Competitive Markets
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
PED
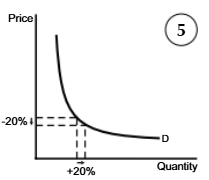
A measure of how the quantity demanded changes in response to change in its price
Formula of a PED
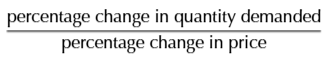
Elastic PED
PED>1
Inelastic PED
0<PED<1
Unit elasticity of demand
PED=+-1
Unit Elasticity of demand means
When change in quantity demanded = change in price
Elastic PED diagram
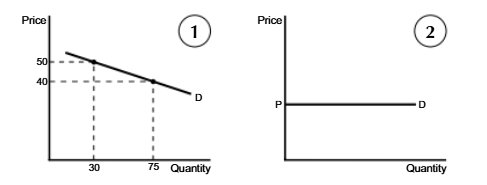
Inelastic PED Diagram
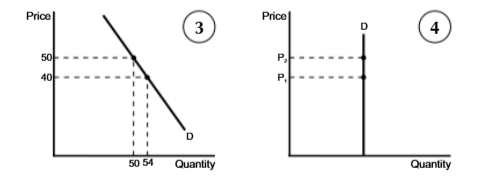
Unit Elasticity of D Diagram
YED means
Measure of how much quantity demanded of a good changes in response to change in price
YED
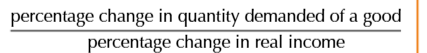
YED Elastic
YED>1
YED Inelastic
YED<1
YED perfectly inelastic
YED=0
Elastic YED Diagram
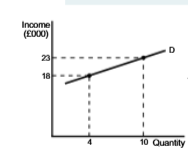
Inelastic YED Diagram
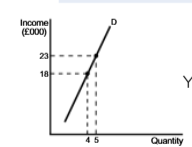
Perfectly Inelastic YED Diagram
XED means
A measure of how the quantity demanded of one good responds to a change in the price of another good
XED Formula
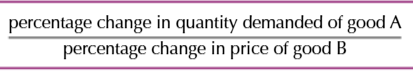
The XED for substitute goods is
Positive
The XED for complementary goods is
Negative
Factors, influencing PED
Number of substitutes, type of good, percentage of income spent on good, time
Total Revenue/PED diagram
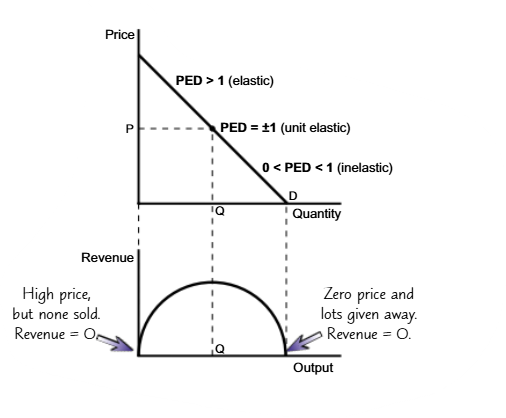
When does firm maximize its profit?
At PED=+-1/Unit elastic
If a good’s PED is elastic, then

If a good’s PED is inelastic

When XED=0, the goods are
Unrelated
Factors, influencing Supply
Changes to the costs of production, improvements in technology, Changes to the productivity of factors of production, indirect taxes and subsidies, Changes to the prices of other goods, number of suppliers
Joint supply means when
Production of one good or service, involves the production of another
Competitive supply means
when two alternative goods or services can be produced using the same number of factors of production. Potatoes and carrots, for instance
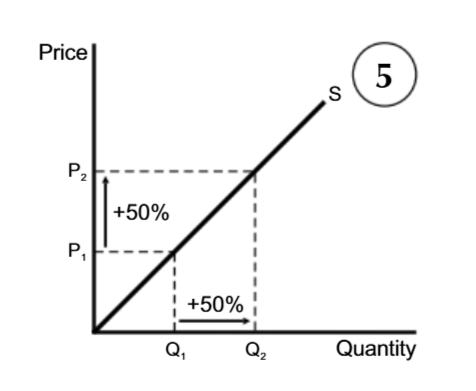
PES means
measure of how the quantity supplied of a good changes in response to change in its price.
PES Formula
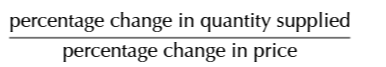
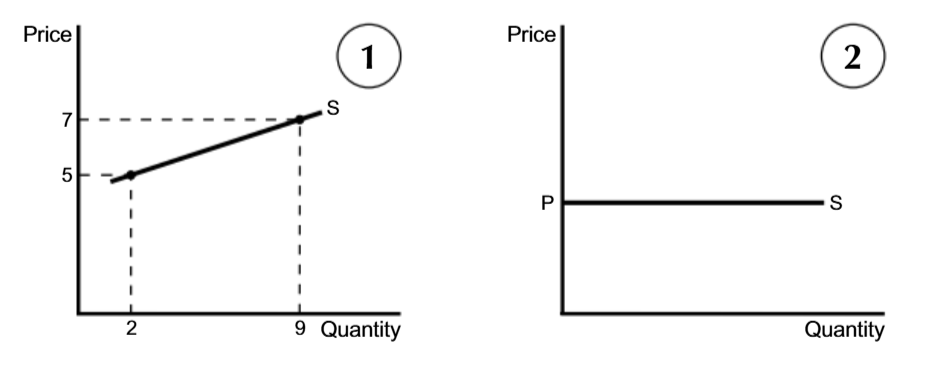
Elastic PES
PES>1
Inelastic PES
0<PES<1
Unit elasticity of supply
PES=+1
Elastic PES Diagram
Inelastic PES Diagram
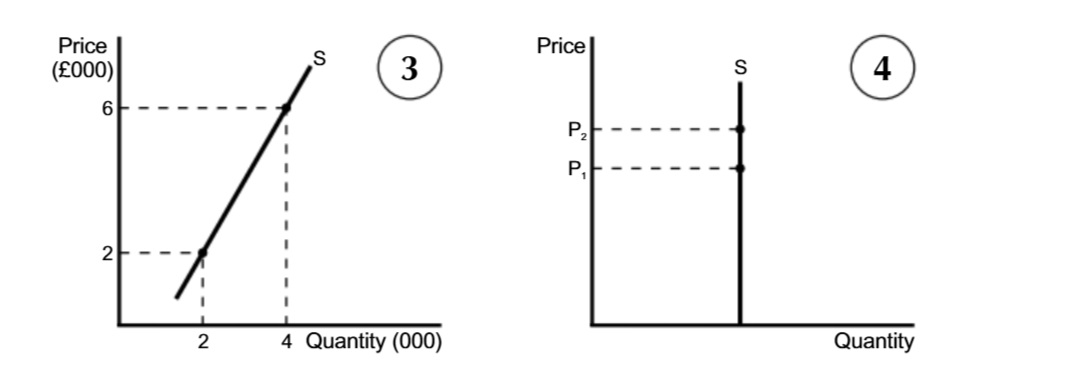
Unit Elasticity of Supply Diagram
The best PES for firms is the and why
Elastic PES, since it lets firms react to changes in prices very quickly (in case of inelastic PES, it takes firms too much time to start producing more and selling more)
How can firms increase their elasticity
Impose new technologies, methods, have skillfull labour, having spare production capacity (start producing a lot, without increasing costs)
What type of supply dominates in the short run
Inelastic supply
Why is supply inelastic in the short run
Firms cannot produce significantly a lot in the beginning, since at least of their factors of production is fixed.
What type of Supply is in the long run and why
Elastic Supply, since all factors of production in the long run are variable, so the firm can produce more in the long run, firms have longer to react to changes in price and demand
What is the reason for large distinctions in time for supply to change across different industries
Whether the industry is capital-intensive or not
Factors, affecting PES
Periods of unemployment provide rather elastic supply, perishable goods have inelastic supply, firms with high stock level usually have elastic supply, firms with mobile factors of production have higher elasticity of supply
In inelastic PED or PES, curve shifts have higher impact on
The price
In elastic PED or PES, curve shifts have higher impact on
The quantity demanded/supplied
Under what conditions do competitive markets exist

What is the price mechanism

The price mechanism has three main functions

Consumer surplus


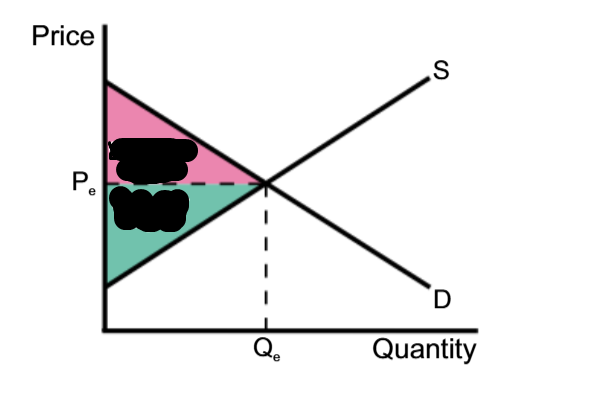
Consumer Surplus, Producer Surplus
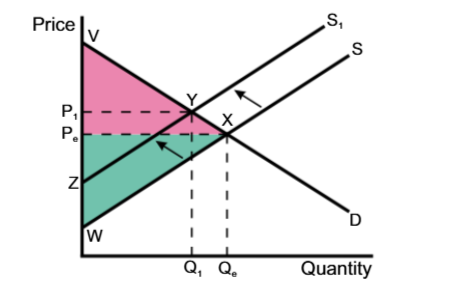
Supply decreased, price increased, both surpluses decreased
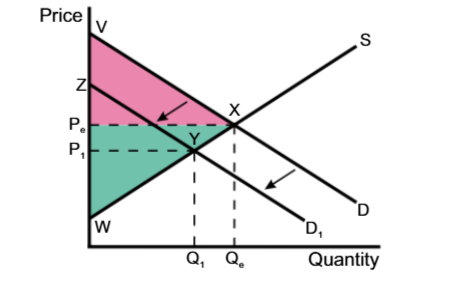
Demand decreased, price decreased, both surpluses decreased
Subsidies and Indirect taxes lead up to
shifts in Supply curve
The main task of a subsidy
Increase demand
The main task of an indirect tax
Decrease demand
The relative amounts of benefit gained by producers and consumers from both interventions are dependent on
the price elasticity of demand and supply
The rather inelastic demand provides more gain to
The consumer
The rather elastic demand provides more gain to
The producer
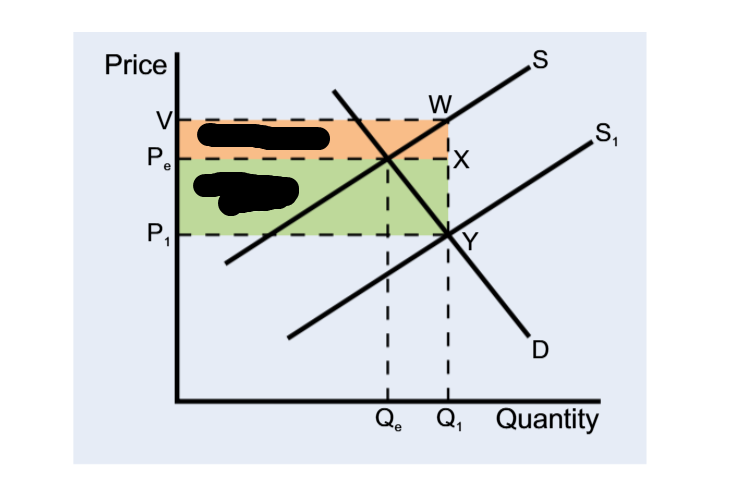
Inelastic demand, more gain to the consumer
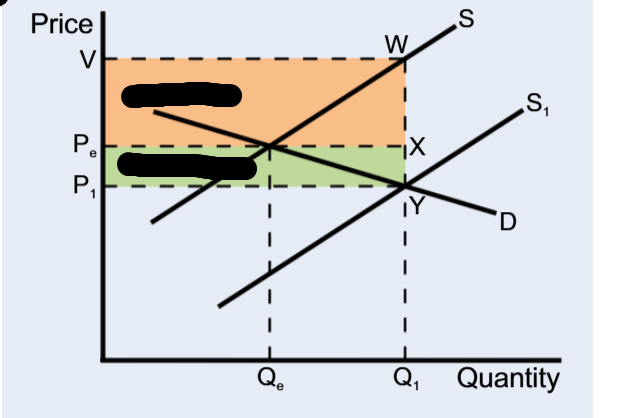
Elastic demand, more gain to the producer
The indirect taxes
Make the Supply curve shift to the left
The rather inelastic demand is, the more the
consumer suffers
The more elastic demand is, the more the
Producer suffers
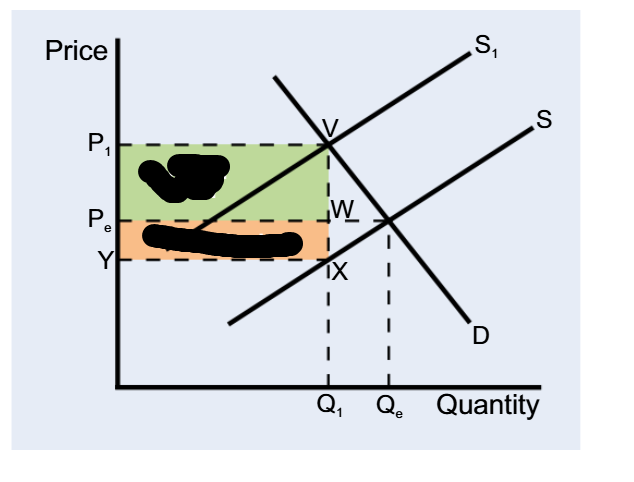
Inelastic demand, consumer pays more
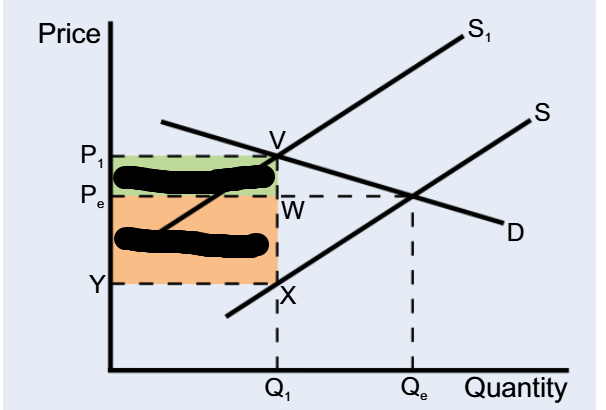
Elastic demand, producer pays more