Ophthalmic Optics Midterm 2 - [McCleary] Optical/Physical Characteristics of Ophthalmic Lenses (Handouts 5 & 6)
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
The angle through which the surface turns into a unit length of arc, "R":
Curvature
The distance from the center of a circle to the perimeter – usually in meters, "r":
Radius
Unit of measurement for curvature "R" is "reciprocal meters" aka:
Diopters
A decrease in radius will _______________ curvature.
Increase
A increase in radius will _______________ curvature.
Decrease
ANY geometric line segment whose endpoints both lie on the circle:
Chord
What is referred to as the lens diameter?
Chord
Half of the lens diameter/chord is:
h
The distance between a point on a circle and the midpoint of a chord, "s":
Sagitta
Which formula solves for the exact sagitta?
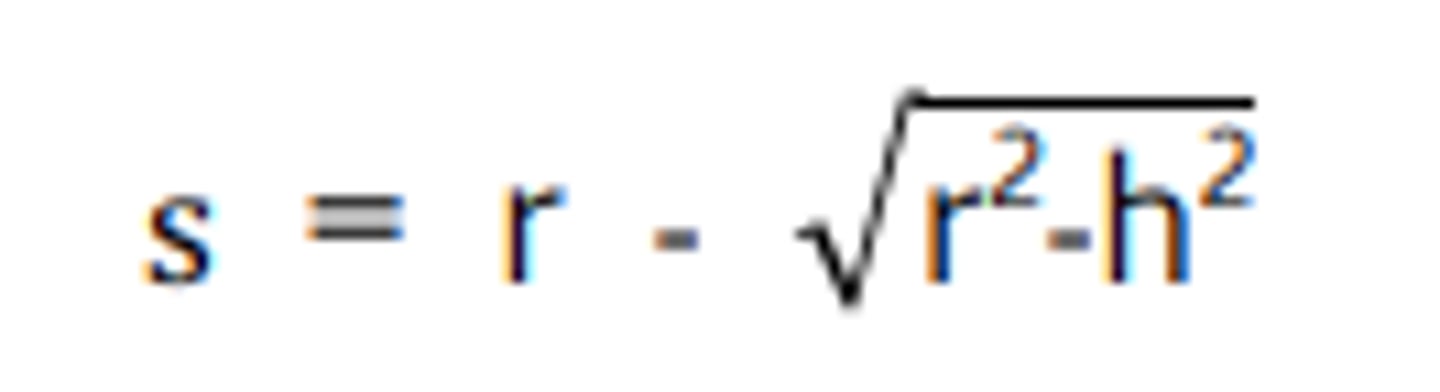
Use the exact sagitta formula to calculate the sag of a glass surface of 65 mm radius, 40mm in diameter:
3.2 mm
When chord diameter is kept constant, and curvature is decreased, the lens power will ____________________.
Decrease
When chord diameter is kept constant, and curvature is decreased, the sagitta will ____________________.
Decrease
Aka lens measure, aka lens guage, aka geneva lens measure:
Lens clock
The lens clock measures surface curvature using the _____________.
Sagitta
The ______________ is the distance between the two endpins on the lens clock.
Chord
Most lens clocks are calibrated to an index of 1.523 which is the index for ____________.
Trivex
The lens clock equation:
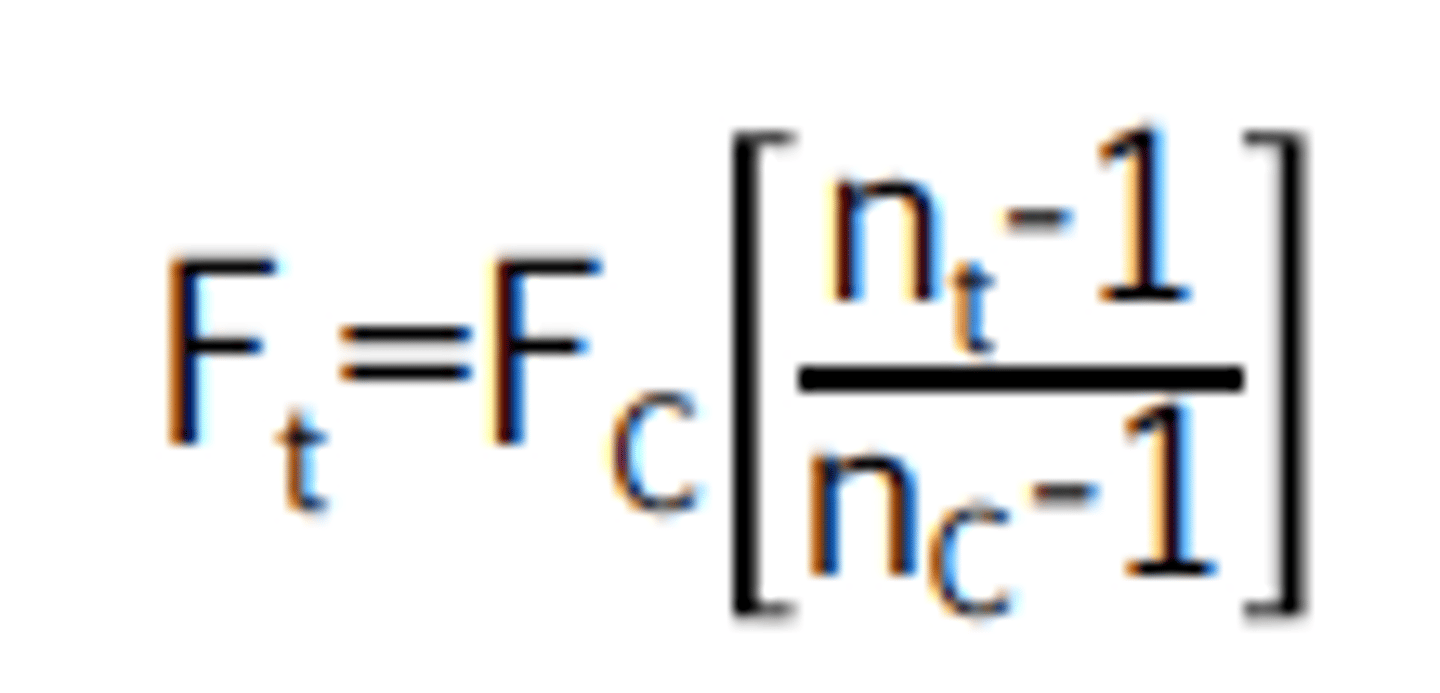
What is the true power of a lens surface made out of polycarbonate (n = 1.586) measuring +5.00D with a lens clock calibrated to 1.53?
+5.50 D
In diopters, what is the curvature of a circle that has a radius of 40cm?
2.50 D
In diopters, what is the curvature of a circle that has a radius of 50cm?
2.00 D
In diopters, what is the curvature of a circle that has a radius of 1 m?
1.00 D
Use the exact sag formula to calculate the sag of a glass surface of 50mm radius and 60mm diameter.
10 mm
3 multiple choice options
Use the exact sag formula to calculate the sag of a plastic surface with a refractive power of +16.00 D, 38mm diameter, and an index of refraction of 1.586.
5 mm
3 multiple choice options
What is the true power of a polycarbonate lens surface (n = 1.586) measuring +4.00D with a lens clock calibrated to 1.53?
+4.42 D
3 multiple choice options
What is the approximate power of a bent lens (meniscus lens) have a spherical front surface power of +5.00 D and a spherical back surface power of -1.50 D?
+3.50 D
3 multiple choice options
When the index of refraction of a lens is LESS than nc, then the power of the lens is _________ than the power the lens clock reads.
Less
2 multiple choice options
When the index of refraction of a lens is GREATER than nc, then the power of the lens is _________ than the power the lens clock reads.
Greater
2 multiple choice options
Refers to lens shape due to the front and back surface curvatures of the lens:
Lens form
Which spherical lens form is the simplest?
Plano-convex or plano-concave
When one surface has no power and the other surface has either a +/- sphere power, it is a _________________ spherical lens.
Plano-convex or plano-concave
A _______________________ spherical lens may be equal/unequal power on each surface.
Biconvex or biconcave
The modern spherical lenses are ______________________ lenses with a convex front surface and concave back surface.
Bent or meniscus
Which meridian of a non-spherical lens has no power?
Axis meridian
Which meridian of a non-spherical lens has the full cylinder power?
Power meridian
The ____________________ has the full cylinder power and is always 90 degrees away from axis.
Power meridian
The cylinder axis is defined as the meridian with ________________.
No power
A toric or ___________________ lens is required for a patient who has myopia or hyperopia in addition to astigmatism:
Spherocylindrical
A __________________ lens has one surface that is spherical (the front) and another surface that is toric on the other side. They are 90 degrees apart.
Spherocylindrical
When the toric surface is on the FRONT of the lens then the lens was ground in __________ cylinder form.
Plus
When the toric surface is on the BACK of the lens then the lens was ground in __________ cylinder form.
Minus
A back surface toric surface will minimize _________________ compared to a front surface toric.
Distortion
What is the spectacle Rx of a lens having the following powers: Front Surface: +6.00 sph / Back Surface: -3.00 power on the 090 meridian AND -5.00 power on the 180 meridian -> In minus cylinder form?
+3.00 -2.00 x090
3 multiple choice options
What is the spectacle Rx of a lens having the following powers: Front Surface: +6.00 sph / Back Surface: -3.00 power on the 090 meridian AND -5.00 power on the 180 meridian -> In PLUS cylinder form?
+1.00 +2.00 x180
3 multiple choice options
The lens curve on the surface of a lens, from which the other curves are determined:
Base curve
Base curve is always on the _________ surface of single vision lenses.
Front
For minus cylinder form, spherocyl lenses, the ____________ sphere curve is the base curve.
Front
The base curve is always a _______________ curve, because a toric surface will not be ground on the same side as a multifocal segment.
Spherical
T/F: It is common for a lens manufacturer to group lenses into ranges of powers and to make all lenses within a particular group with the same curvature on one surface.
True
1 multiple choice option
The locus of points showing the relationship between the power of a surface (front or back) and the power of the lens for which oblique astigmatism is eliminated:
Tscherning's Ellipse
A careful selection of _______________ by the manufacturer minimizes monochromatic aberrations/distortions.
Base curve
Usually, _____________ base curves cover a full range of Rx's.
4-6
3 multiple choice options
Lenses designed to minimize oblique astigmatism & curvature of image are called _______________________________.
Corrected curve or best form
Aka “radial astigmatism” or “marginal astigmatism”:
Oblique astigmatism
The ____________________ occurs when light passes obliquely through a spherical surface to form an interval of Sturm rather than a point focus.
Oblique astigmatism
Ophthalmic lenses form curved not plane images, this is called the ___________________.
Curvature of image
The curvature of the image is a function of the correcting lens and the image surface which is known as:
Petval's surface
The ___________________ affects how shapes and straight lines appear.
Base curve
T/F: Base curves change the way centrally viewed objects are perceived.
False
1 multiple choice option
T/F: Some individuals are very sensitive to changes in base curve/distortions.
True
1 multiple choice option
A patient returns to your office unable to adapt to his newest pair of glasses, you confirm that the correct Rx was made. You should now check the ________________ of the lens.
Base curve
How do we measure the base curve of a lens?
Lens clock
A ____________ lens will have an increased edge thickness.
Minus
A __________________ lens will have increased center thickness.
Plus
Weight increases and thickness changes are more pronounced for lens Rx's that are greater than +/- __________________.
4.00 D
What equation would you use if you need to find center thickness and are given the edge thickness, and both sagitta?
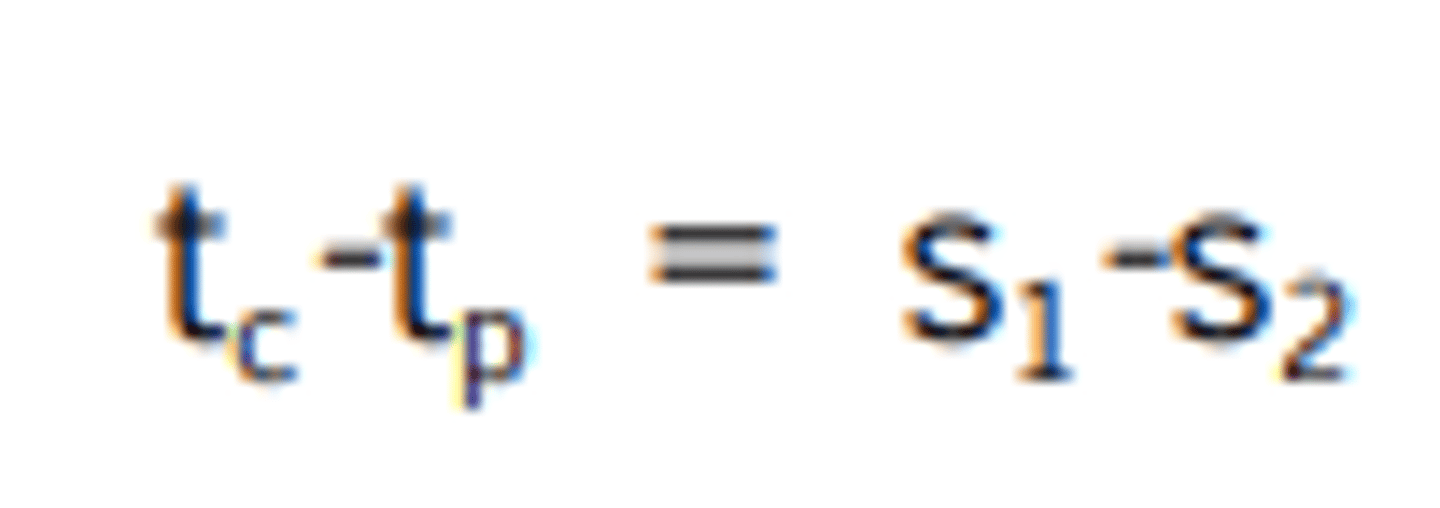
For a meniscus/bent lens, the front surface sag is 2mm, the back surface sag is 4mm, and the center thickness is 1mm. What is the edge thickness?
3 mm
3 multiple choice options
For a meniscus/bent lens, the front surface sag is 5mm, the back surface sag is 2mm, and the edge thickness is 1mm. What is the center thickness?
4 mm
3 multiple choice options
The approximate sagitta formula (the only ones on our actual formula sheet.. you can use these two to solve all the problems though):
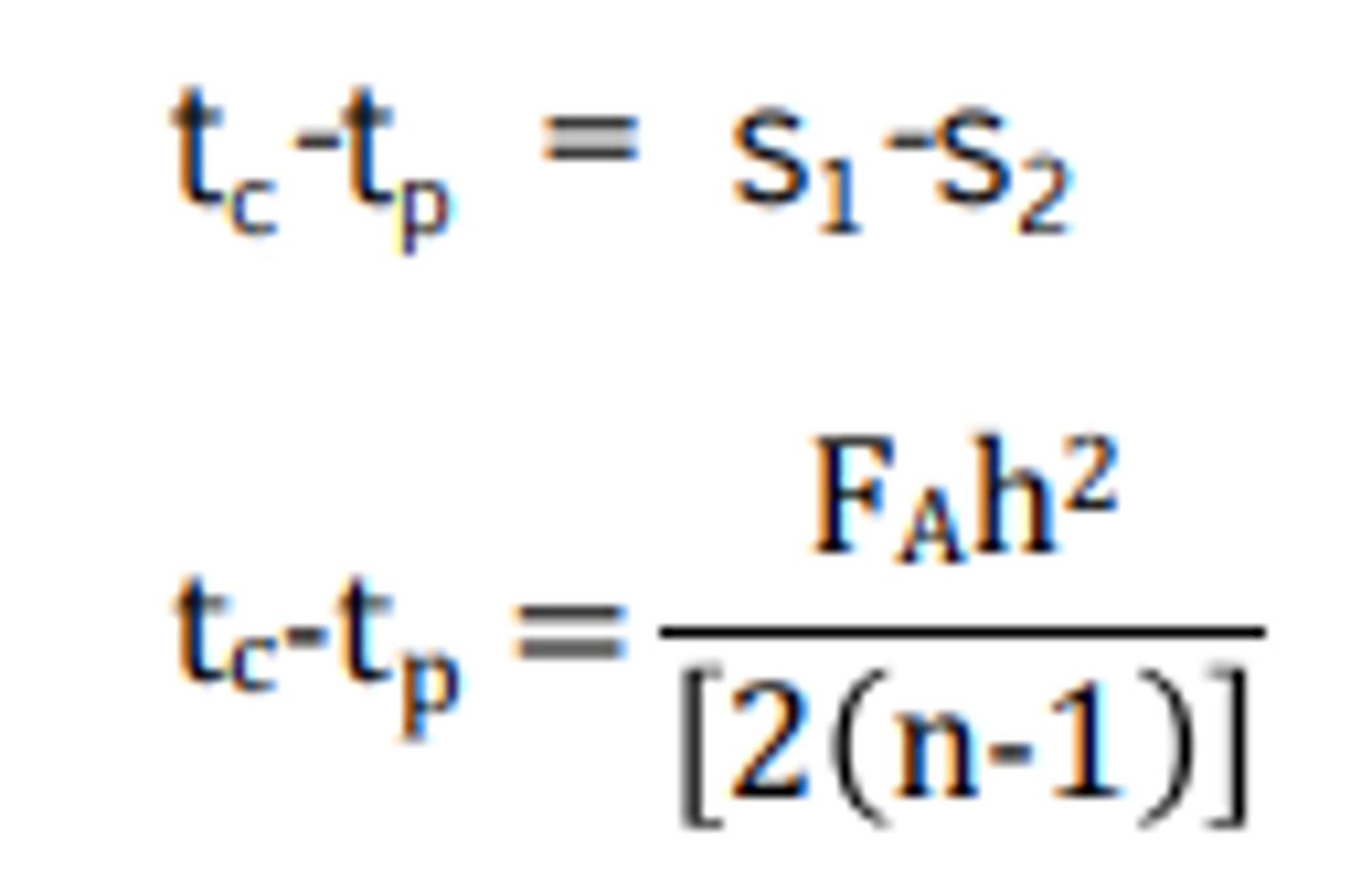
Given a round, meniscus lens, having sagittae s1=5.2mm, s2=3.6mm, a diameter (chord length) of 48mm, and an index of refraction of 1.53, find the approximate power of the lens (use approx. sag formula).
+2.94 D
3 multiple choice options
Given a round lens, having front surface power (F1) of +12.00D, a back surface power (F2) of -8.00D, a diameter of 54mm, an index of refraction (n) of 1.586, and an edge thickness of 2.0mm, what is the center thickness (tc) using the approx. sag formula?
4.49 mm
3 multiple choice options
The ____________ sagitta formula is not accurate for highly curved surfaces.
Approximate
When moving the power of a lens away from the axis meridian, you should use what equation?
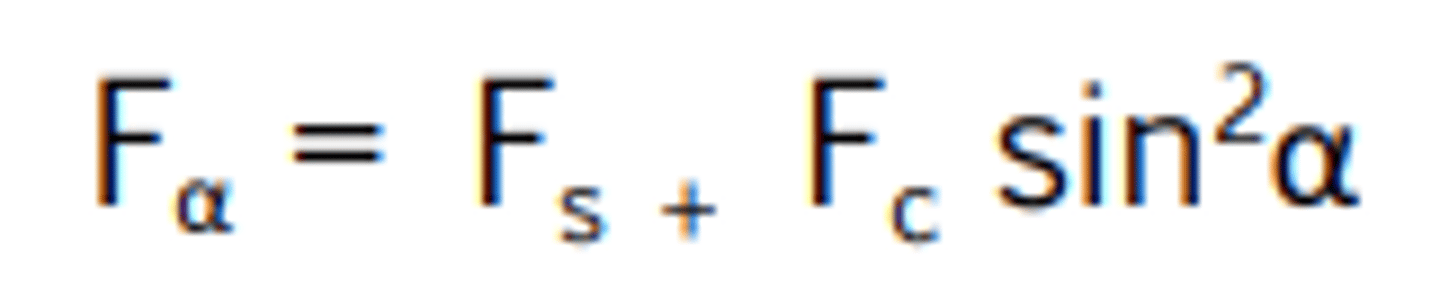
When moving the power of a lens away from the power meridian, you should use what equation?
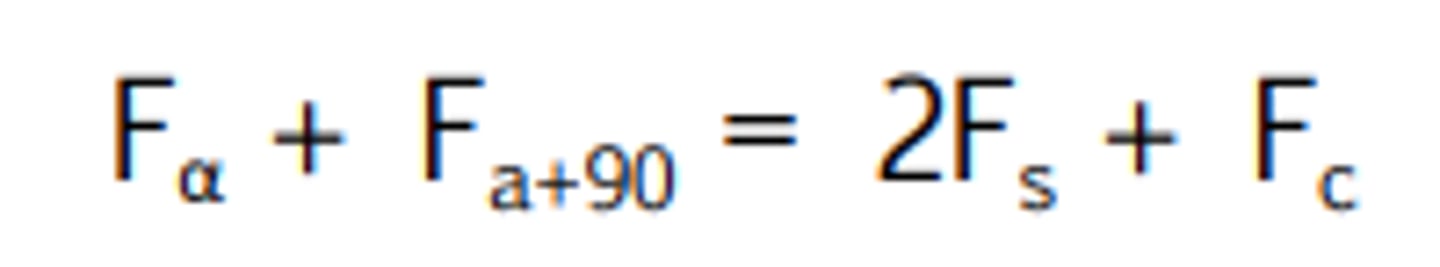
What is the power of a -4.00 cylinder, 30 degrees from the axis meridian?
-1.00 D
3 multiple choice options
What is the power of a -3.50-2.00x180 lens, 30 degrees from the axis meridian?
-4.00 D
3 multiple choice options
What is the power of a -4.00-2.00x180 lens, 60 degrees from the axis meridian?
-5.50 D
3 multiple choice options
What is the power of a -8.00 cylinder, 30 degrees from the power meridian? The power 30 degrees from the axis meridian is -2.00.
-6.00 D
3 multiple choice options
What is the power of a -4.00-3.00x180 lens, 30 degrees from the power meridian? The power 30 degrees from the axis meridian is -1.00.
-10.00 D
3 multiple choice options
SHORTCUT method for obliquely crossed cylinders: When both cylinders have the ____________ sign, the resulting axis is between the original axes.
Same
SHORTCUT method for obliquely crossed cylinders: If the two cylinders are of equal power, the resulting axis is ____________ between the two.
Halfway
SHORTCUT method for obliquely crossed cylinders: If the two cylinders are of unequal power, the resultant axis is shifted toward the _____________ of the two cylinders.
Stronger
If the following two lenses are obliquely crossed, what would the resulting power be in minus cylinder format?
Lens 1: +1.00+1.00x100 ---- Lens 2: +2.50+1.50x070
+5.84 -2.18 x172
3 multiple choice options
If the following two lenses are obliquely crossed, what would the resulting power be in plus cylinder format?
Lens 1: +1.00+1.00x100 ---- Lens 2: +2.50+1.50x070
+3.66 +2.18 x082
3 multiple choice options
If the following two lenses are obliquely crossed, what would the resulting axis be in plus cylinder format?
Lens 1: +1.00-0.75x100 ---- Lens 2: +3.00+4.00x050
045
3 multiple choice options
If the following two lenses are obliquely crossed, what would the resulting axis be in minus cylinder format?
Lens 1: +1.00-0.75x100 ---- Lens 2: +2.00-4.00x075
080
3 multiple choice options
A ___________________ tilt will cause rotation along the 180 axis.
Pantoscopic
A ___________________ tilt will cause rotation along the 090 axis.
Faceform
SHORTCUT method for calculating resultant power when tilting a lens: Sphere will ________________ and has the same power/sign as the original sphere.
Increase
SHORTCUT method for calculating resultant power when tilting a lens: Cylinder is created and has the same power/sign as the original _______________.
Sphere
SHORTCUT method for calculating resultant power when tilting a lens: The axis of induced cylinder is ___________ to the axis of rotation of the lens (the same).
Parallel
A +5.00 spherical, polycarbonate lens is given 18 degrees pantoscopic tilt. What is the resultant power?
+5.15 +0.54 x180
3 multiple choice options
A +5.00 spherical, polycarbonate lens is given 18 degrees pantoscopic tilt. What is the resultant power?
+5.69 -0.54 x090
3 multiple choice options
What is the resultant induced power of a -6.00 DS lens with a pantoscopic tilt of 30 degrees?
-6.50 -2.17 x180
3 multiple choice options
What is the resultant induced power of a -6.00 DS lens with a faceform tilt of 30 degrees?
-6.50 -2.17 x090
3 multiple choice options