OB High Risk newborns
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Preterm infant
<37 weeks
Low birth weight
<2500 grams
very low birth weight
<1500 grams
small for gestational age
<10%
large for GA
>90%
macrosomia
>4000 g
challenges for preterm infant Respiratory
less surfactant —> harder to keep alveoli open
smaller airways —> obstruction / collapse
periodic breathing vs apnea - which one is normal? which one is abnormal
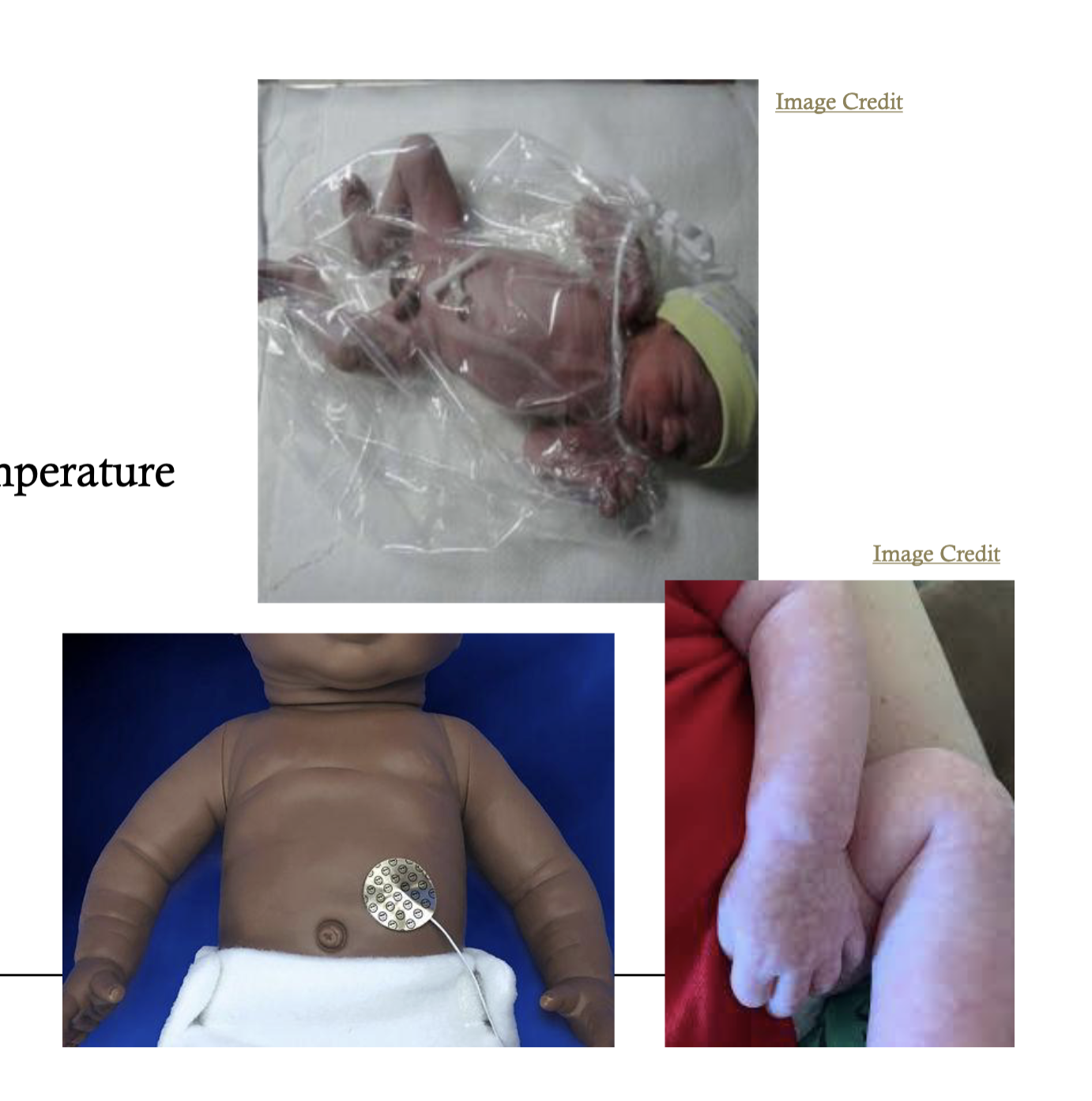
challenges for preterm infant thermoregulation
temperature instability
increased body surface area, minimal fat, poor muslce tone —> heat loss
underdeveloped brain
work harder to maintain temp —> utilization of 02 adn glucose
phsyiological changes for preterm infant
central nervous system
risk for intracranail bleeding and hypoxia
GI/metabolic system
impaired feeding reflexes (suck/swallow, gag, reflex, coordination with breathing)
difficulty absorbign nutrients
hematologic system
fragile capillaries, prolonges clotting times, less RBC’s —> brain bleed
risk for anemia
risk for hyperbilirubenemia
Corrected age
GA + postnatal age = corrected age
Example: infant born at 32 weeks and has been in nicu for 2 weels, corrected age is 34 weeks
infant born at 28 weeks adn 2 days spent 4 weeks adn 3 days in nicu, corrected agae 32 and 5
important because need to see when if infant is meeting milestoens, they will be a little behind on normal milestones
Respiratory care
preterm infants more likely to require advanced resuscitation efforts
oxygen therapy
continous postivie airway pressure (CPAP)
delivers 02 or air to infant with added pressure to help keep alveoli open (prevent collapse)
intubation mechanical ventilation
when other methods ar enot effective
surfactant
can be given to preterm infant untile he / she can produce their own
thermoregulation
pre warmed radiant warmer or incubator
polyethylene bag
sticker probe used ot maintain stable body temperature
hypothermia
symptoms
acrocyanocis, cool skin, pale, hyporeactivity, low blood sugar,
gradeal rewarming recommended
weight gain and fluid balance weight gain and caloric needs
caloric nutirent adn fluid requirements are higher than that of a healthy term neonate
weight gain / loss monitored daily
could lose up to 15% of birth weight - Term newborn is 10% weightloss
dont under or over feed
advance feeds gradually
Symptoms of feeding intolerance
throwup, spitup, vomiting, abdominal distension, discomfort,
weight gain and fluid balance, feeding method and nutrition
feeding method
oral bottle / breastfeeding
must have adequeate strength and GI function
cavage - NG tube or OG tube
if ifnant too sick or premature for feeding
via syringe or infusion pump
parenteral IV infusion
infants unable to retain addequate fluids calories byt enteral feeds
nutrition
breast milk / formula
pain assessment
symptoms can be behavorial
Whimpering, chin quivering, brow furrowed,
eyes tightly closed, thrashing, fist clenching, etc
anticipate and manage pain without wiating for multiple sigsn to appear
non-pharmacological interventiions
swaddling, sucking, warmth, distraction techniques
pharmacological interventions
Morphine or fentenyal iv infusion
developmental care
decrease stimulation
lights noise
minimizxe sleep disruption
scheduled care times —> minimize sleep disruption
parental support in NICU
Issuee = difficult bonding / relating to their infant
goal = recognize competence, self conidence in infant care
promoting bonding / attachment
physical touch
participate in caregivcing activities
updates prn (video feeds, pictures, pjone updates)
educate about
equipment, medications, plan of care
realistic expecations fo rtheir infant - use GA
encourage them to express feelings about labor, birth, preterm infant
preterm compliications
respiratory distress syndrome
lack of pulmonary surfactant —> atelecatasis, difficultyy breathing independently
symptoms
grunting, wheezing, retractions, nasal flaring
treatment
oxygen, ventilation (prn), surfactant
preterm complicatiosn retinopathy of prematuirty (ROP)
hypoxi —> scarring, capillary hemorrhage in retina vessels —> visual impairment
early detection with ophthalmologist (31-32 weeks)
prevention - monitor blood oxygen levels maintain adequate 02 sats
Preterm complications intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH)
small capillaries in brain susceptible to fluctaitons in BP —> hemorrhage —> damage
associated with GA <32 weeks, hypoxia, birth asphyxia, RDS, pneomothorac
interventiosn
thermoregulation, reduce handling (72hrs) elevated HOB (head of bed), monitor BP closely
Preterm complications Necrotizing enterocloitiz
inflammatory disease of the GI mucose —> bowel necorsis and perforation
progression: hypoxic event bacteria in GI tract, and enteral feedin
rarelty among infants who are exclusively BF
interventiosn
bowel rest, parenteral nutrition ,orogastric tube with suction, antibiotics, surgery
preterm compkcatiosn neonatal sepsis
significant cause of infant morbidity adn death
early onset <72 hours after birth (maternal intrapaturm transfer
late onset >72 hours after brith ( likely hospital aquired post natal)
symptoms
lethargy, poor feeding, hypotonia, hypothermia, tachypnea, apnea, grunting, tachycardia
infant of diabetic mother
significant impact on neonatal morbidity/mortality
pathophysiology
maternal hyperglycemia —> high fetal insulin production
maternal supply cut off (delivery ) —> fetal hypoglycemia
complications
Macrosomia/ LGA – enlarged organs
• Birth injury/ hypoxia
• Congenital anomalies – early hyperglycemia – 3-5x increased risk
• Polycythemia & Hyperbilirubinemia
• Respiratory Distress Syndrome
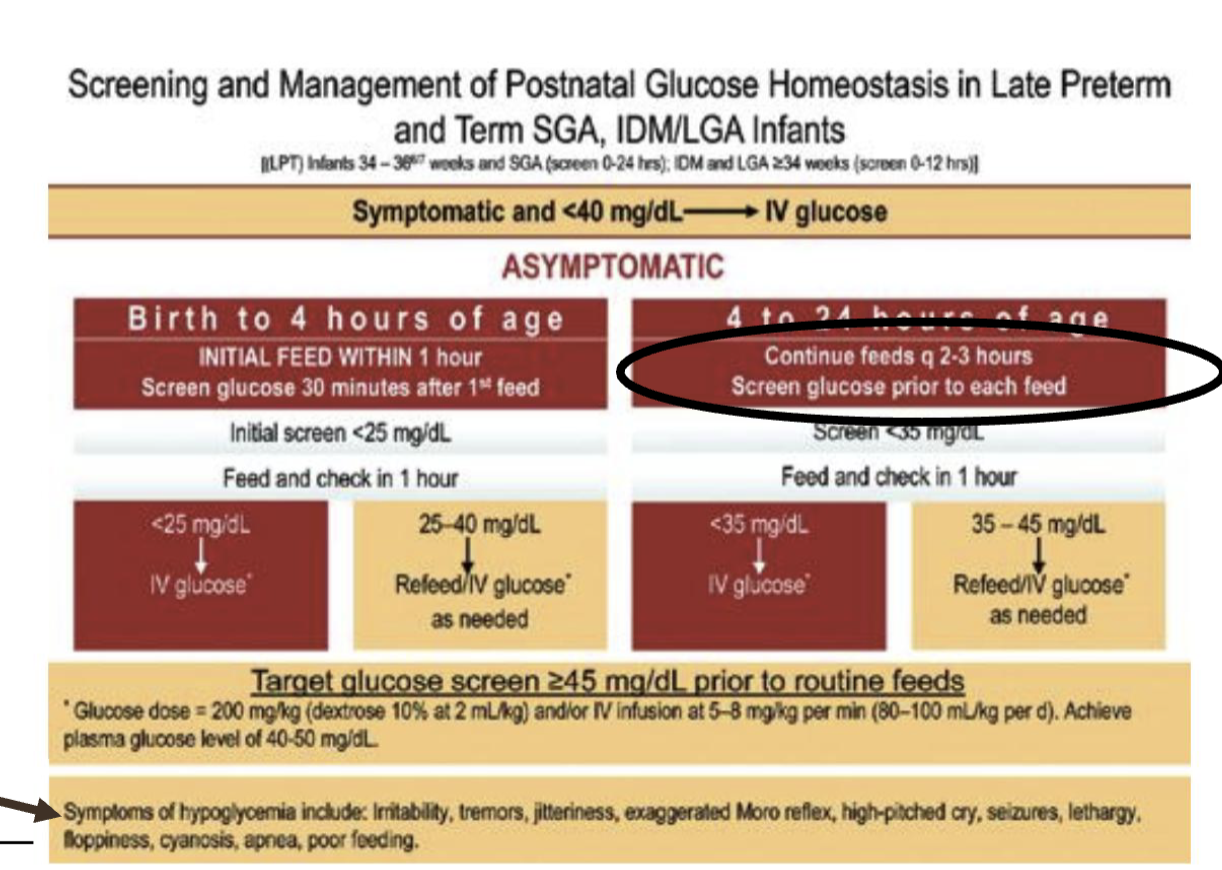
hypoglycemia
inadequate blood glucose levels to support normal functioning
level < 40 mg/dl (in a newborn)
main risk factor
LGA, SGA, LBW
IDM
maternal beta blocker
usualyt within first 6 huors of brith
symptoms
Jittery
Lethargic
Poor feeding
Hypotonia
Apnea / cyanosis
High-pitched or weak cry
Seizures (late)
Hypoglycemia Protocol (Condensed)
Check glucose (screen at-risk infants).
If <40 mg/dL (early) or <45 mg/dL (later) →
Feed immediately (breastfeed or expressed milk).Recheck glucose in 15–30 min.
If still low → oral glucose gel + feed.
If persistently low or symptomatic → IV D10W bolus or infusion.
Monitor until three normal readings in a row.
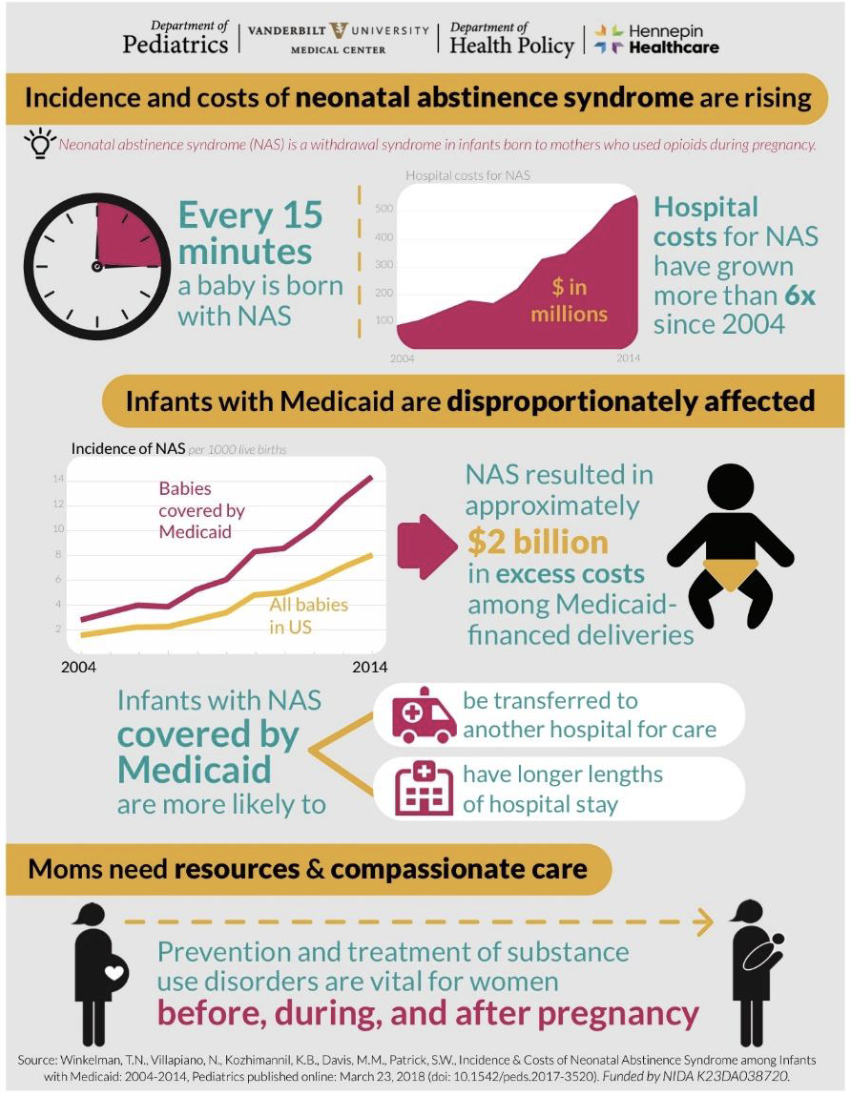
neonatal abstinence syndrome
symptoms r/t intrauterine exposure to opioids
closer drugs use to birht —> more severe symptoms and delayed onset
symptoms
hyperiirtablity - crying, jittery
GI dysfucntion - diarhhea
autonomic instability - sweating, temperature instability, faster respiratory rate
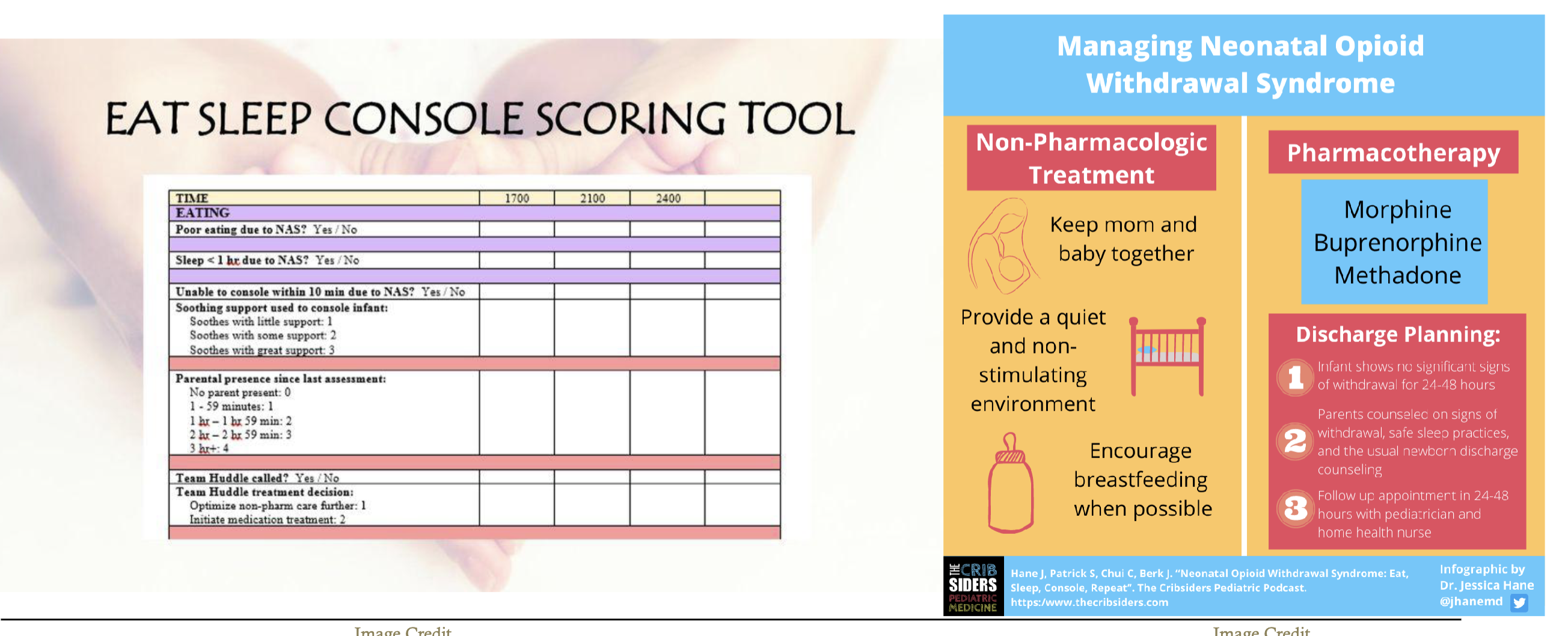
scoring tools - finnegan NAS scale, eat, sleep console
treatment
non pahrmocaologic vs pharmacologic
breastfeeding recommended for women who are stable on meds
NAS scoring and management

Hemoltyci anemia
destruction of RBC’s faster than the body can repoduce them
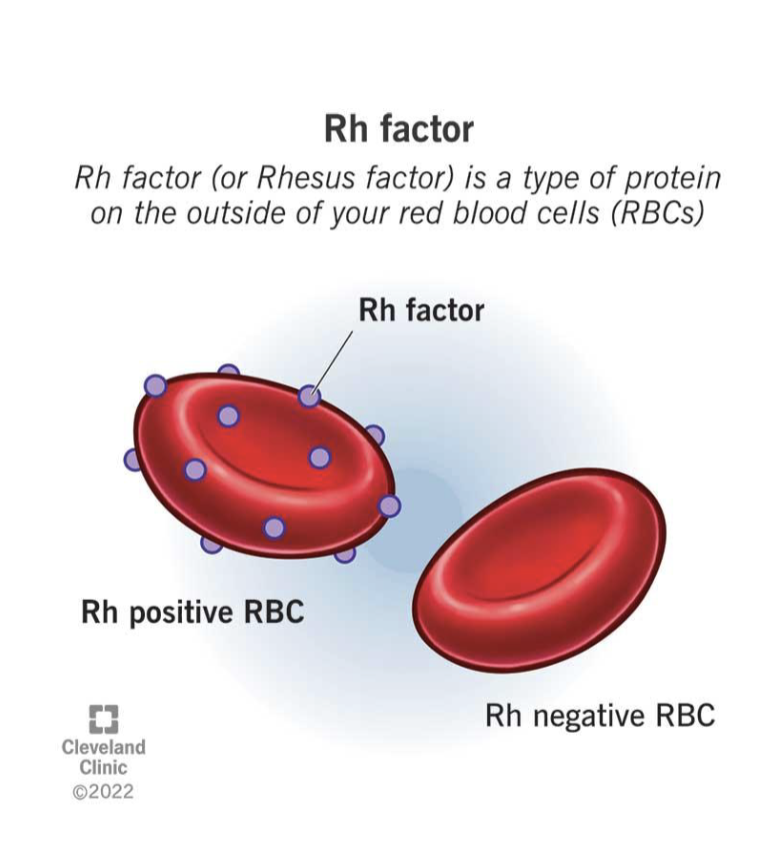
Rh incompatibility
Rh motehr and Rh+ fetus
maternal Rh antibodies corss placenta —> lysis of fetal RBC’s —> anemia
prenatal prevention method
rhogam
ABO incompatibilyiy
maternal blood type O exposed to fetabl blood type a, b or ab
result - hyperbilirubinemia
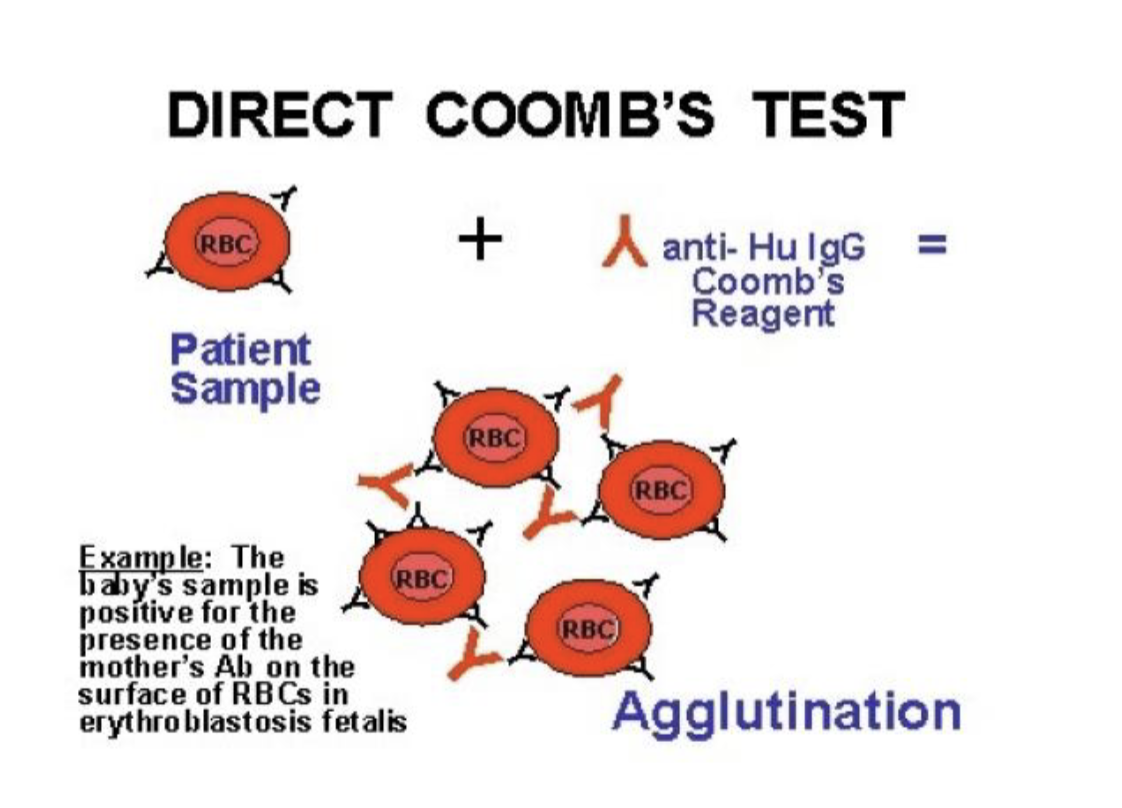
COOMBS test / direct antiglobulin test (DAT)
tests for presence of antibodies on fetal RBC’s
antibodies can be related to RH factor OR blood type
blood

Postiive = antibodies present
which places the newborn at high risk for hyperbilirubinemia