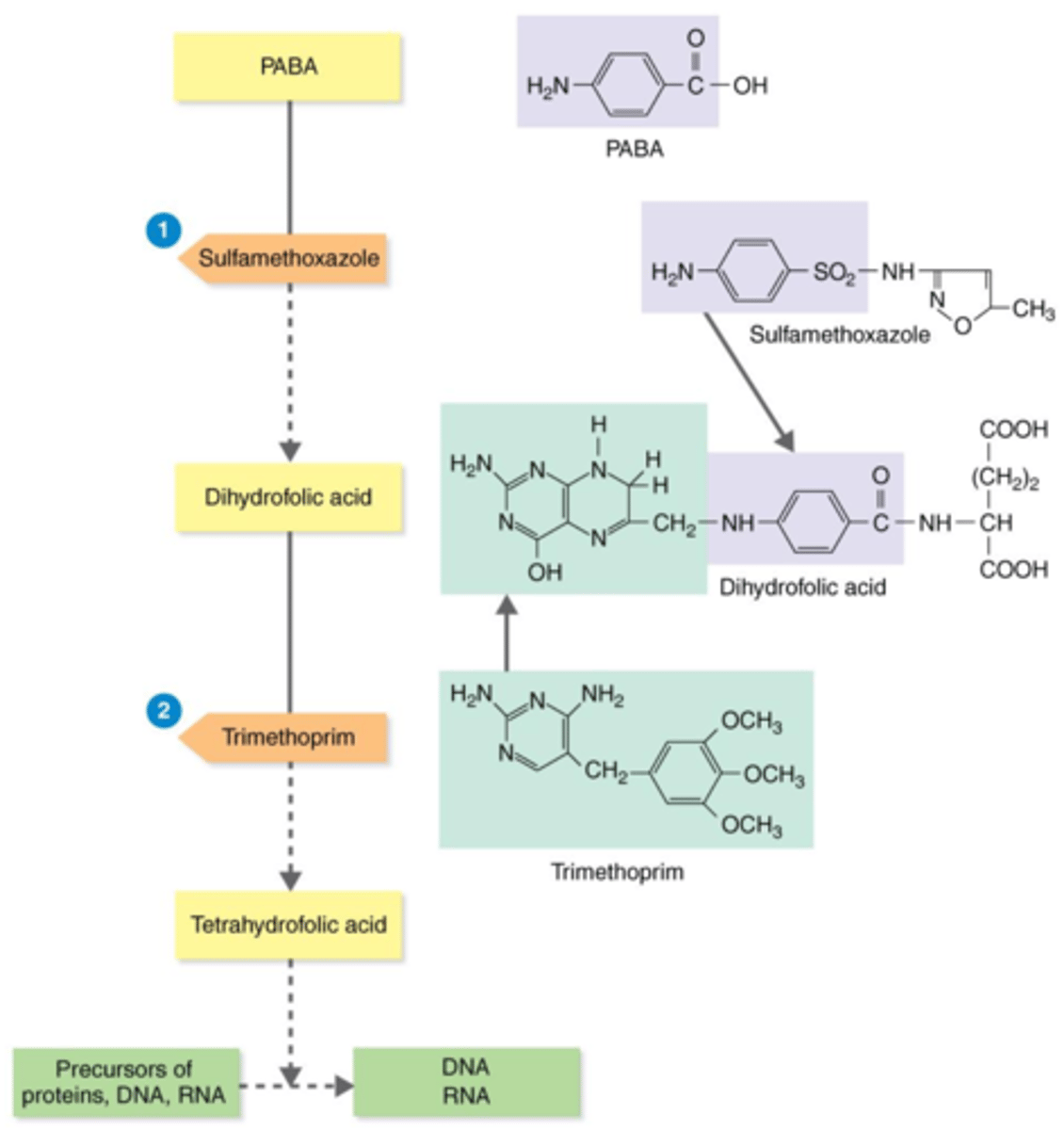
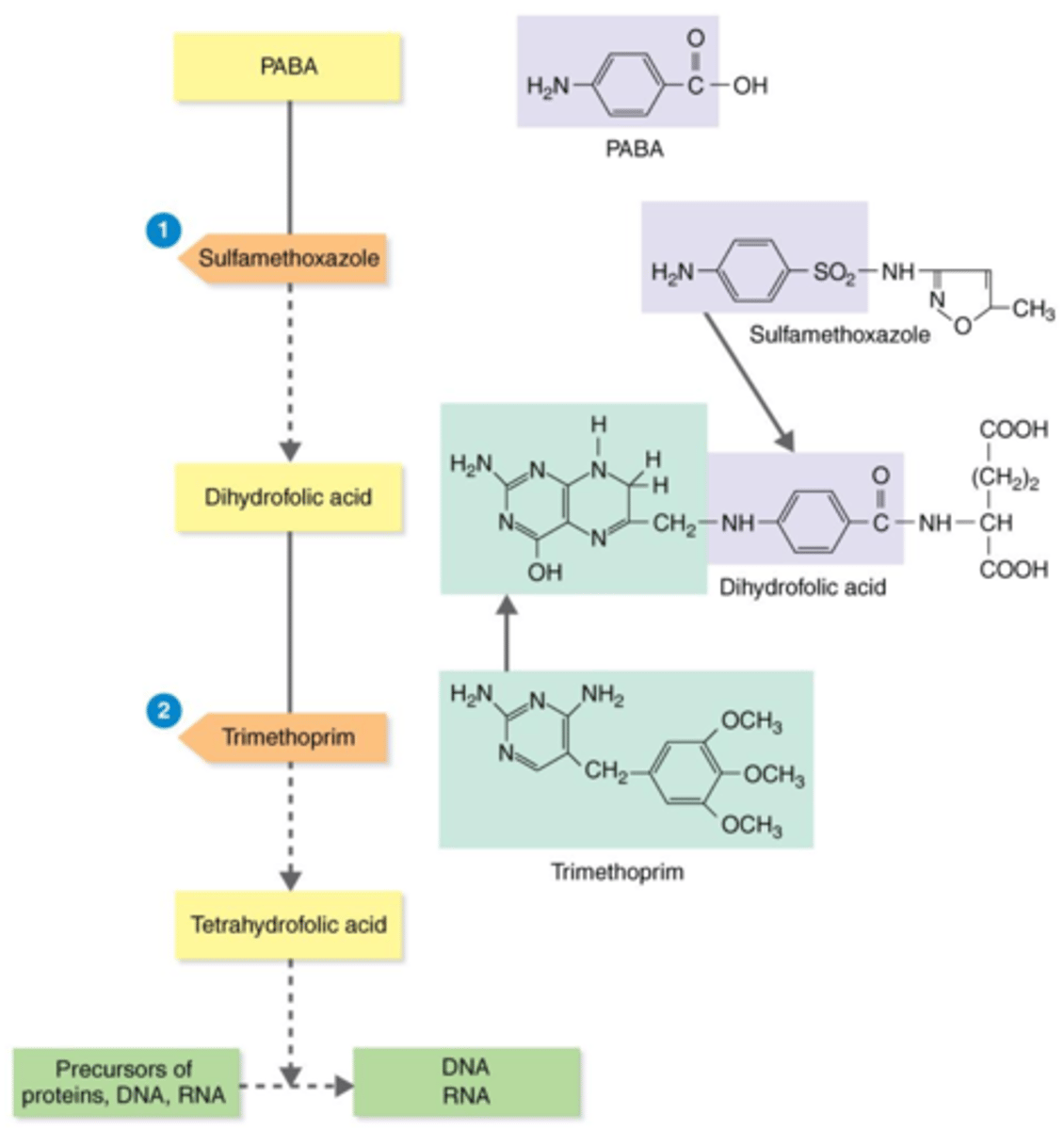
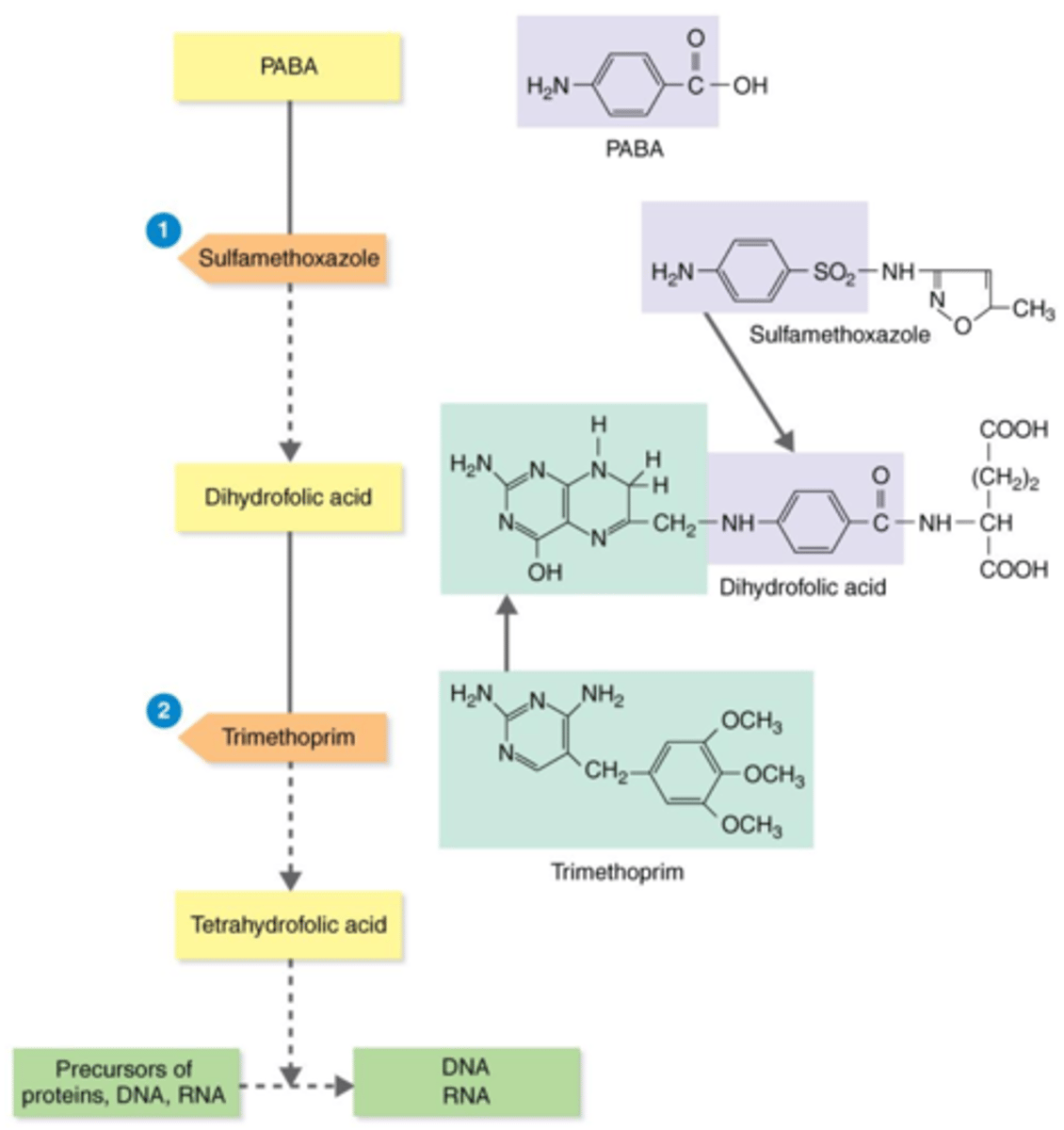
TMP-SMZ (trimethoprim + sulfamethoxazole)
Antibiotics that Inhibit the Synthesis of Essential Metabolites
A sulfonamide (sulfa drug), which interferes with different enzymes needed in the metabolic pathway for making tetrahydrofolic acid — a precursor for proteins, DNA, and RNA.
drug synergism
Antibiotics that Inhibit the Synthesis of Essential Metabolites
When the effect of 2 drugs together is greater than the effect of either one alone. Examples include:
- Penicillin + beta-lactamase inhibitor clavulanic acid
- Trimethoprim + sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMZ)
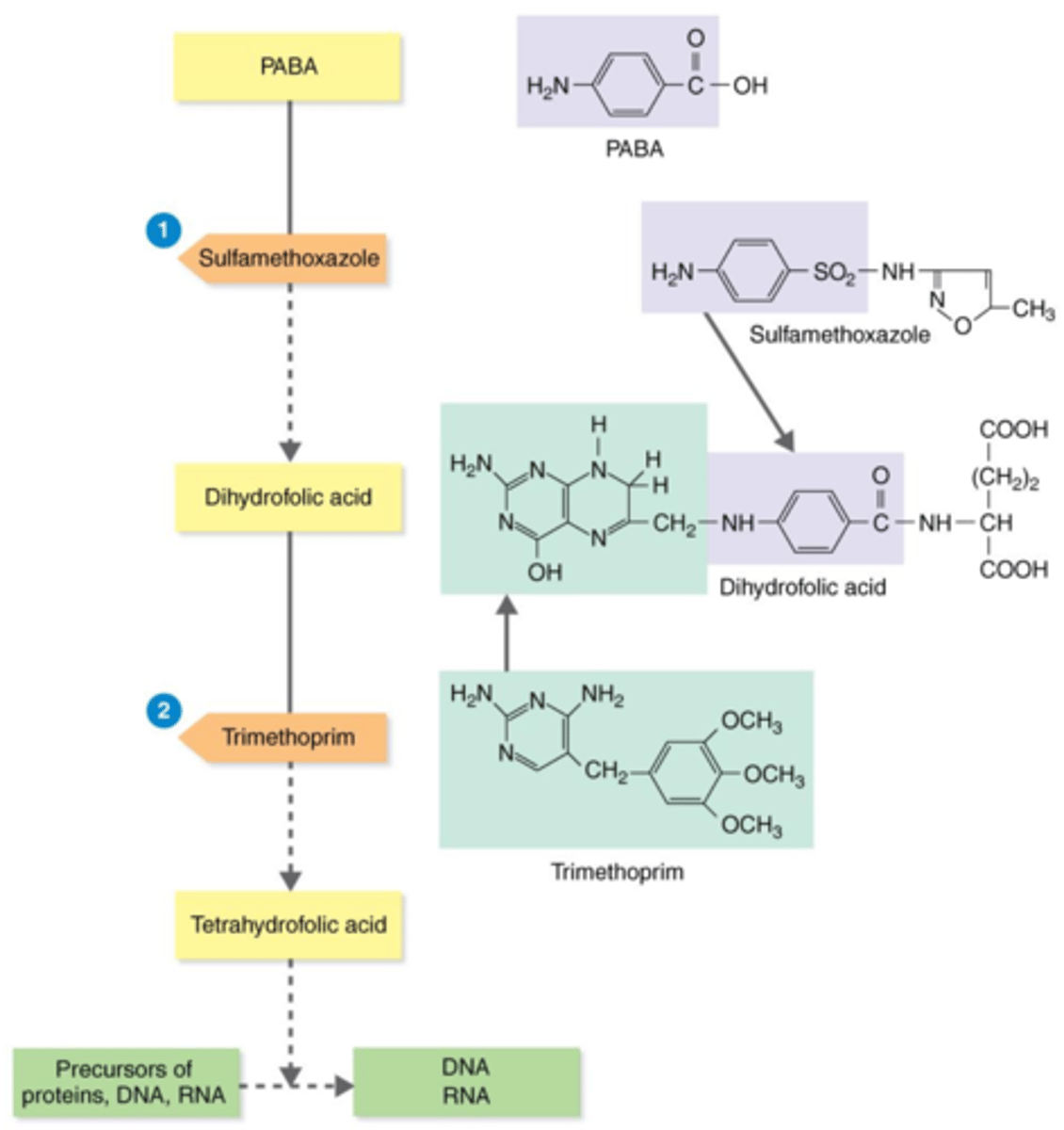
drug synergism
Antibiotics that inhibit the synthesis of essential metabolites
TMP-SMZ (trimethoprim + sulfamethoxazole) is an example of what?
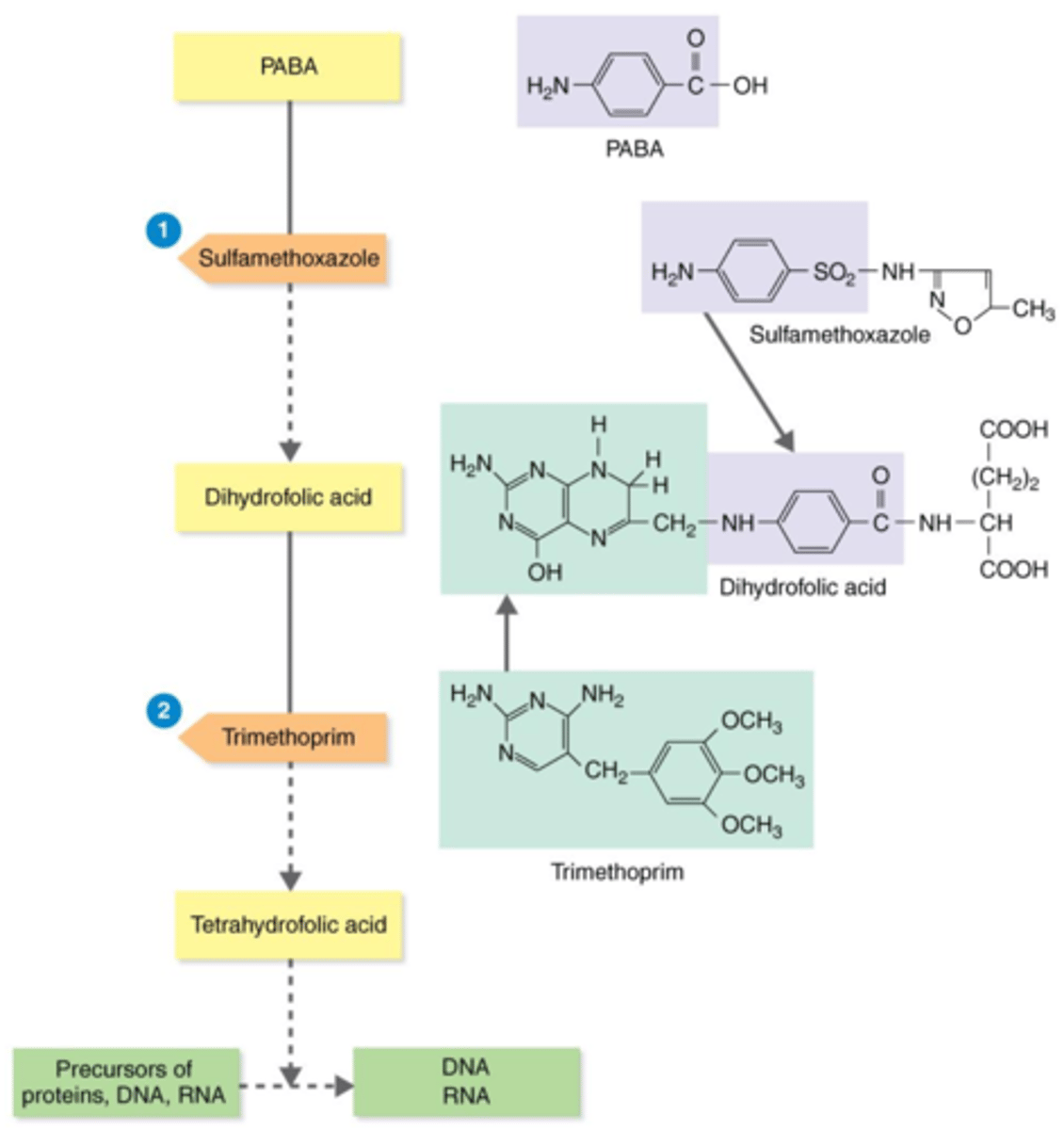
tetrahydrofolic acid
Actions of the Antibacterial Synthetics TMP-SMZ
Bacteria need the substrates PABA and dihydrofolic acid to produce this precursor for proteins, DNA, and RNA.
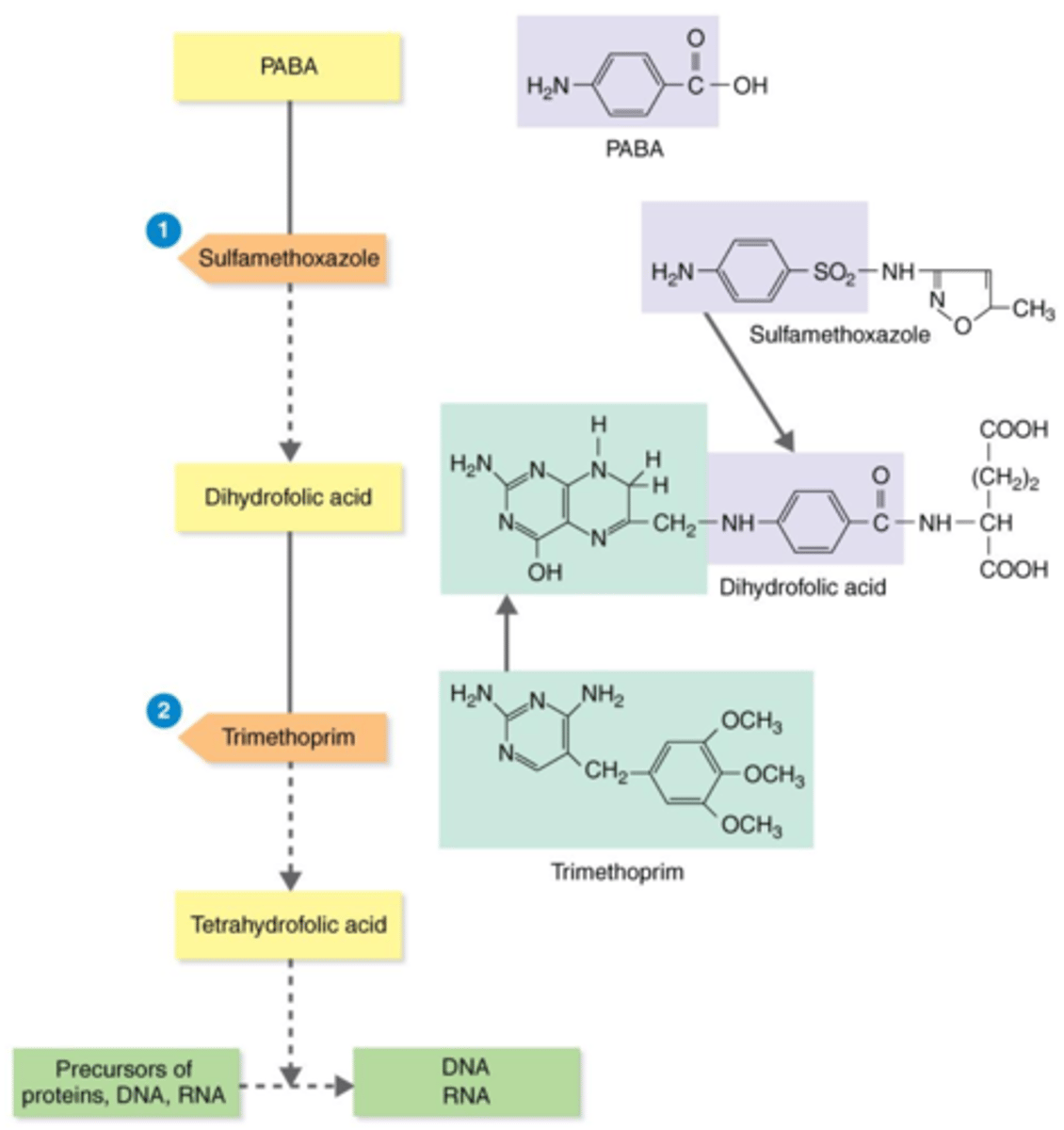
competitive inhibitors
Actions of the Antibacterial Synthetics TMP-SMZ
During bacteria's production of tetrahydrofolic acid, sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) and trimethoprim (TMP) act as what?
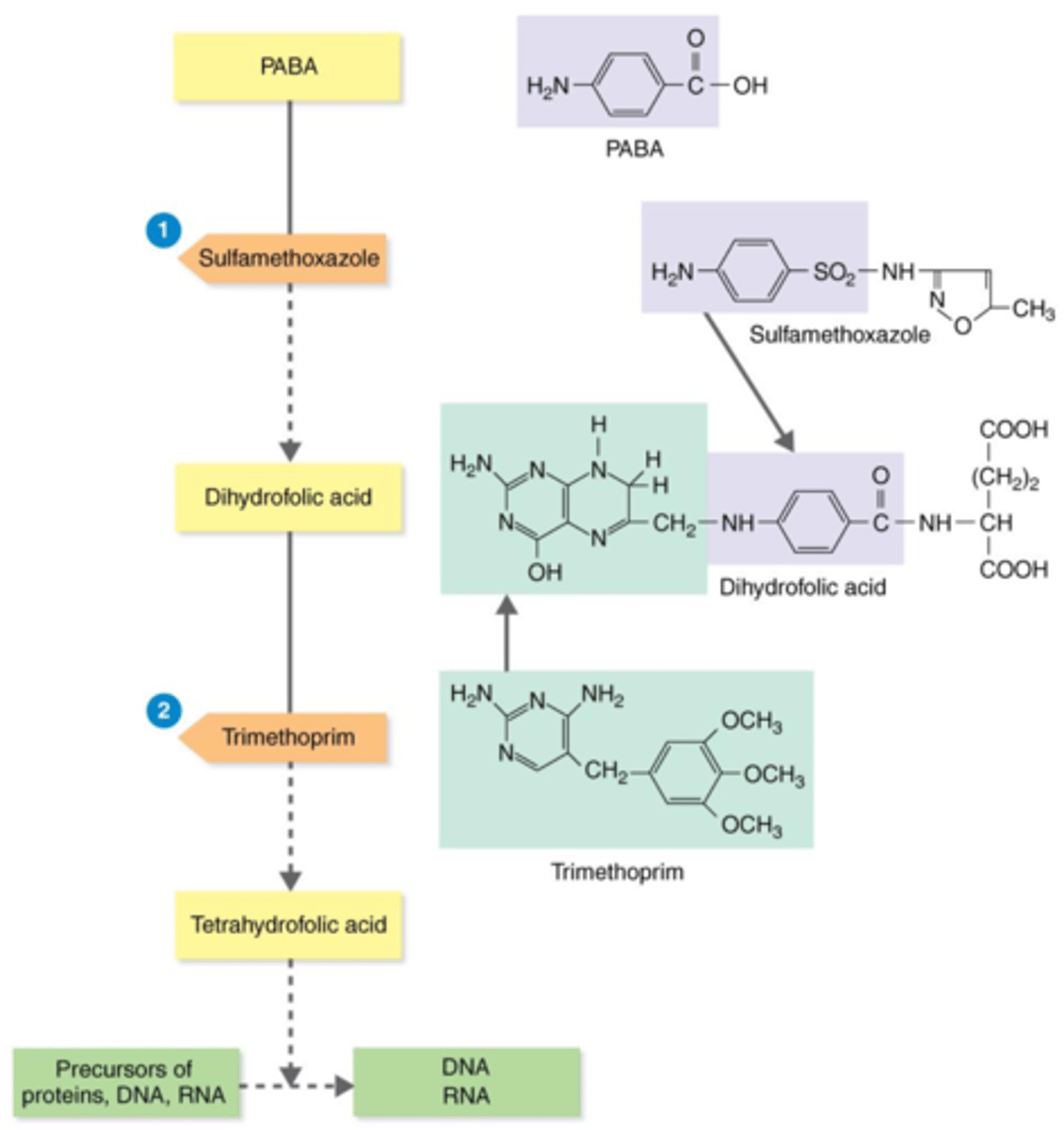
PABA
Actions of the Antibacterial Synthetics TMP-SMZ
Sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) acts as a competitive inhibitor of this substrate, thus inhibiting the production of tetrahydrofolic acid.
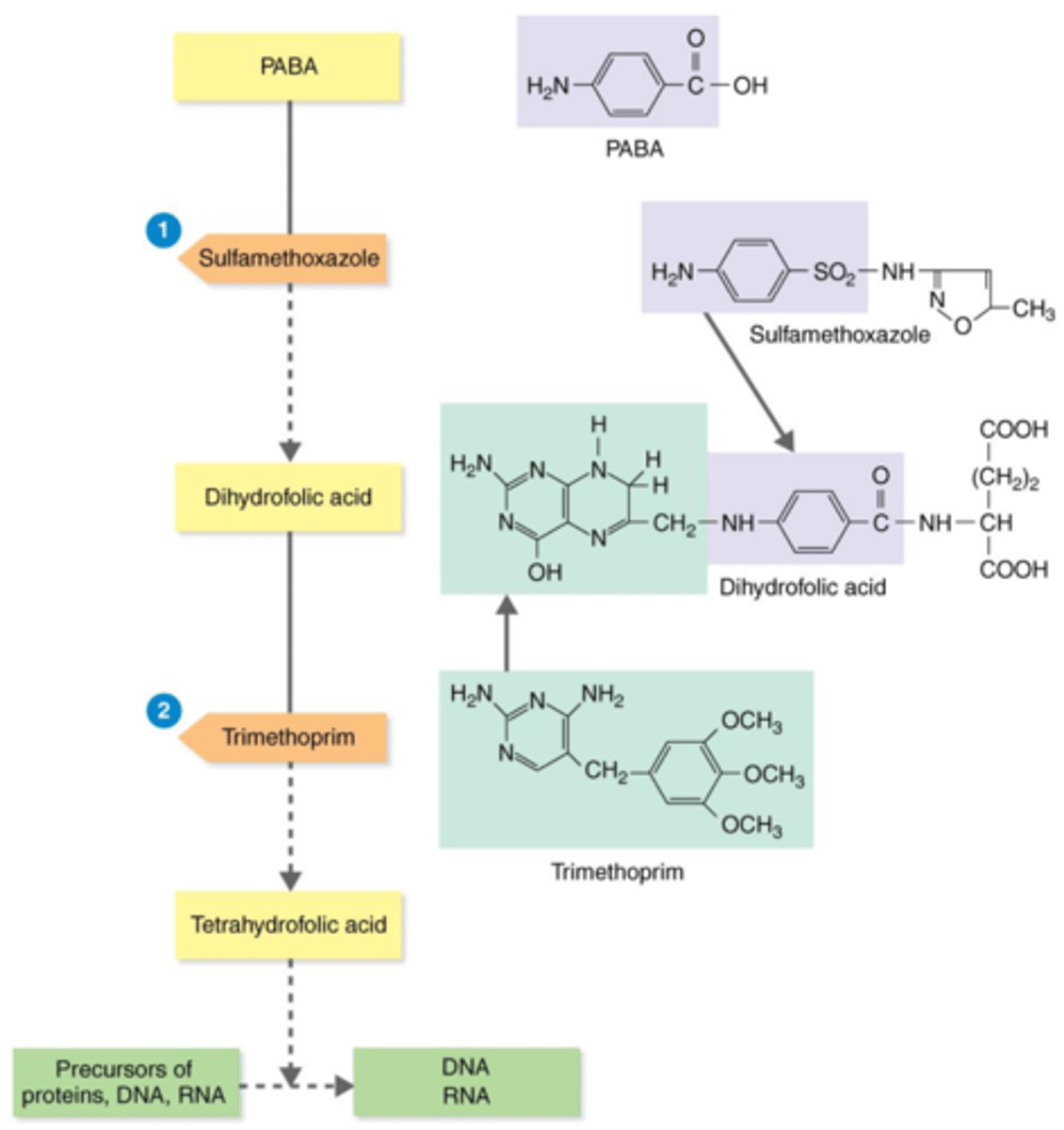
dihydrofolic acid
Actions of the Antibacterial Synthetics TMP-SMZ
Trimethoprim (TMP) acts as a competitive inhibitor of this substrate, thus inhibiting the production of tetrahydrofolic acid.
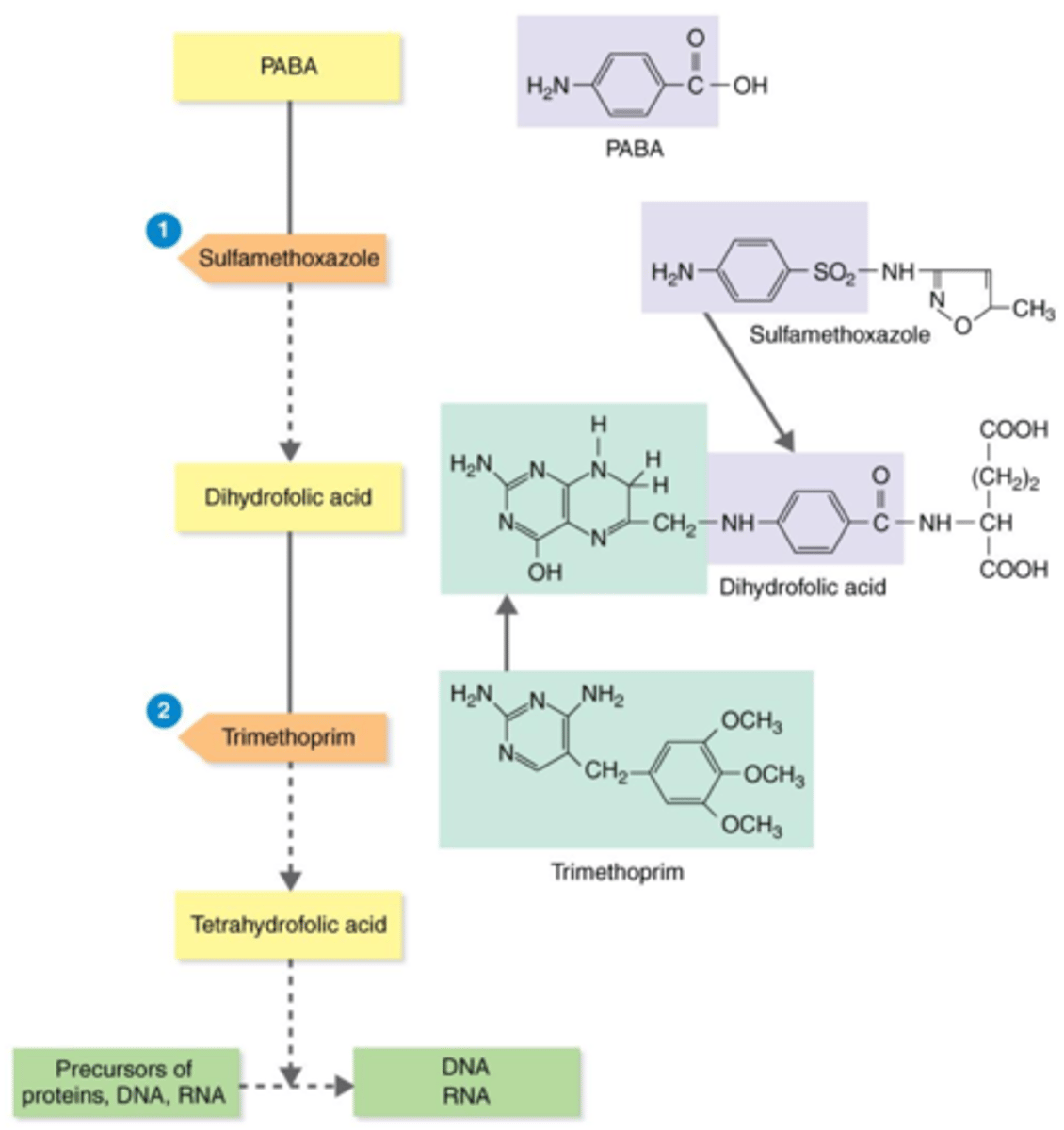
proteins, DNA, RNA
Actions of the Antibacterial Synthetics TMP-SMZ
Trimethoprim (TMP) + sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) inhibit the production of precursor tetrahydrofolic acid. Therefore, they inhibit production of what?
diet
Actions of the Antibacterial Synthetics TMP-SMZ
Trimethoprim (TMP) + sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) inhibit the production folic acid, but can be recovered through?
no
Actions of the Antibacterial Synthetics TMP-SMZ
Do humans require PABA's or dihydrofolic acid's enzymes for the production of folic acid?
antiviral drugs
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs
Antimicrobial drugs that act against viruses. Include:
1. Nucleoside and nucleotide analogs
2. Enzyme or protein inhibitors
3. Interferons
nucleoside
Antiviral Drugs
- Building blocks of nucleic acids
- Nucleotide base, sugar, no phosphate
- Have a 3-prime end (OH)
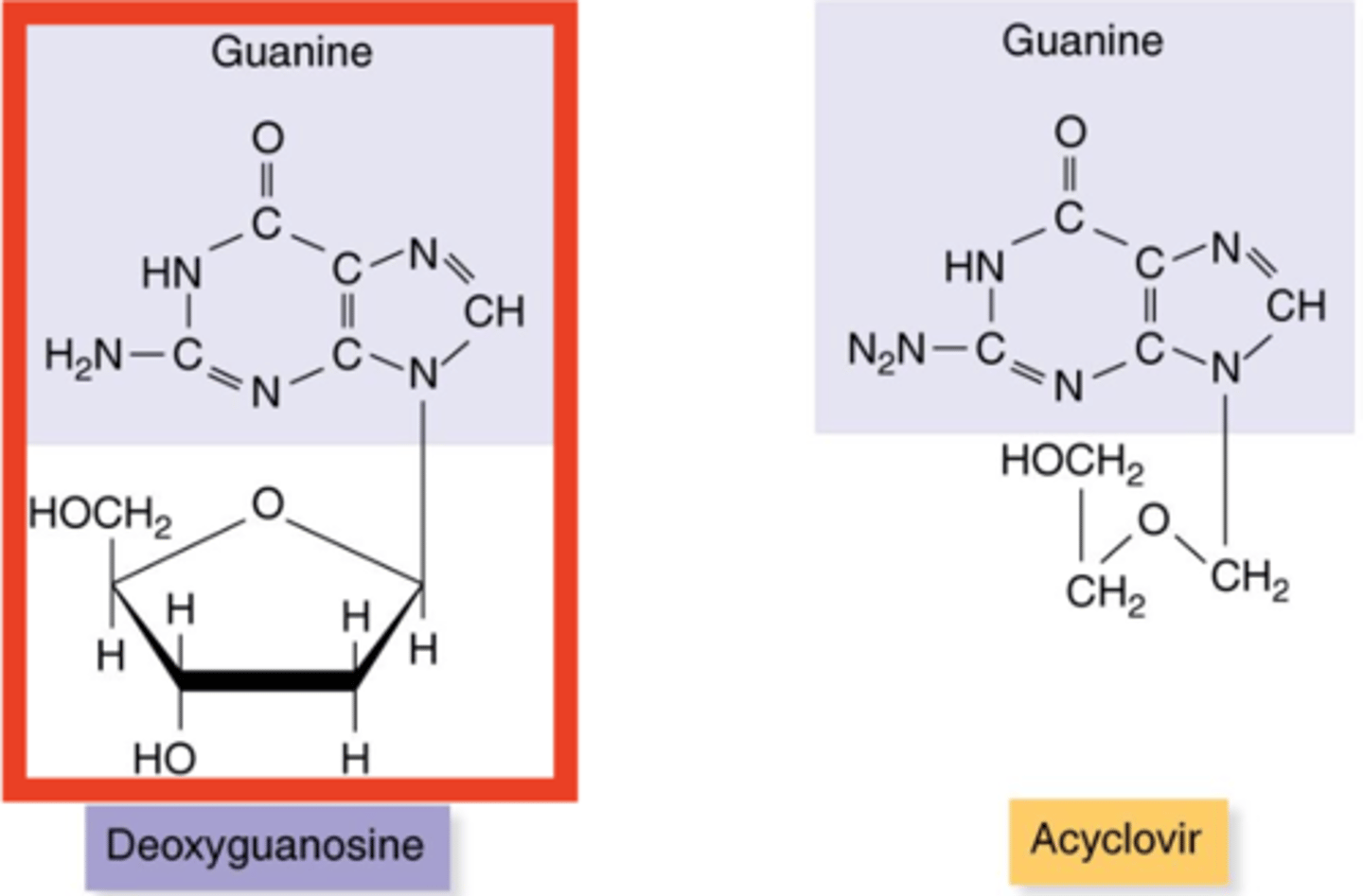
nucleoside analog
Antiviral Drugs
- Synthetic nucleoside and drug such as acyclovir and zidovudine (AZT)
- No 3-prime end (OH)
- Prevents further elongation of DNA or RNA during synthesis
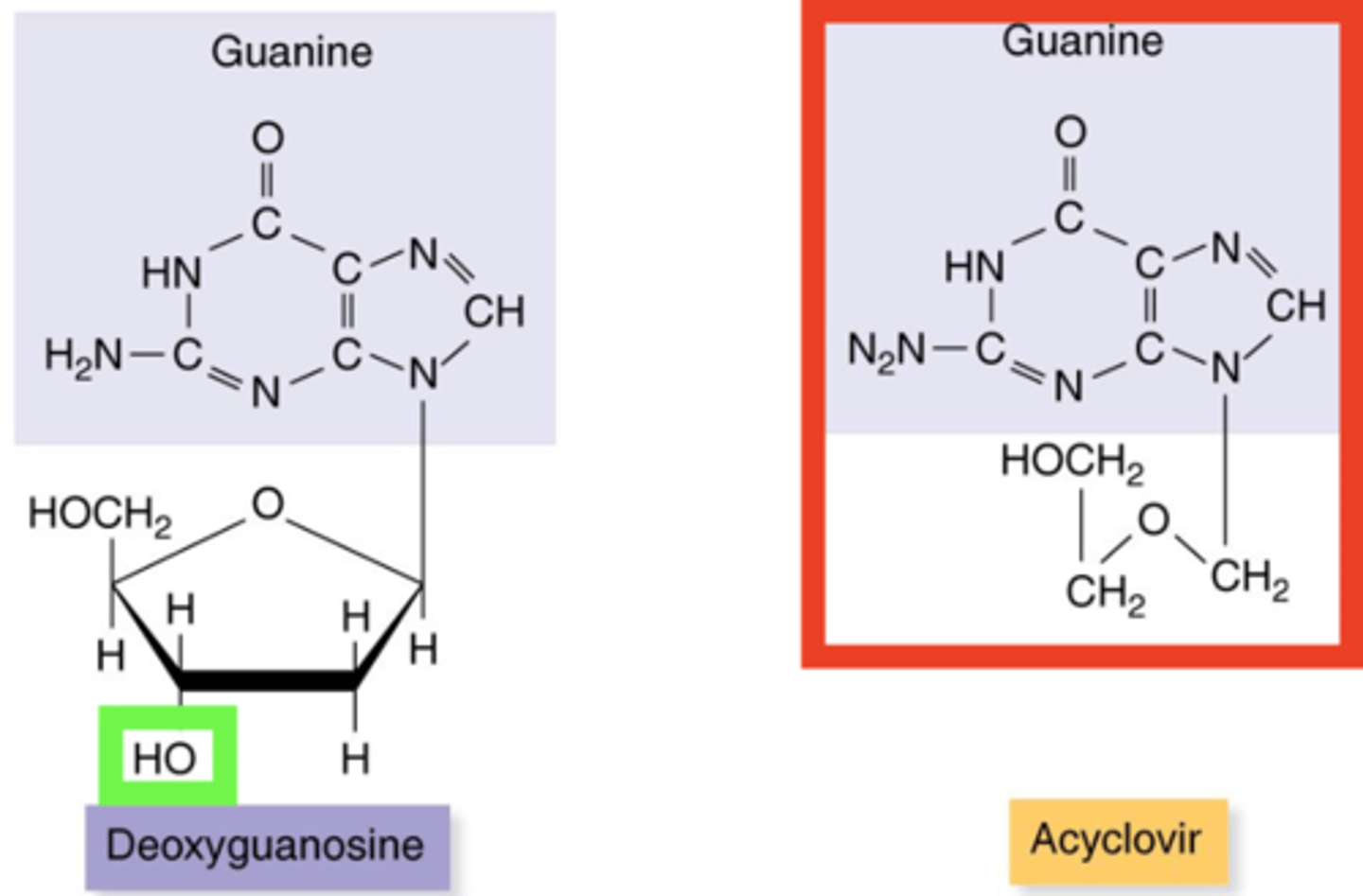
acyclovir
Nucleoside Analogs
- Nucleoside analog and drug
- Compatible with phosphorylator thymidine kinase
- Prevents further elongation of DNA during synthesis
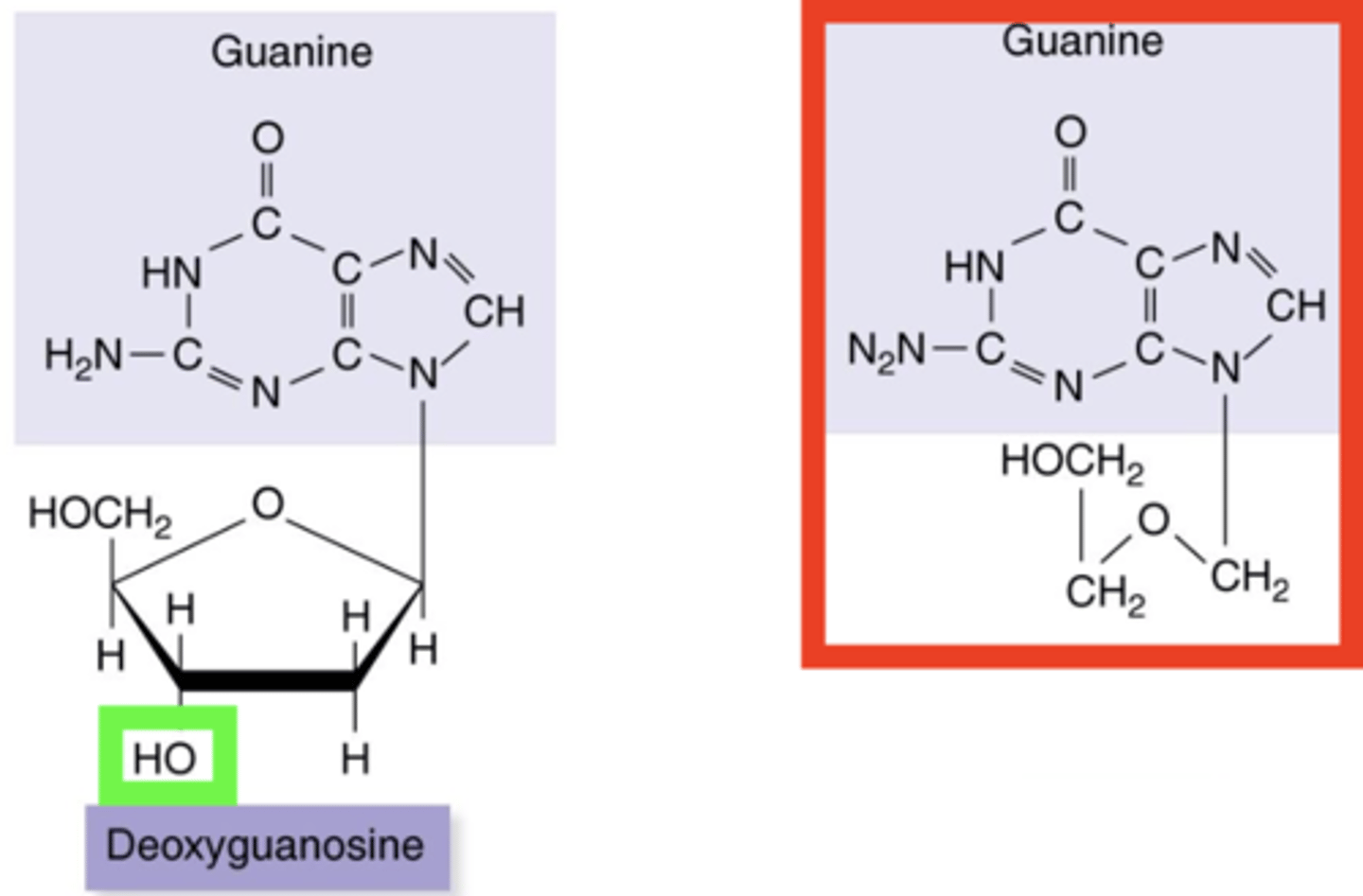
DNA
Nucleoside Analogs
Does acyclovir work against DNA viruses, RNA viruses, or both?
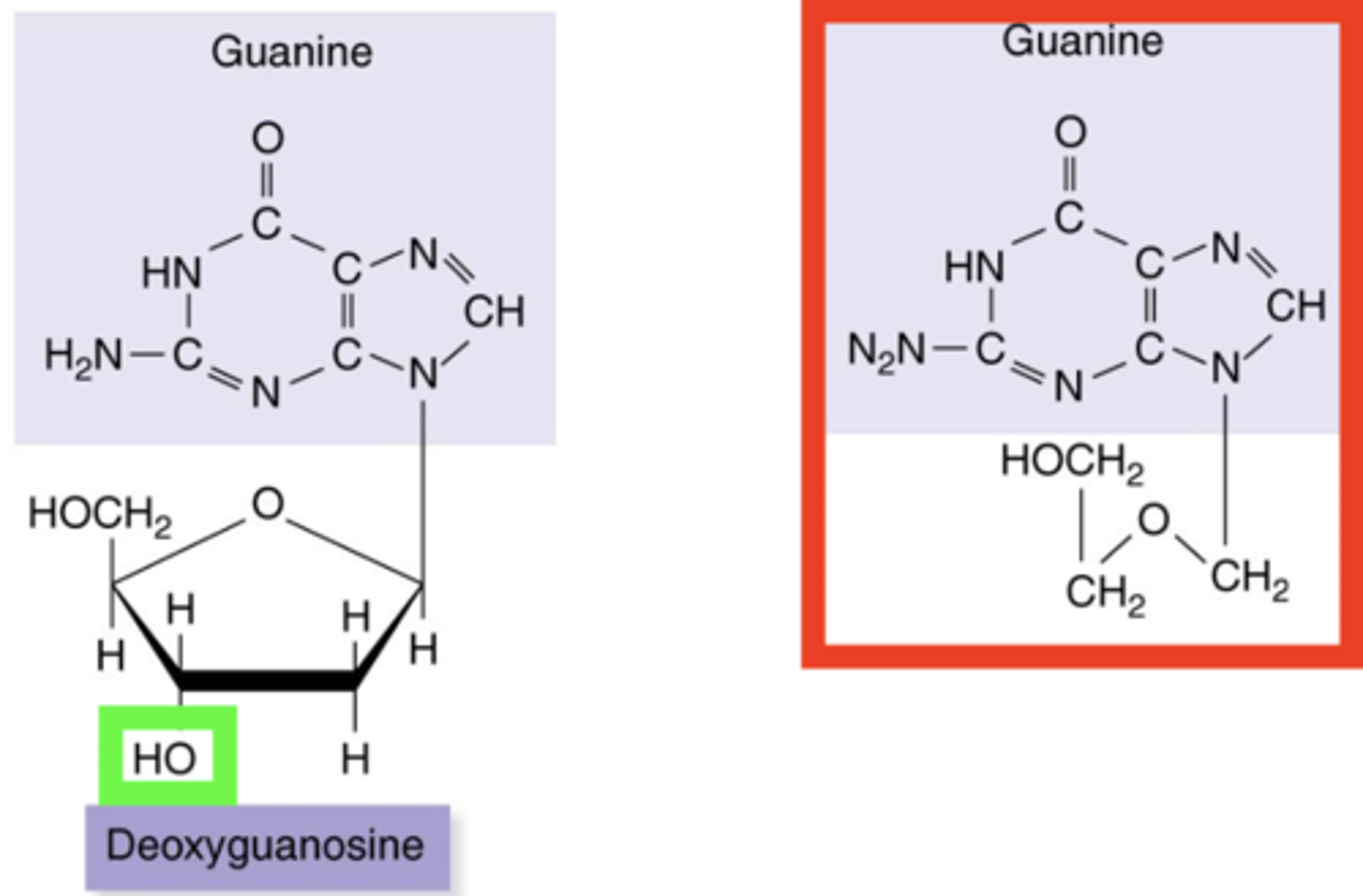
thymidine kinase
Nucleoside Analogs
- Enzyme that mistakes acyclovir for its substrate thimidine
- Phosphorylates acyclovir and incorporates it into DNA as a false nucleotide
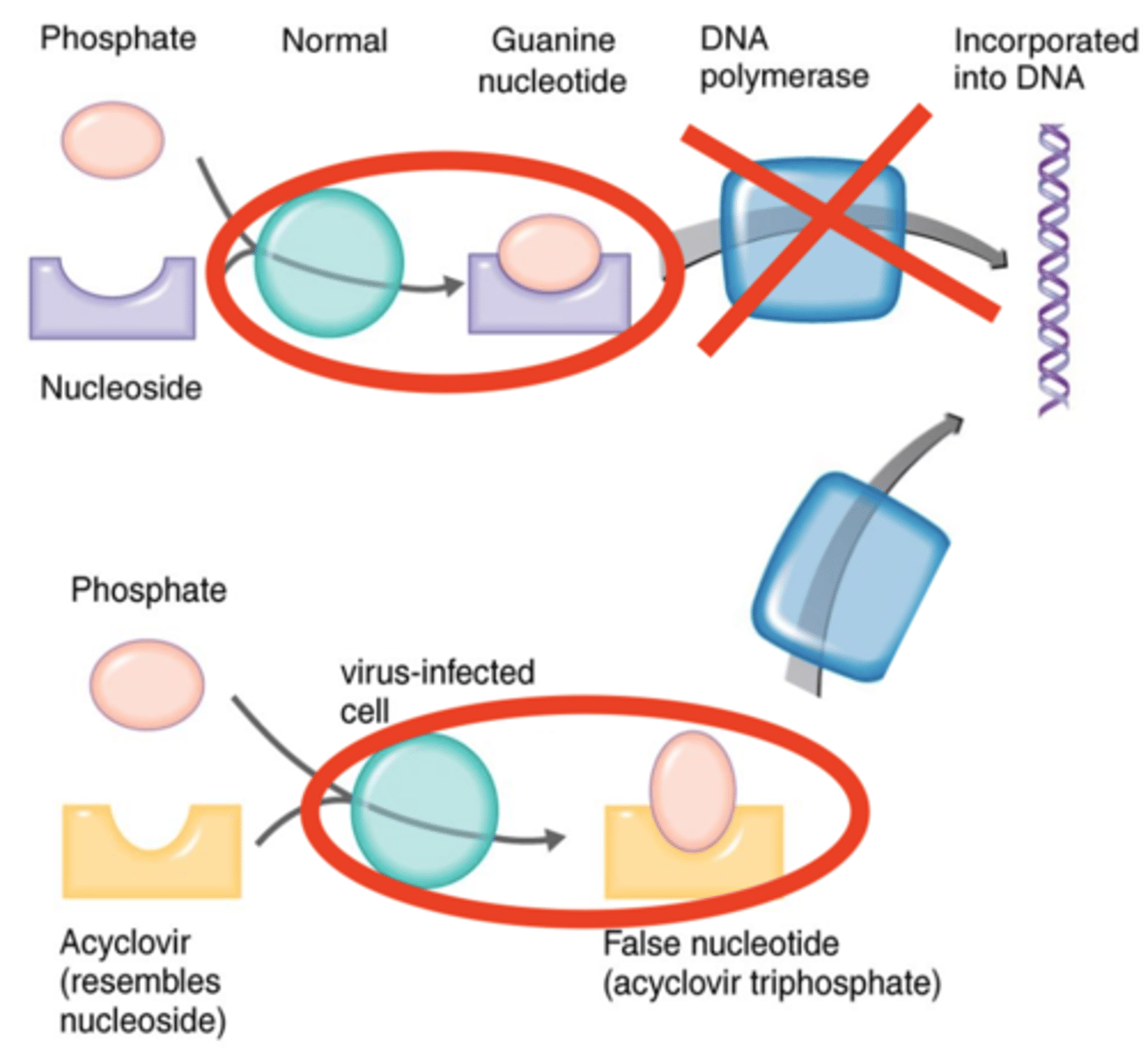
3-prime end
Nucleoside Analogs
Once thymidine kinase phosphorylates and incorporates acyclovir into DNA, DNA polymerase will not be able to attach because acyclovir has no what?
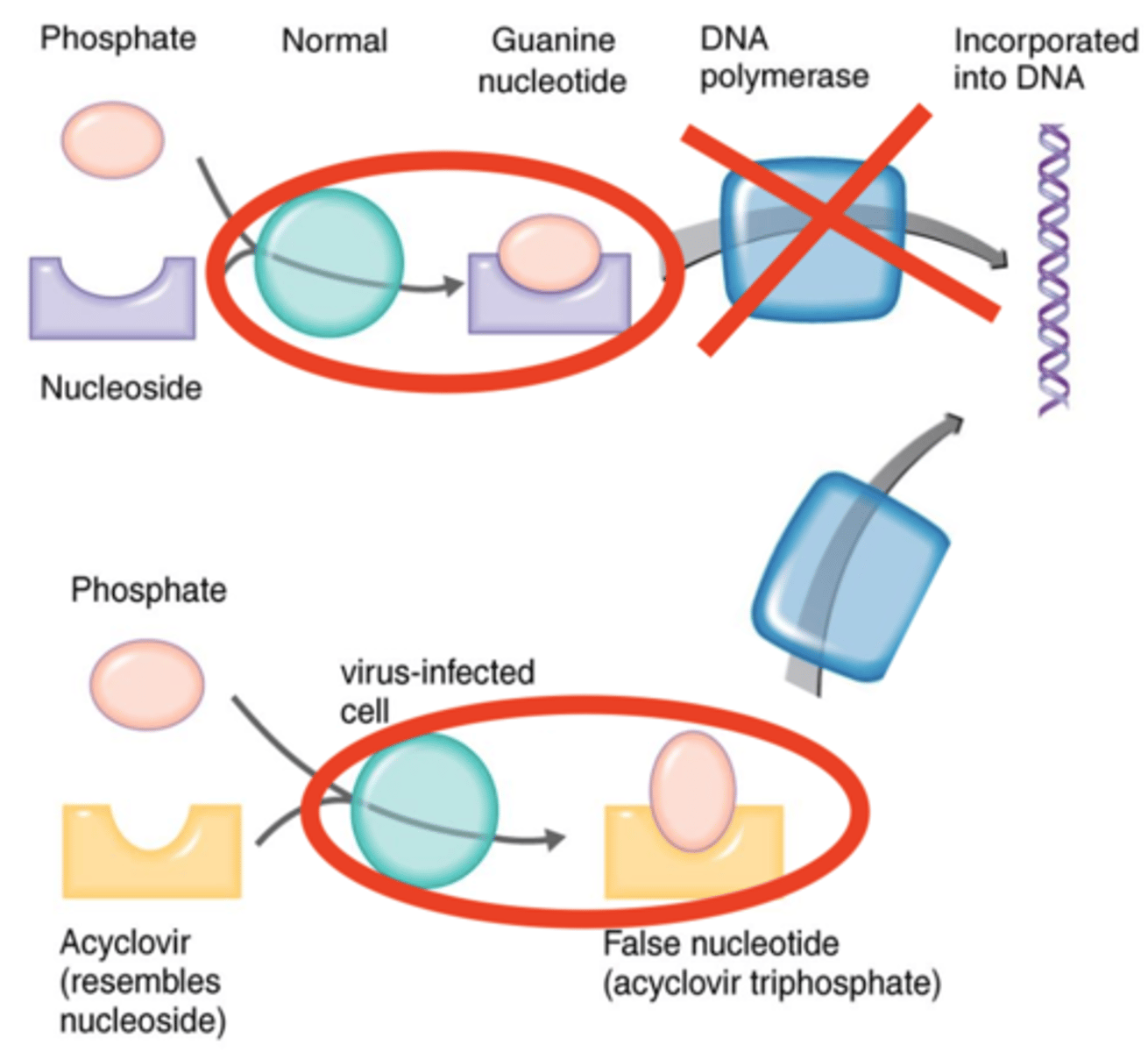
acyclovir
Antivirals that are Nucleoside/Nucleotide Analogs
- Nucleoside analog used against Herpes simplex virus (HSV) and Varicella zoster virus (VZV)
- Inhibits DNA replication
HSV, VZV
Antivirals that are Nucleoside/Nucleotide Analogs
Acyclovir is used against which viruses?
zidovudine (AZT)
Antivirals that are Nucleoside/Nucleotide Analogs
- Nucleoside analog that mimics thymidine
- Used against reverse transcriptase; nucleoside RT inhibitor
- Used to treat HIV
- Is incorporated into dsDNA and inhibits DNA synthesis
AZT-resistant RT
Antivirals that are Nucleoside/Nucleotide Analogs
- A form of reverse transcriptase with selected resistance against zidovudine (AZT)
- Accepts thymidine but rejects zidovudine (AZT)
non-nucleoside RT inhibitors
Antivirals that Inhibit Viral Enzymes
- Inhibit reverse transcriptase
- Not nucleosides
- Often used to treat HIV
- Prevents production of dsDNA from ssRNA
protease inhibitors
Antivirals that Inhibit Viral Enzymes
- Block the cleaving of viral proteins such as with ritonavir.
- Prevent the maturation of HIV virions
ritonavir
Antivirals that Inhibit Viral Enzymes
- Competitive inhibitor to protease's substrate
- Inhibits protease from "cleaving" proteins needed to produce fully-mature virions
- Protease inhibitor used to treat HIV
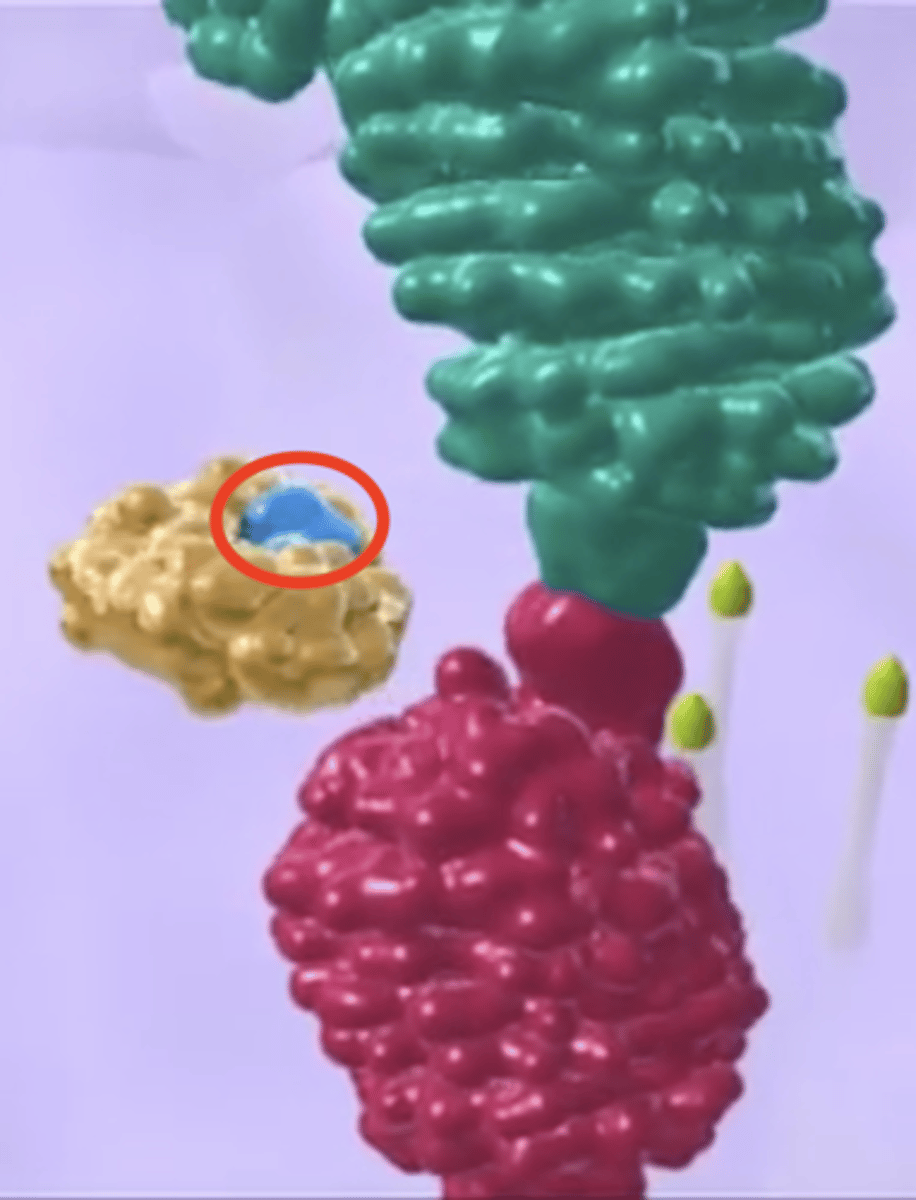
integrase inhibitors
Antivirals that Inhibit Viral Enzymes
- Prevent the integration of viral DNA into the host DNA
- Most are HIV drugs
neuraminidase inhibitors
Antivirals that Inhibit Viral Enzymes
Inhibit spike proteins that release Influenza virions from host cells
fusion inhibitors
Antivirals that Inhibit Viral Enzymes
- Some are made for HIV
- Prevent the viral envelope from fusing with the host cell membrane, thus blocking entry
IFN-alpha
Interferons as Antiviral Drugs
Interferons used to treat hepatitis such as with imiquimod
ergosterol
Antifungals that Target the Plasma Membrane
A steroid and major component of fungal cell walls, much like cholesterol. Synthesis is inhibited by antifungals such as:
- Amphotericin B
- Miconazole
amphotericin B, miconazole
Antifungals that Target the Plasma Membrane
Name 2 antifungals that inhibit synthesis of ergosterol
metronidazole
More Drugs
Interferes with anaerobic metabolism. Can be used against bacteria and protozoa.
mebendazole
More drugs
Inhibits formation of microtubules in the cytoplasm which blocks absorption of nutrients by some helminths.
praziquantel
More drugs
Kills by altering the permeability of the plasma membrane. Used against tapeworms and flukes (trematodes).
exoenzyme
Quiz question
Penicillinase is an endo or exoenzyme?
nucleosides
Quiz question
What does Acyclovir mimic?
methicillin
Quiz question
Which antimicrobial drug inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis, but is resisted by MRSA?